Canada’s construction market operates under unique pressures shaped by geography, climate, and regulatory standards. From large metropolitan developments to remote industrial and energy projects, decision-makers are expected to deliver facilities that are durable, compliant, and operational within strict timelines. Within this environment, modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions have become established tools for organizations seeking predictable outcomes without sacrificing quality.
Across provinces with varying climate conditions and labor markets, these construction systems support both temporary and permanent building strategies. For public authorities, industrial investors, and multinational contractors, they offer a controlled and scalable approach that aligns with Canada’s high expectations for safety, performance, and long-term value.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Canada
One of the strongest drivers behind the adoption of modular buildings in Canada is labor cost. Skilled construction labor is expensive and often limited, particularly in northern regions or areas experiencing resource-driven growth. Modular construction significantly reduces on-site labor requirements by transferring production to factory environments, where efficiency and workforce planning are easier to control.
Construction timelines are another critical factor. Canada’s short building seasons in many regions create scheduling pressure for conventional projects. Modular buildings allow off-site manufacturing to proceed independently of weather conditions, while site preparation continues in parallel. This overlap shortens project delivery and reduces exposure to seasonal delays.
The balance between temporary and permanent building needs also plays a role. Canada’s economy includes industries such as mining, oil and gas, renewable energy, logistics, and public infrastructure that rely on both relocatable and long-term facilities. Modular systems are well suited for temporary camps and phased developments, while prefabricated solutions support permanent institutional and commercial buildings.
Country-specific sectors further reinforce demand. Energy projects require fast deployment in remote locations. Public sector initiatives often need rapid expansion of schools or healthcare units. Logistics and industrial developments depend on scalable office and storage spaces. In these contexts, modular buildings fit operational realities without compromising compliance.
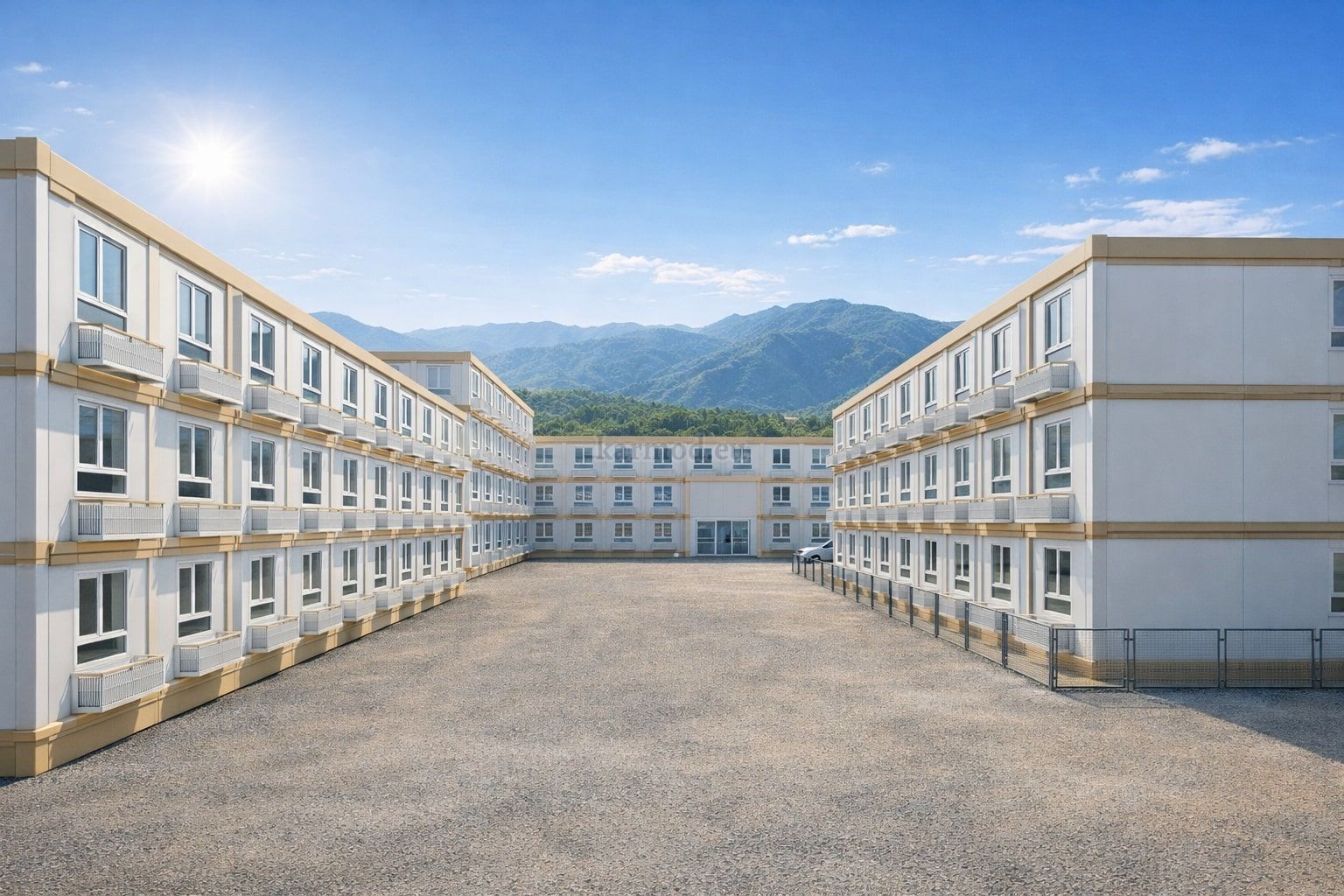

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
Understanding the distinction between modular buildings and prefabricated building systems is essential for project planning in Canada.
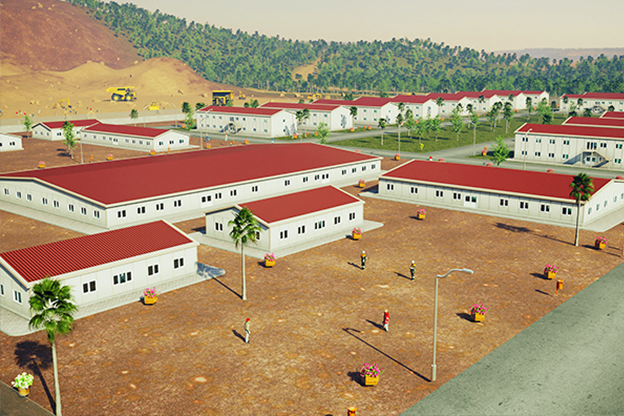
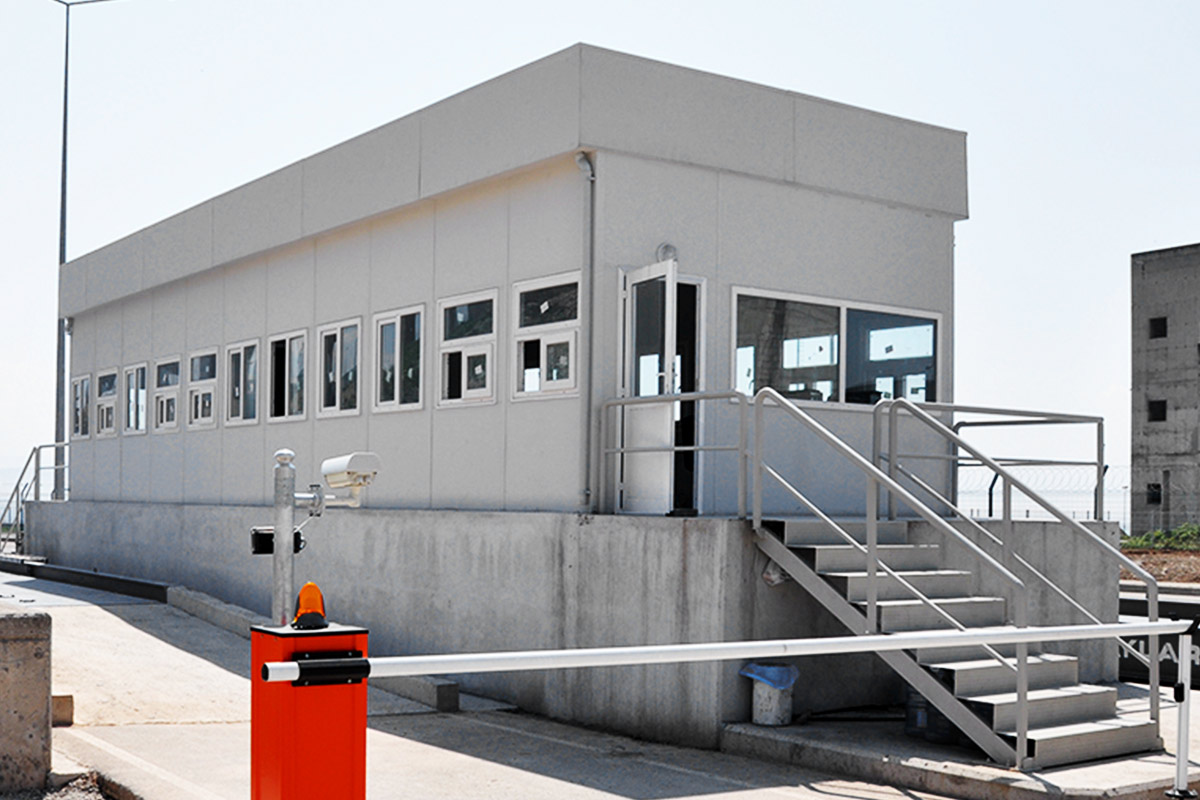
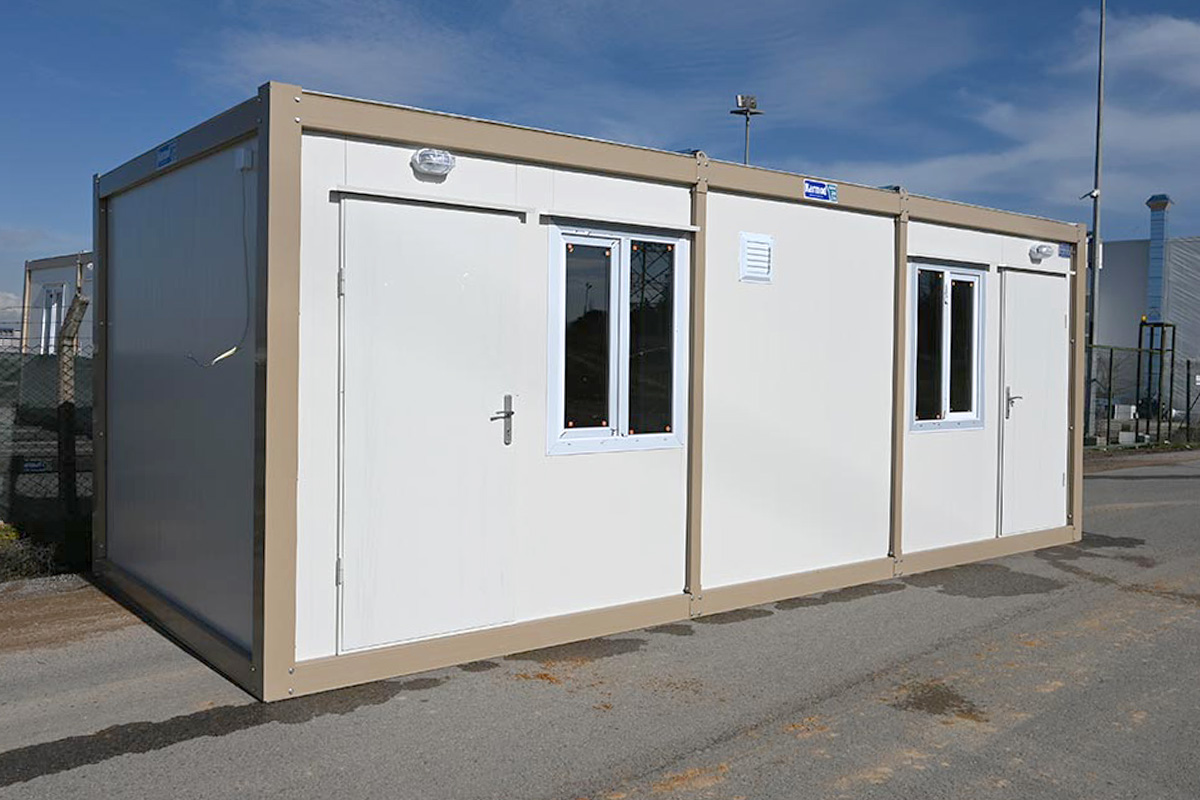
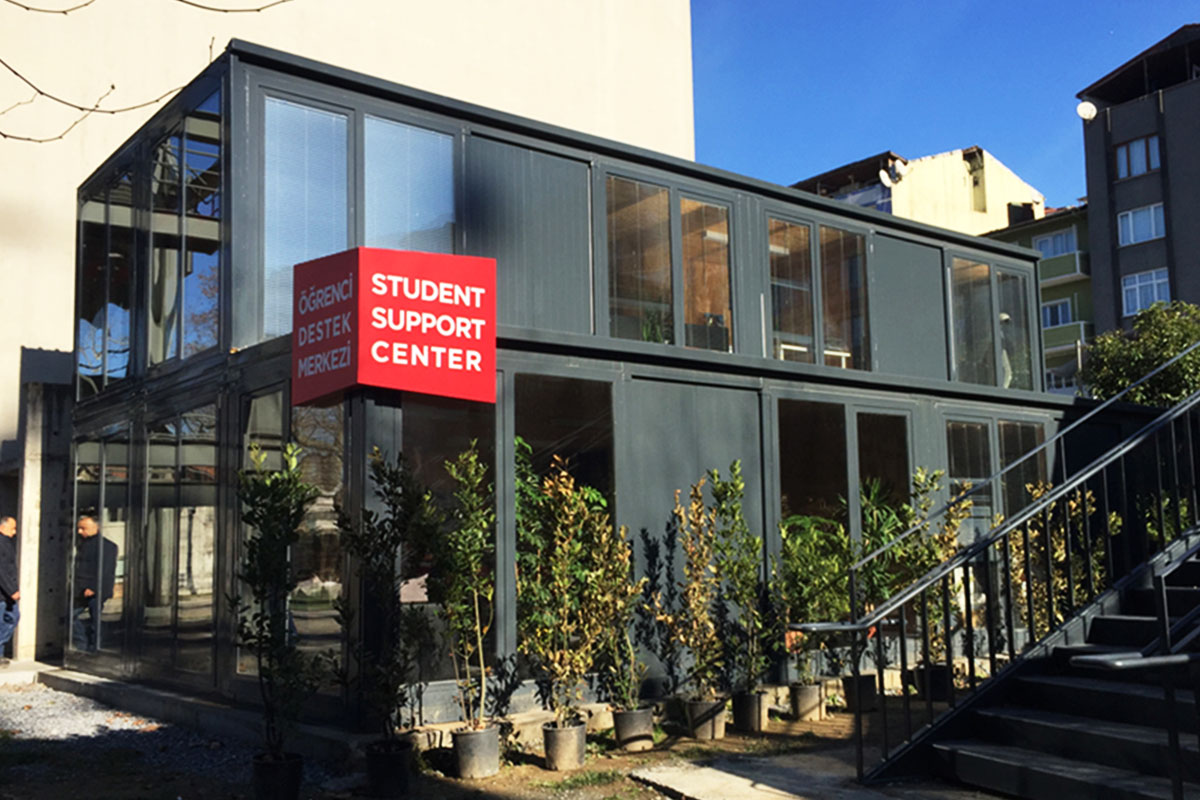
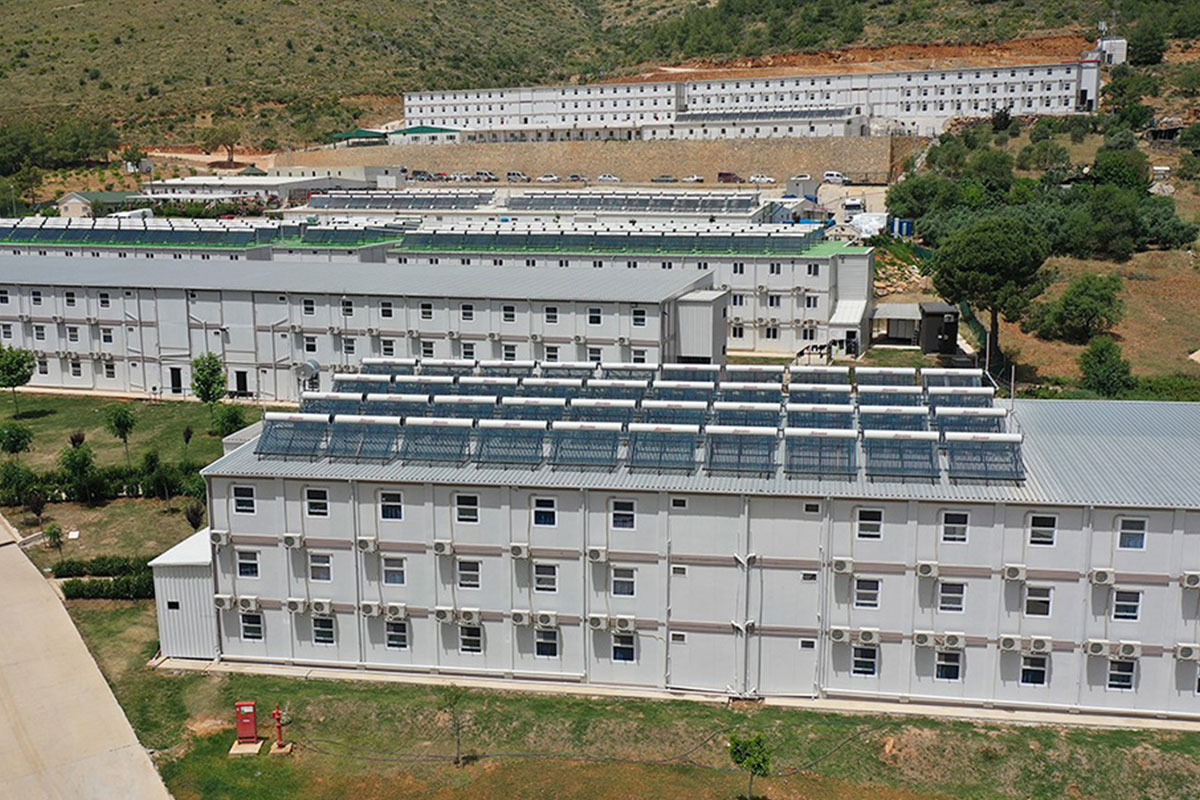
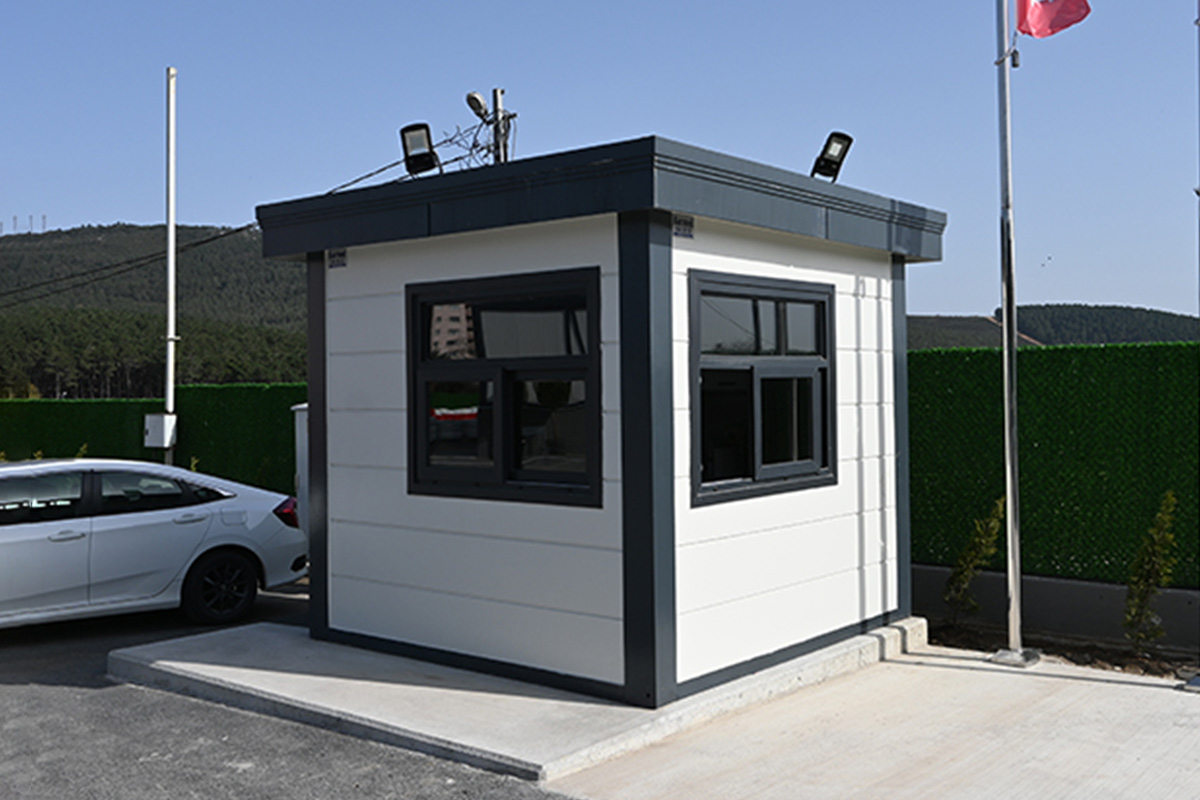
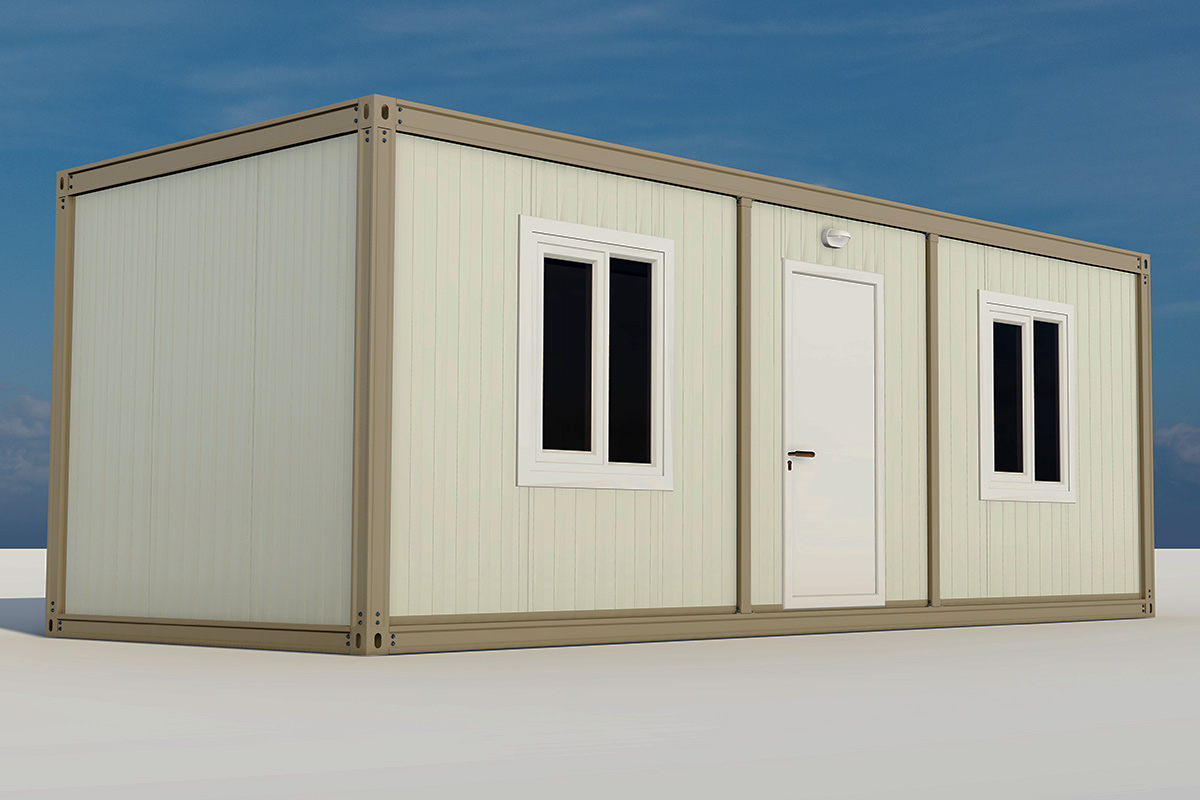
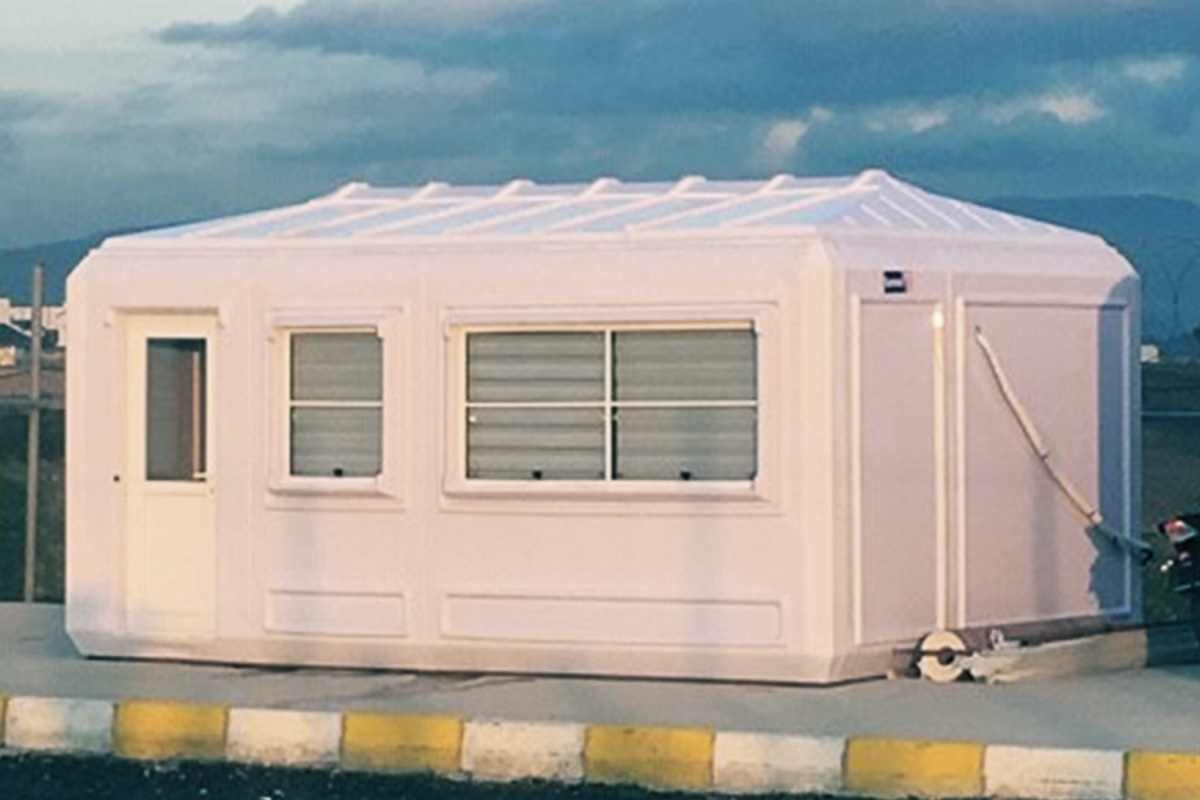
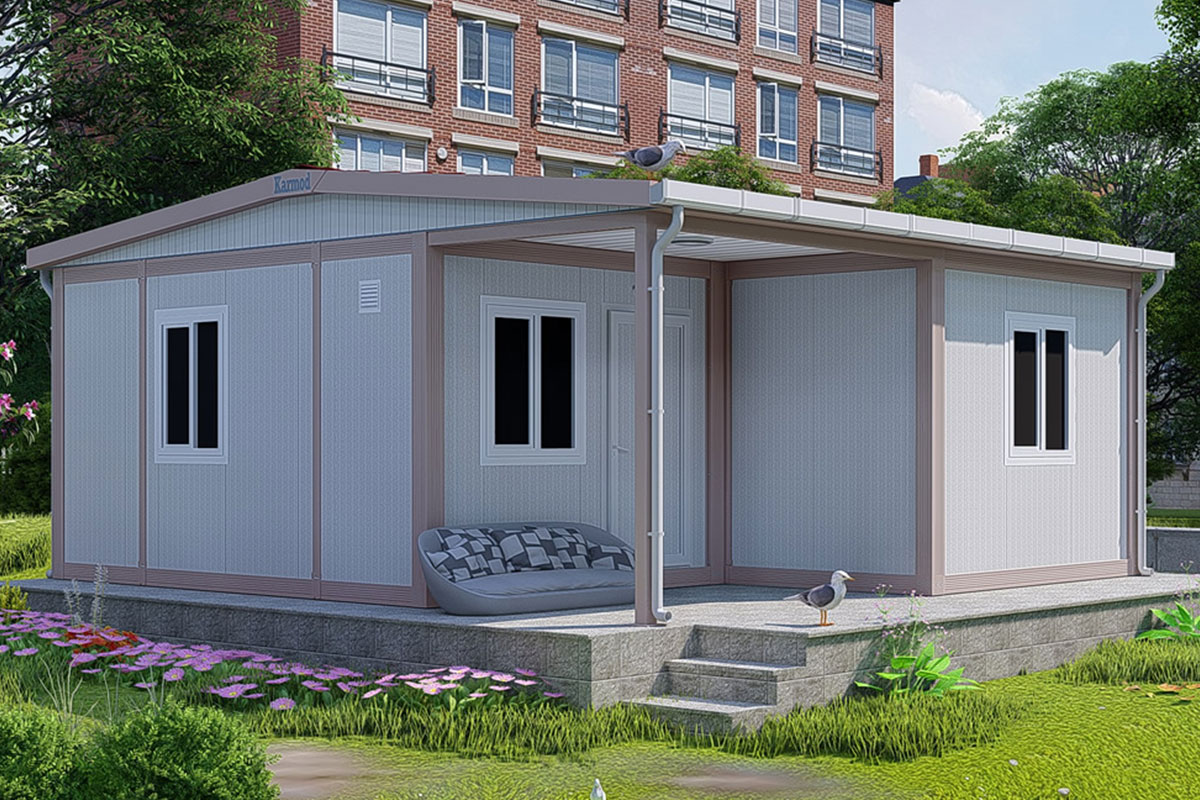
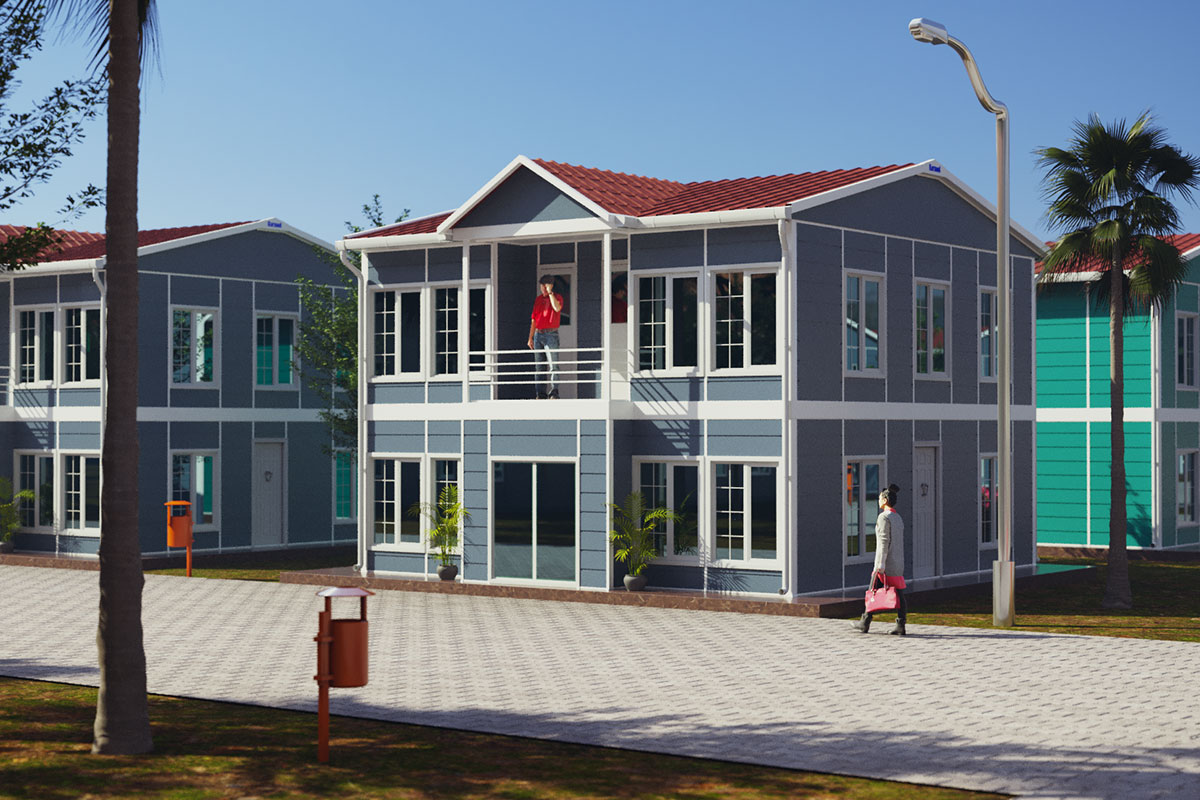
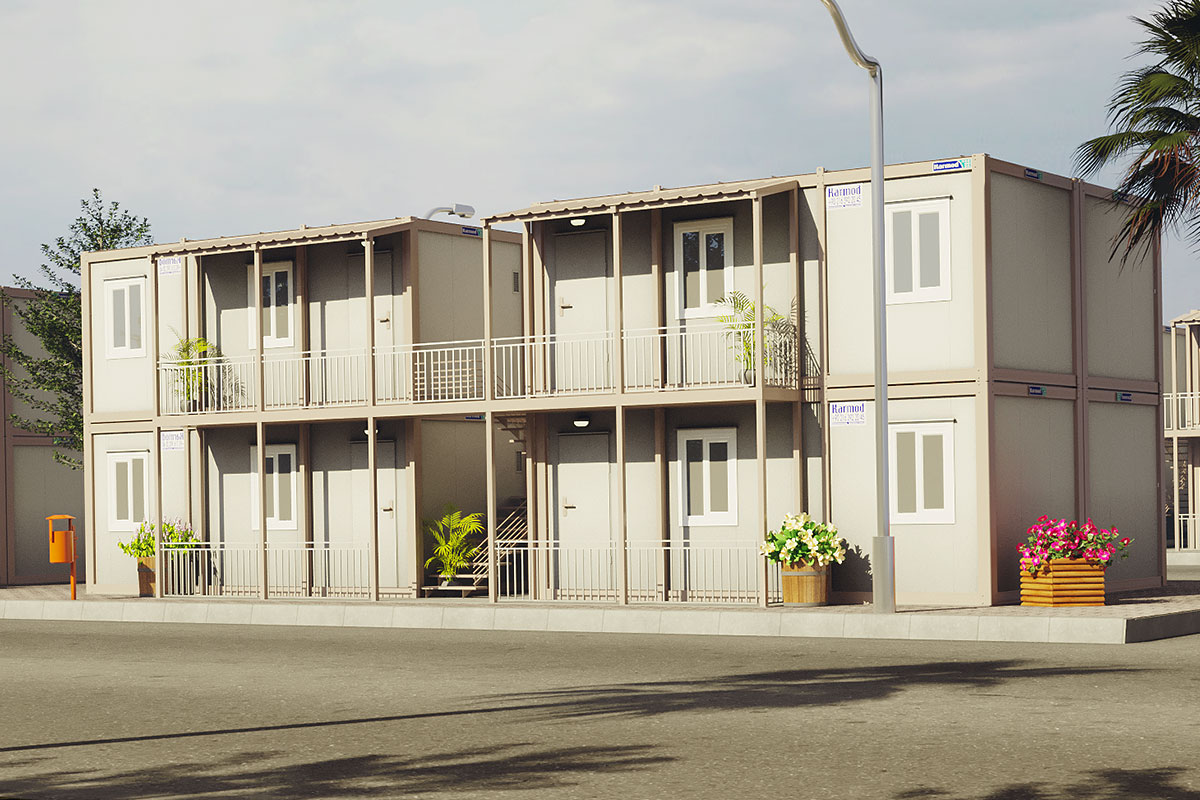
Modular buildings are produced as complete volumetric units. Each module is structurally independent, transportable, and designed to connect seamlessly with others. This makes modular buildings ideal for projects that may expand, relocate, or adapt over time. In Canada, they are commonly used for worker accommodation, site offices, and temporary public facilities where flexibility is a priority.
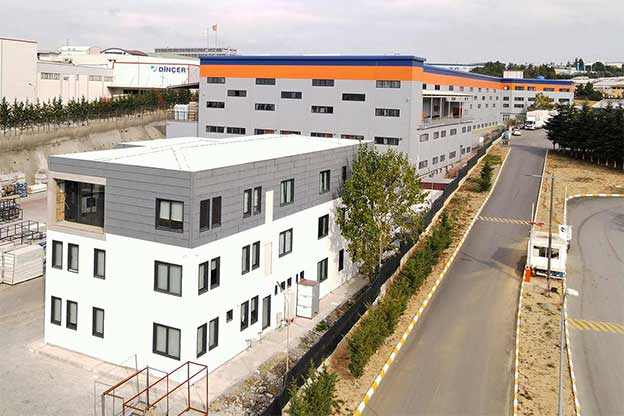
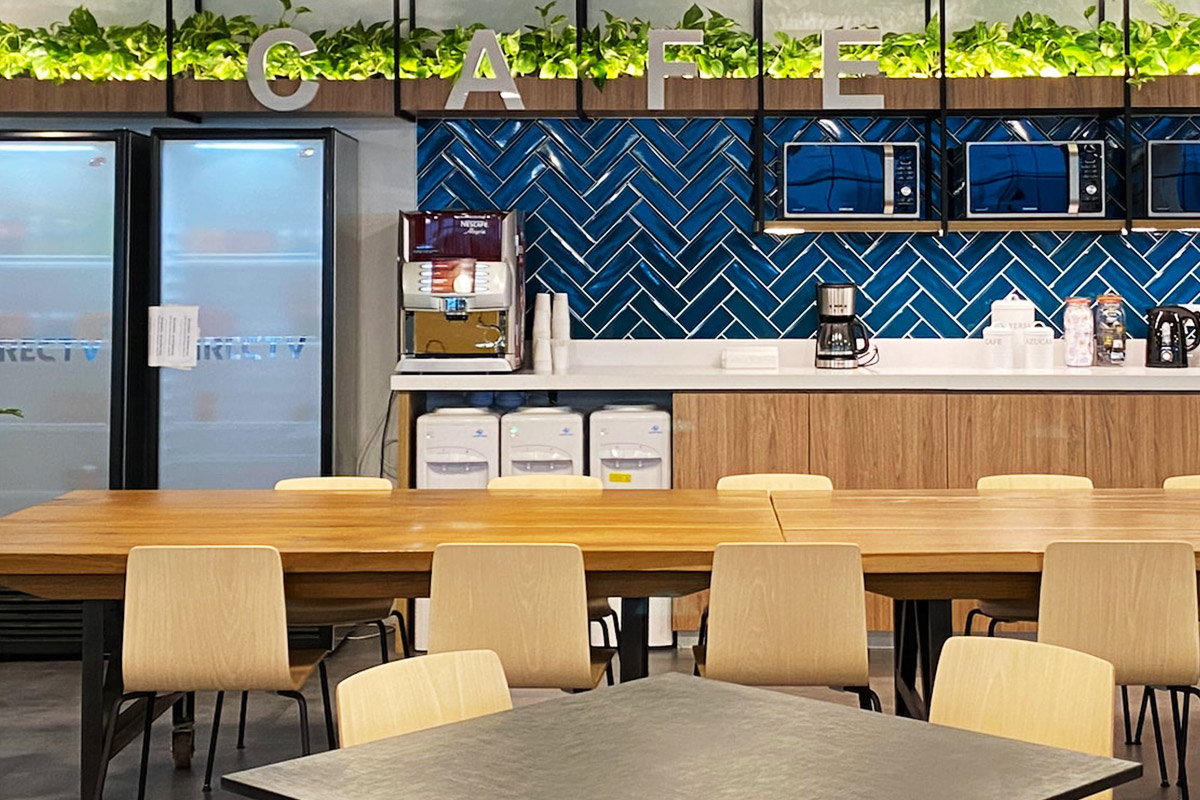
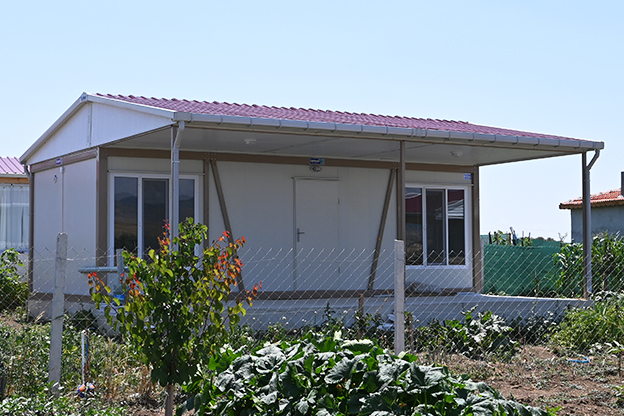
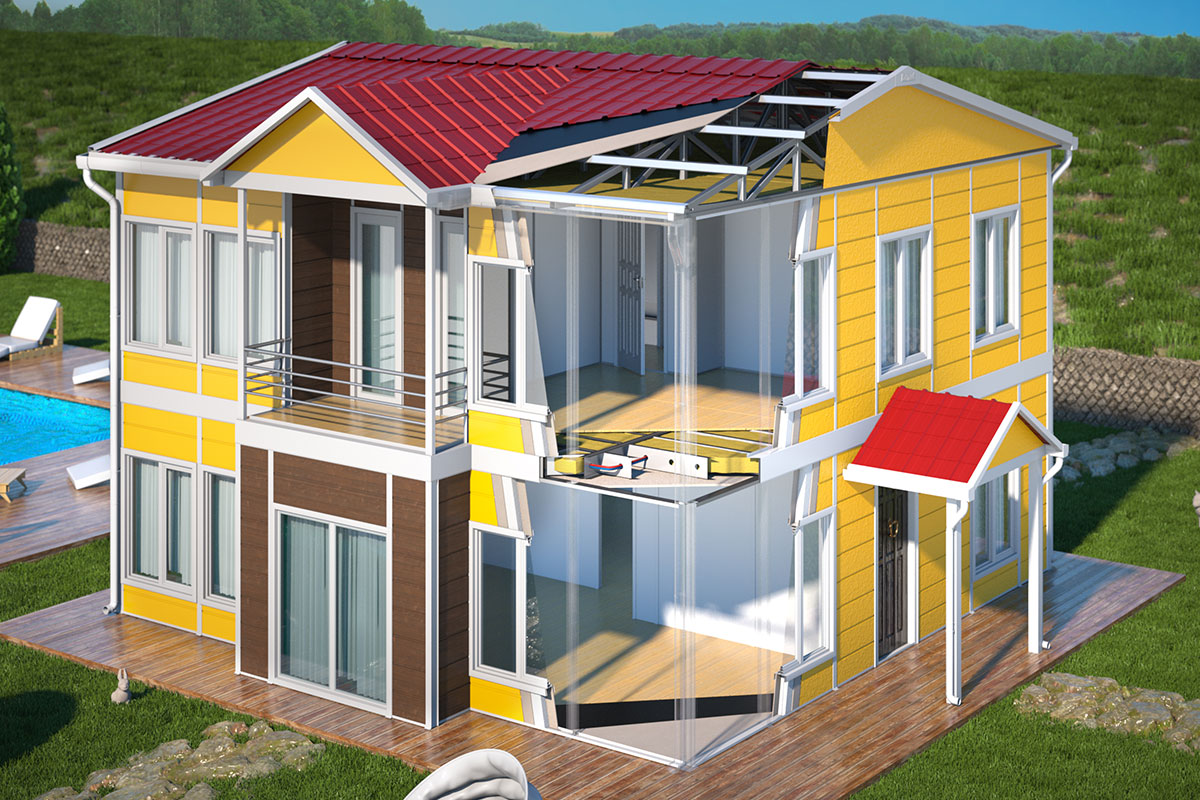
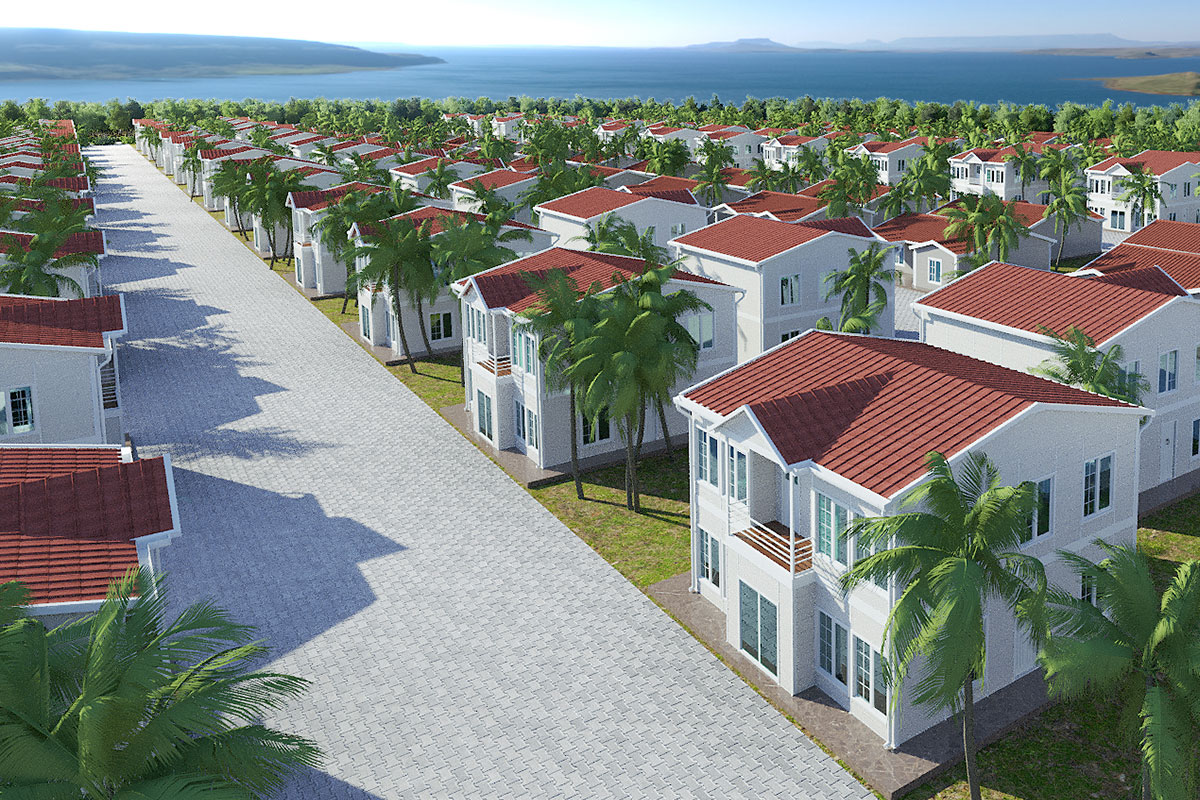
A prefabricated building, by contrast, is assembled from panels or pre-engineered structural components delivered to the site. These systems are typically selected for permanent buildings that require architectural integration, long service life, and fixed foundations. Offices, educational facilities, and healthcare buildings in urban or suburban settings often rely on prefabricated building systems.
In practice, modular buildings are preferred for speed and adaptability, while prefabricated building solutions are chosen for permanence and architectural consistency. Canadian projects frequently combine both approaches within the same development strategy.
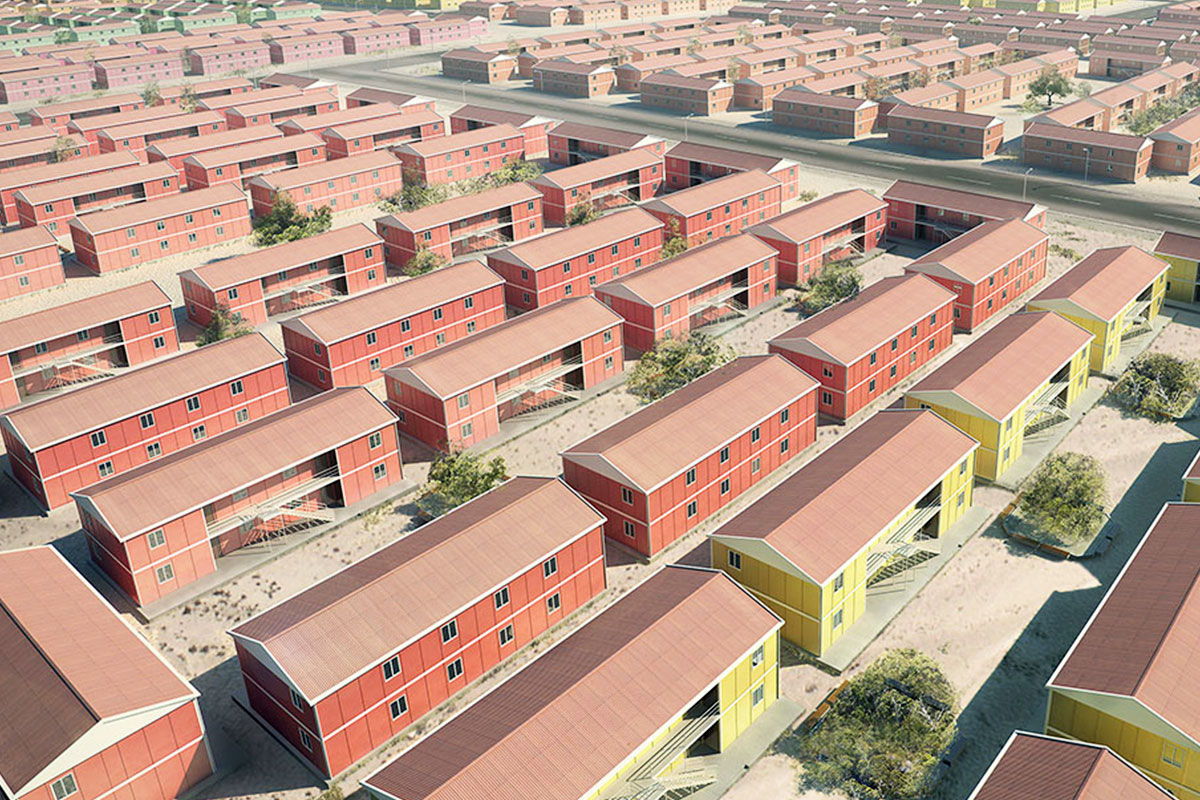
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Canada
Modular and prefabricated construction methods are widely applied across Canada in the following areas:
- Site offices & construction camps for infrastructure, energy, and industrial projects
- Worker accommodation buildings in remote or climate-challenged regions
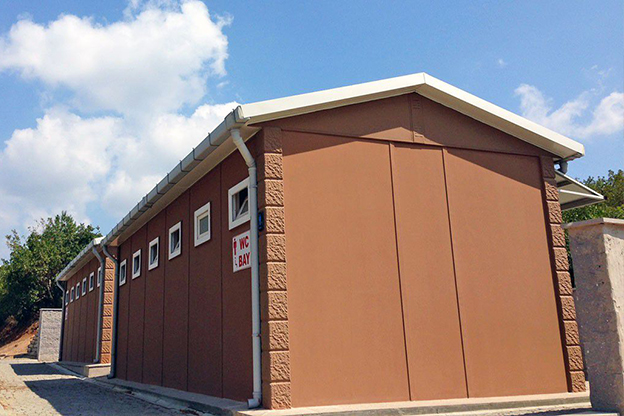
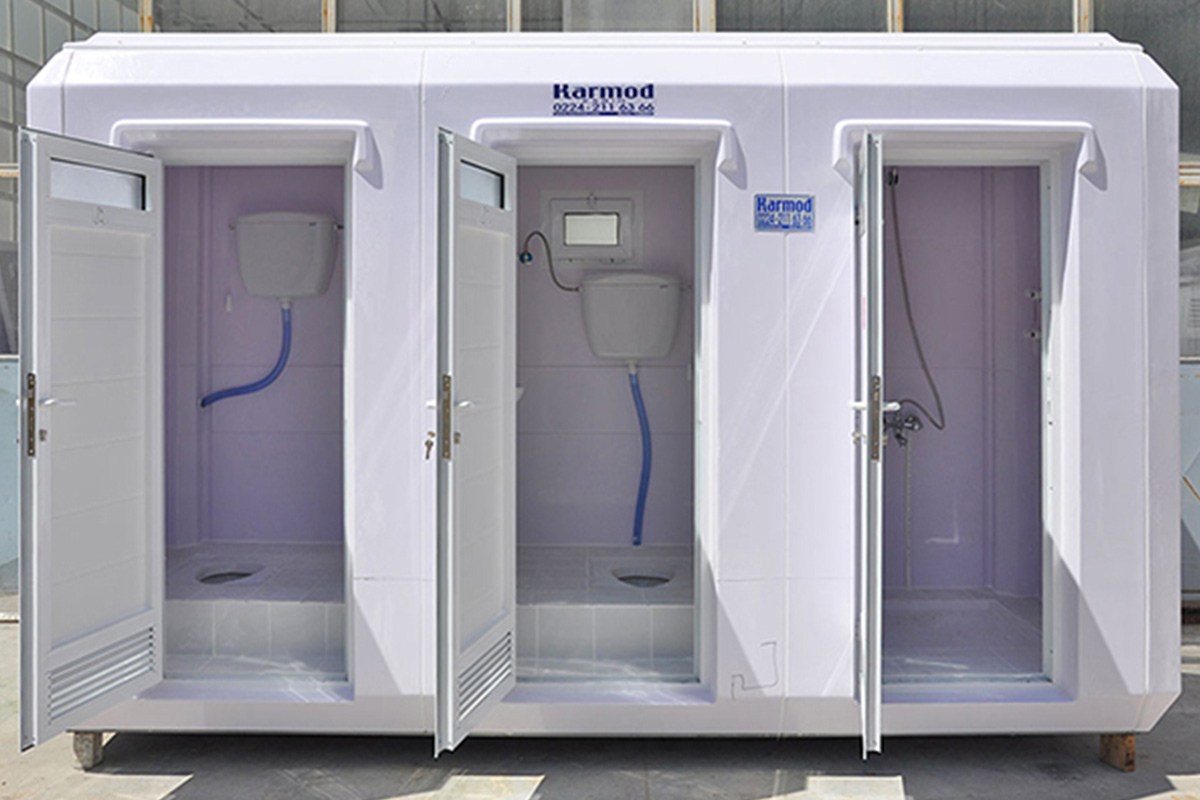
- Temporary schools & healthcare units supporting public sector capacity needs
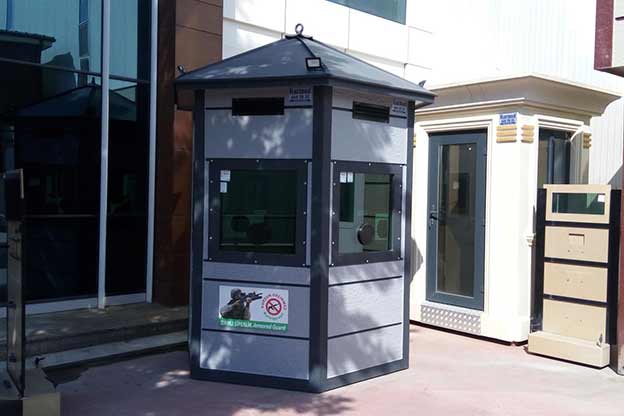
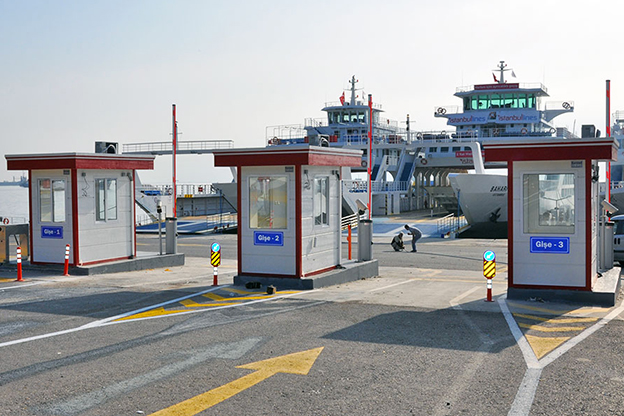
- Security buildings & technical units for controlled access and operations
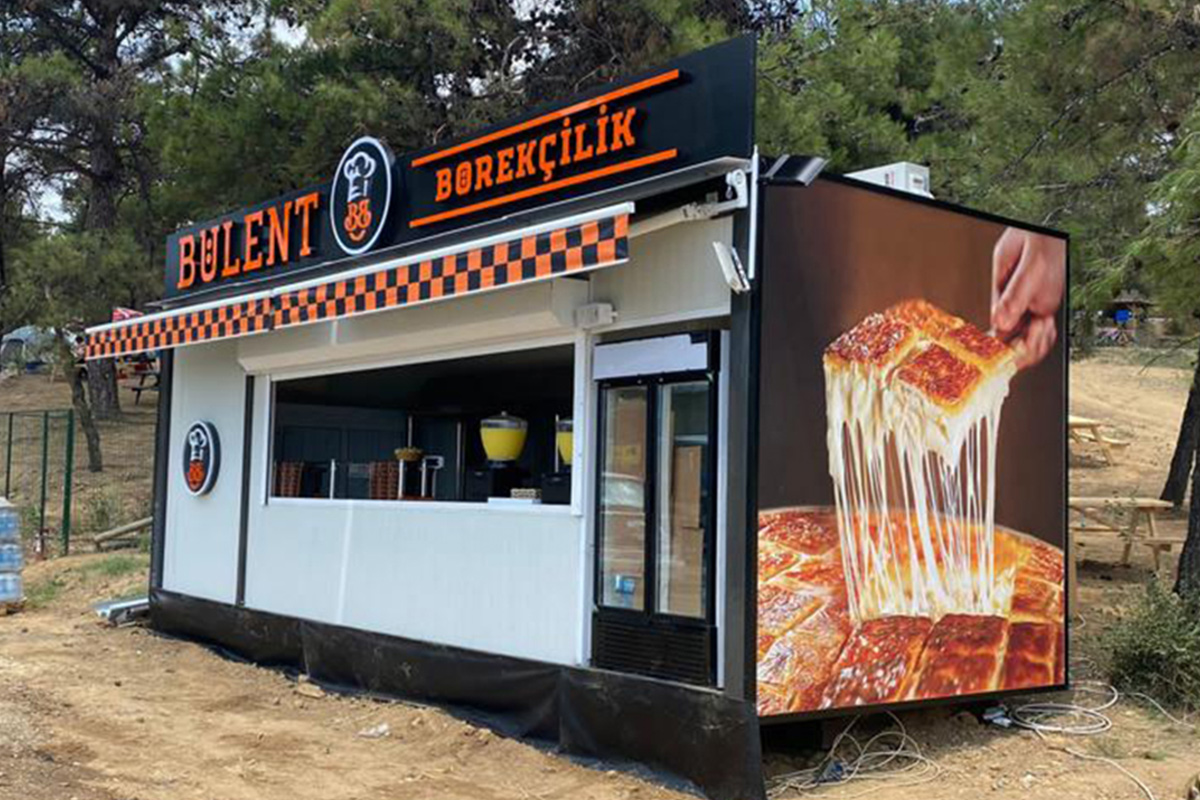
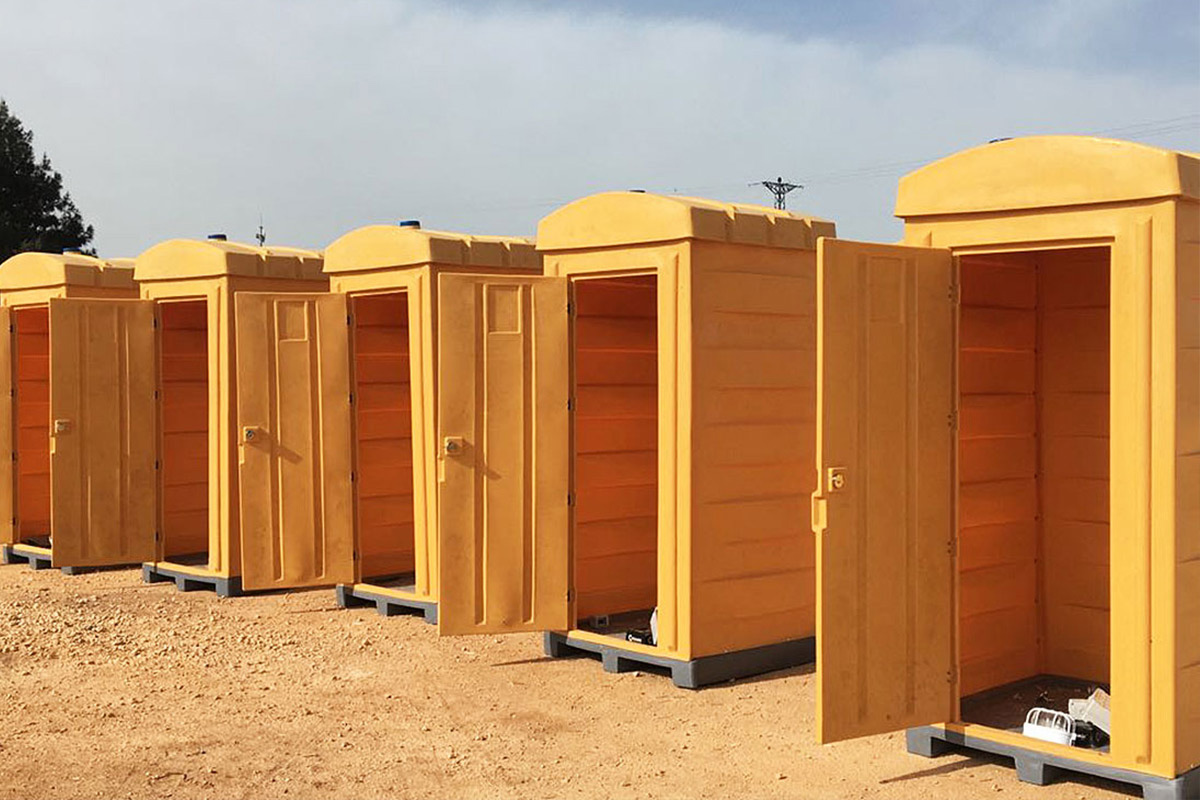
- Storage and logistics facilities serving transportation and supply chain hubs
These applications benefit from standardized quality and predictable delivery, regardless of location.

From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The delivery process for modular buildings and prefabricated building systems in Canada follows a structured sequence that minimizes risk for stakeholders.
The process begins with project needs analysis. Space usage, occupancy requirements, climate exposure, and regulatory obligations are defined in detail, often with input from multiple stakeholders.
Custom design and specifications follow, ensuring layouts, insulation systems, and structural components meet Canadian codes and operational expectations.
Factory production is then carried out under controlled conditions, allowing consistent quality and traceability. This stage is particularly valuable for projects in regions where on-site construction is logistically complex.
Delivery to Canada is planned with transportation regulations and site access in mind, ensuring smooth logistics even for remote destinations.
On-site installation completes the process, typically within a compressed timeframe that allows facilities to become operational quickly and efficiently.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Canada
Several technical factors require particular attention in Canadian projects.
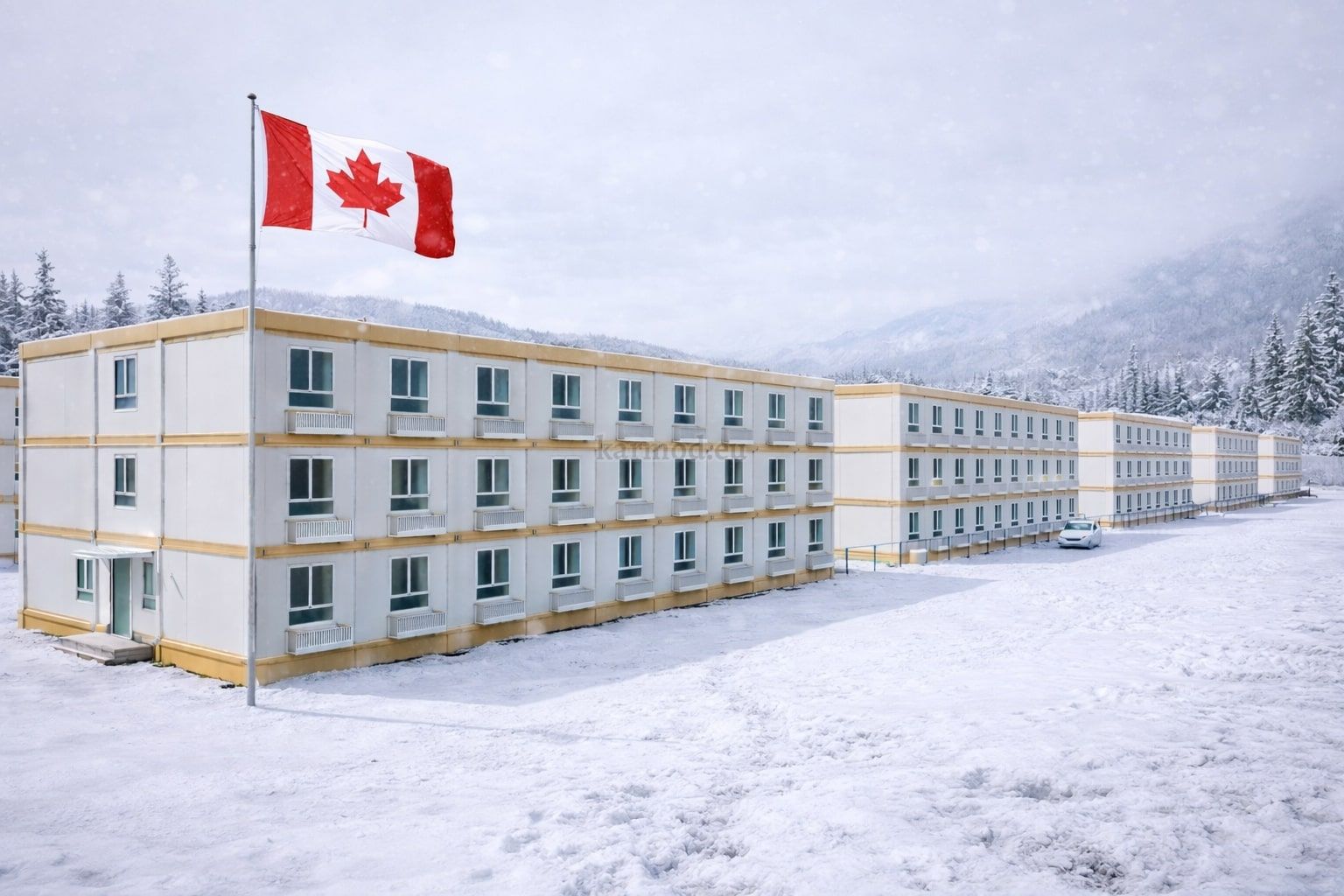
Thermal insulation is critical due to extreme temperature variations across regions and seasons. Proper insulation directly impacts energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
Fire safety standards are strictly regulated in Canada, requiring materials and systems that meet national and provincial codes.
Climate suitability must account for snow loads, wind exposure, and long-term durability under harsh conditions.
Custom layouts allow buildings to support operational workflows rather than forcing adaptation to standard designs, which is especially important for institutional and industrial users.
Manufacturers such as Karmod apply international experience to these requirements. Karmod modular building solutions are designed to perform reliably in demanding climates, drawing on project knowledge gained across Europe and other global markets. This background supports Canadian clients seeking dependable modular buildings and prefabricated building systems that align with regulatory and operational expectations.
For organizations planning facilities across Canada, these construction methods provide a disciplined, transparent path from concept to occupancy—supporting informed investment decisions and long-term operational confidence.