Australia’s construction landscape has been undergoing a structural shift over the last decade. Rising labour costs, geographically dispersed project locations, and the need for faster, more predictable delivery models have made modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions a strategic choice rather than an alternative. For corporate decision-makers, government bodies, and large-scale operators, these systems offer a practical response to Australia’s operational and environmental realities.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Australia
One of the primary drivers behind the growing adoption of modular buildings in Australia is workforce availability and cost. Skilled labour shortages, particularly in regional and remote areas, have significantly increased on-site construction expenses. Modular construction reduces on-site labour dependency by shifting most of the work to controlled factory environments, where productivity and quality can be managed more efficiently.
Construction timelines are another critical factor. Large infrastructure, mining, and energy projects often operate on strict schedules, where delays can lead to substantial financial losses. Modular buildings allow parallel processes—site preparation and building production happen simultaneously—shortening overall project durations.
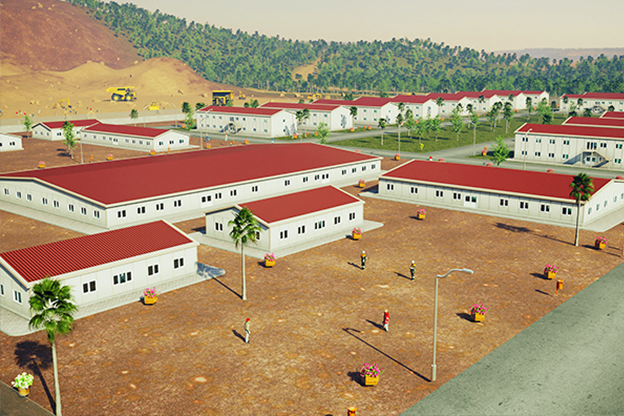
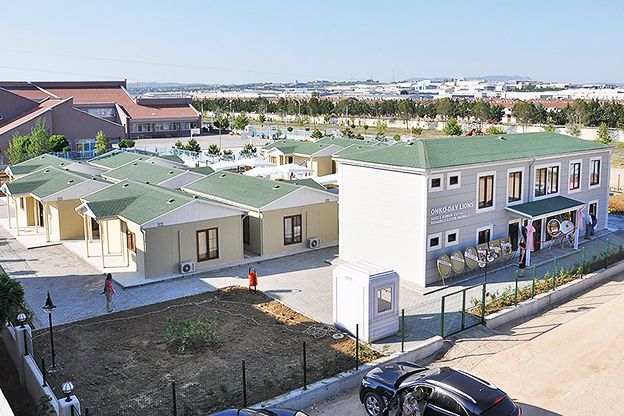
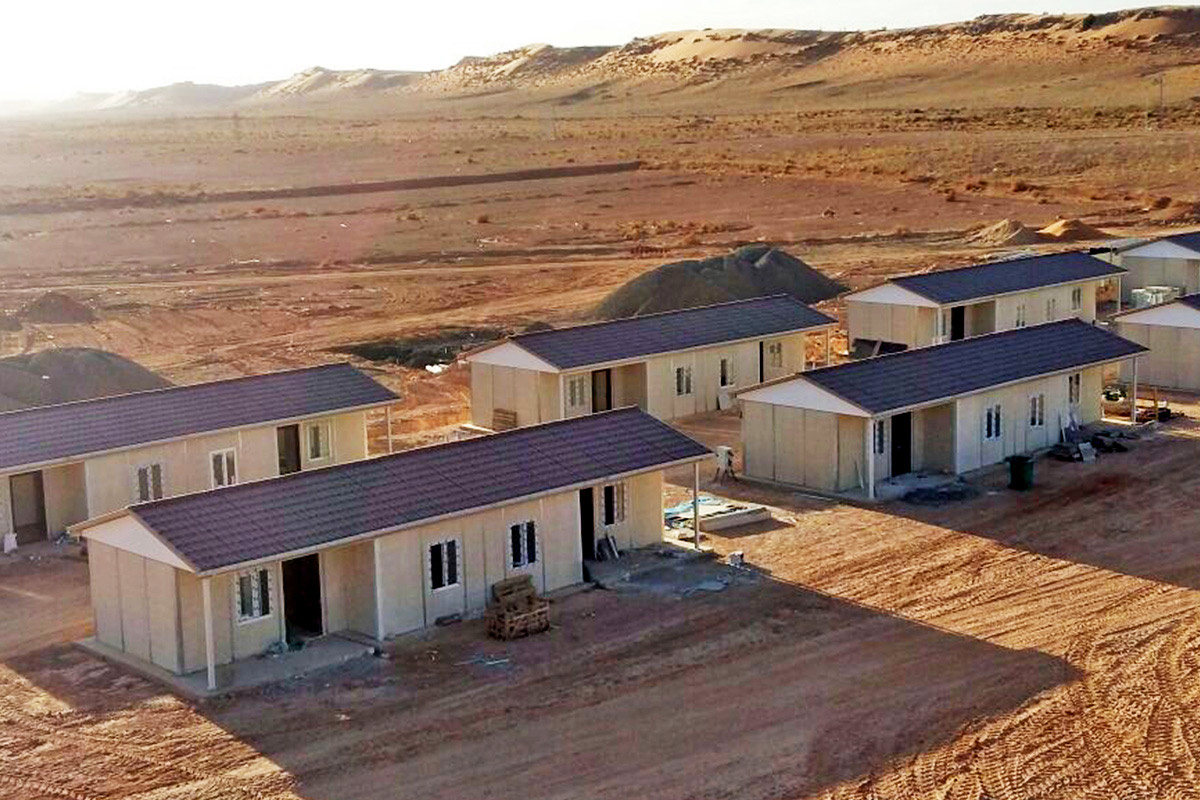
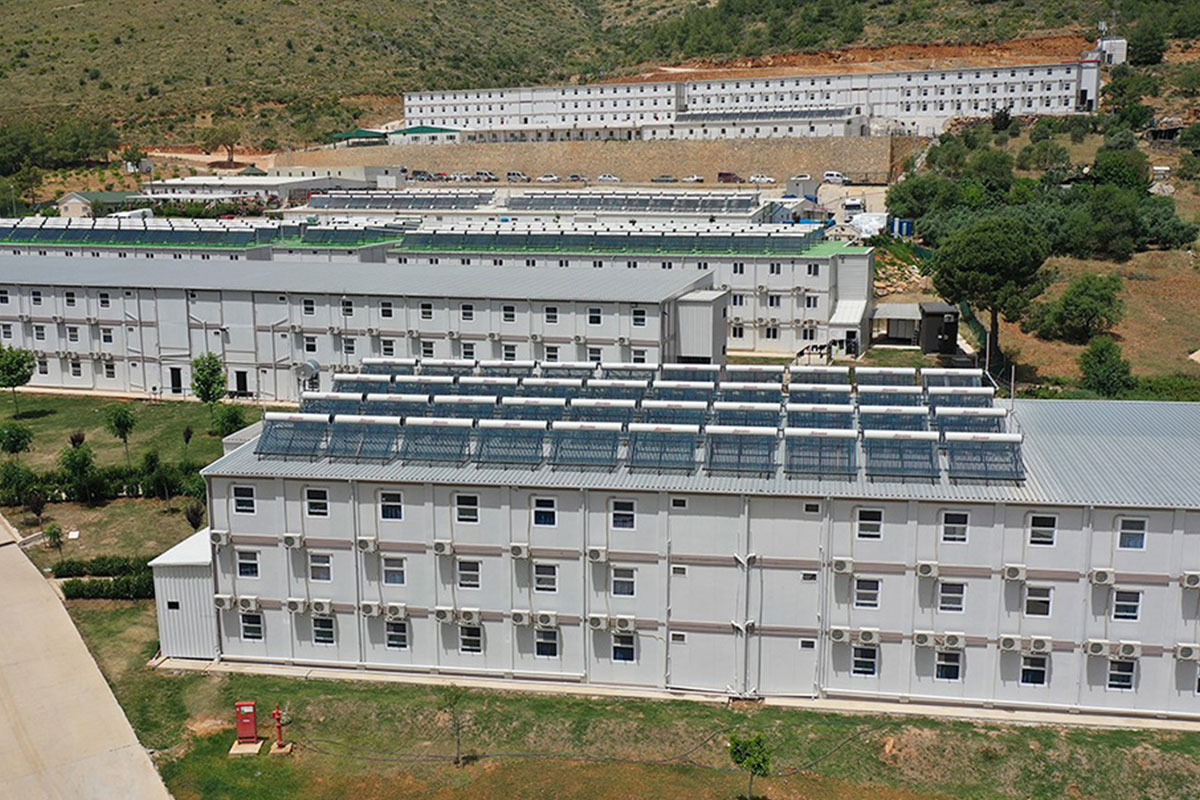
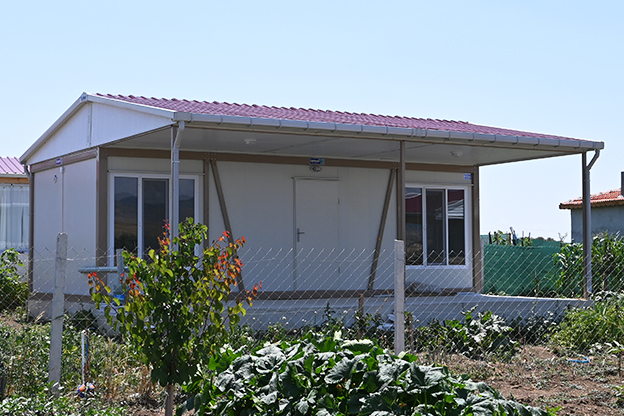
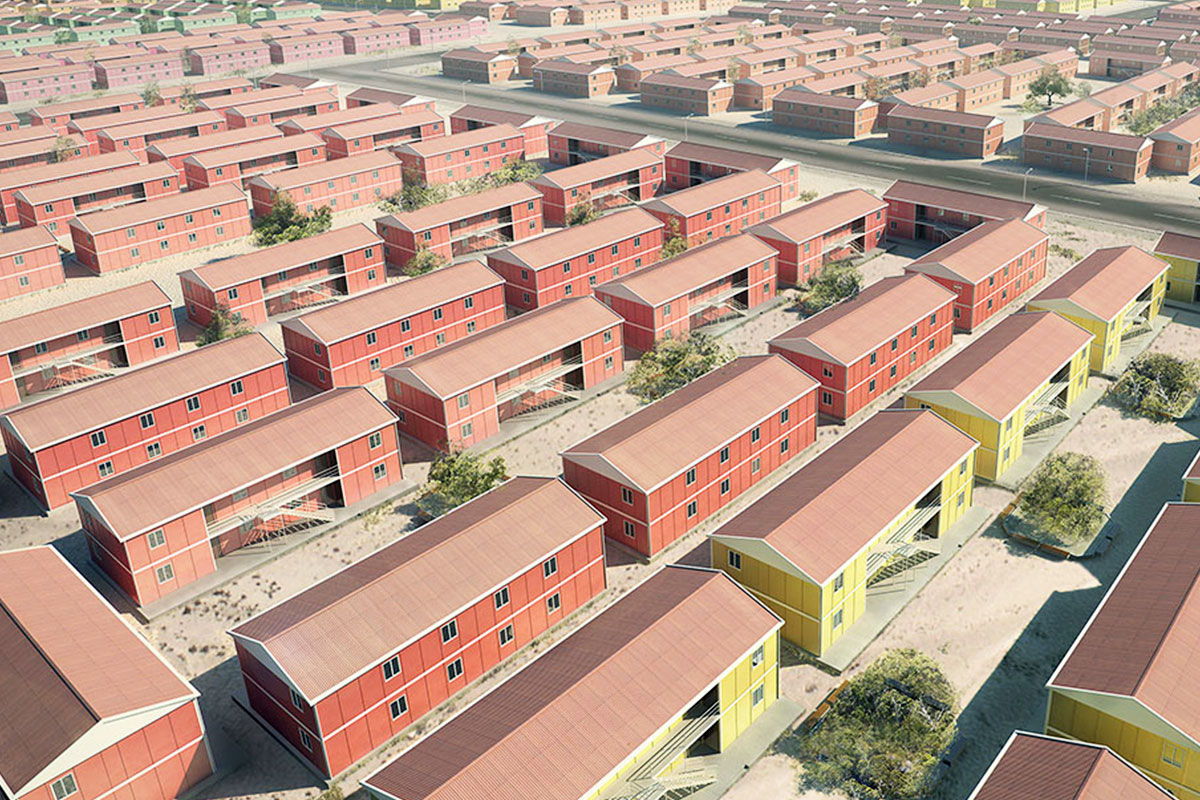
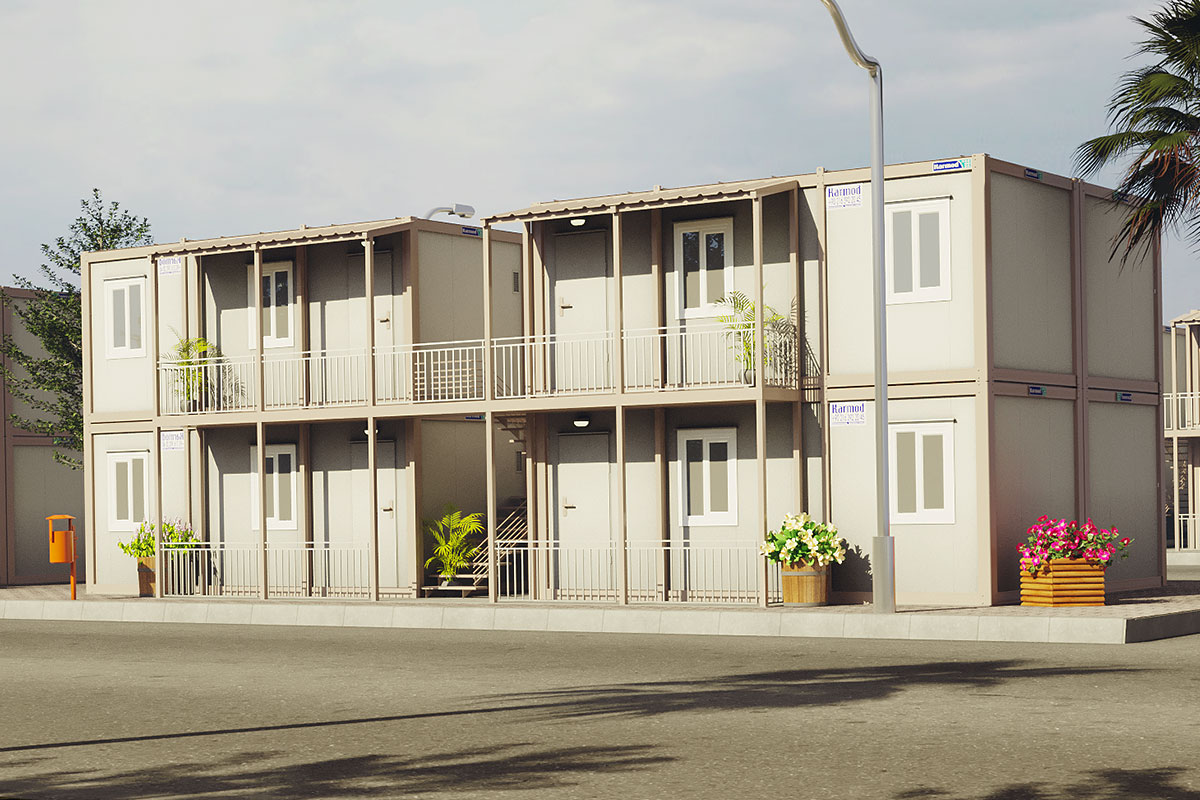
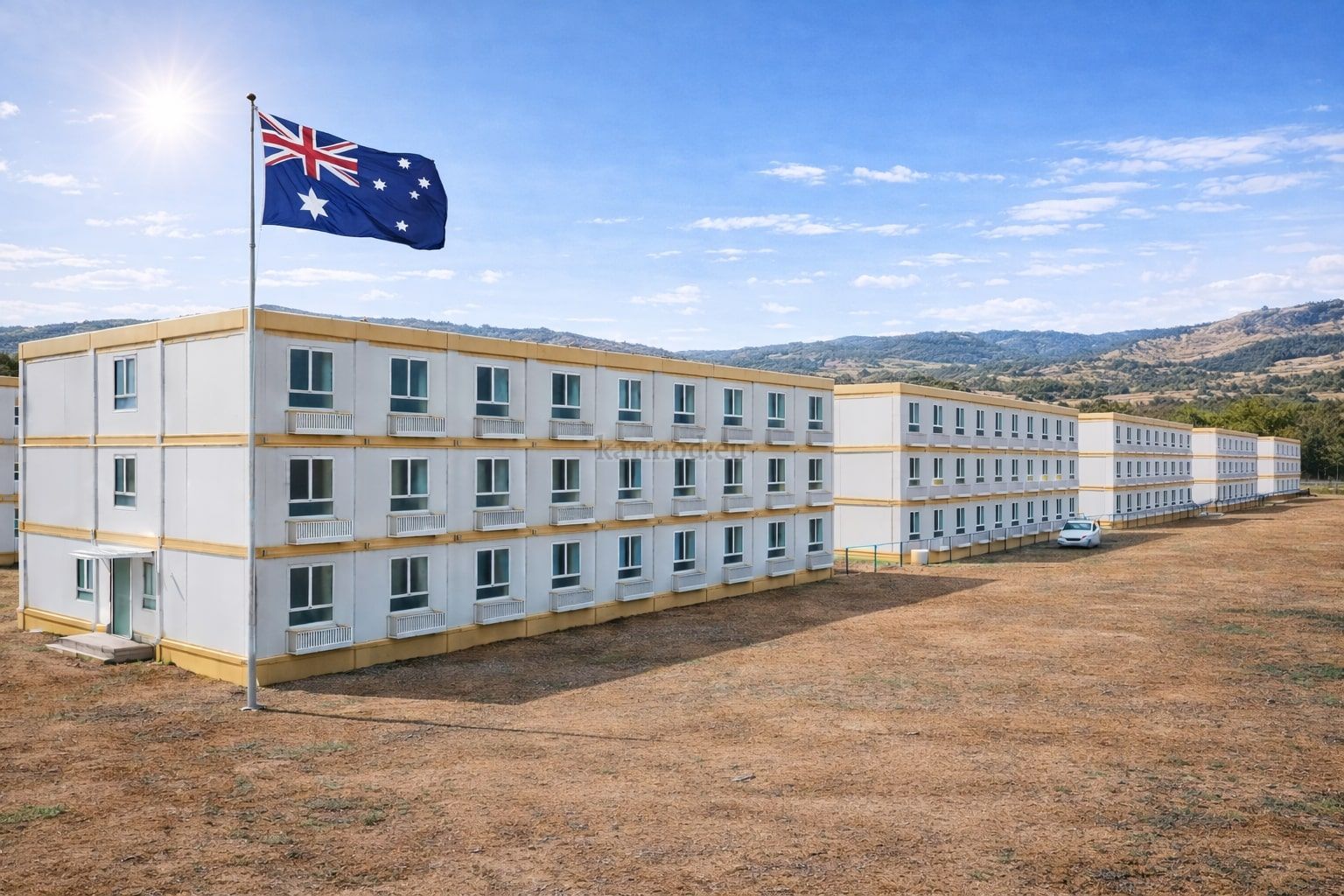
Australia also has a strong demand for both temporary and permanent structures. Mining camps, infrastructure projects, and remote community facilities frequently require relocatable buildings, while education, healthcare, and public-sector projects increasingly prefer permanent prefabricated solutions that meet long-term performance standards.
Sector-specific demand plays a major role as well. Logistics hubs near ports, industrial zones, renewable energy projects, and public infrastructure developments all benefit from scalable and fast-deployment building systems. In these contexts, modular and prefabricated approaches align well with Australia’s project-based economy.

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve different functional needs.
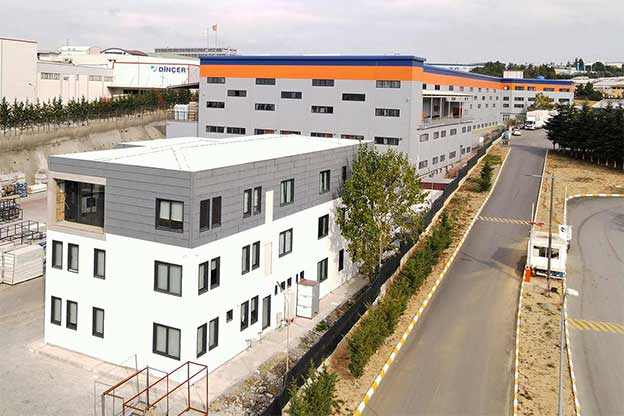
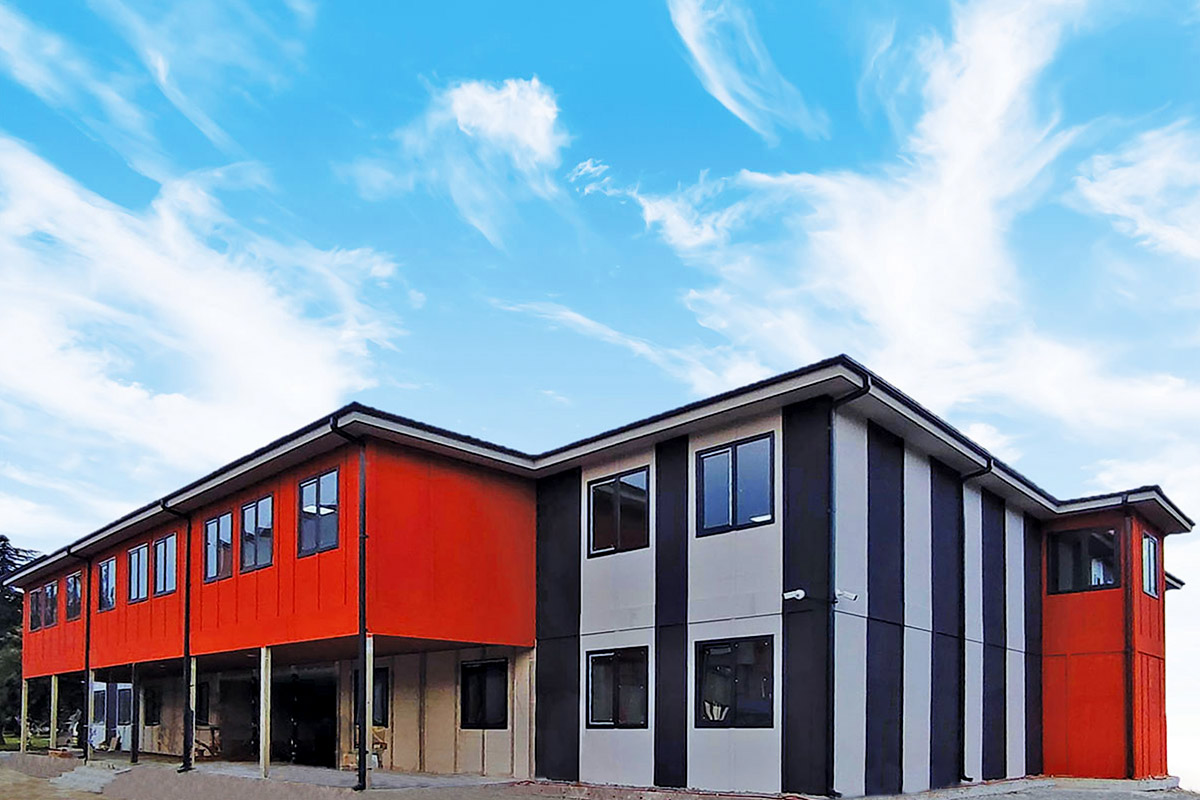
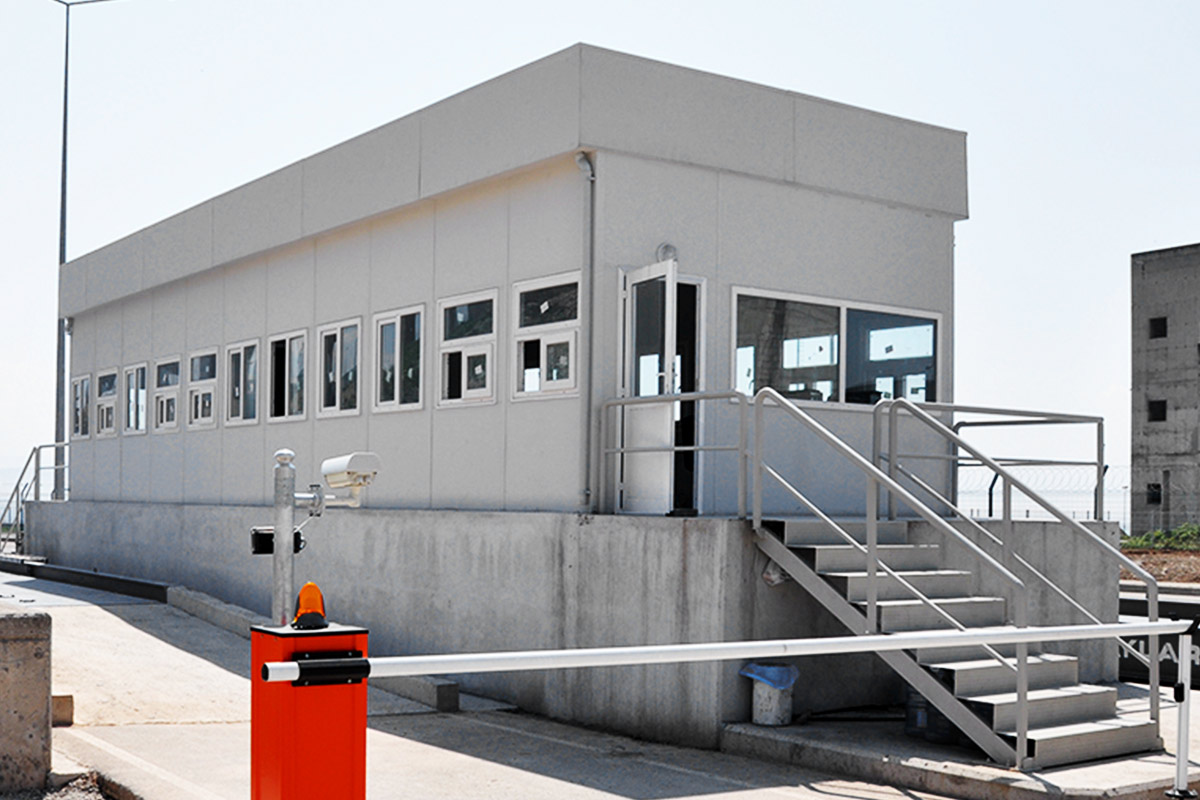
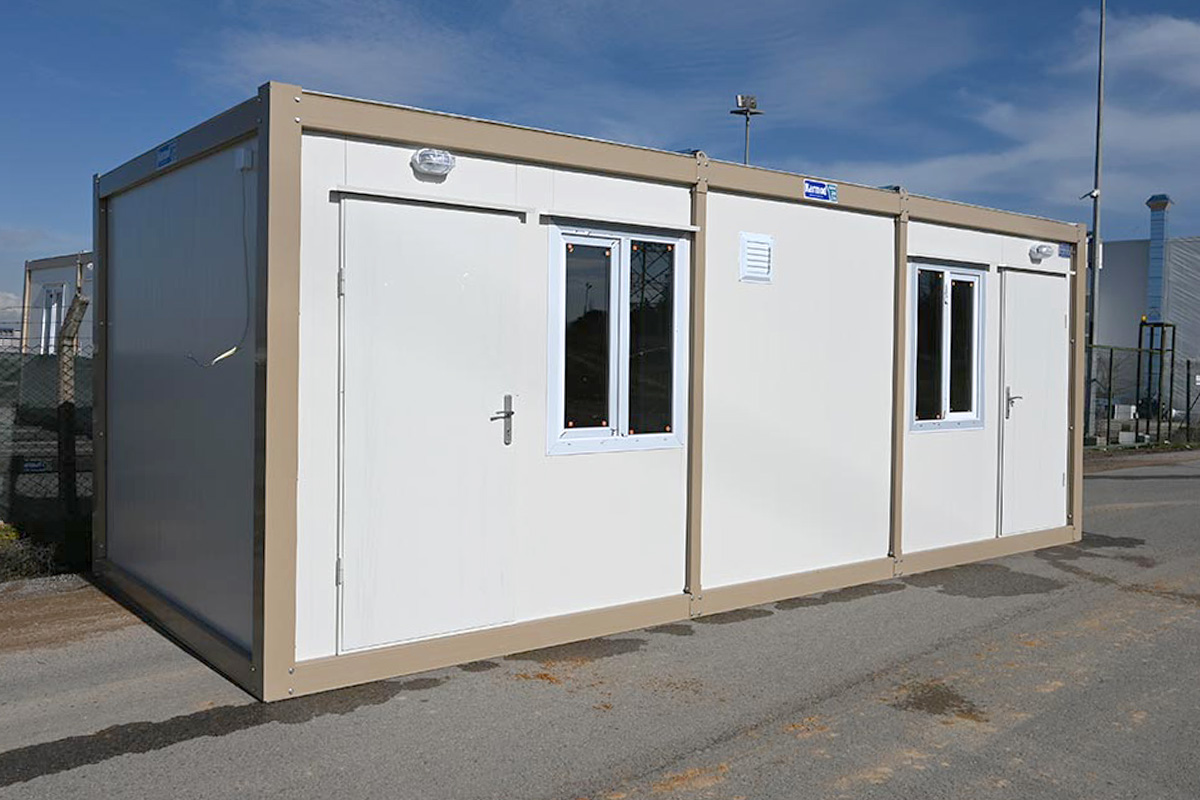
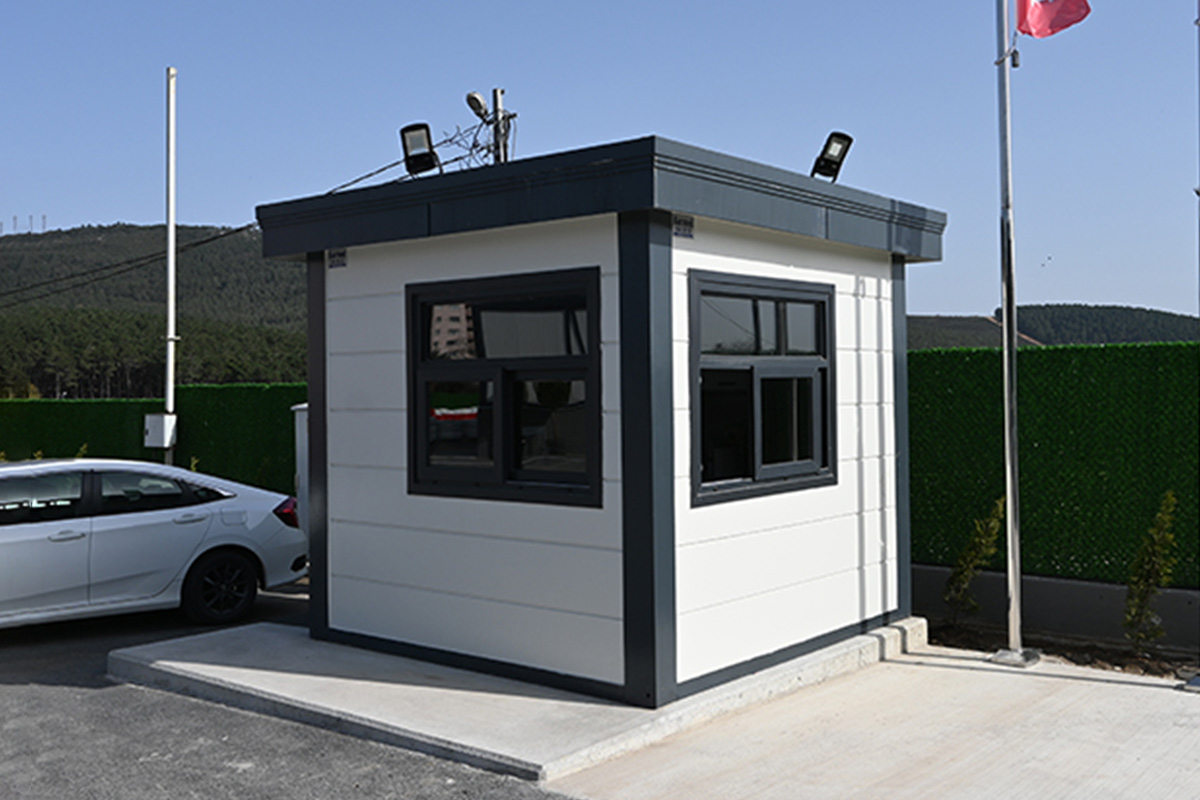
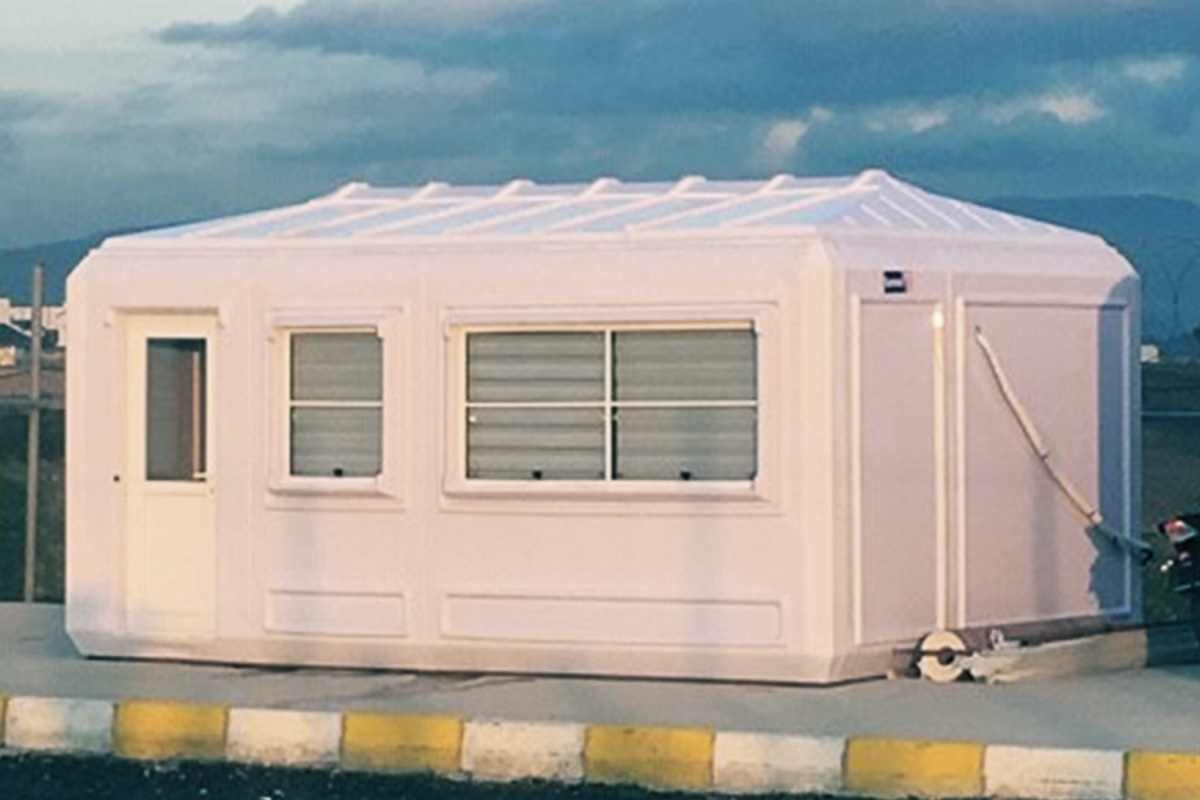
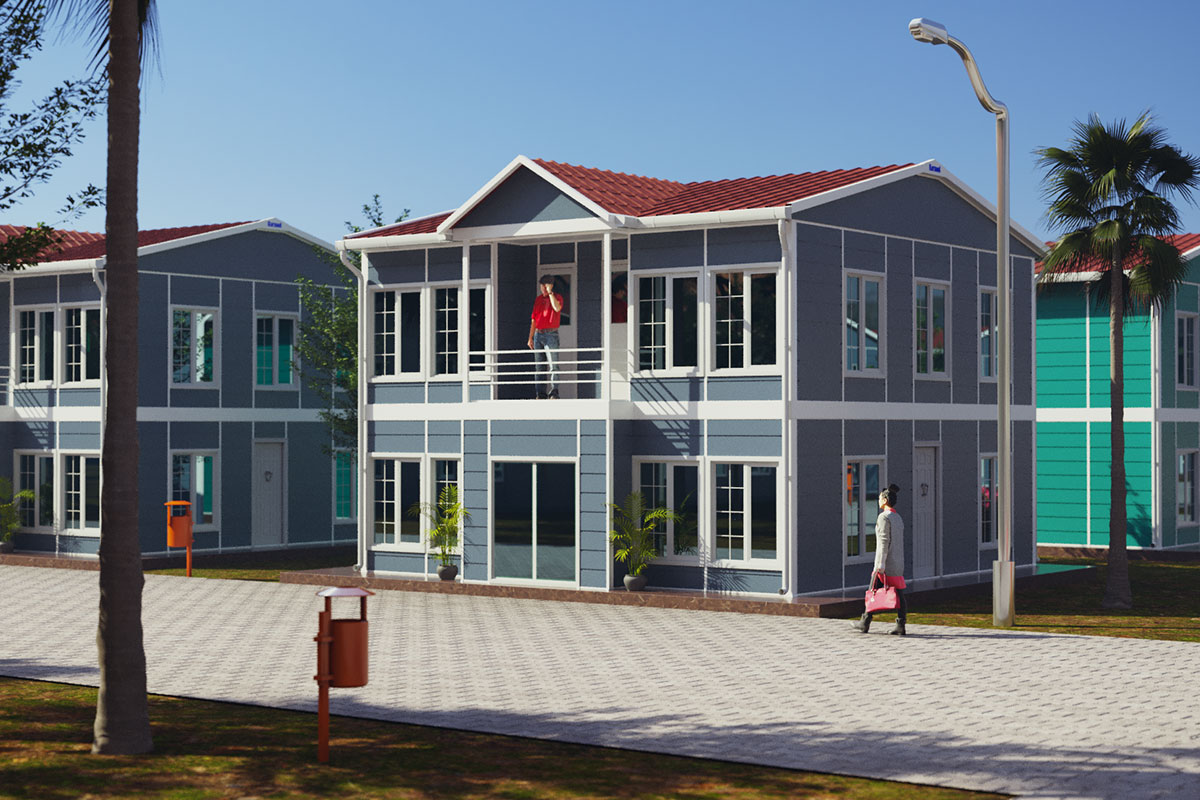
Modular buildings are produced as volumetric units, fully or partially fitted out in the factory. These modules are transported to site and assembled quickly. Their key advantage lies in mobility and expandability. In Australia, modular buildings are frequently used for site offices, worker accommodation, and facilities that may need to be relocated or expanded as projects evolve.
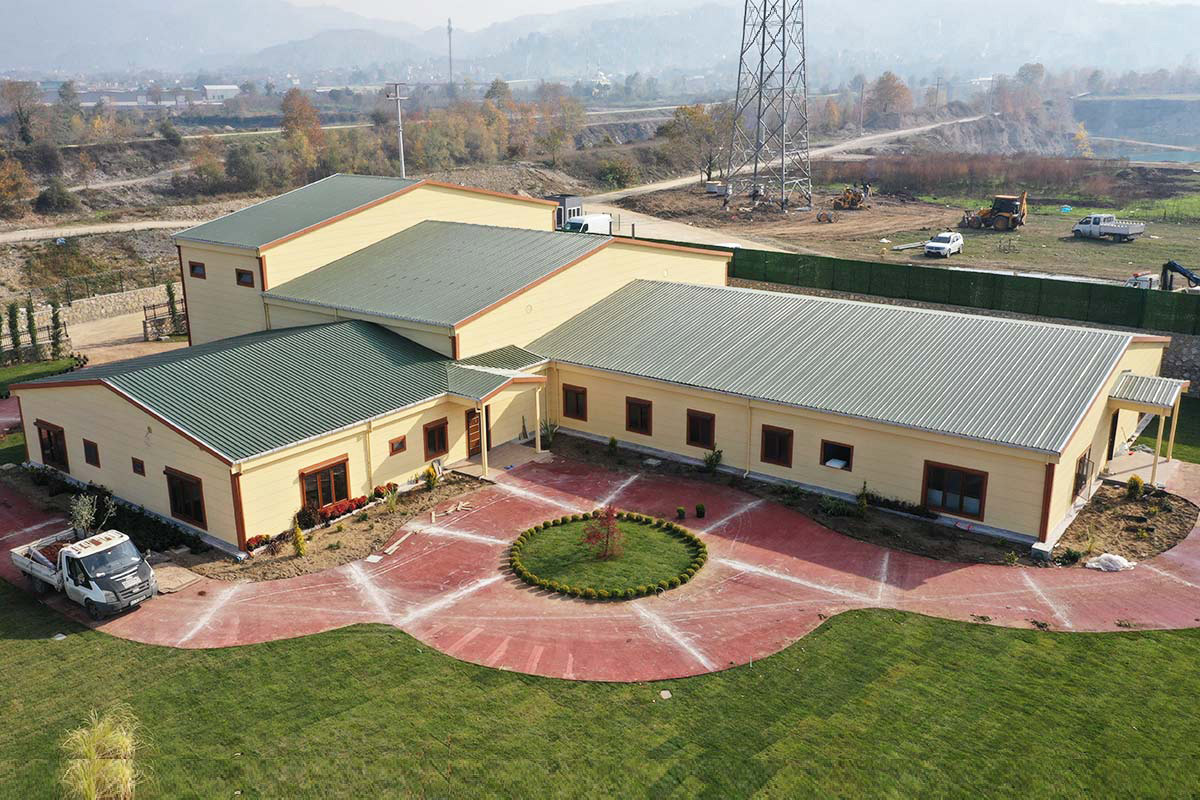
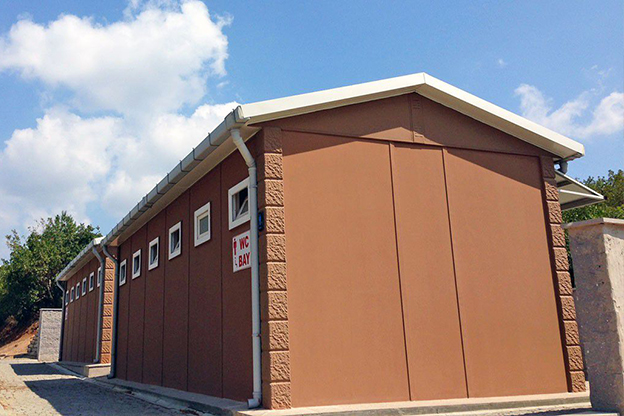
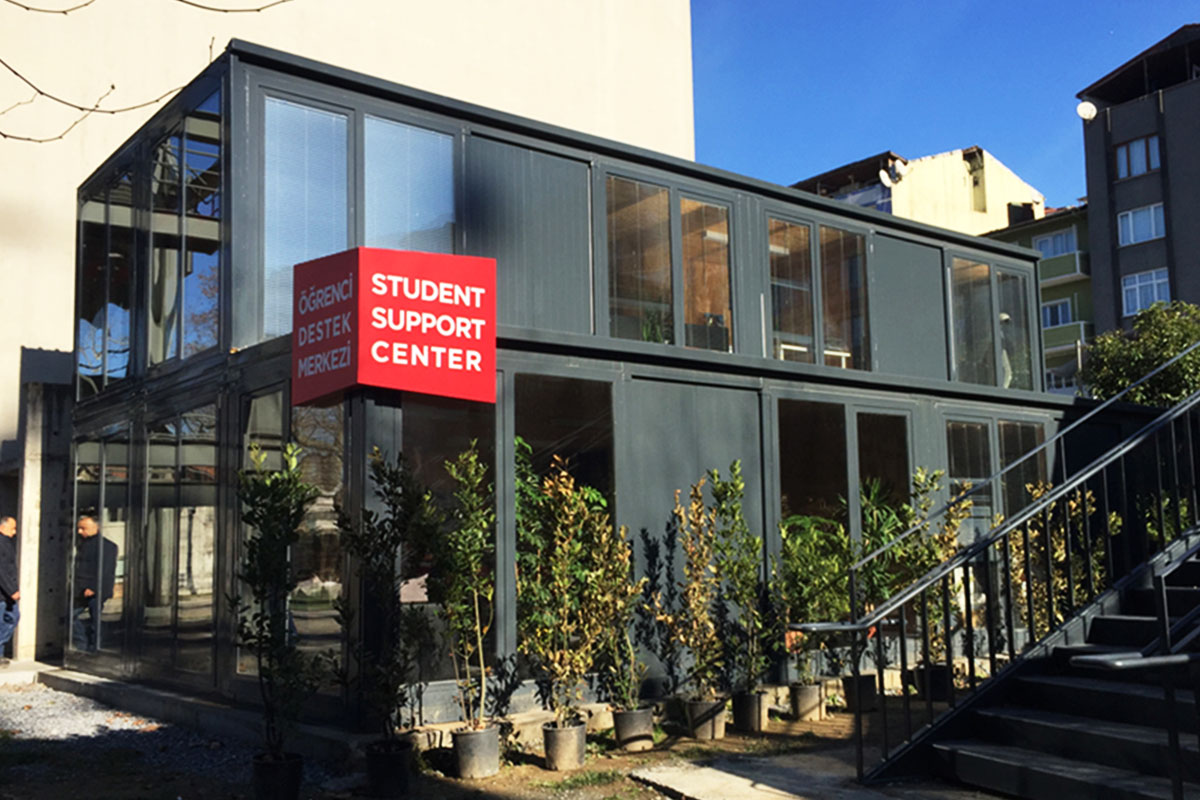
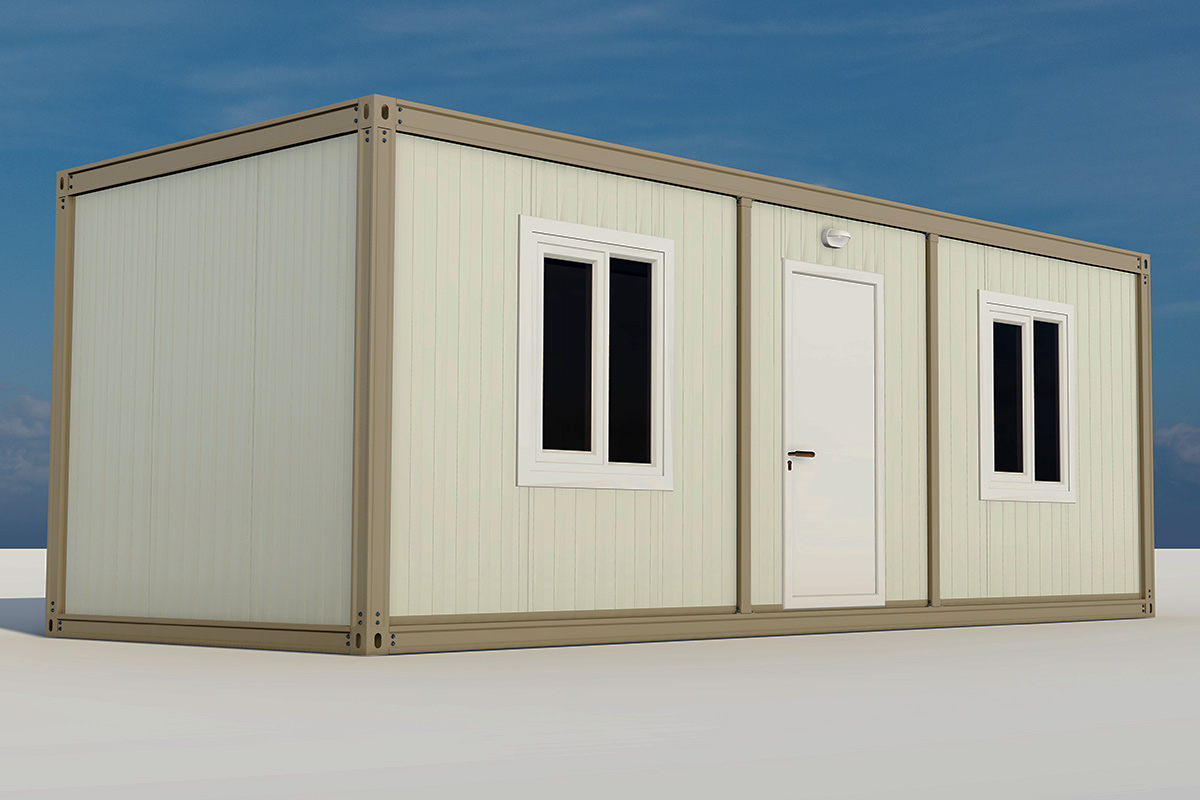
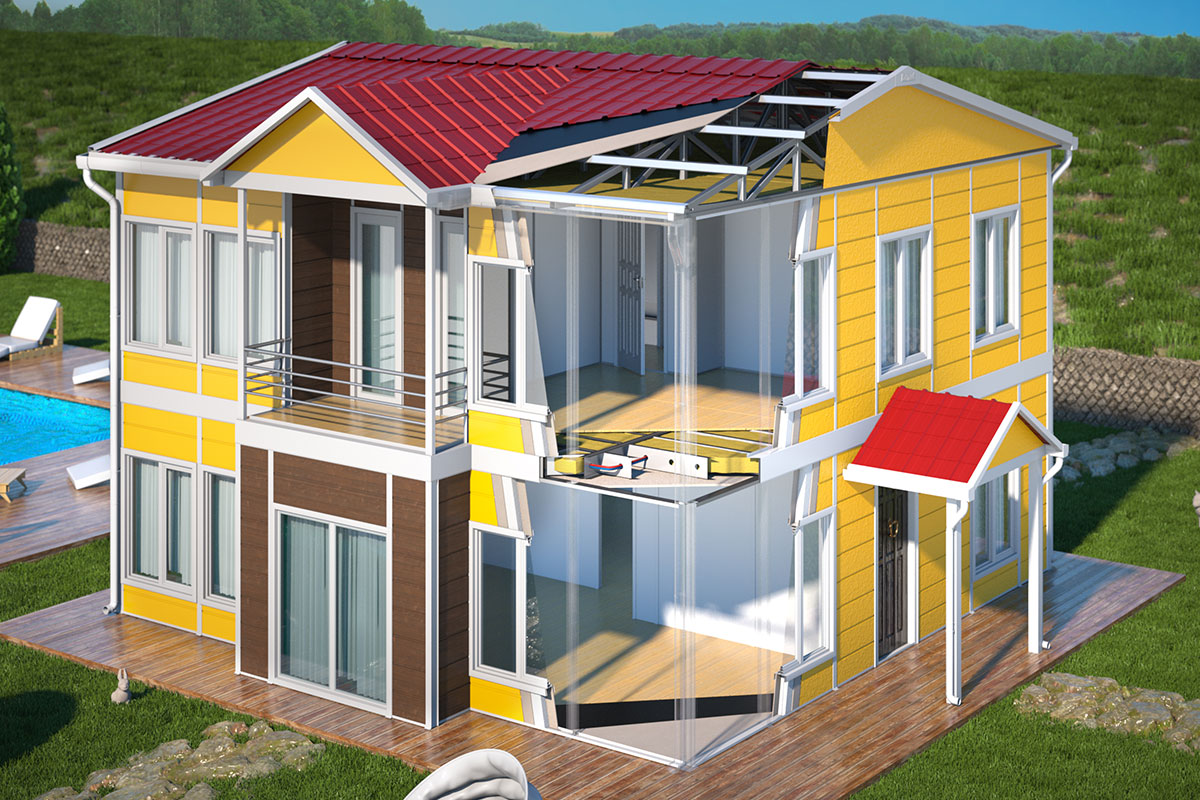
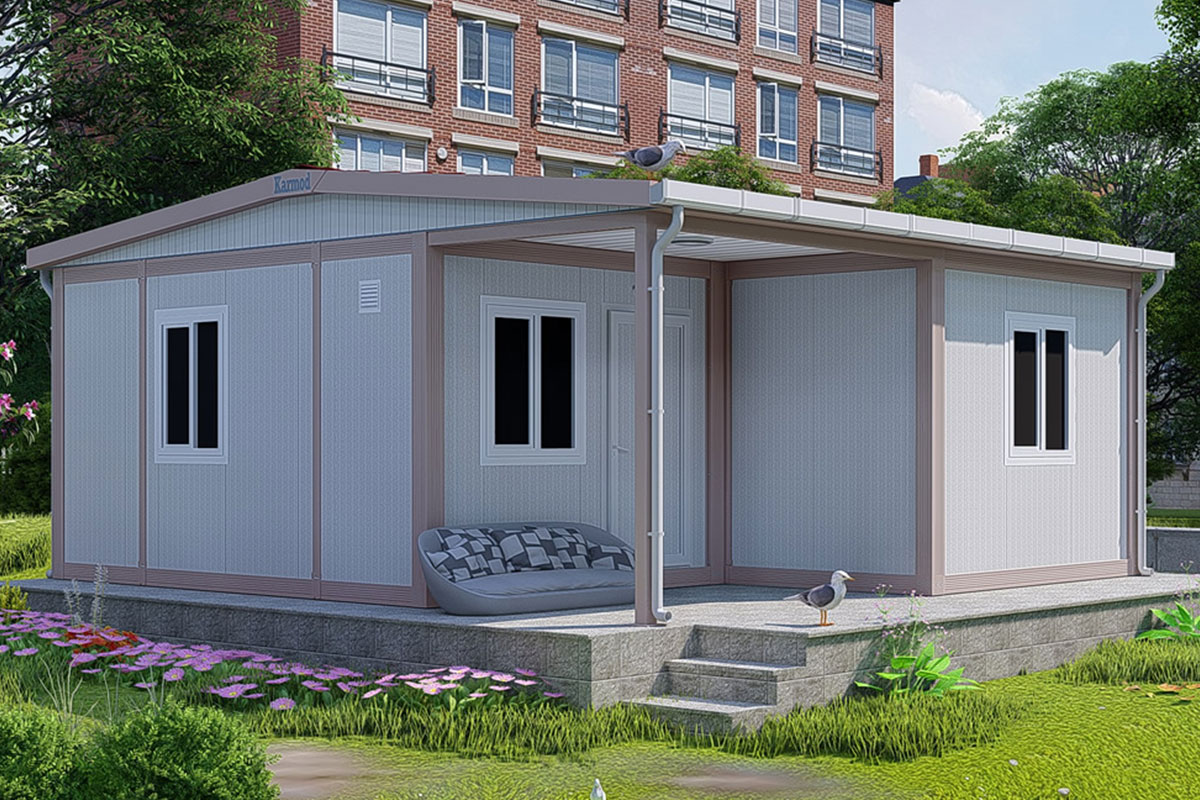
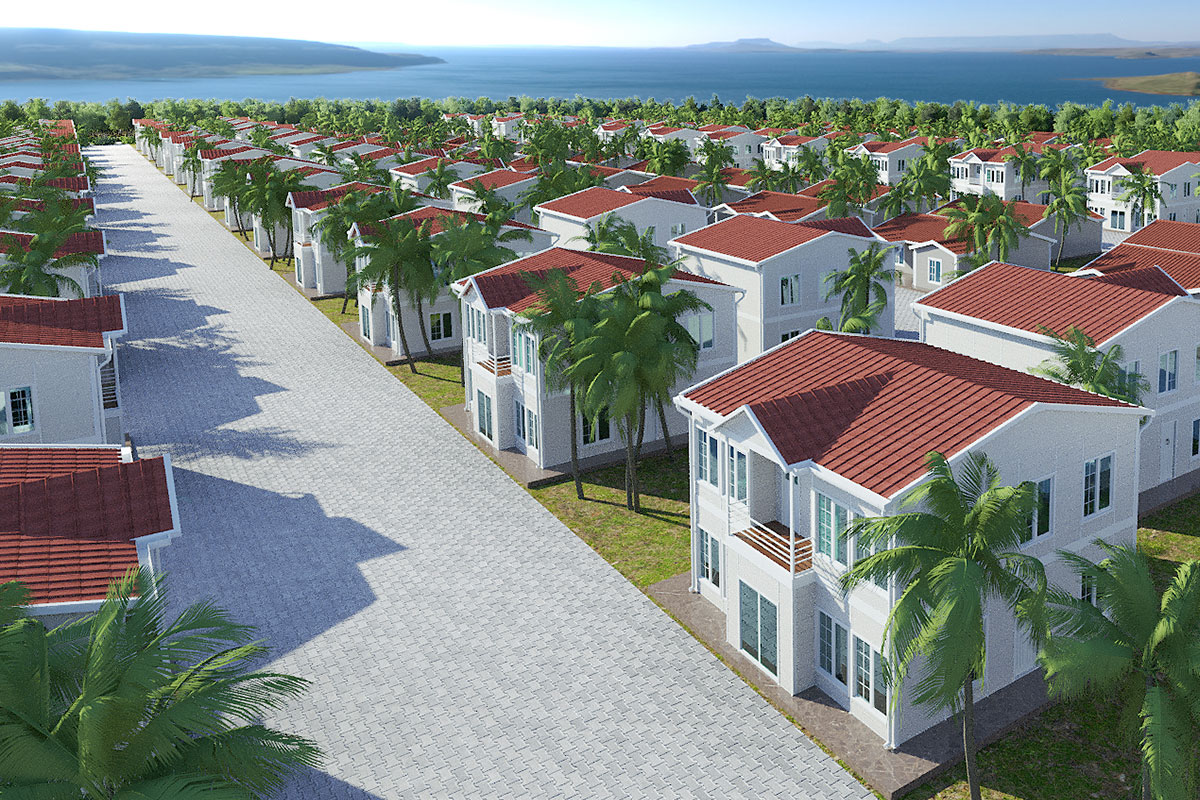
A prefabricated building, on the other hand, is typically based on panels or structural components manufactured off-site and assembled on location into a permanent structure. This approach is well suited for long-term facilities such as schools, healthcare units, and administrative buildings where architectural integration and lifecycle performance are priorities.
In Australia’s remote and regional projects, modular buildings are often preferred due to logistics efficiency and rapid deployment. In metropolitan or long-term public projects, prefabricated building systems are commonly selected for their durability and compliance with permanent building regulations.
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Australia
Modular and prefabricated solutions are used across a wide range of sectors, responding to Australia’s diverse geographic and operational needs:
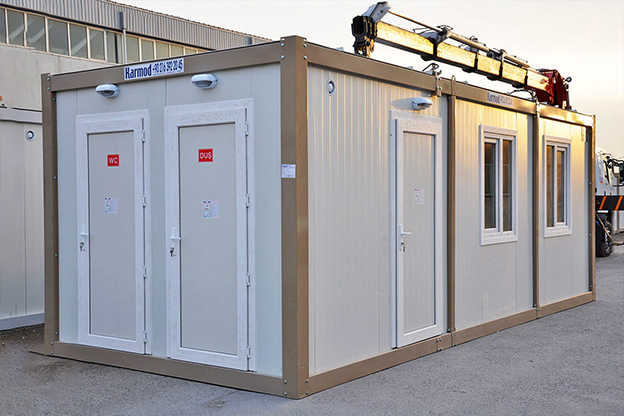
- Site offices & construction camps for infrastructure, mining, and civil engineering projects
- Worker accommodation buildings in remote regions, mining sites, and large-scale energy developments
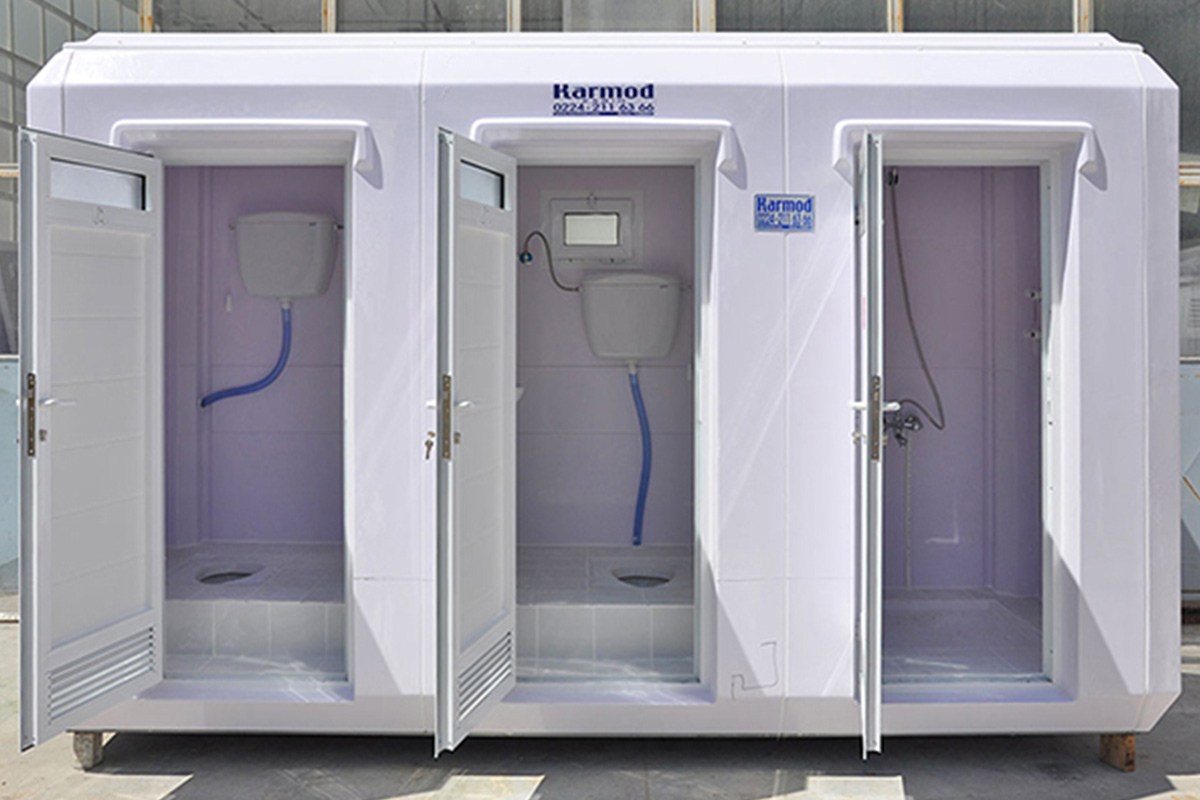
- Temporary schools & healthcare units to support growing populations or emergency needs
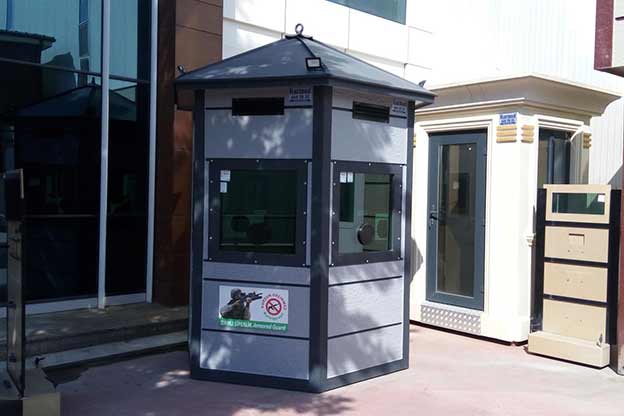
- Security buildings & technical units for controlled access points, utilities, and critical infrastructure
- Storage and logistics facilities near ports, industrial zones, and transport corridors
These applications demonstrate how modular buildings adapt to both short-term operational requirements and longer-term strategic investments.

From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The process begins with a detailed project needs analysis. Functional requirements, site conditions, regulatory constraints, and operational timelines are evaluated to define the most suitable building approach.
This is followed by custom design and specification development. Layouts, materials, insulation levels, and technical systems are tailored to Australian standards and climate conditions. At this stage, coordination between engineering, logistics, and compliance teams ensures that the building will perform as intended once installed.
Factory production is where modular and prefabricated systems gain their efficiency advantage. Controlled manufacturing environments improve quality consistency and reduce weather-related delays. Components or modules are completed to a high level before leaving the factory.
Delivery across Australia is planned with logistics efficiency in mind, particularly for remote or regional sites. Transport dimensions, access routes, and installation sequencing are carefully managed to avoid disruptions.
On-site installation is typically rapid. Modules are positioned and connected, or prefabricated components are assembled, allowing buildings to become operational in a fraction of the time required by traditional construction methods.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Australia
Thermal insulation is a major consideration due to Australia’s varied climate zones, ranging from hot, arid regions to cooler southern areas. Proper insulation design directly affects energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
Fire safety standards must comply with Australian regulations, especially for public buildings and worker accommodation. Modular and prefabricated systems need to integrate certified materials and fire-rated assemblies from the outset.
Climate suitability extends beyond temperature. Wind loads, humidity, and exposure conditions influence material selection and structural design, particularly in coastal or cyclone-prone regions.
Custom layouts are essential for meeting operational needs. Australian projects often require flexible internal arrangements to support changing workforce sizes or functional requirements over time.
Manufacturers with international experience, such as Karmod, approach these considerations with a system-based mindset rather than a one-size-fits-all model. Karmod modular building solutions are designed to adapt to regional requirements while maintaining consistent quality standards. Drawing on experience gained across multiple markets, Karmod has developed modular and prefabricated systems that align well with Australia’s regulatory and operational expectations.
For organisations evaluating modular buildings or prefabricated building strategies in Australia, the focus is no longer solely on speed. Reliability, compliance, and long-term performance are equally important. Providers like Karmod, with established production capabilities and sector experience, contribute to reducing project risk while supporting scalable growth in a demanding construction environment.