France’s construction market is shaped by strict regulatory frameworks, high labour standards, and strong public investment in infrastructure, education, healthcare, and energy transition projects. At the same time, urban densification and sustainability targets are forcing organisations to rethink how buildings are delivered. In this environment, modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions have become reliable options for companies and public bodies seeking speed, compliance, and long-term operational efficiency. Rather than being viewed as temporary alternatives, these systems are now integrated into strategic planning across multiple sectors in France.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in France
Labour costs are one of the most decisive factors influencing construction decisions in France. Skilled labour is expensive, and on-site productivity is often constrained by regulatory requirements, safety obligations, and working-hour limitations. Modular buildings reduce the intensity of on-site labour by transferring much of the construction process to factory environments, where workflows are standardised and less exposed to delays. This approach allows project owners to better control budgets while maintaining quality standards.
Construction timelines are equally important. Public-sector projects, in particular, operate under fixed delivery schedules tied to funding approvals and service continuity. Traditional construction methods can be slowed by permitting processes, weather conditions, and coordination between multiple subcontractors. Modular buildings enable parallel progress, with site preparation and building production taking place at the same time. This significantly shortens project delivery and reduces disruption to surrounding environments.
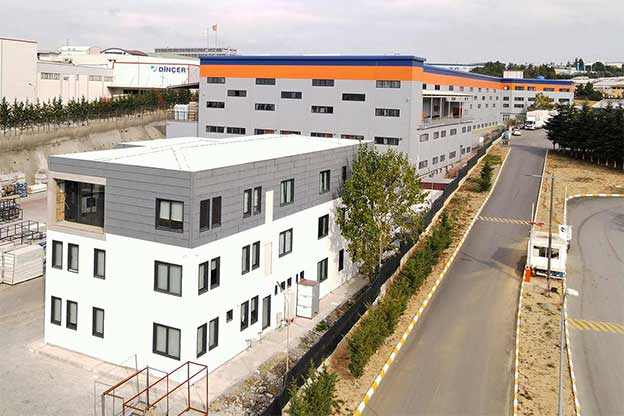
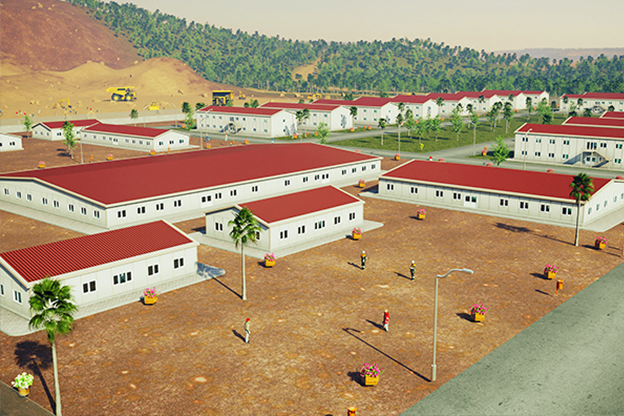
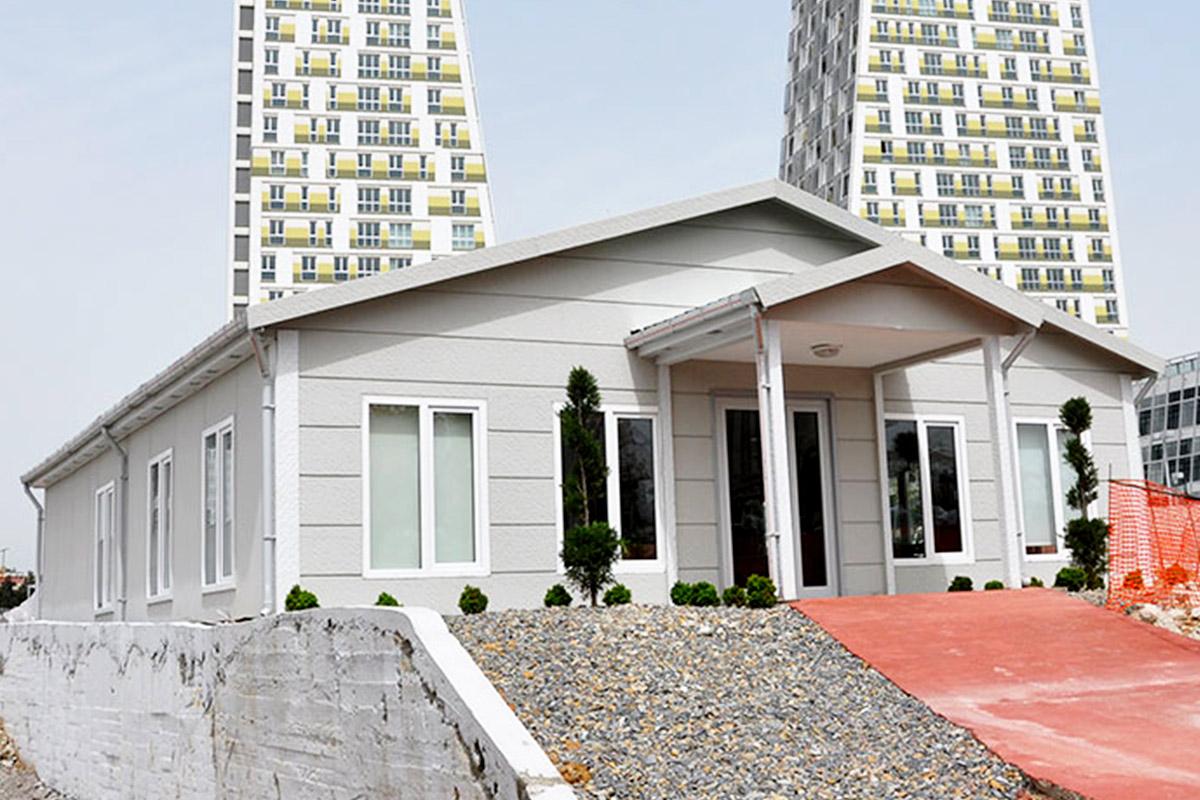
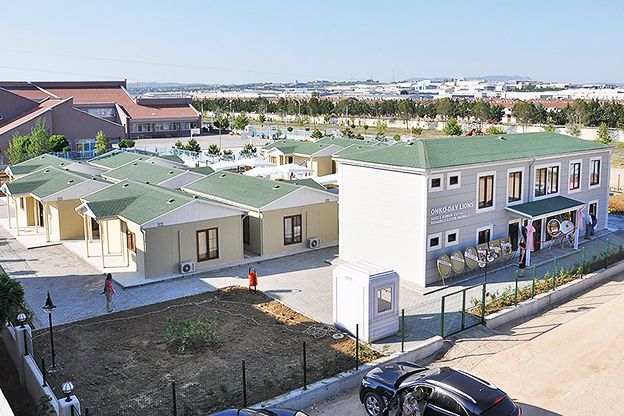
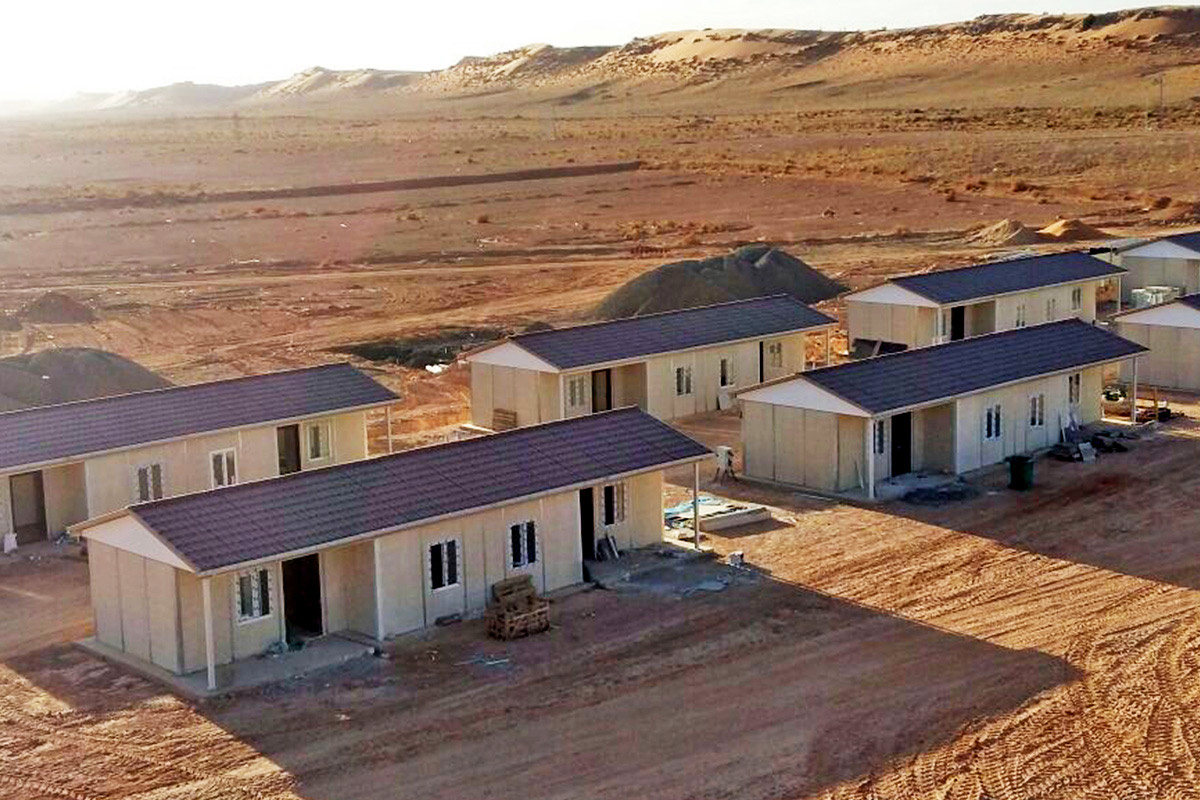
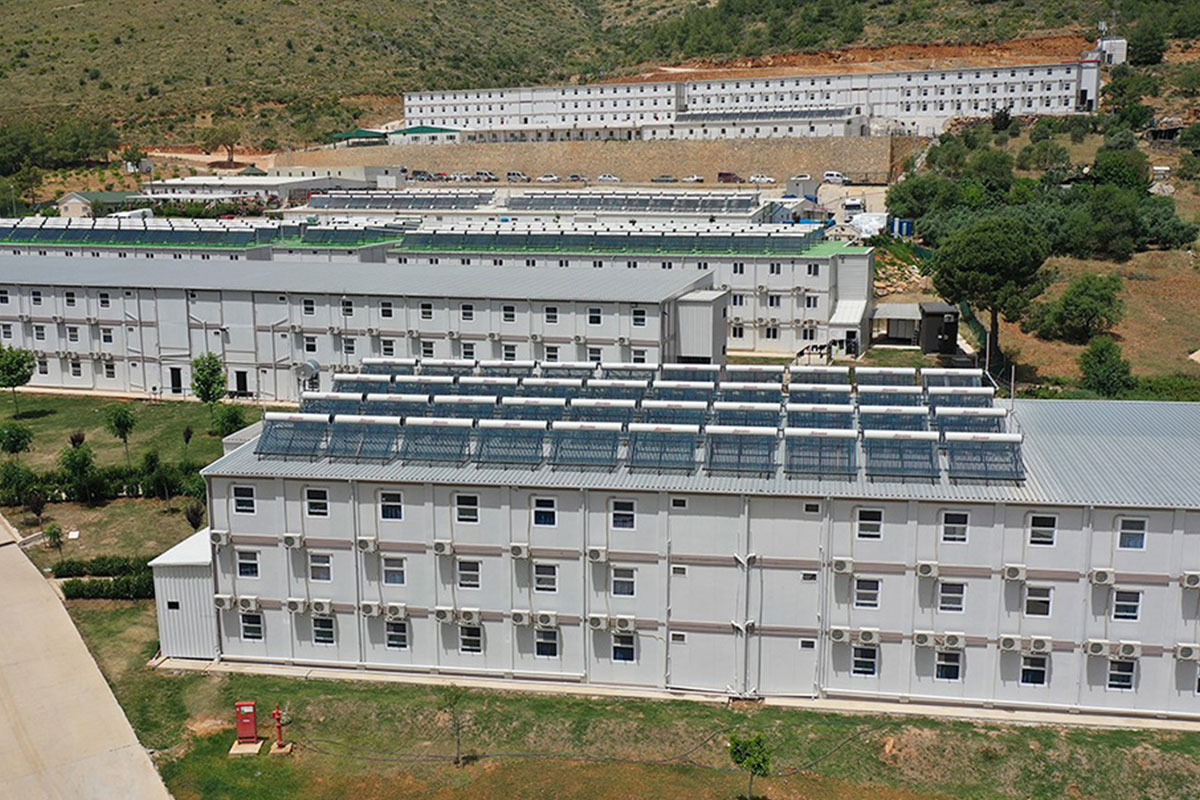
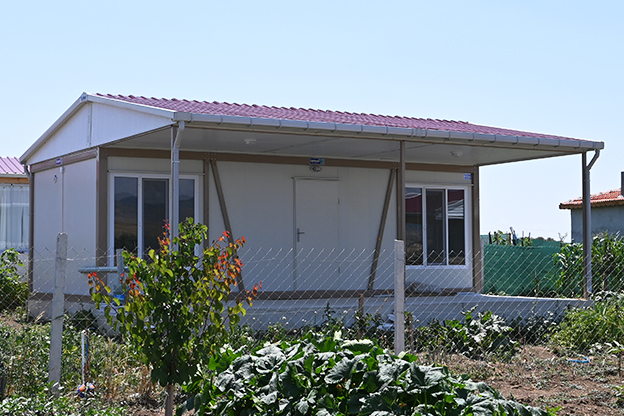
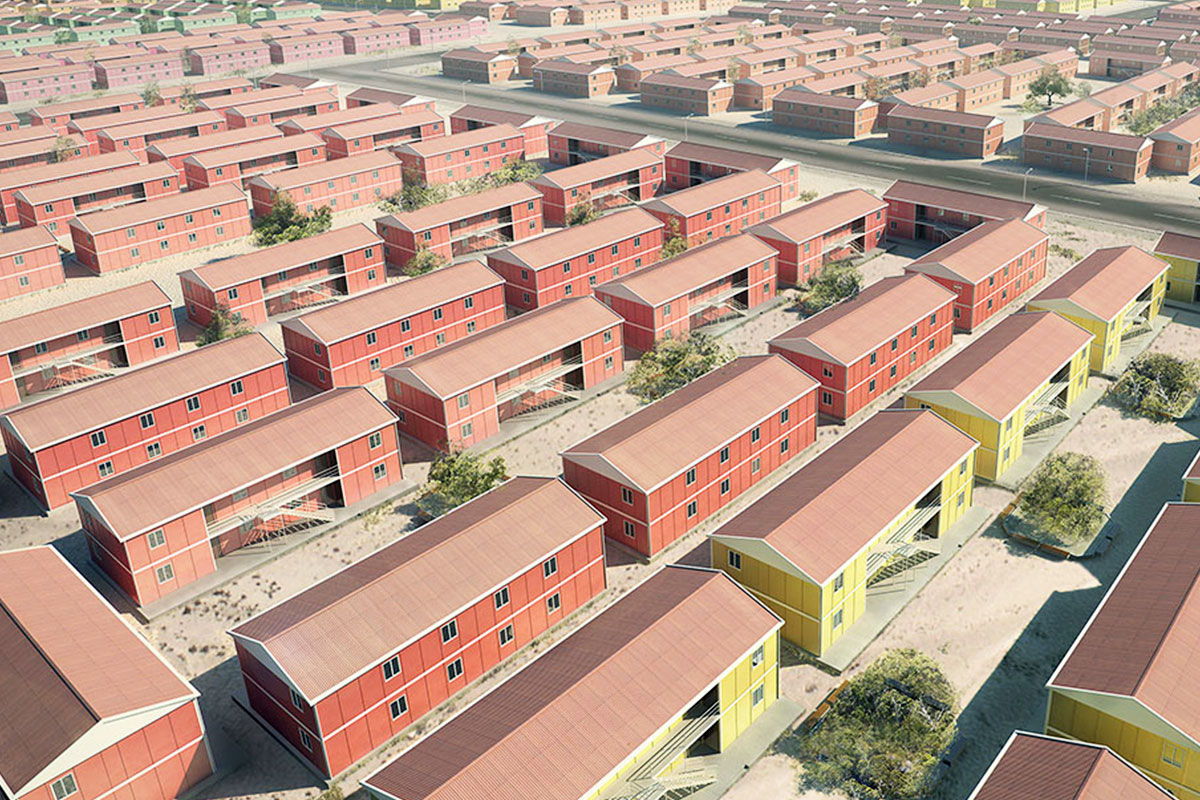
France also demonstrates a balanced demand for temporary and permanent building solutions. Temporary structures are widely used for infrastructure upgrades, rail and transport projects, industrial expansions, and urban redevelopment phases. At the same time, permanent facilities are required for schools, healthcare centres, administrative buildings, and industrial operations. Modular buildings are well suited to both scenarios, offering relocatable units or long-term installations designed to meet French building standards.
Sector-specific demand further supports adoption. Logistics and distribution facilities continue to grow alongside e-commerce and regional supply chains. Public-sector investment in education and healthcare drives demand for rapidly deployable buildings. Energy and utility projects, including renewable energy developments, often require technical units delivered within strict timelines. In these sectors, modular buildings align well with France’s operational and regulatory landscape.

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
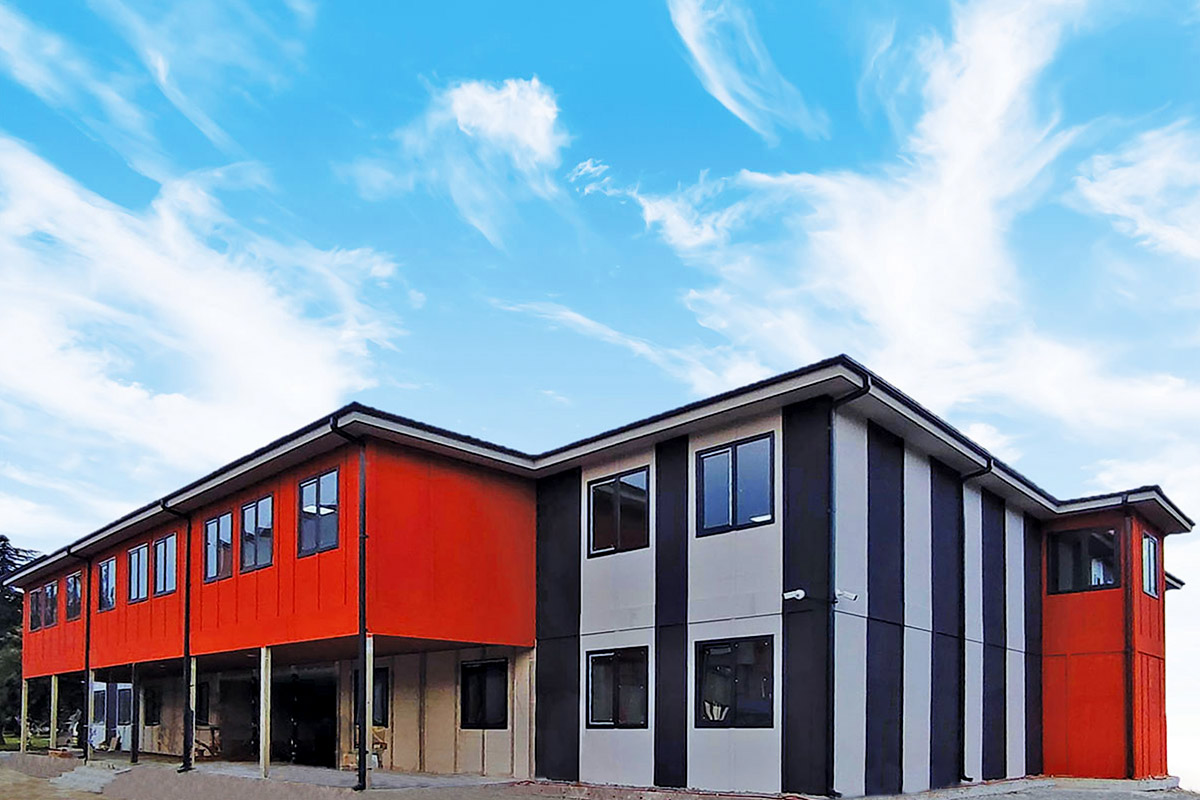
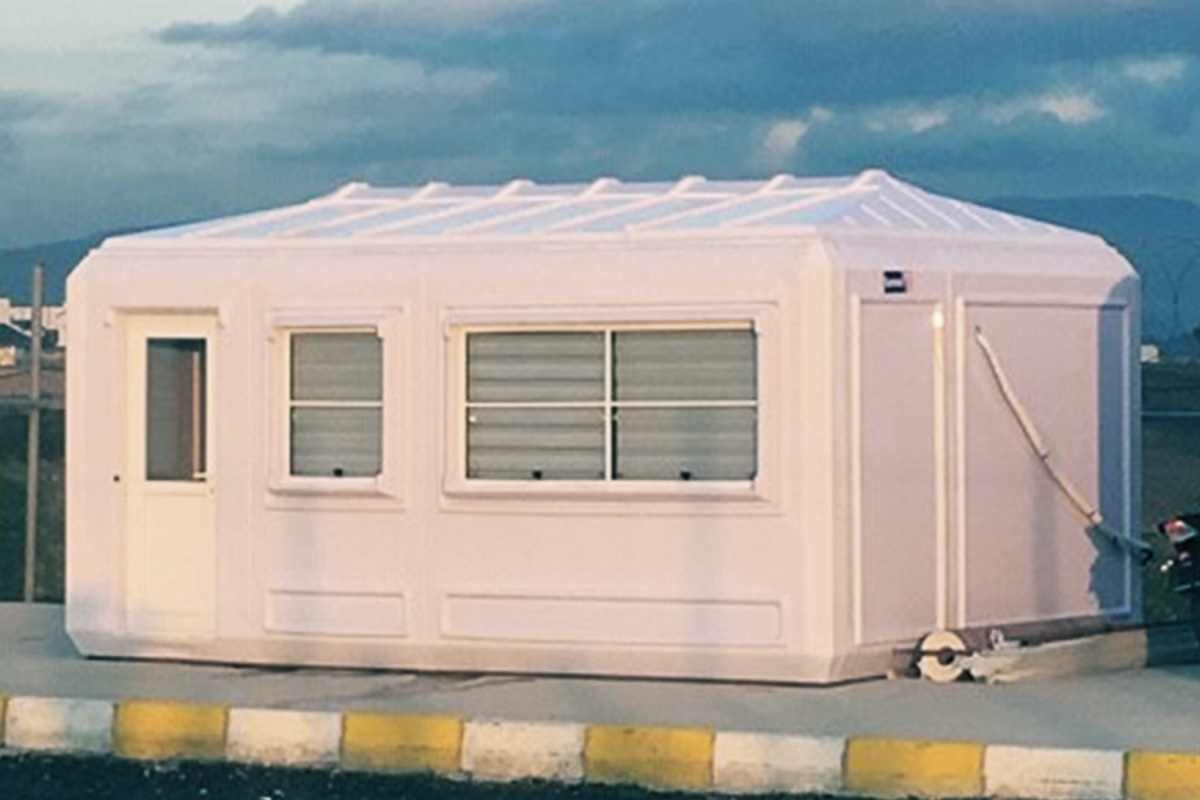
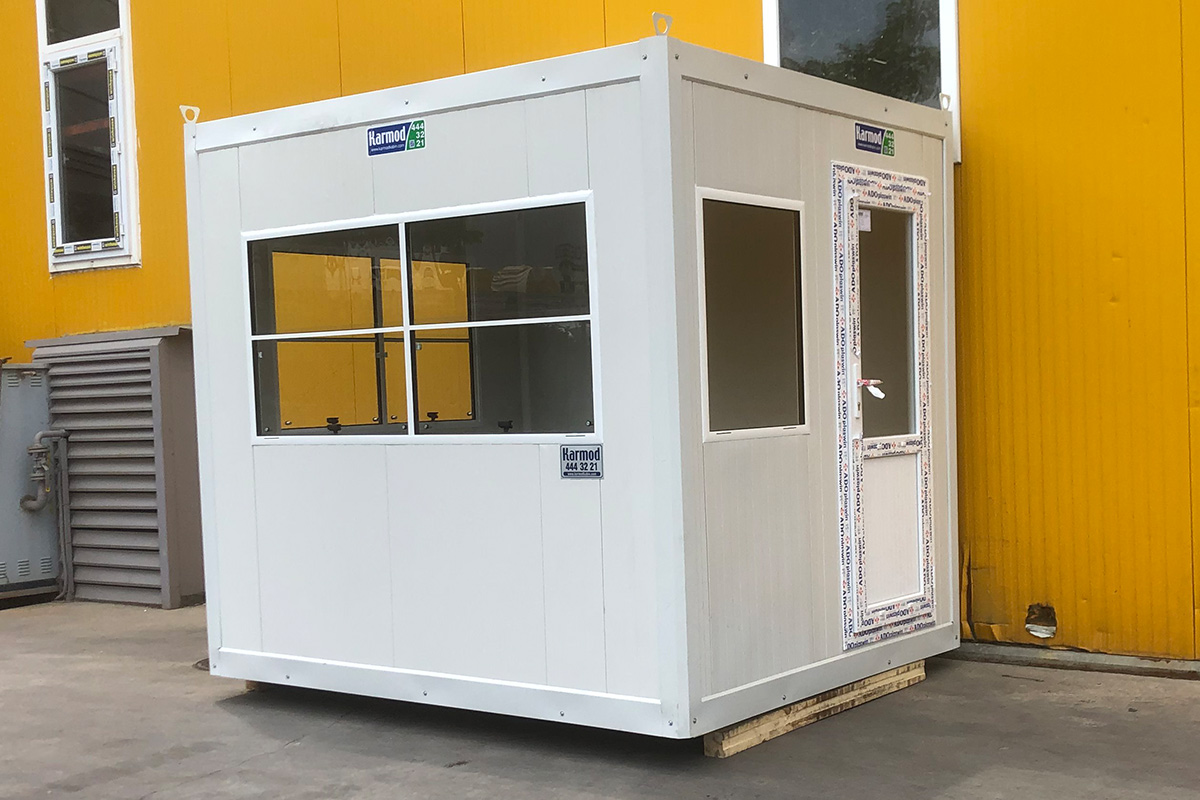
Although often mentioned together, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems differ in structure and intended use. Modular buildings are volumetric units produced in factories as near-complete modules. These modules are transportable, quick to install, and can be expanded or relocated as needs evolve. This makes modular buildings particularly suitable for projects that require flexibility, phased growth, or temporary deployment.
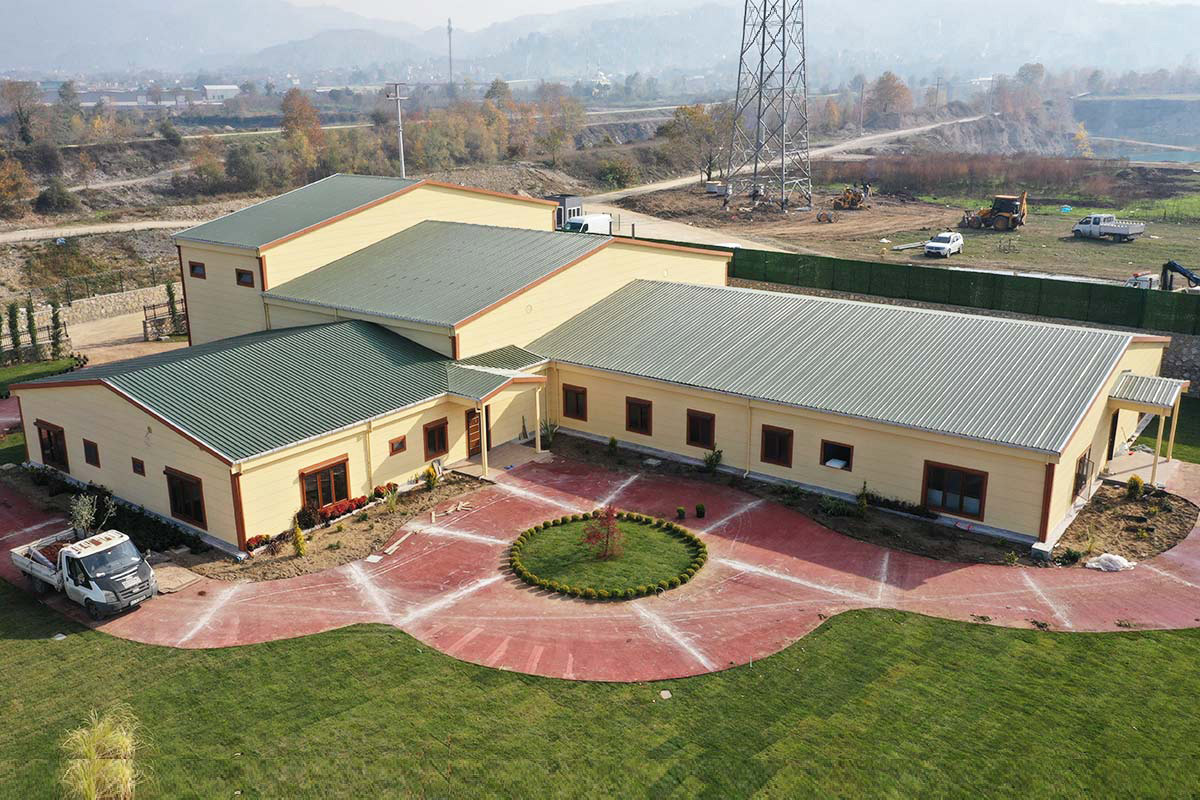
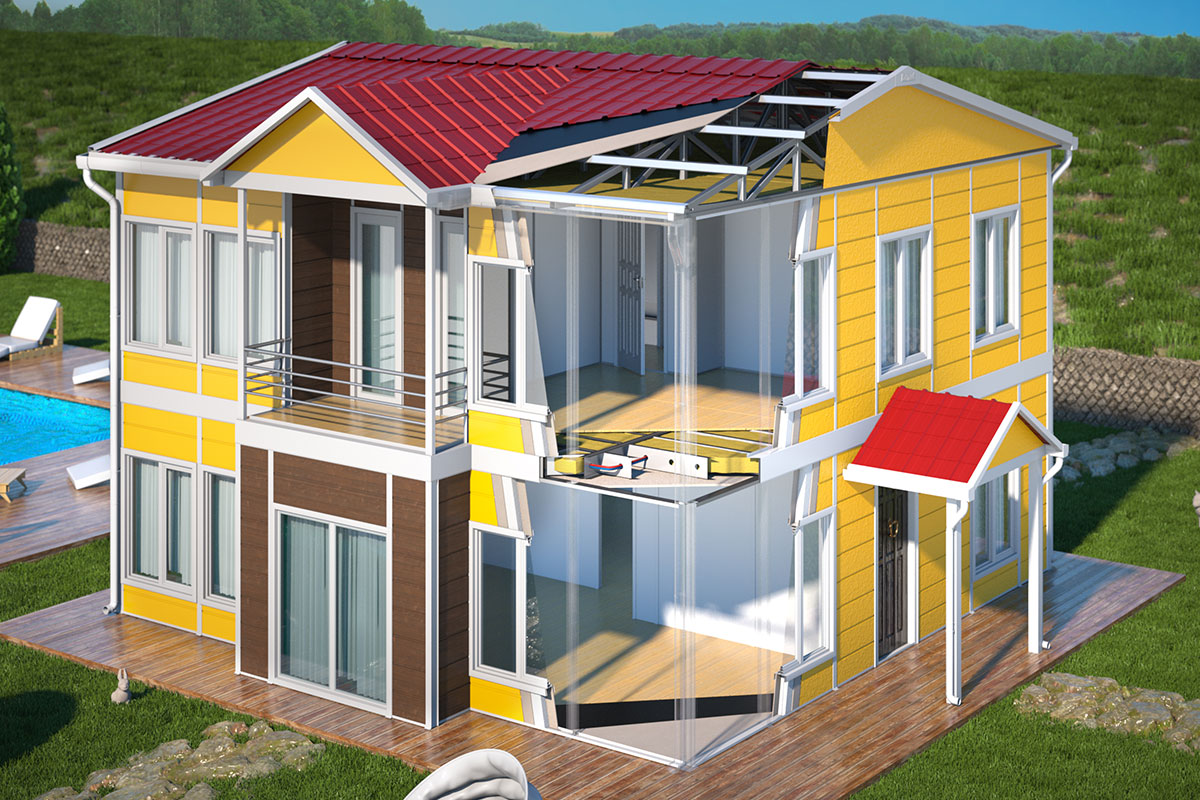
A prefabricated building, by contrast, is assembled from panels or pre-engineered structural components manufactured off-site and installed permanently on location. These systems are generally selected for long-term use, where architectural integration and fixed layouts are priorities. Prefabricated building methods allow organisations to benefit from factory-controlled quality while maintaining a permanent construction approach.
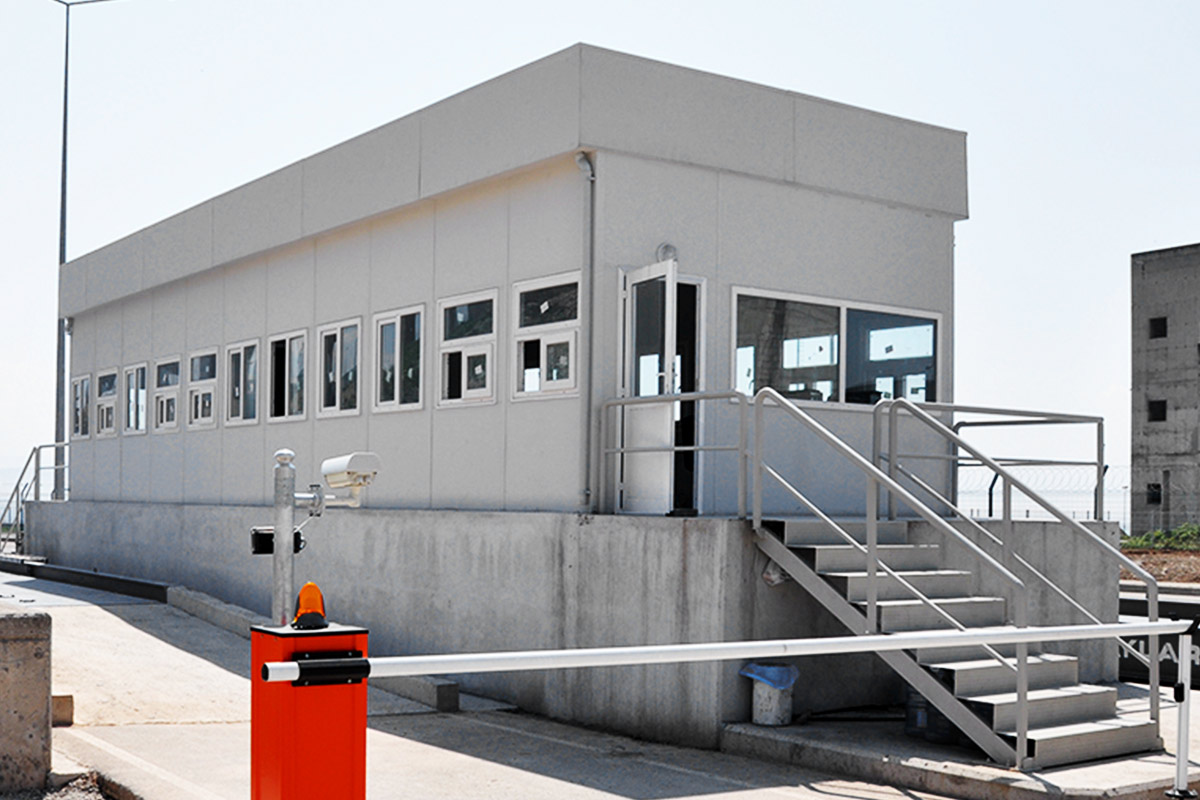
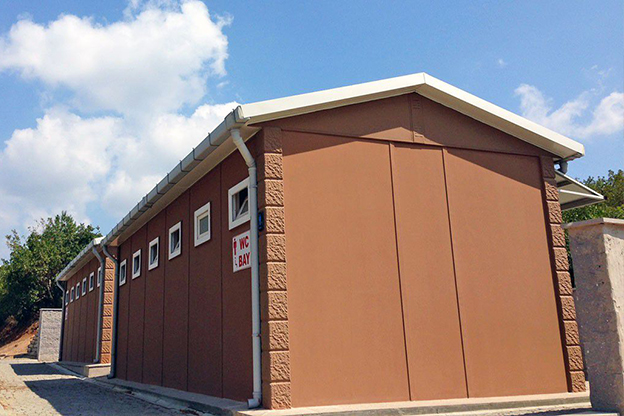
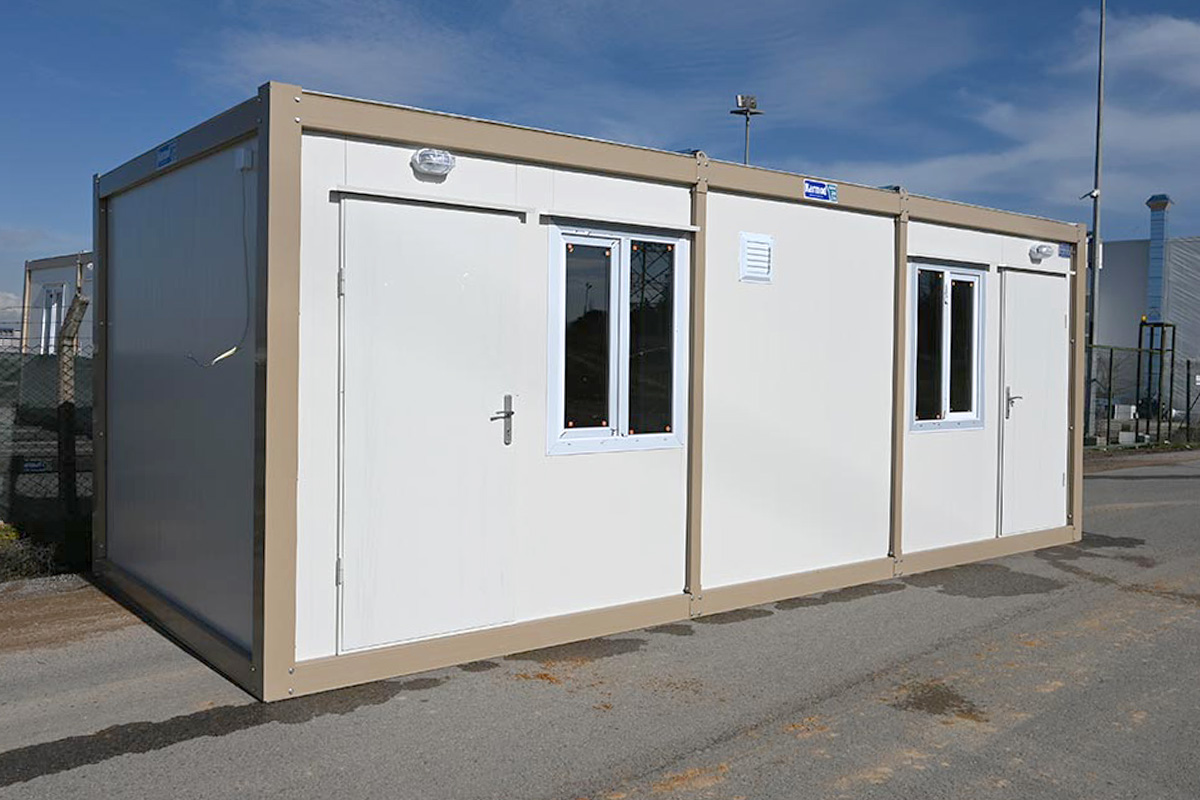
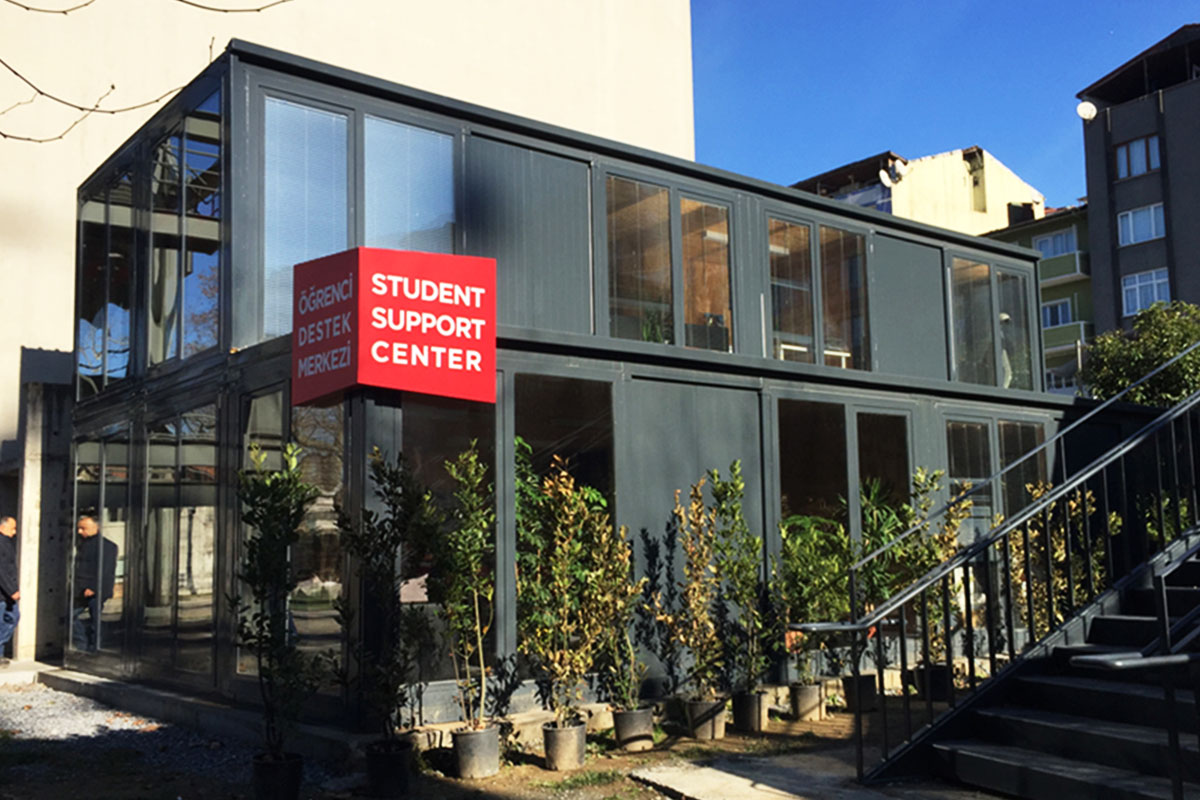
In France, modular buildings are commonly preferred for site offices, temporary classrooms, healthcare extensions, and accommodation linked to infrastructure or industrial projects. Prefabricated building systems are more often chosen for permanent schools, hospitals, administrative facilities, and industrial buildings where durability and long service life are essential. Selecting the right system depends on functional requirements, regulatory context, and long-term planning objectives.
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in France
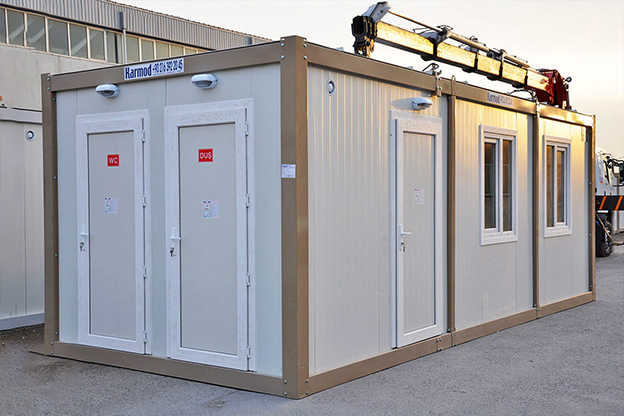
- Site offices & construction camps supporting infrastructure, transport, and large-scale commercial projects
- Worker accommodation buildings for industrial developments, energy projects, and remote construction sites
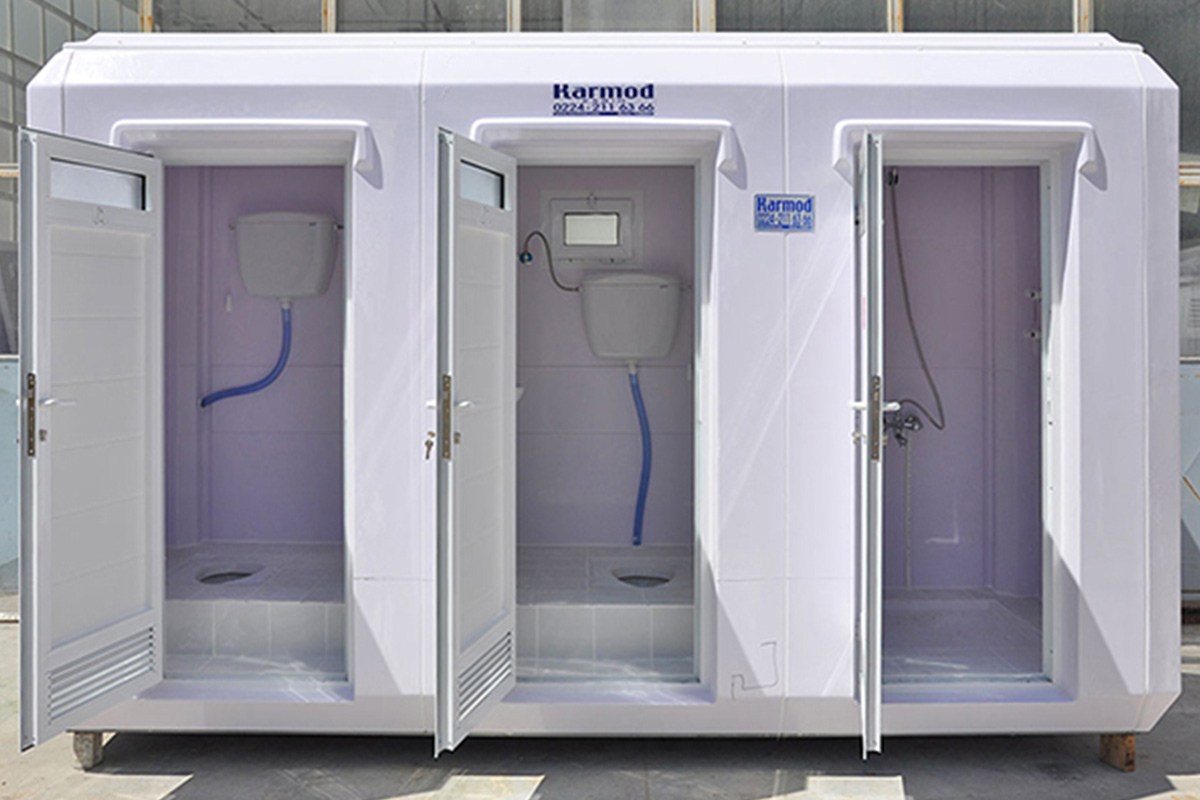
- Temporary schools & healthcare units enabling capacity expansion during renovations or demand peaks
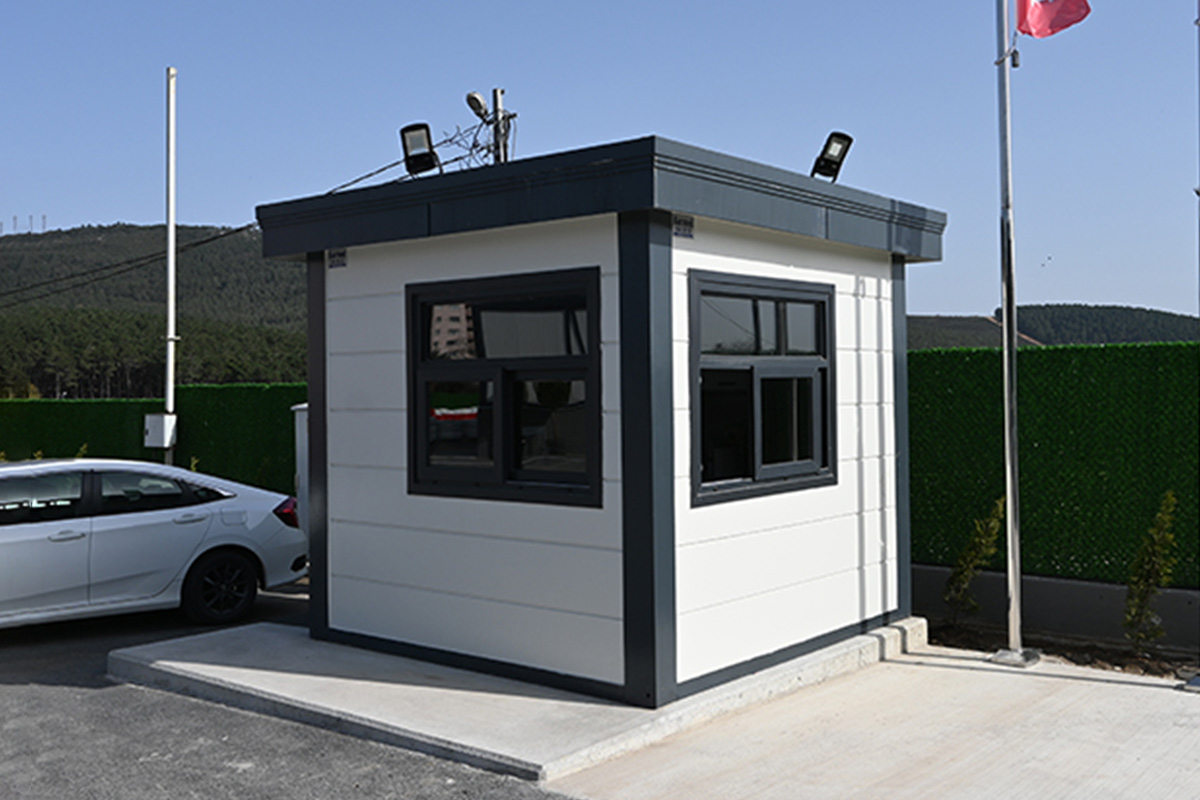
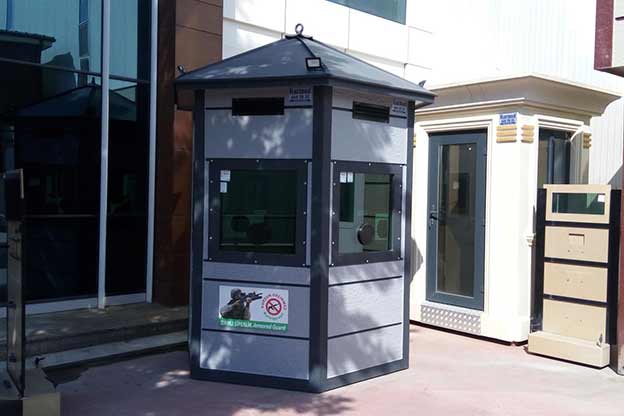
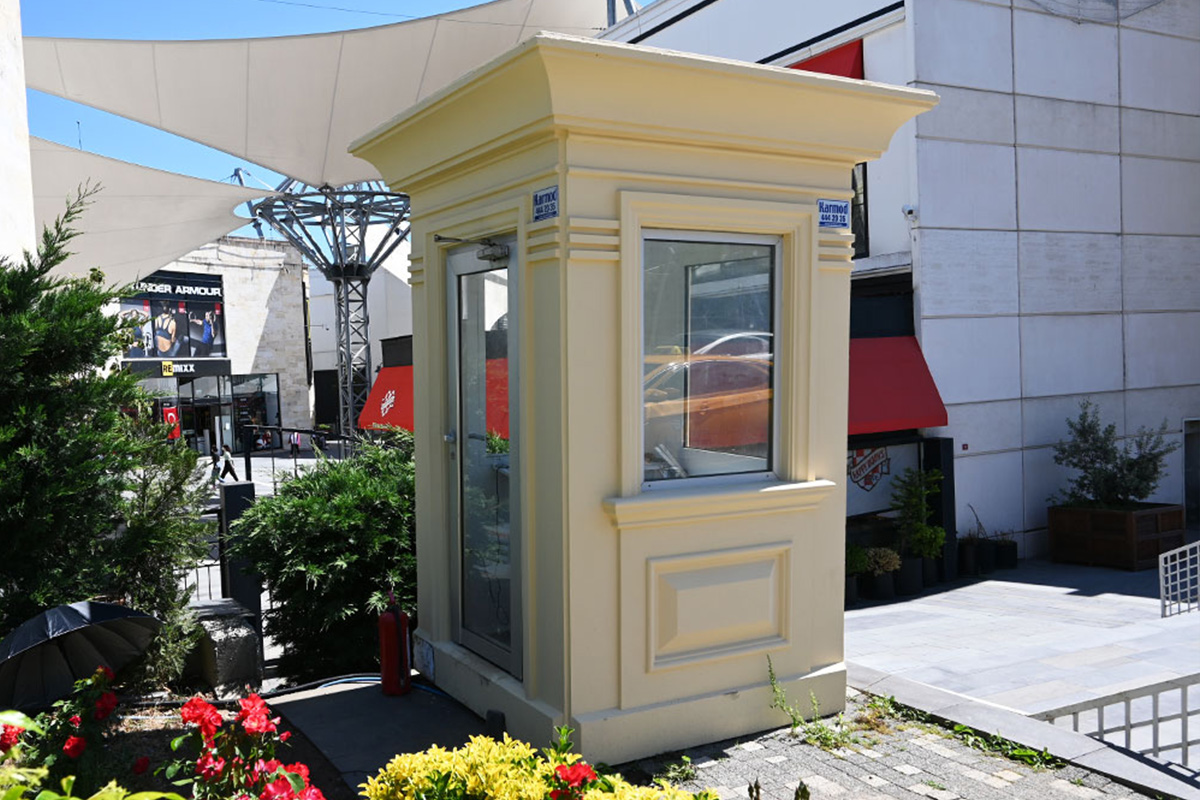
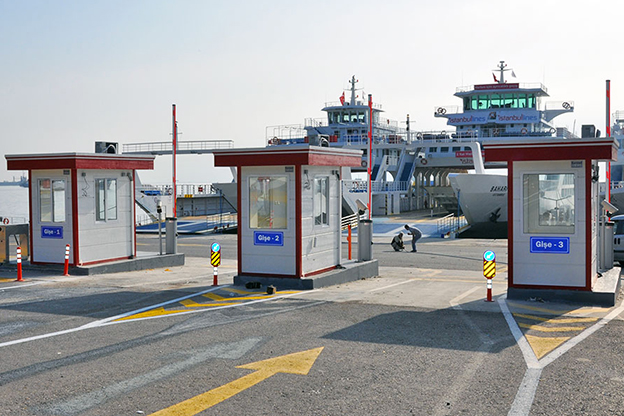
- Security buildings & technical units for controlled access points, utilities, and critical infrastructure
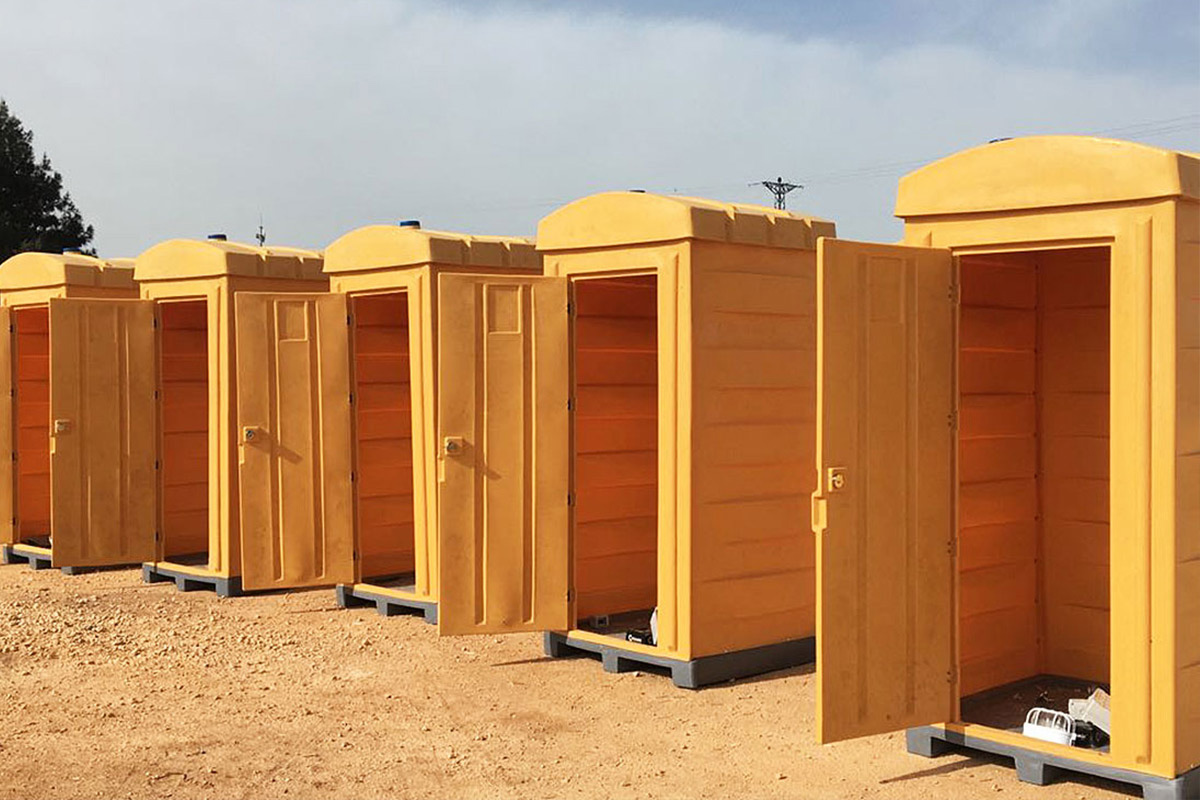
- Storage and logistics facilities supporting distribution networks and industrial zones
These applications highlight how modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions integrate smoothly into France’s structured project environments.

From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The process begins with a detailed project needs analysis. This phase defines functional requirements, occupancy levels, compliance obligations, and site conditions specific to France. Early alignment with regulatory expectations reduces approval risks and supports efficient project execution.
Custom design and specification development follows. Layouts, structural systems, insulation performance, and safety features are tailored to project objectives and local standards. This stage allows organisations to address performance and compliance requirements before production starts.
Factory production is then carried out under controlled conditions. Whether manufacturing complete modules or prefabricated components, this approach ensures consistent quality, reduced material waste, and limited exposure to weather-related delays.
Once production is complete, units are delivered to France through coordinated logistics planning. On-site installation is completed efficiently, often within a short timeframe, enabling facilities to become operational with minimal disruption to surrounding activities.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in France
Thermal insulation is a major consideration due to France’s energy efficiency regulations and climate variations. Buildings must support occupant comfort while meeting stringent performance standards.
Fire safety standards are central to project approval. Compliance with French regulations and project-specific safety requirements must be embedded into design and material selection from the outset.
Climate suitability extends beyond temperature. Moisture resistance, wind loads, and long-term durability influence engineering and material decisions, particularly for permanent installations.
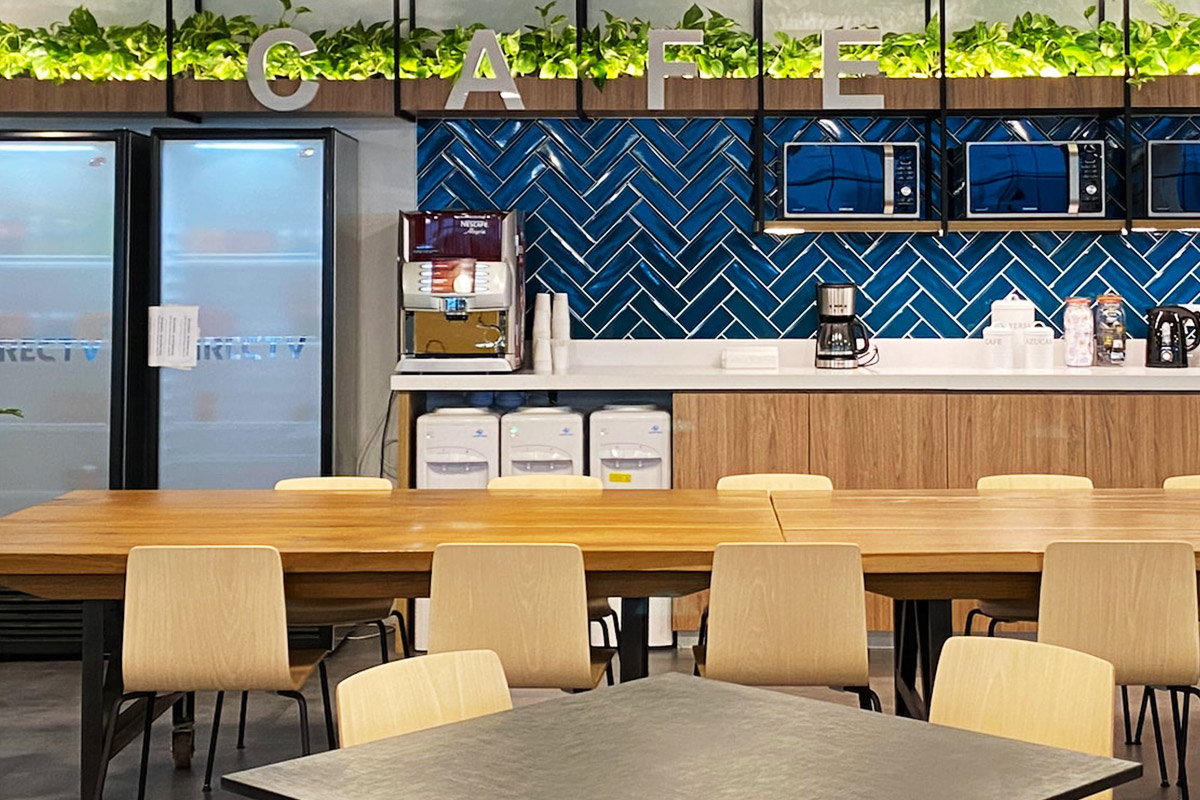
Custom layouts allow organisations to align interior spaces with operational workflows. Flexible planning supports efficient use of space in offices, educational facilities, accommodation units, and technical environments.
With experience gained across European markets, Karmod brings a strong understanding of how modular buildings and prefabricated building systems can be adapted to France’s regulatory and operational context. Drawing on this background, Karmod modular building solutions are designed to balance speed, durability, and compliance while supporting long-term asset strategies. By focusing on controlled production and consistent quality, Karmod provides building solutions that integrate reliably into complex French construction projects and procurement frameworks.