Bangladesh has become one of South Asia’s most dynamic construction markets, driven by rapid urbanization, export-oriented manufacturing, and major public infrastructure investments. In this environment, decision-makers are increasingly evaluating modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions as practical alternatives to conventional construction. These systems are not positioned as short-term fixes; they are now part of long-term planning for industrial, commercial, and public projects across the country.
The preference for factory-produced structures is shaped by Bangladesh’s need for speed, predictability, and quality control. With dense urban areas, challenging site conditions, and strict project timelines, off-site construction methods allow organizations to move faster while maintaining consistent standards. This shift is especially relevant for international investors, EPC contractors, and public authorities seeking reliable delivery models.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Bangladesh
Several structural factors explain the rising demand for modular buildings in Bangladesh. First, labor availability and cost dynamics play a decisive role. While the country has a large workforce, skilled construction labor is unevenly distributed, and productivity on traditional sites can vary significantly. Modular construction reduces on-site labor dependency by transferring most of the work to controlled factory environments.
Construction timelines are another critical factor. Large infrastructure projects, industrial parks, and export processing zones often operate under strict deadlines. Modular buildings enable parallel workflows—site preparation and building production occur simultaneously—cutting total project duration dramatically compared to conventional methods.
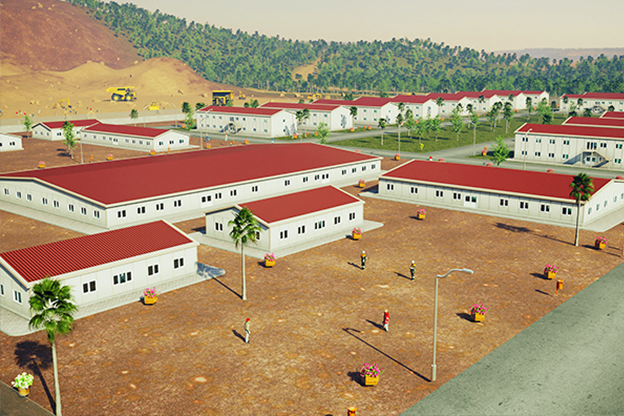
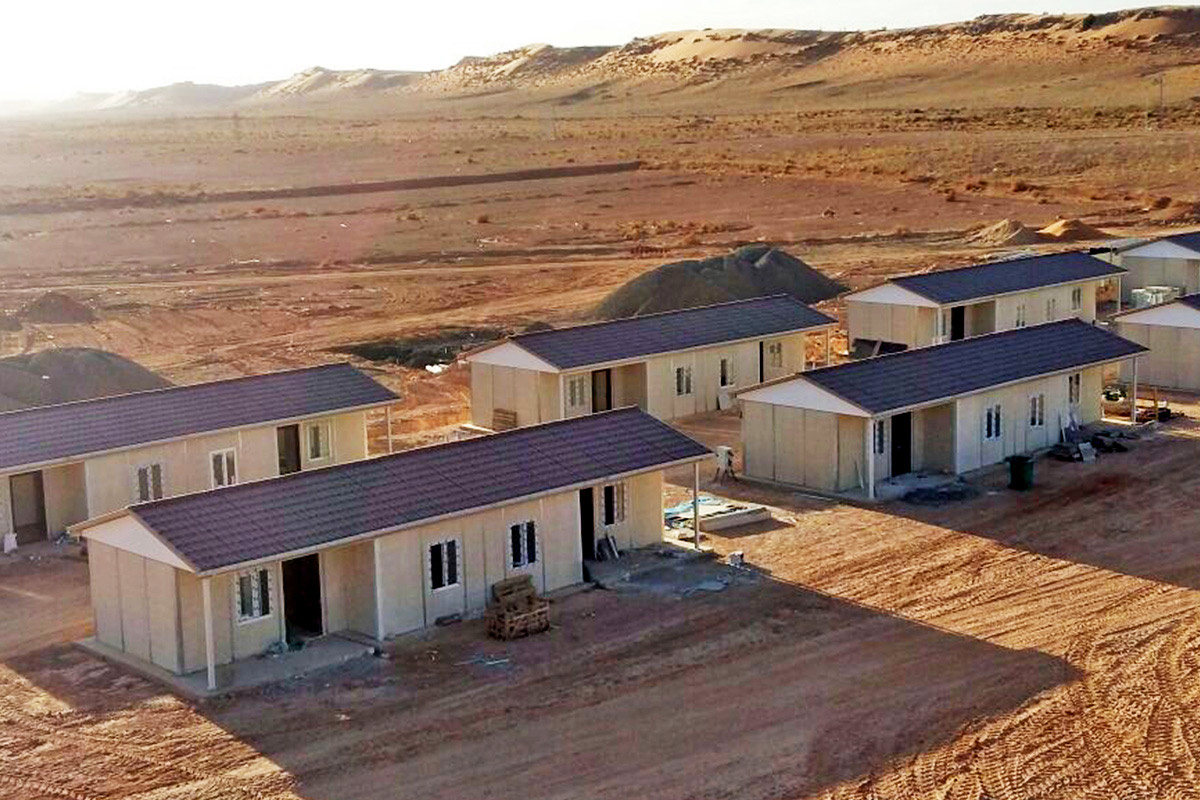
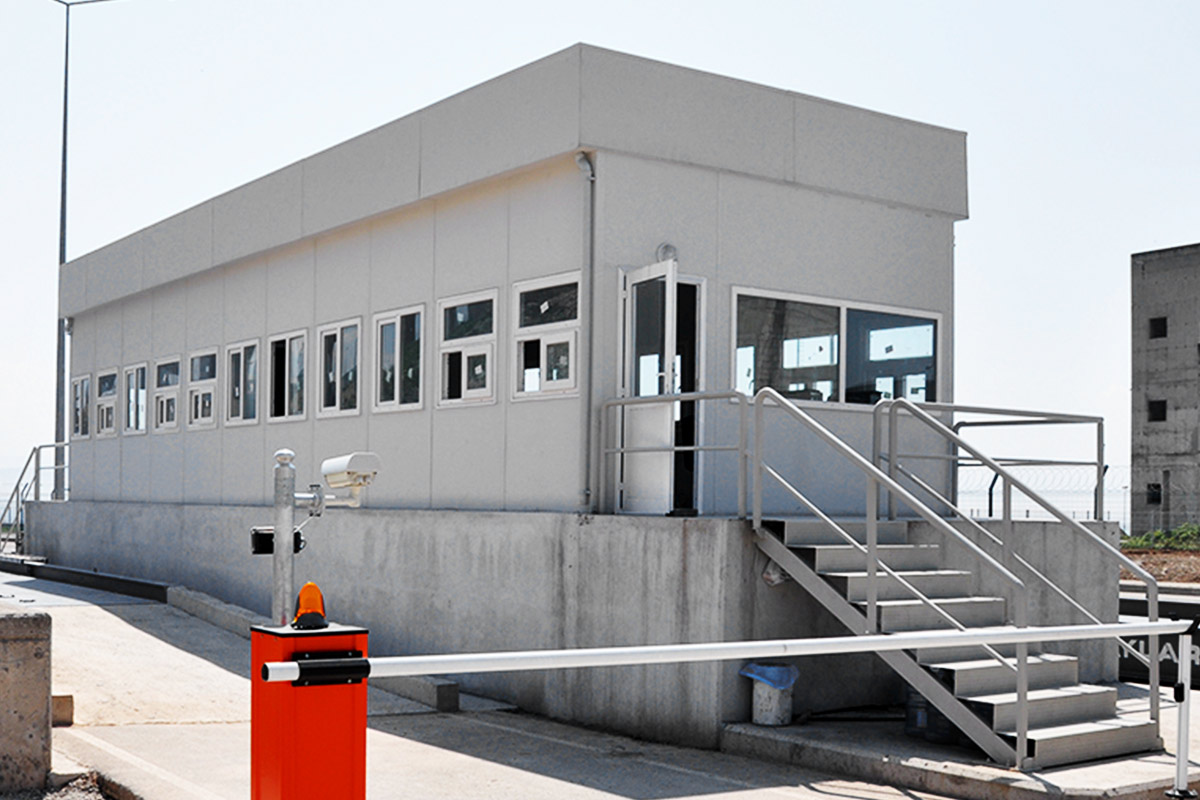
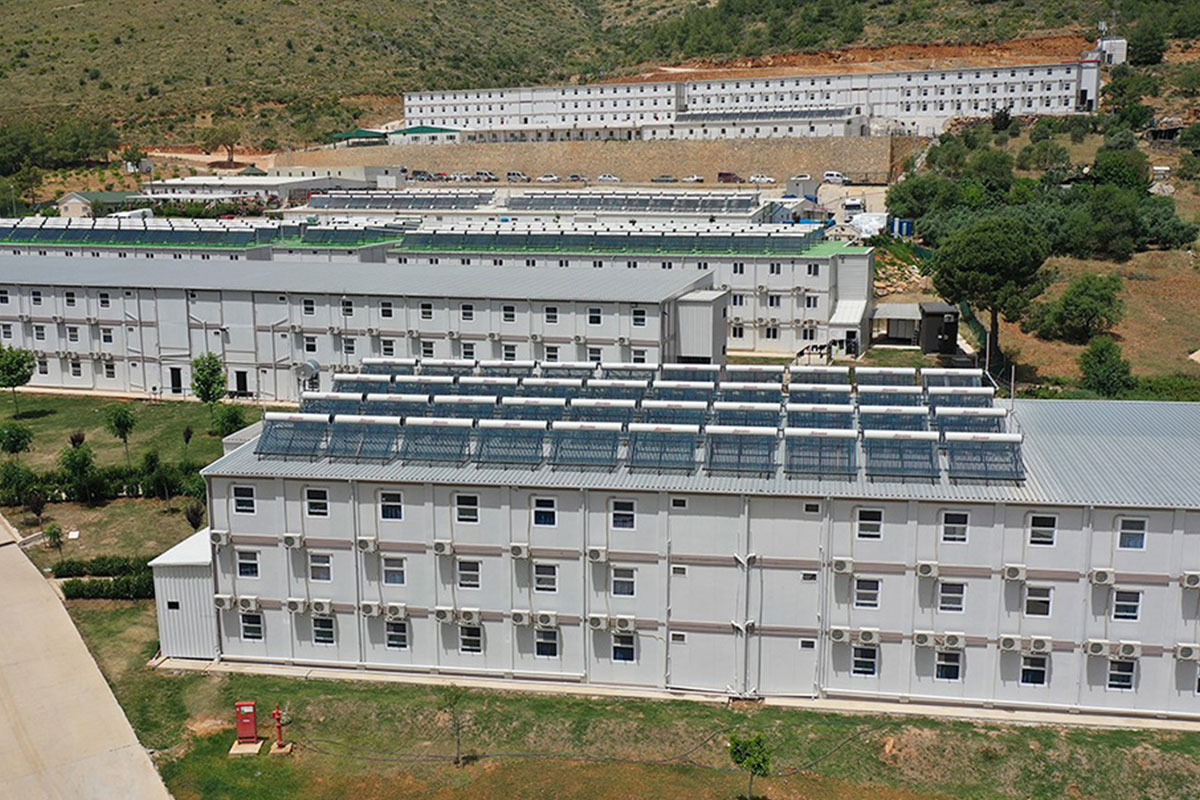
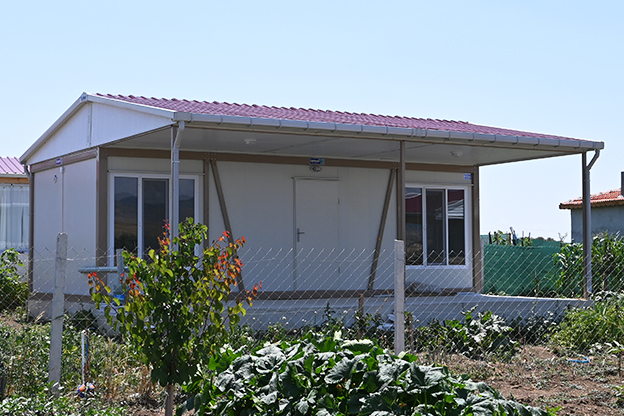
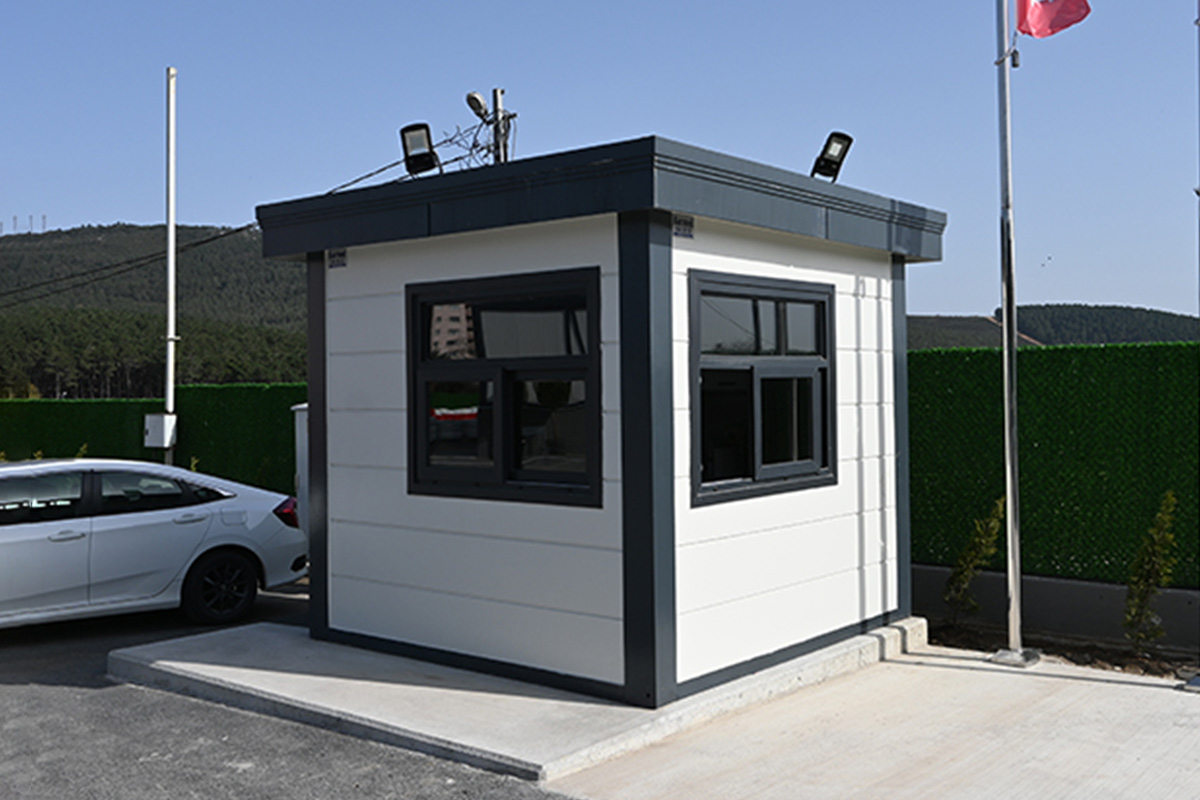
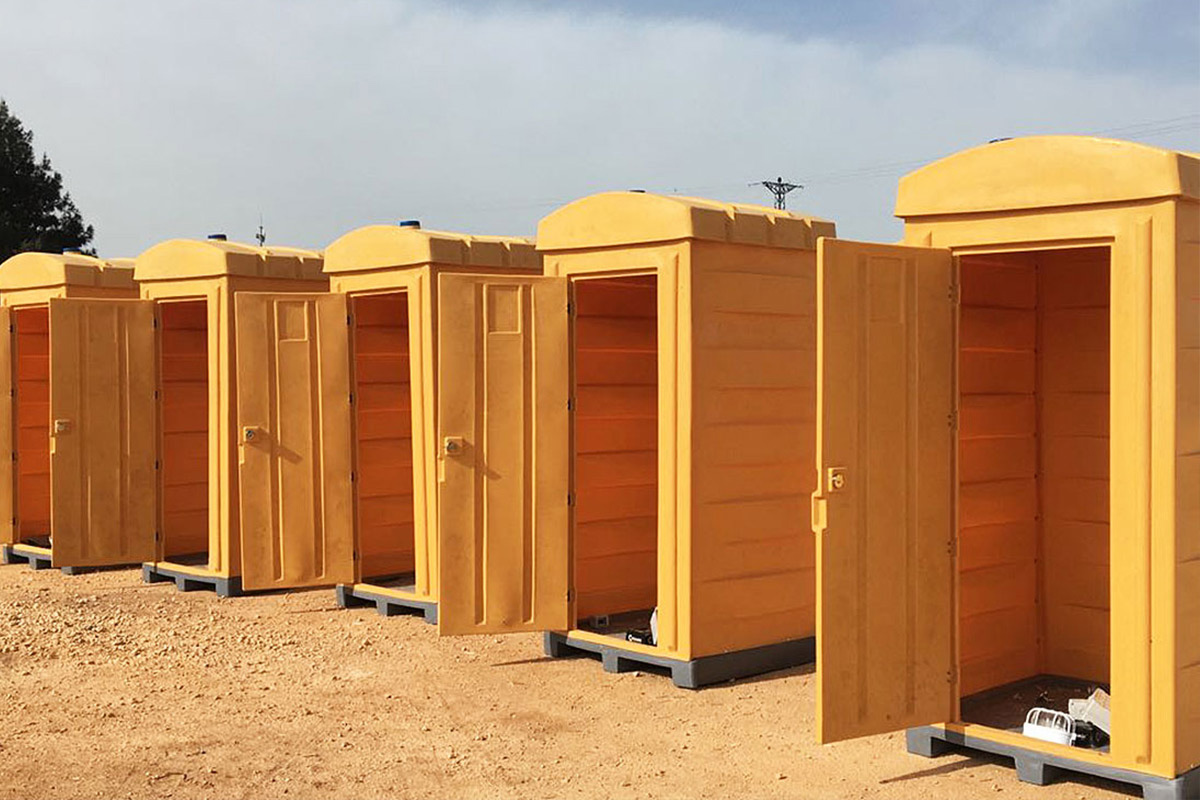
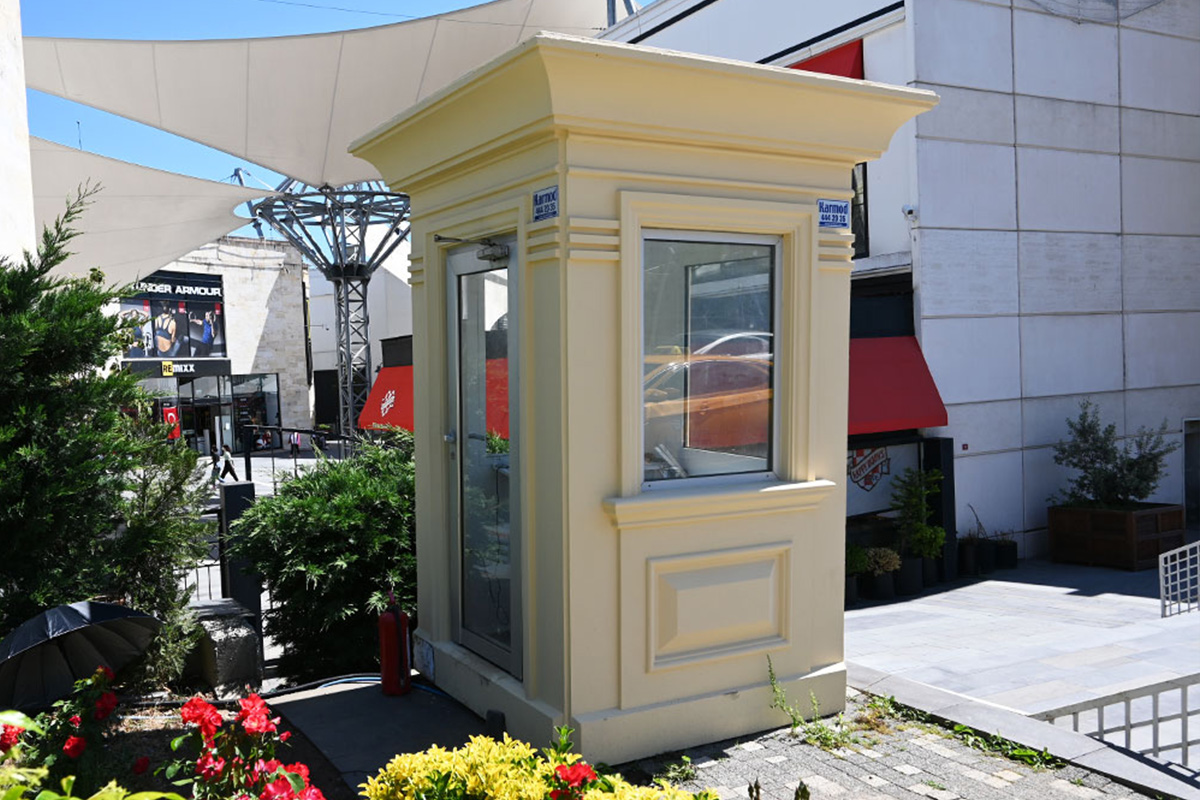
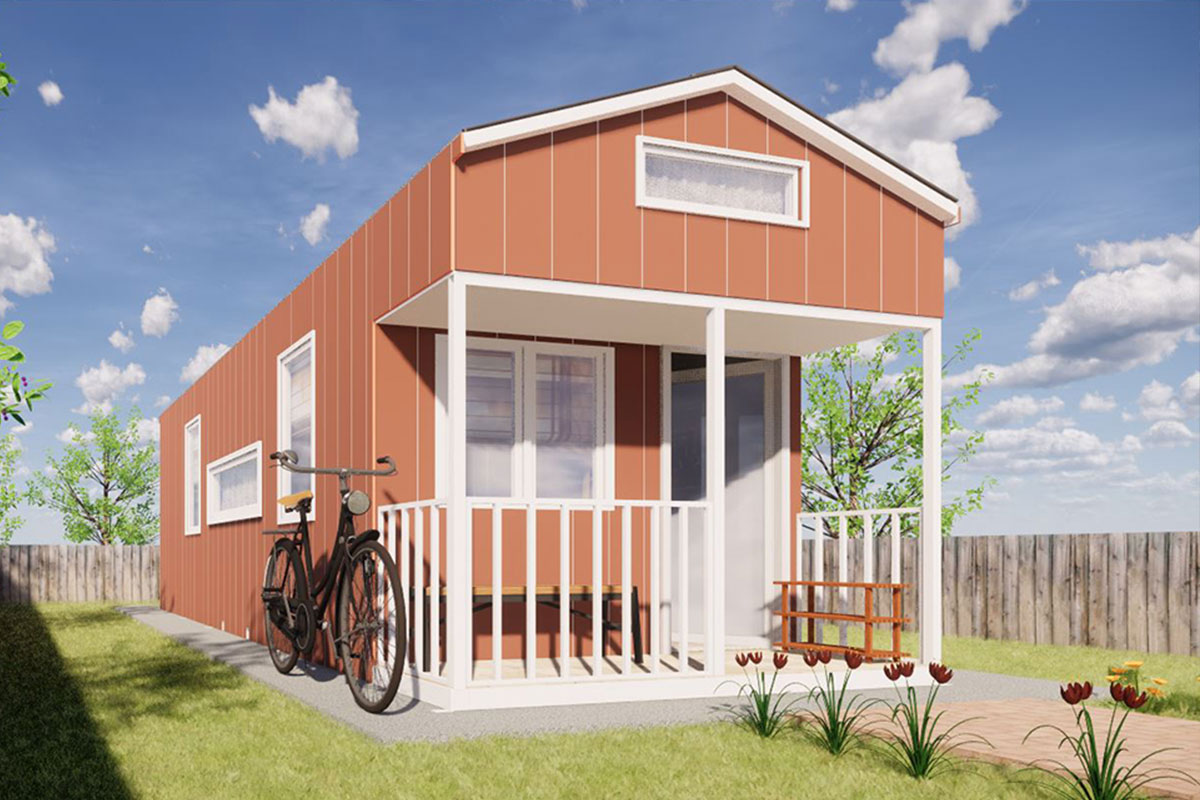
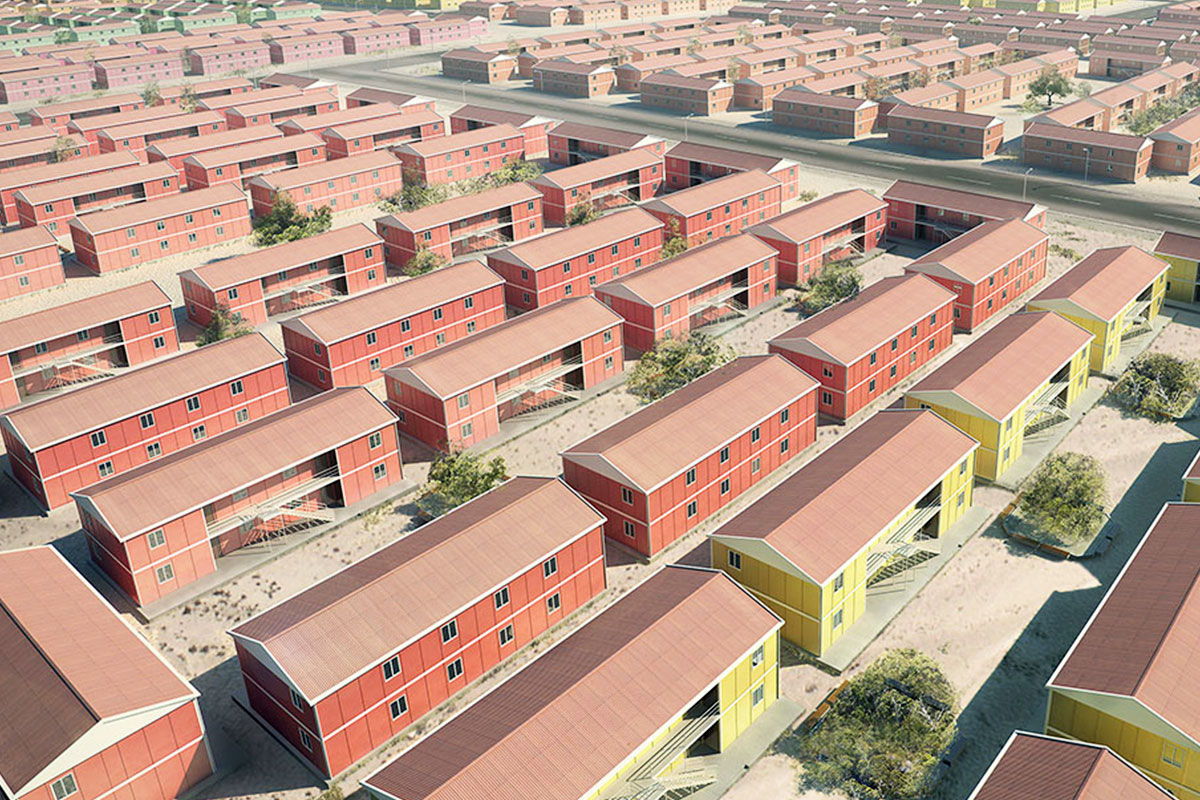
Bangladesh also faces a dual need for temporary and permanent structures. Temporary site offices, worker camps, and technical units are required for large-scale projects, while permanent buildings are needed for factories, logistics hubs, and public facilities. Modular systems offer flexibility in this regard, allowing buildings to be relocated, expanded, or repurposed as project requirements evolve.
Country-specific sectors further reinforce demand. The garment and textile industry, logistics and port operations, energy projects, and public infrastructure all require fast, scalable building solutions. In these sectors, downtime translates directly into financial loss, making speed and reliability decisive criteria.
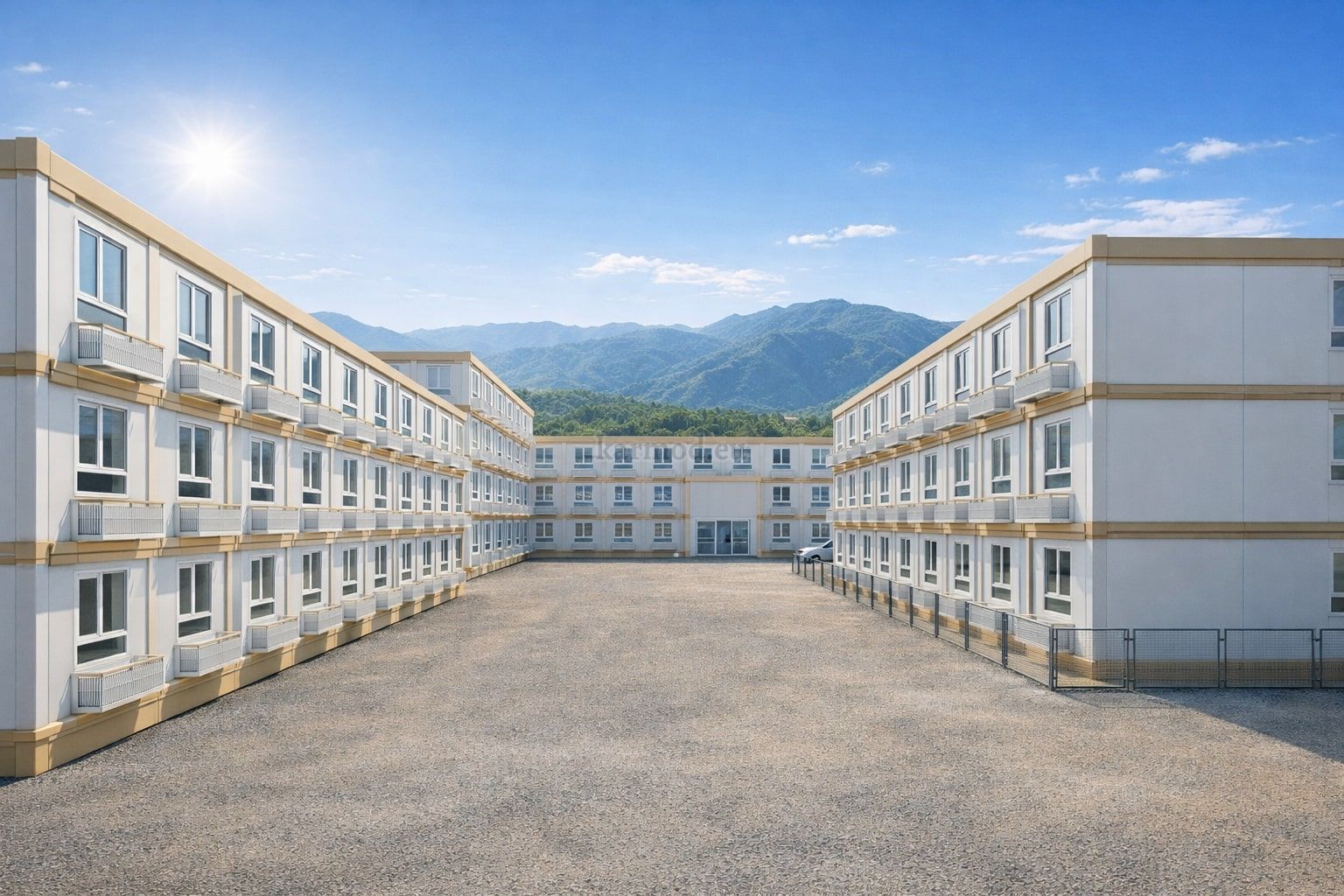

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
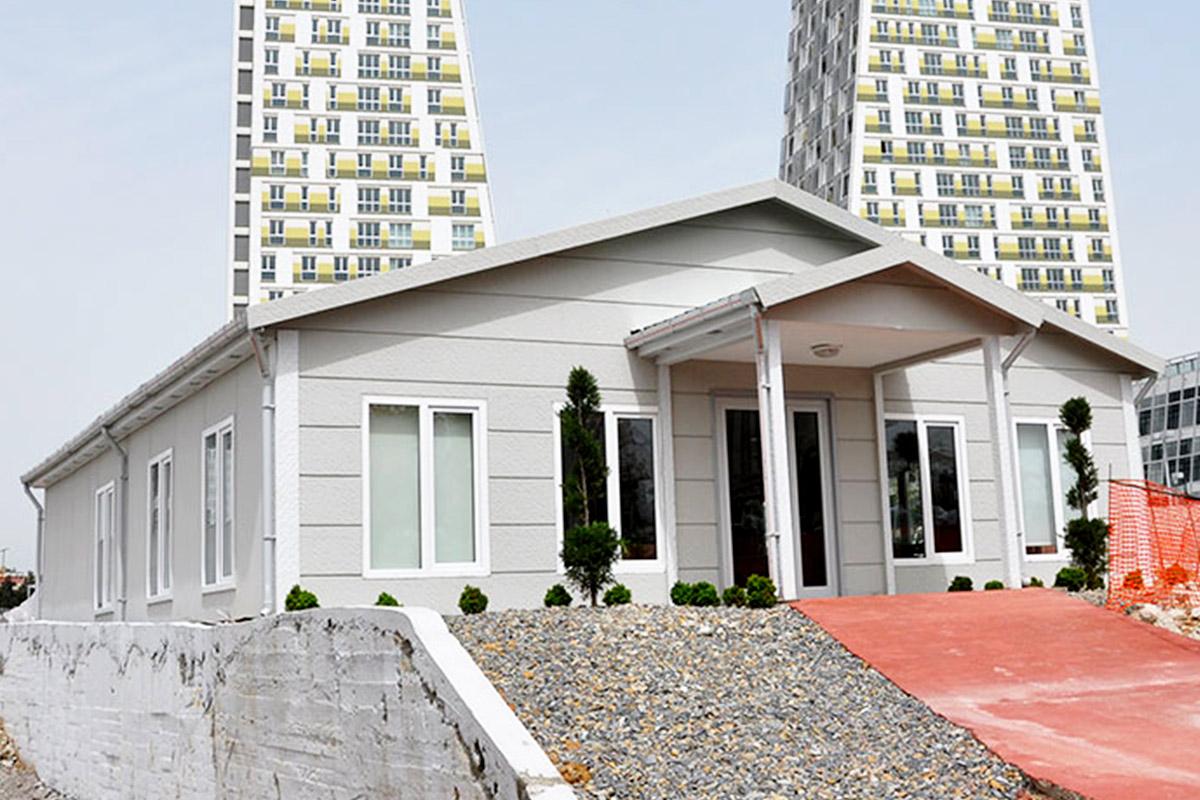
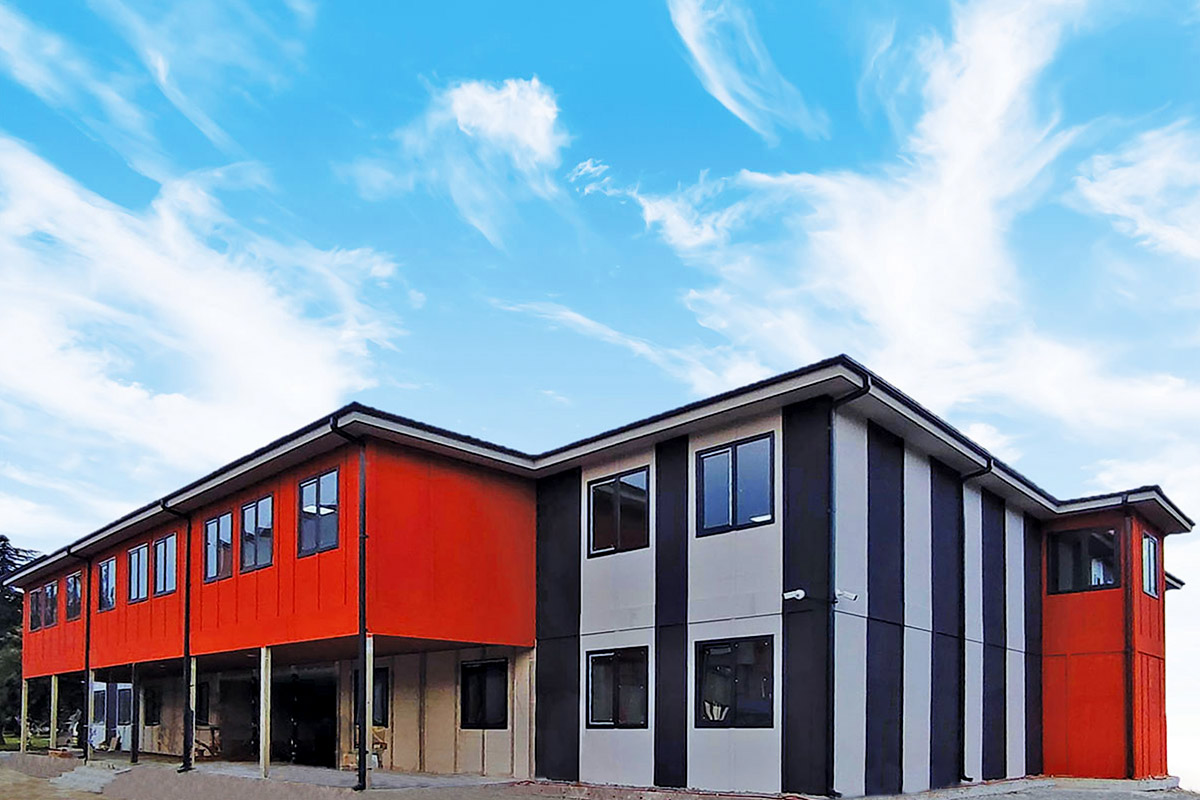
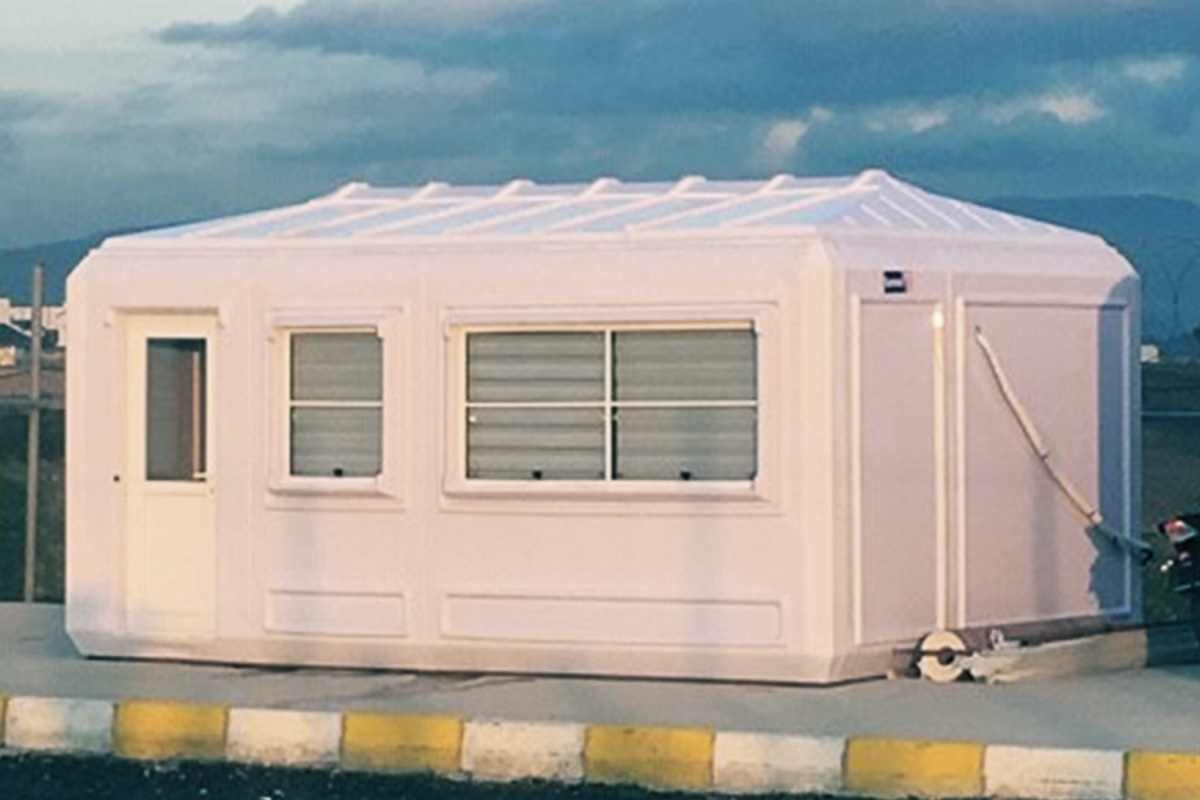
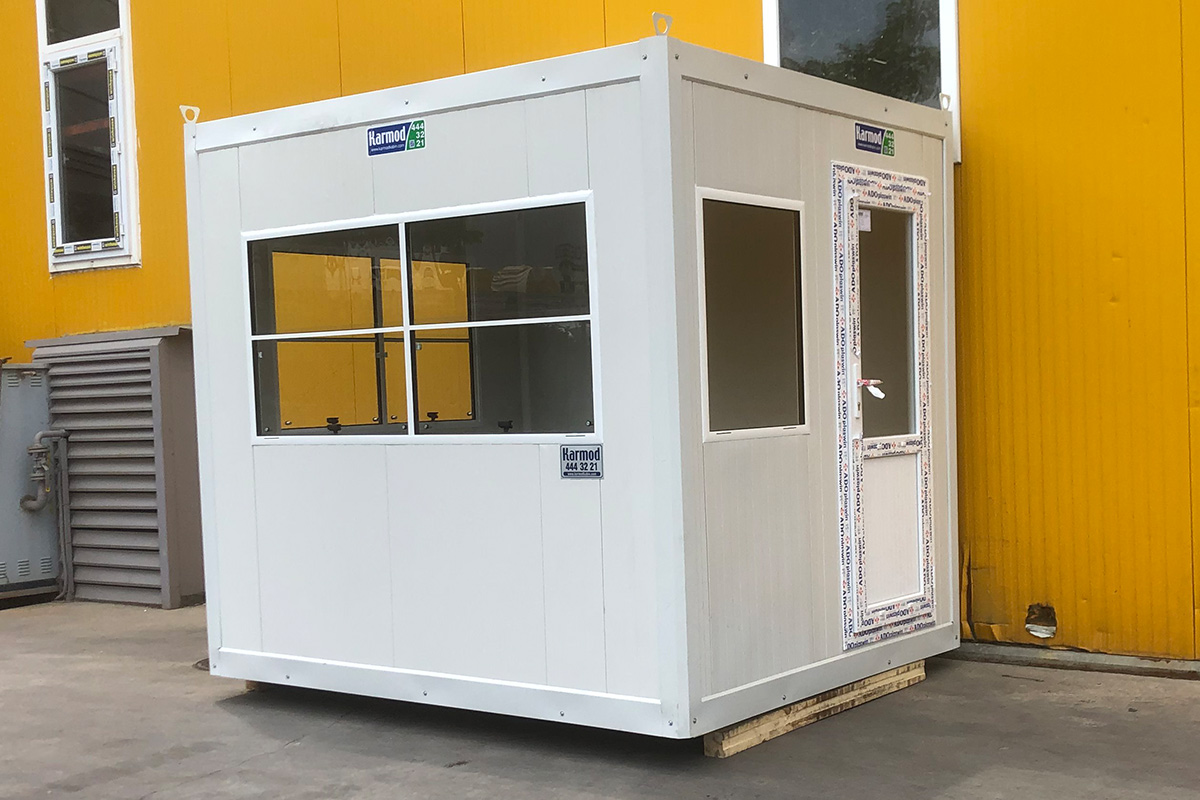
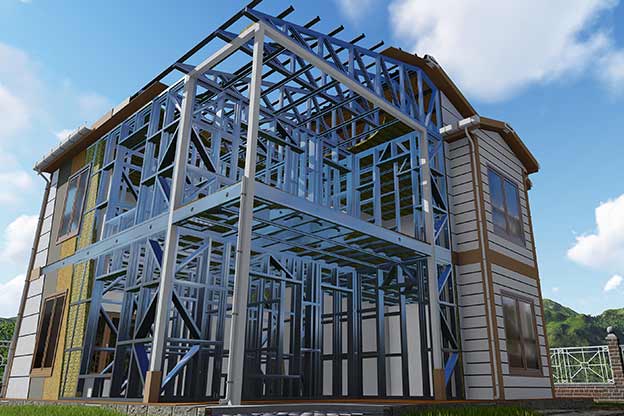
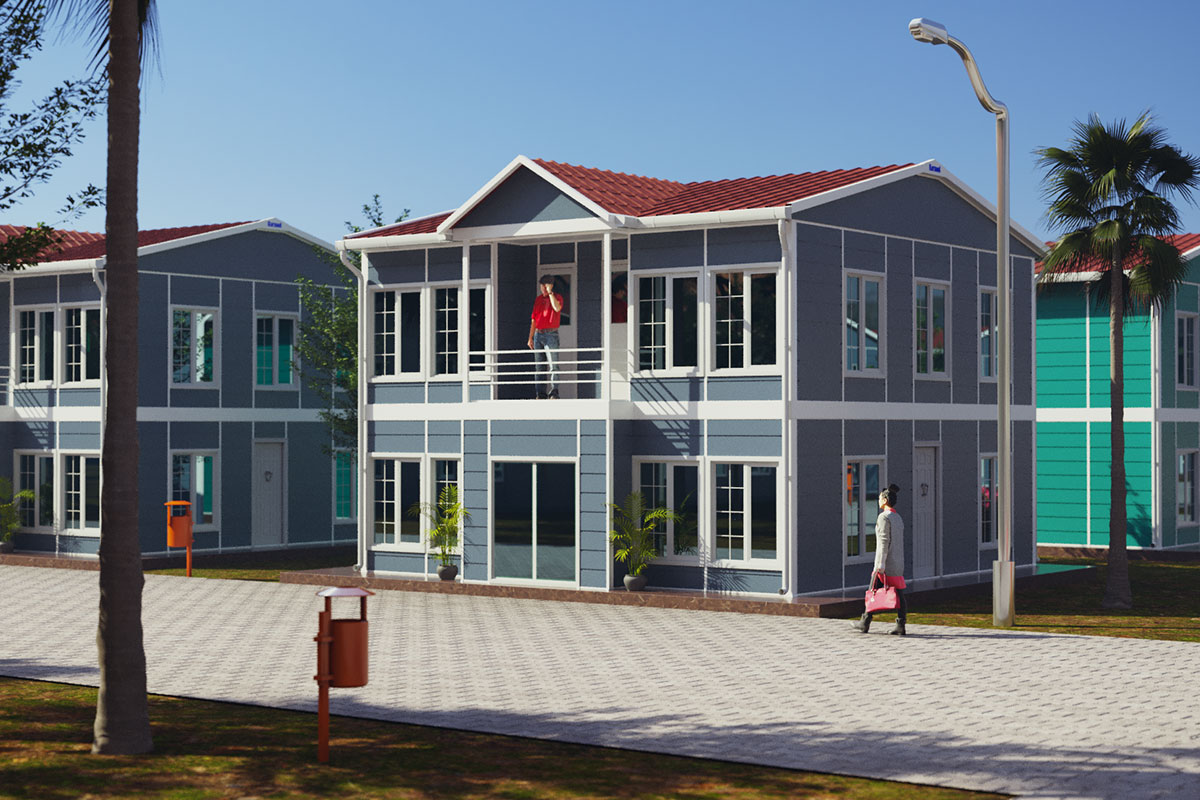
Although often mentioned together, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve different strategic purposes. Modular buildings are produced as volumetric modules in factories. These modules are transportable, can be combined horizontally or vertically, and allow future expansion. This makes them suitable for projects that anticipate growth or relocation, such as industrial camps or logistics facilities.
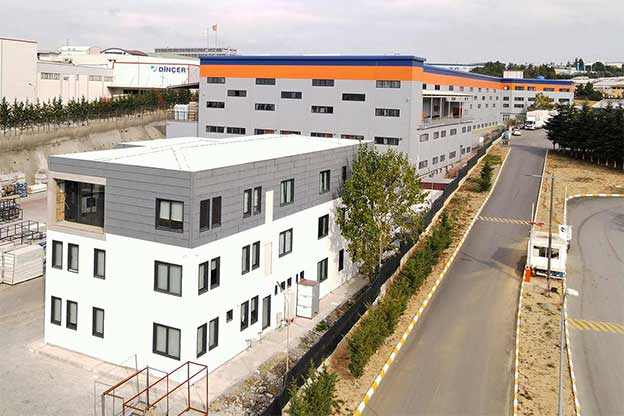
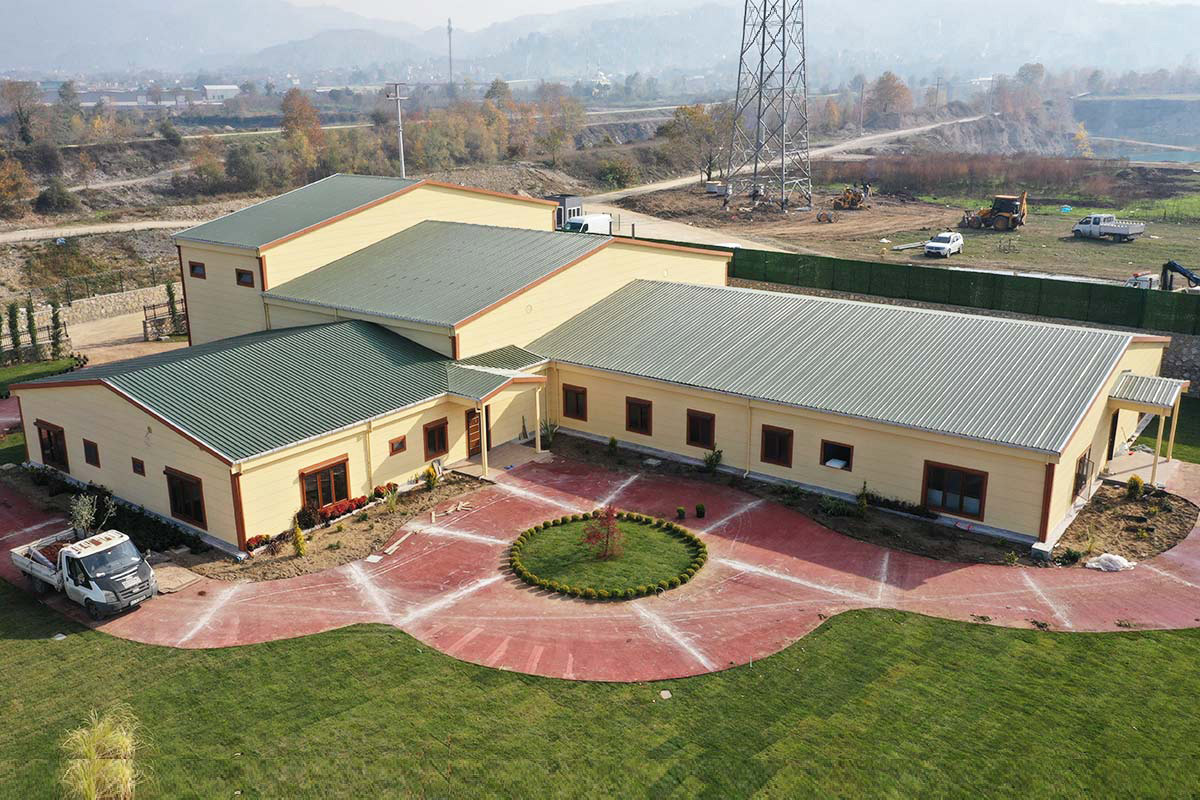
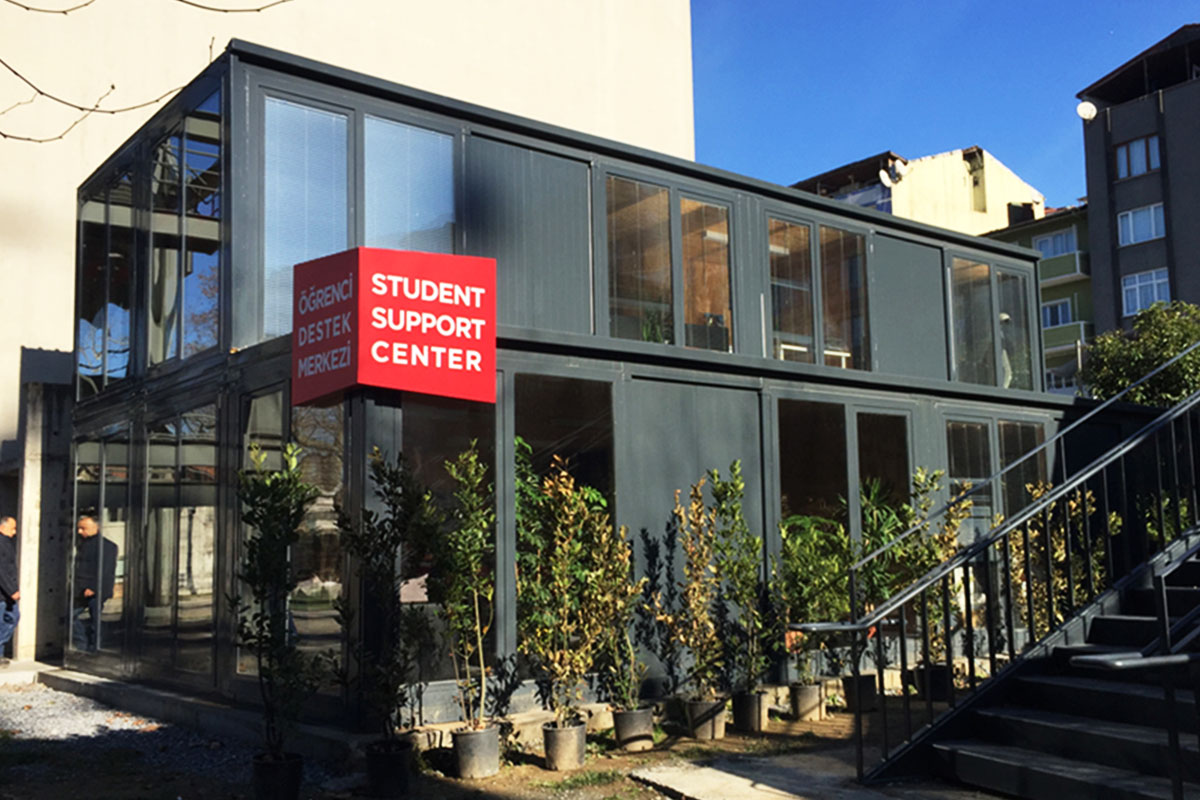
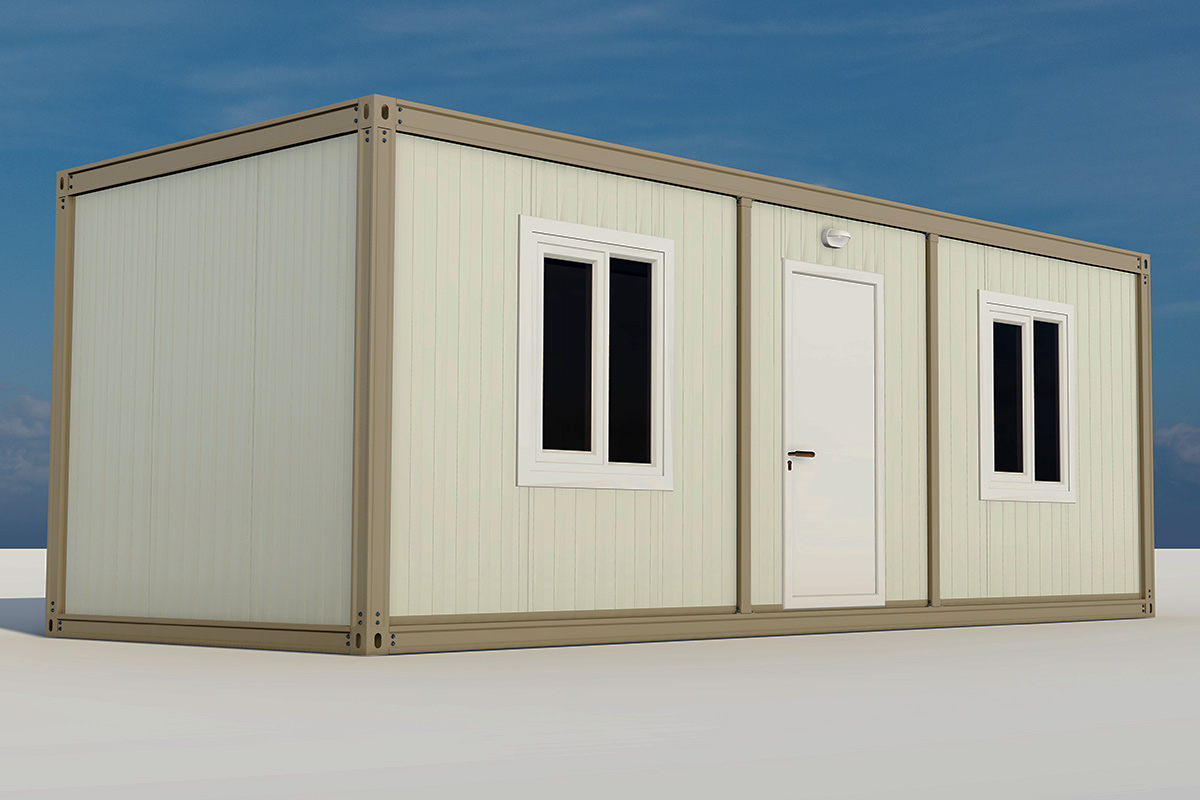
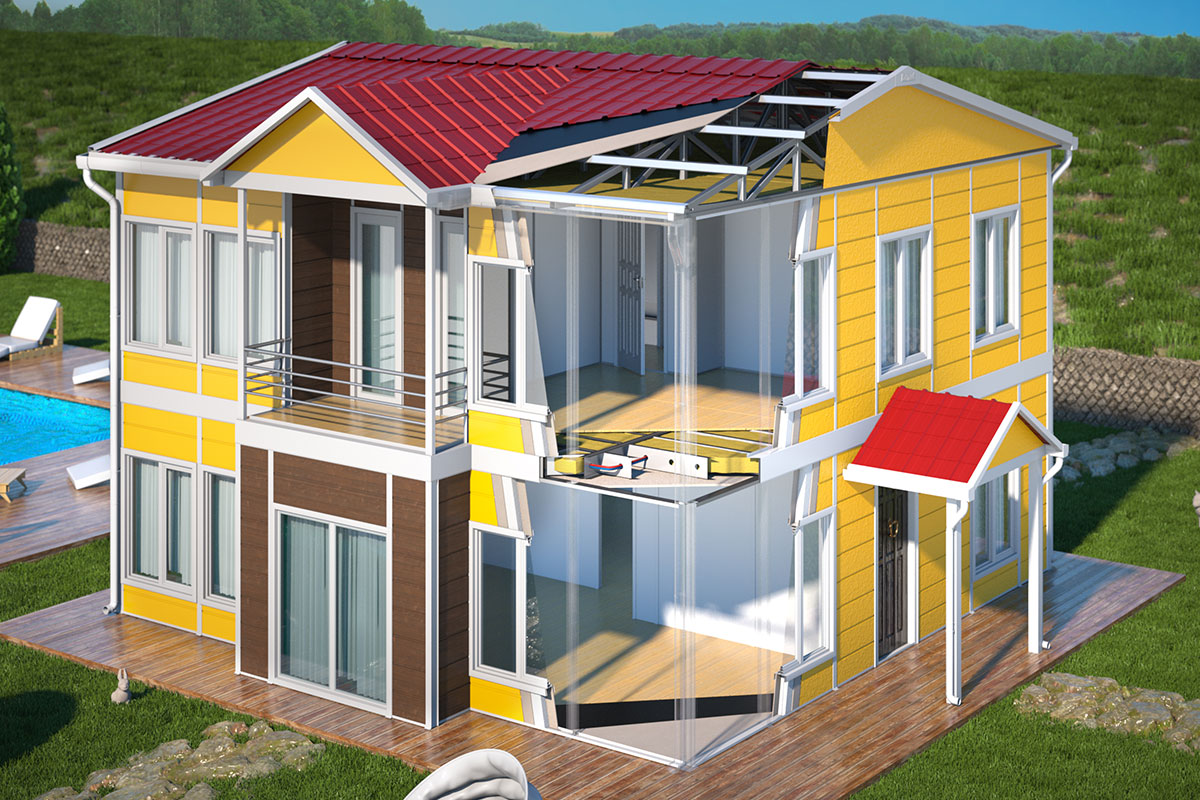
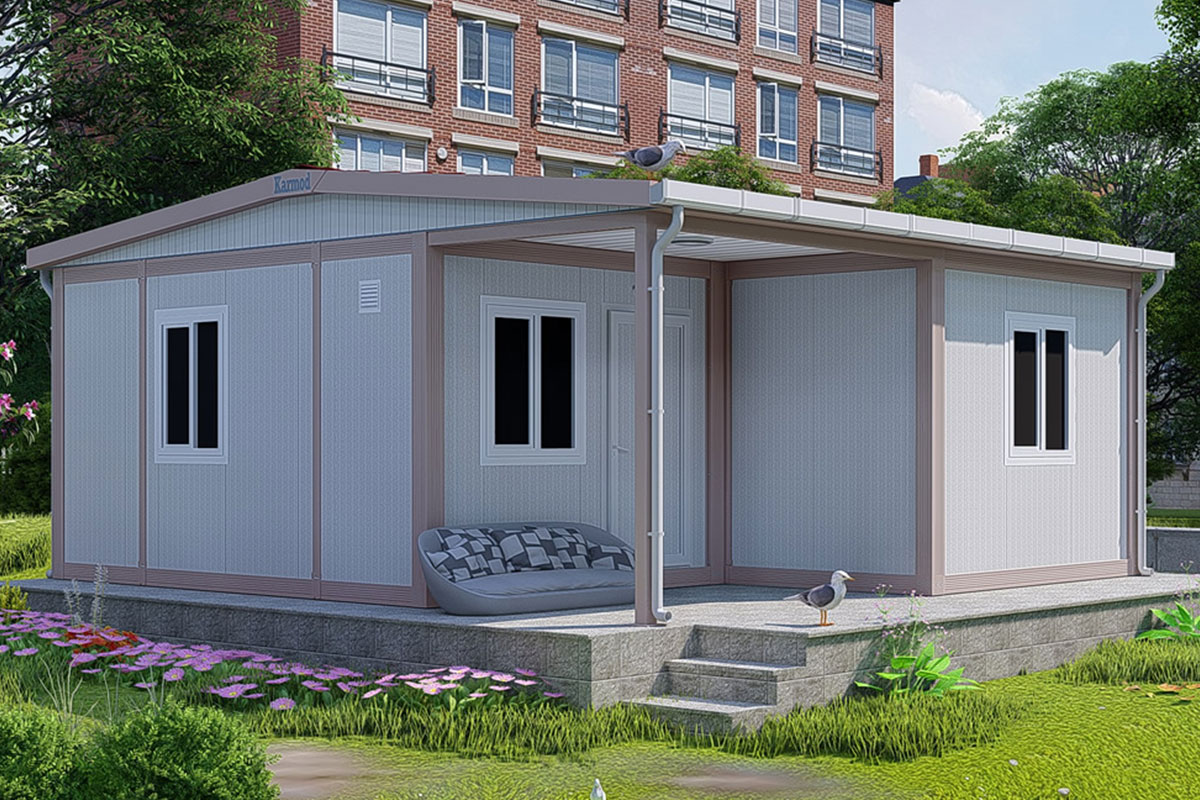
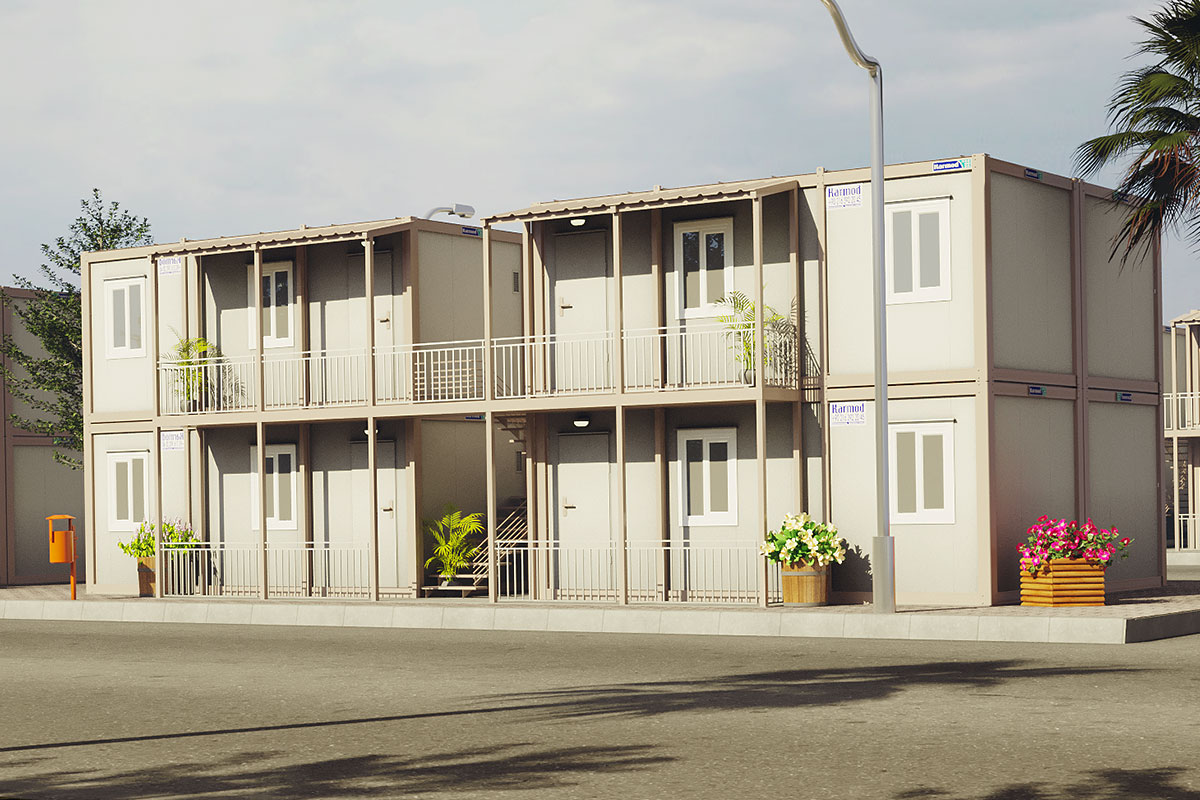
A prefabricated building, by contrast, is typically based on panels or structural components manufactured off-site and assembled on location. These systems are generally used for permanent facilities where long-term stability and integration with the surrounding environment are priorities. They are widely applied in factories, warehouses, and public buildings.
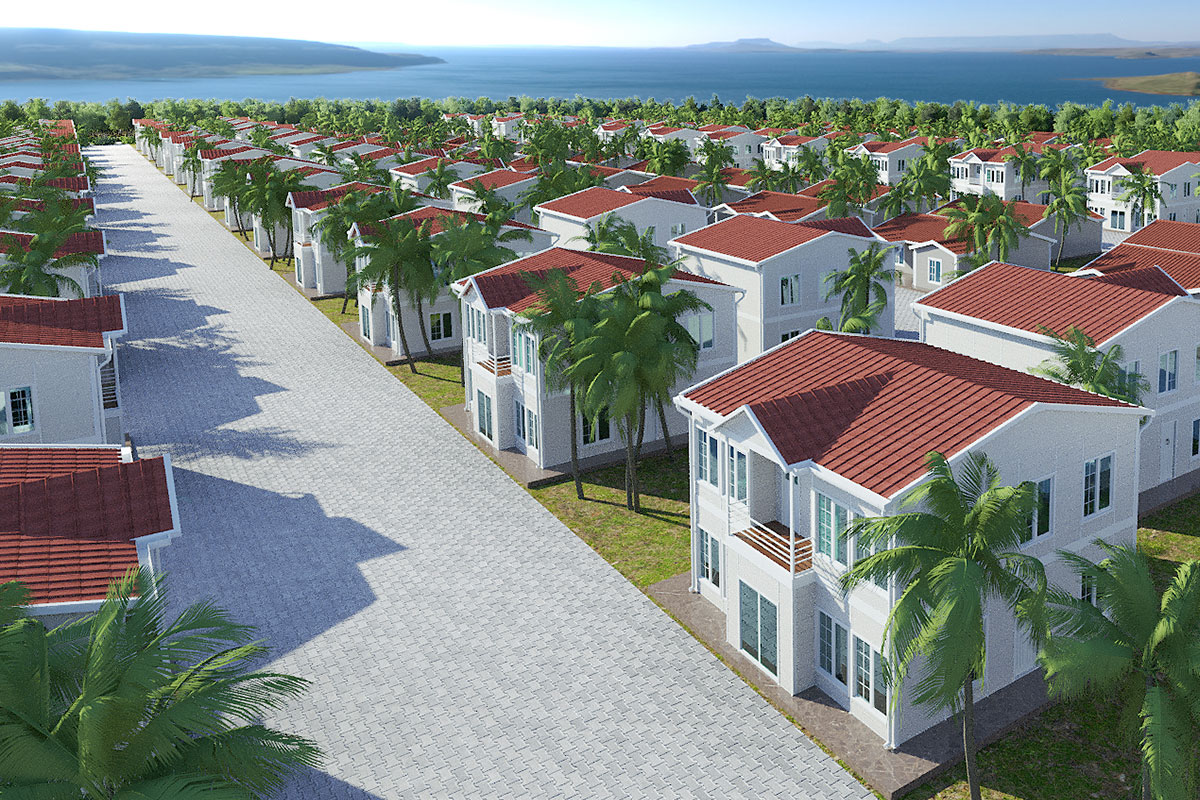
In Bangladesh, modular buildings are often preferred for projects requiring speed and flexibility, particularly in industrial zones and infrastructure developments. Prefabricated building solutions are more common in permanent industrial and institutional projects, where durability and architectural integration are key considerations. Choosing between the two depends on lifecycle planning rather than cost alone.
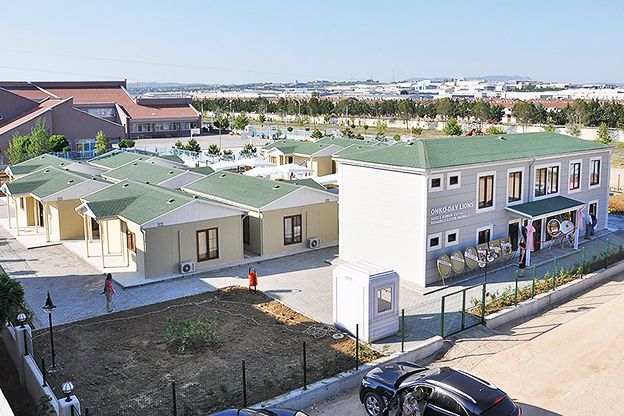
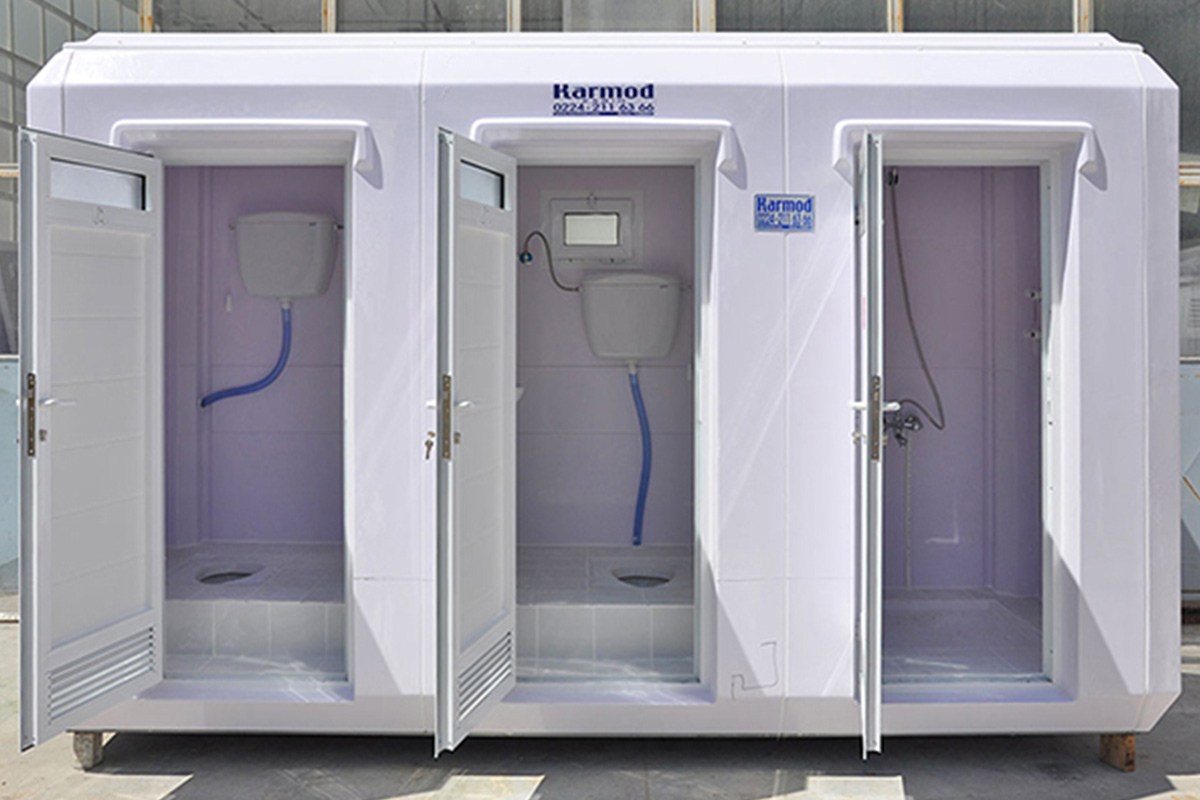
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Bangladesh
Both systems are used across a wide range of applications in Bangladesh, responding to the needs of different sectors:
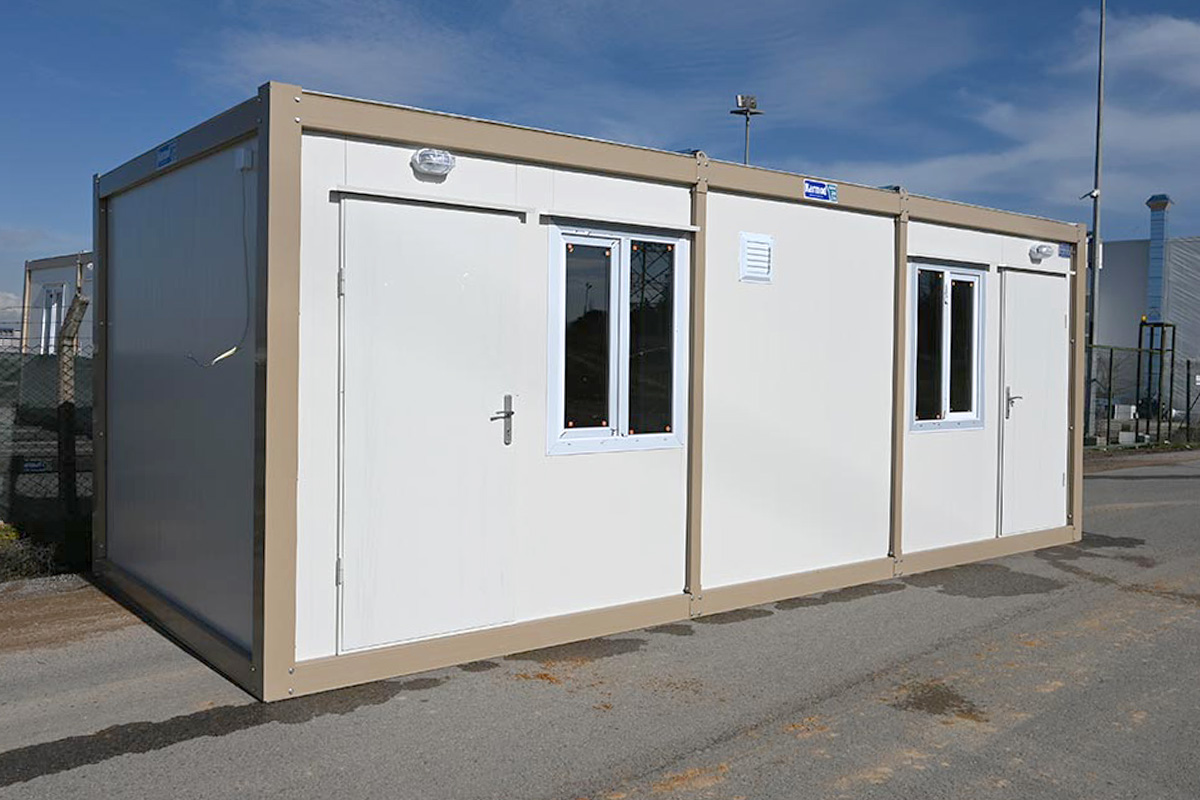
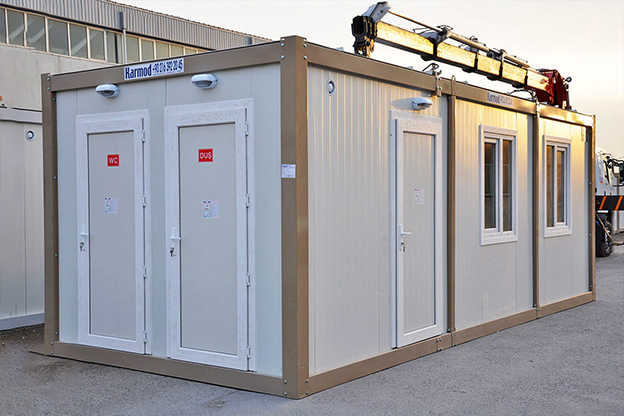
- Site offices & construction camps supporting infrastructure, energy, and industrial projects
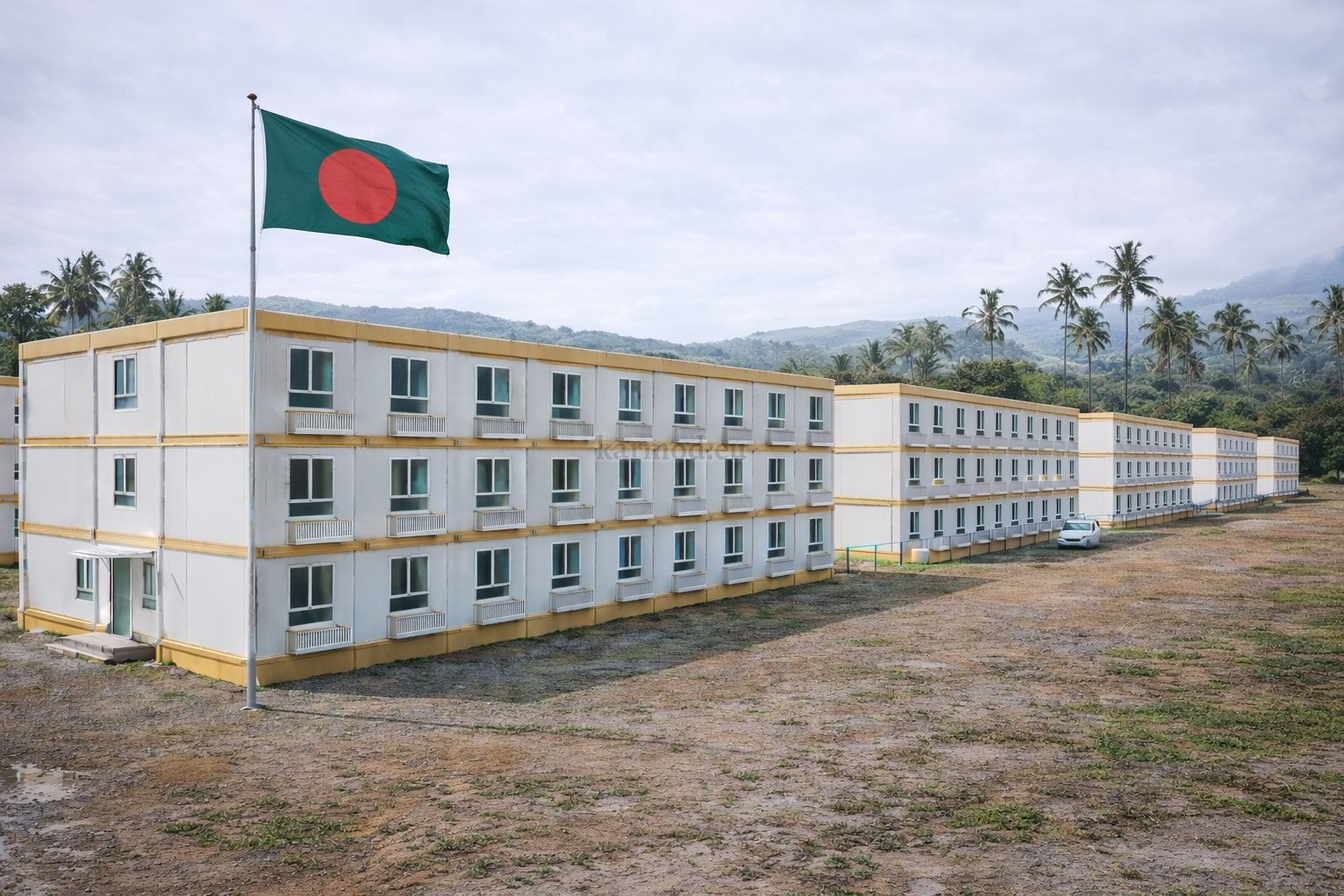
- Worker accommodation buildings for large manufacturing and construction operations
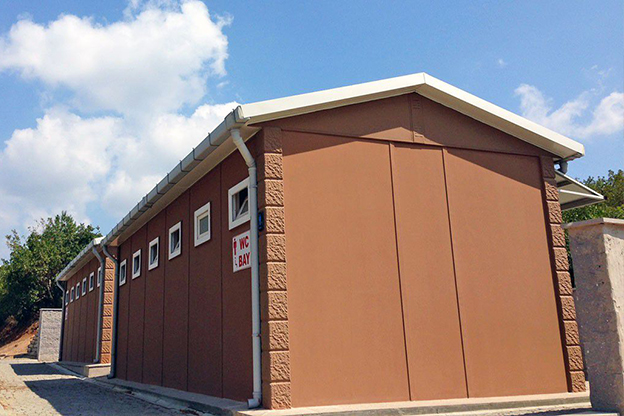
- Temporary schools & healthcare units in fast-growing urban areas and emergency situations
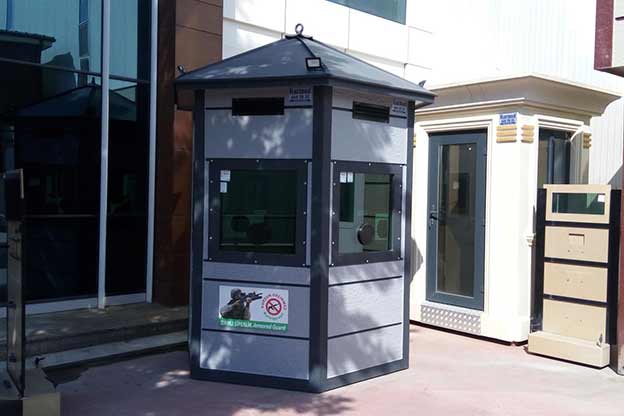
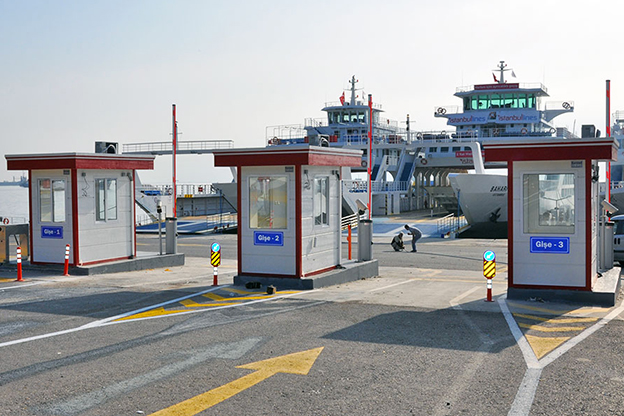
- Security buildings & technical units for controlled access and operational monitoring
- Storage and logistics facilities near ports, highways, and industrial corridors
These applications highlight how modular and prefabricated solutions contribute to operational continuity, especially in environments where traditional construction would be slow or disruptive.

From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The implementation of modular and prefabricated projects follows a structured process designed to minimize risk and uncertainty. It begins with a detailed project needs analysis, where operational requirements, site conditions, and regulatory constraints in Bangladesh are assessed.
This is followed by custom design and specification development. Layouts, materials, and performance criteria are defined in line with local climate conditions and usage scenarios. Once designs are approved, factory production starts under controlled conditions, ensuring consistent quality and reduced waste.
After production, units are delivered to Bangladesh through planned logistics operations, taking into account port access and inland transportation. On-site installation is then completed in a significantly shorter timeframe than conventional construction, often within days rather than months. This predictable process is one of the key reasons international contractors prefer modular approaches.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Bangladesh
Thermal insulation is a primary consideration due to Bangladesh’s hot and humid climate. Proper insulation improves indoor comfort and reduces energy consumption, particularly in worker accommodation and office buildings.
Fire safety standards are equally critical, especially in industrial and residential applications. Systems must comply with local regulations and international safety benchmarks, ensuring occupant protection and regulatory approval.
Climate suitability goes beyond temperature. High humidity, seasonal monsoon rains, and potential flooding require materials and structural solutions that can withstand challenging environmental conditions without compromising performance.
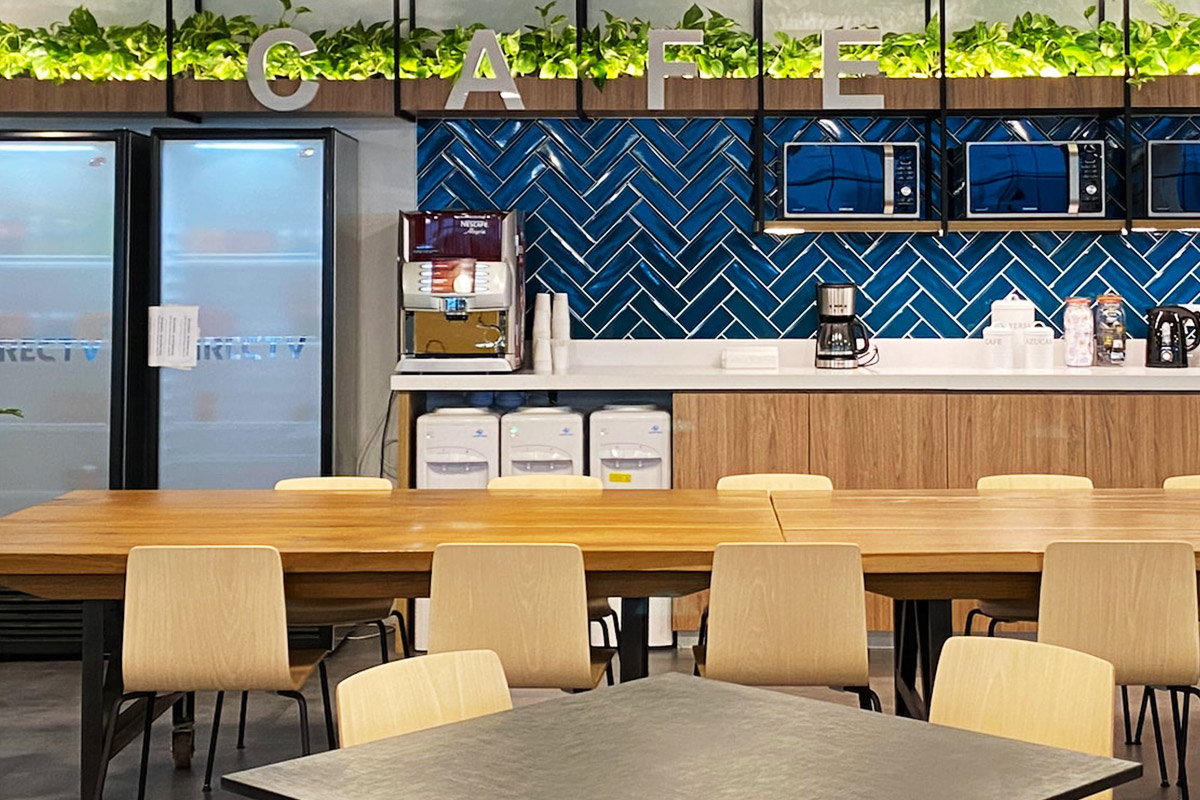
Custom layouts are another decisive factor. Projects in Bangladesh often operate under space constraints or specific operational workflows. Modular systems allow tailored interior configurations, enabling efficient use of available space without extensive on-site modification.
In this context, companies such as Karmod have positioned their solutions around adaptability and long-term performance. Drawing on experience gained across multiple international markets, Karmod modular building solutions are designed to respond to both climatic and operational demands without relying on standardized, one-size-fits-all models. This approach has made Karmod a reference point for organizations seeking reliable, factory-controlled construction methods aligned with project realities.
As Bangladesh continues to expand its industrial and infrastructure capacity, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems are becoming integral to strategic planning. For decision-makers evaluating speed, quality, and lifecycle value together, these solutions provide a structured path from concept to operation—reducing uncertainty while supporting sustainable growth.