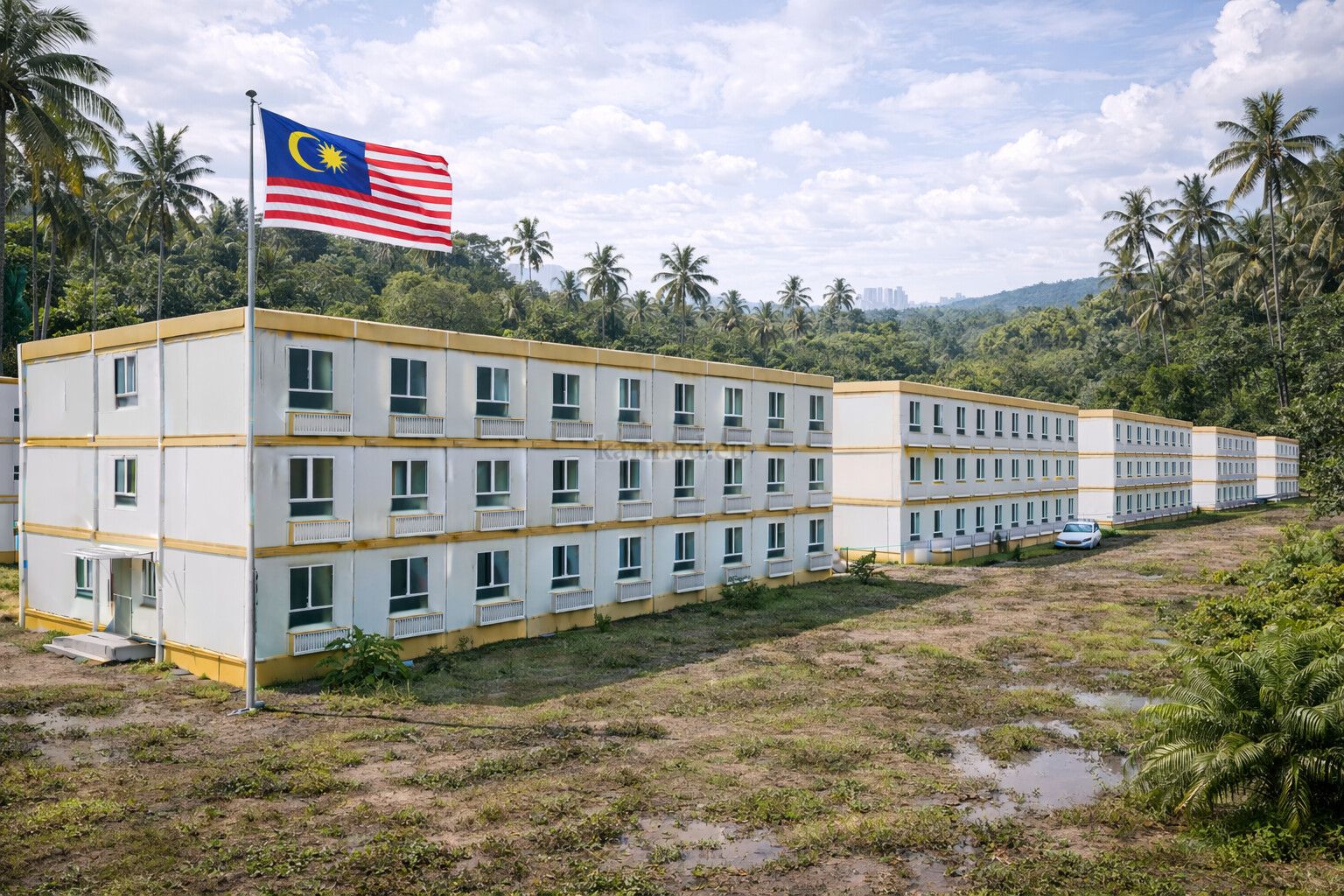
In Malaysia, construction and infrastructure development continue to accelerate in response to urban growth, industrial expansion, and regional connectivity projects. From logistics hubs and manufacturing zones to public facilities and energy developments, organizations are under increasing pressure to deliver buildings faster while maintaining cost control and regulatory compliance. Within this environment, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems are becoming integral to how projects are planned and executed.
Conventional construction methods often face challenges related to labor availability, site congestion, and extended timelines—particularly in dense urban areas or remote industrial zones. Off-site construction approaches provide a structured alternative by shifting production into factory settings, reducing on-site risks, and offering predictable delivery schedules. For Malaysian decision-makers, this combination of speed, quality consistency, and flexibility is increasingly difficult to ignore.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Malaysia
Labor costs and workforce management are key drivers behind the growing interest in modular buildings across Malaysia. While the construction sector remains active, managing skilled labor on complex sites can be challenging, especially for projects that must meet tight deadlines. Modular construction reduces on-site labor dependency by completing most building activities in controlled manufacturing environments, improving productivity and cost predictability.
Construction speed is another decisive factor. Large-scale developments—such as industrial parks, logistics centers, and public infrastructure projects—often operate under strict schedules linked to investment timelines and operational rollouts. Modular buildings enable parallel workflows, allowing site preparation and building production to occur simultaneously. This approach significantly shortens overall project durations compared to traditional construction.
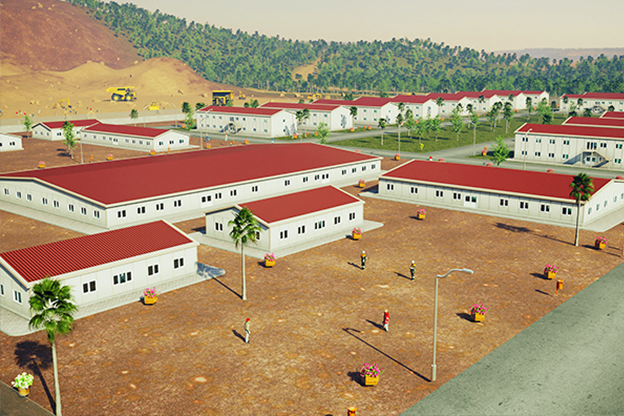
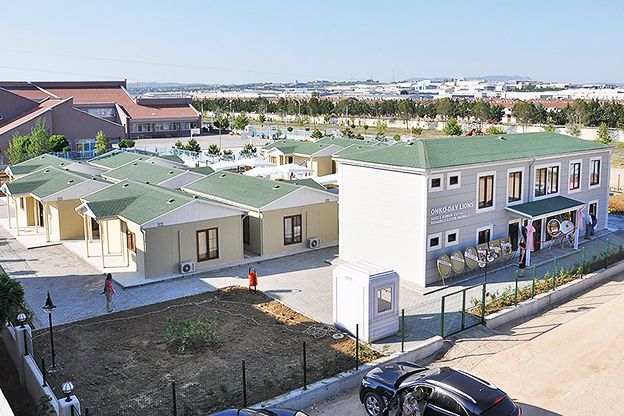
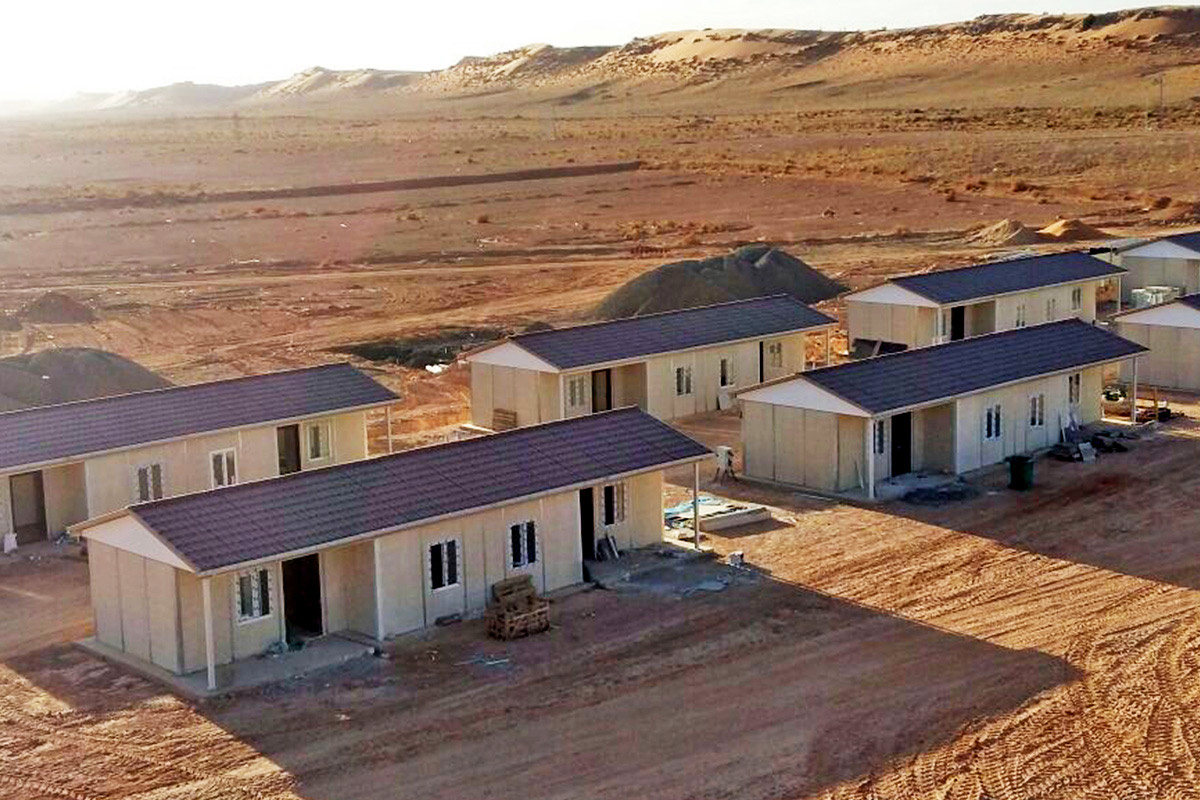
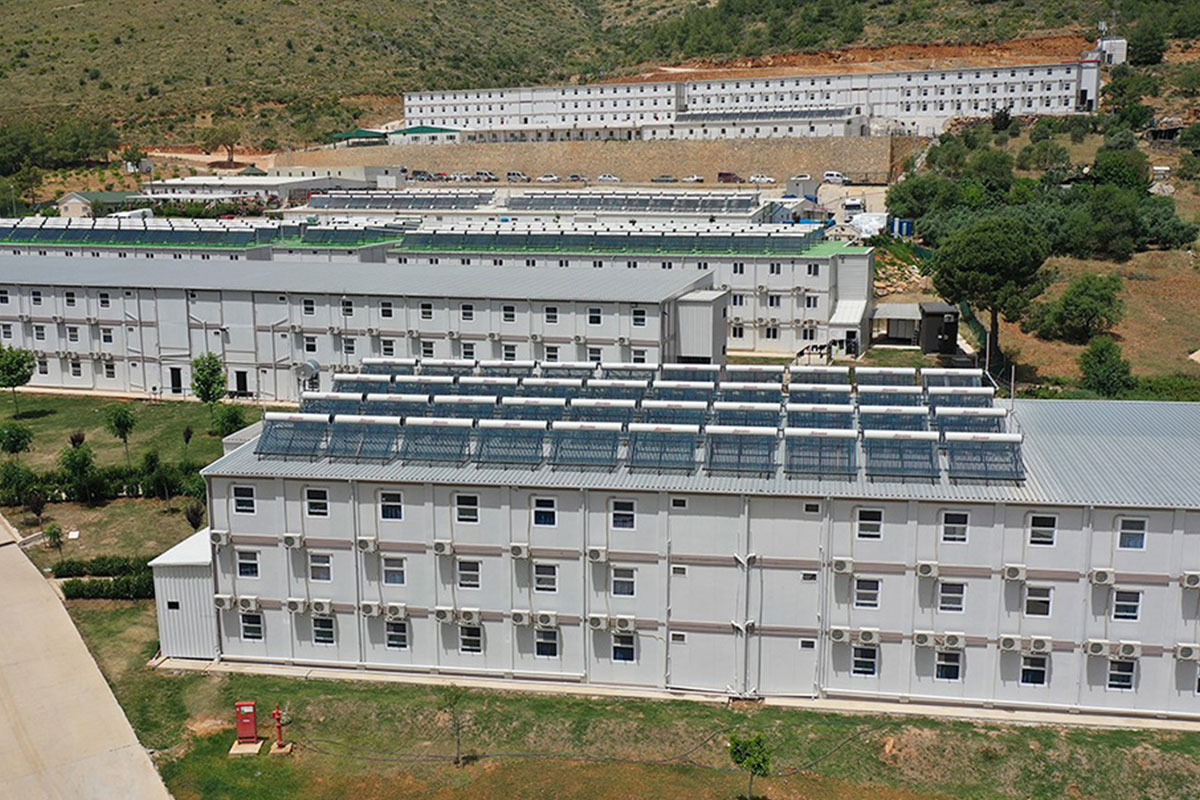
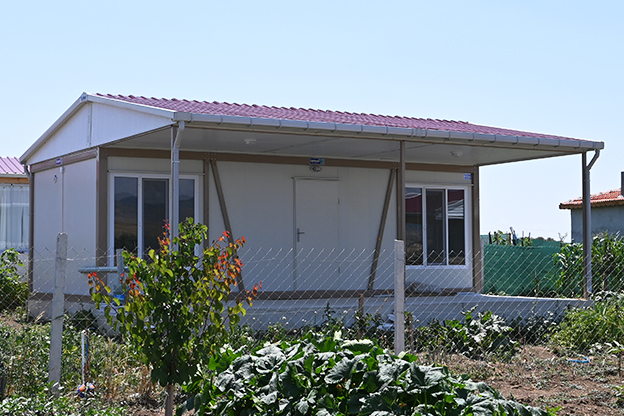
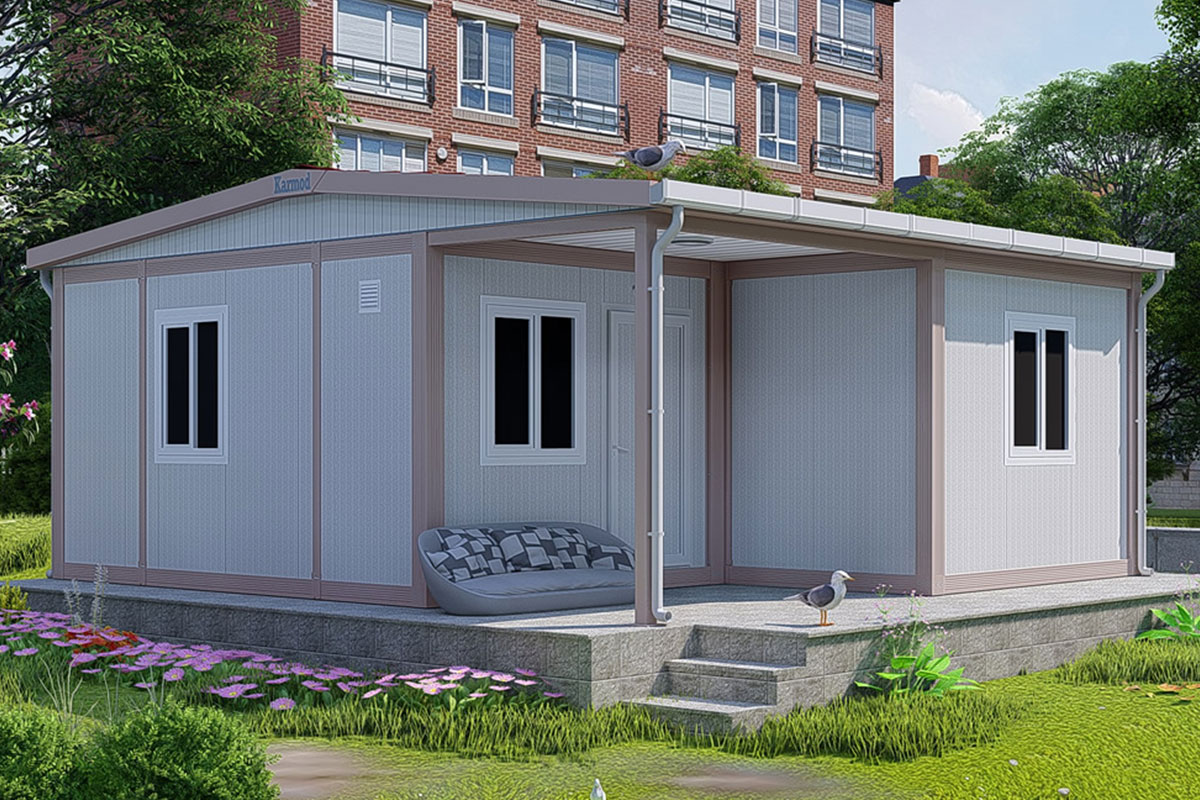
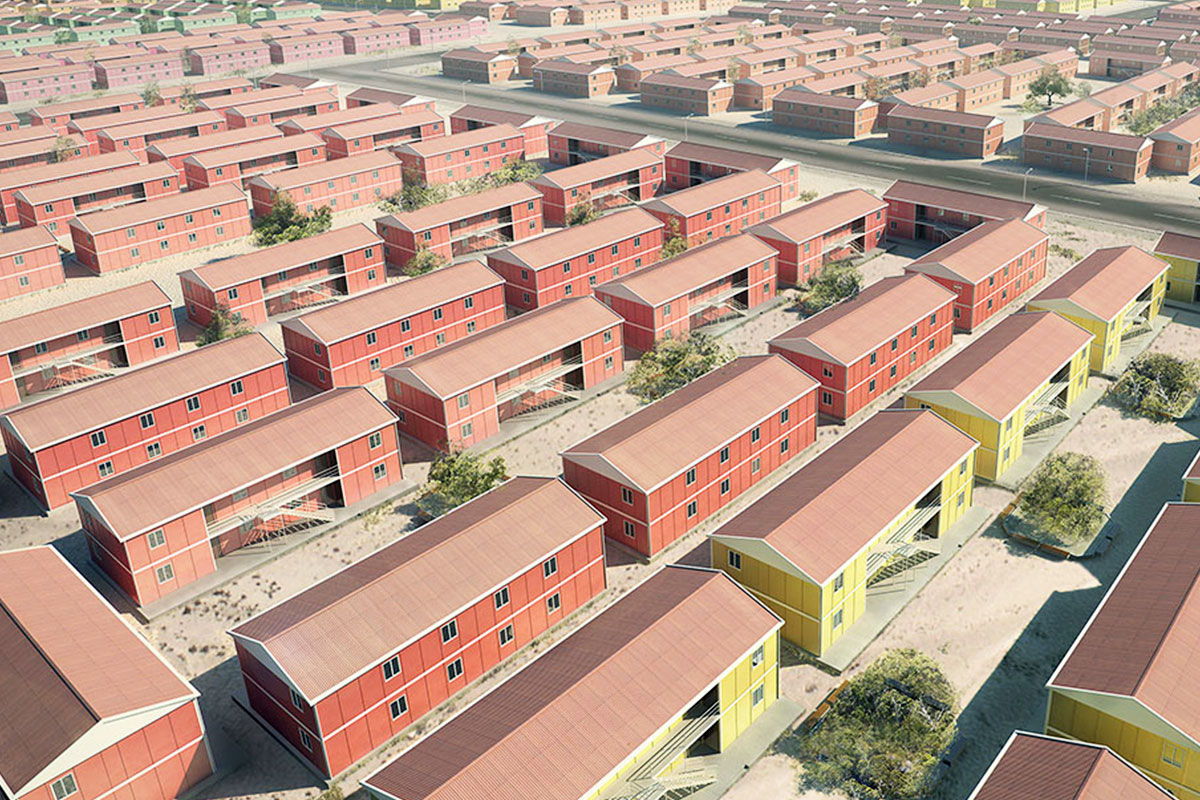
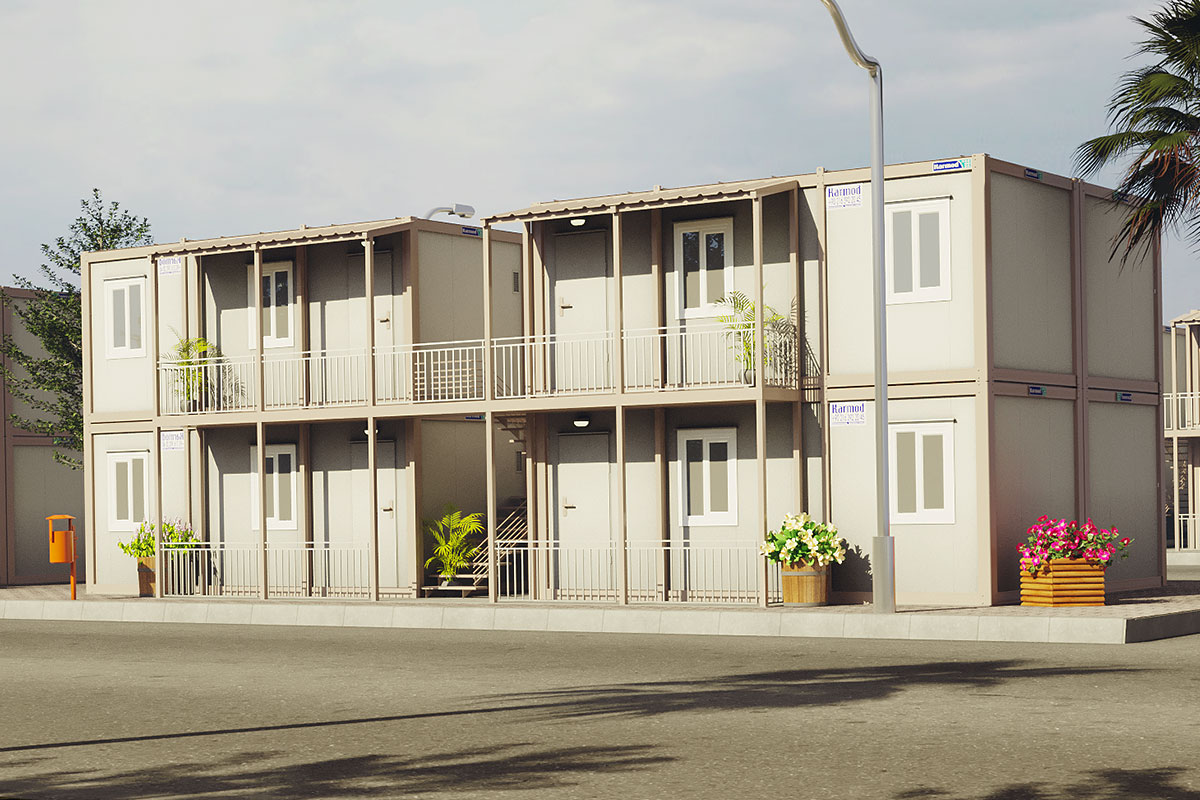
Malaysia also presents a balanced need for both temporary and permanent structures. Temporary buildings are frequently required for construction site offices, worker accommodation, and project support facilities. At the same time, permanent solutions are needed for administrative buildings, educational facilities, healthcare units, and industrial support structures. Modular systems address both scenarios by offering relocatable units as well as long-term installations designed for extended use.
Country-specific sectors further reinforce demand. Logistics and port-related developments, manufacturing and industrial operations, public-sector facilities, and energy projects—including power generation and infrastructure upgrades—all benefit from fast, scalable building solutions that can adapt to evolving operational needs.
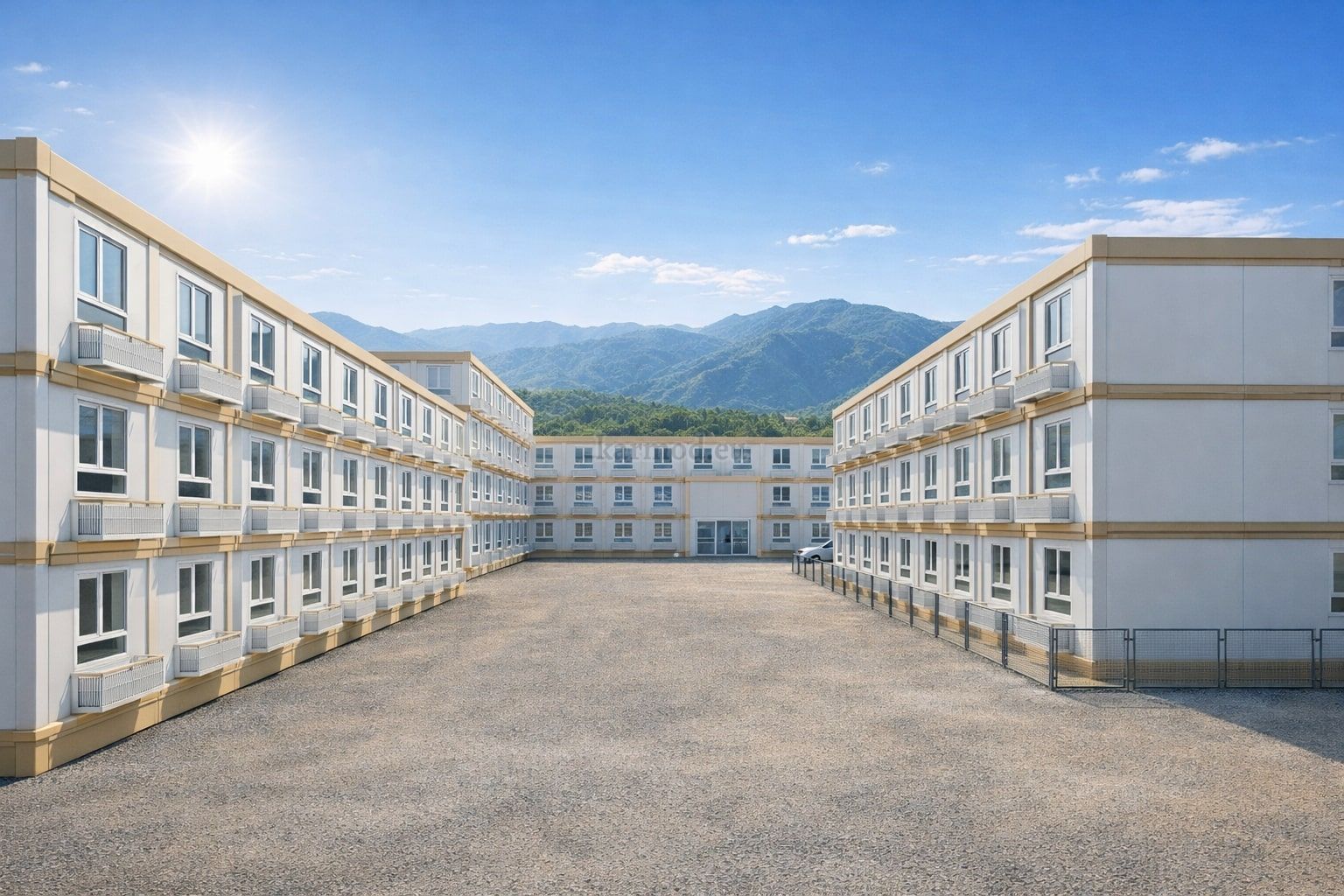

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
Although they share off-site production principles, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve distinct purposes within Malaysia’s construction landscape.
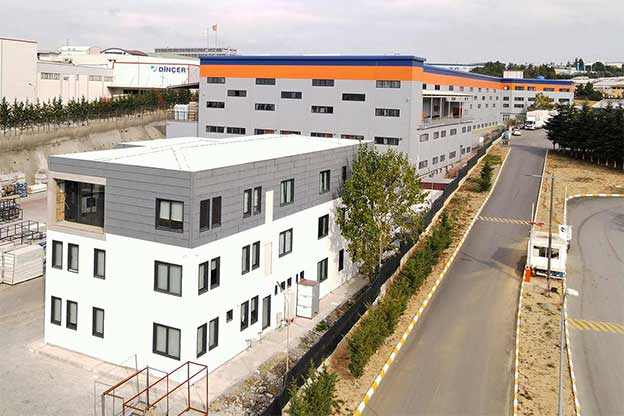
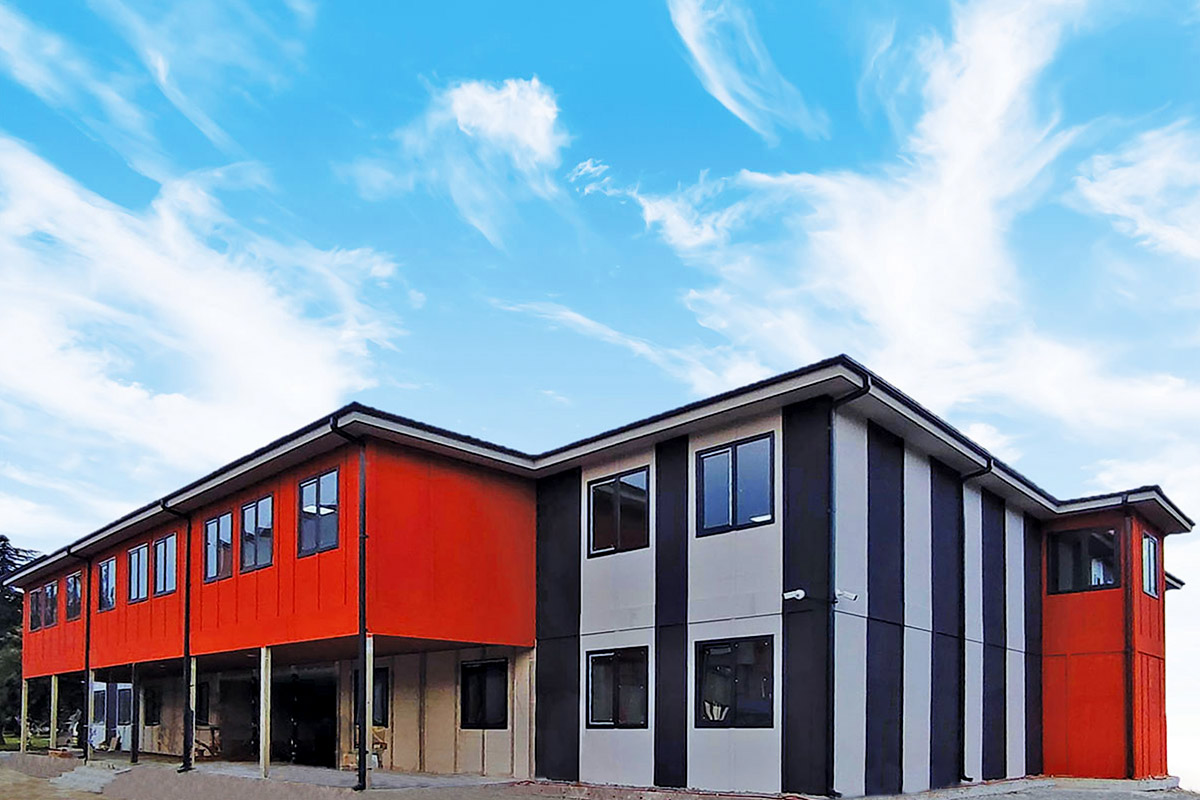
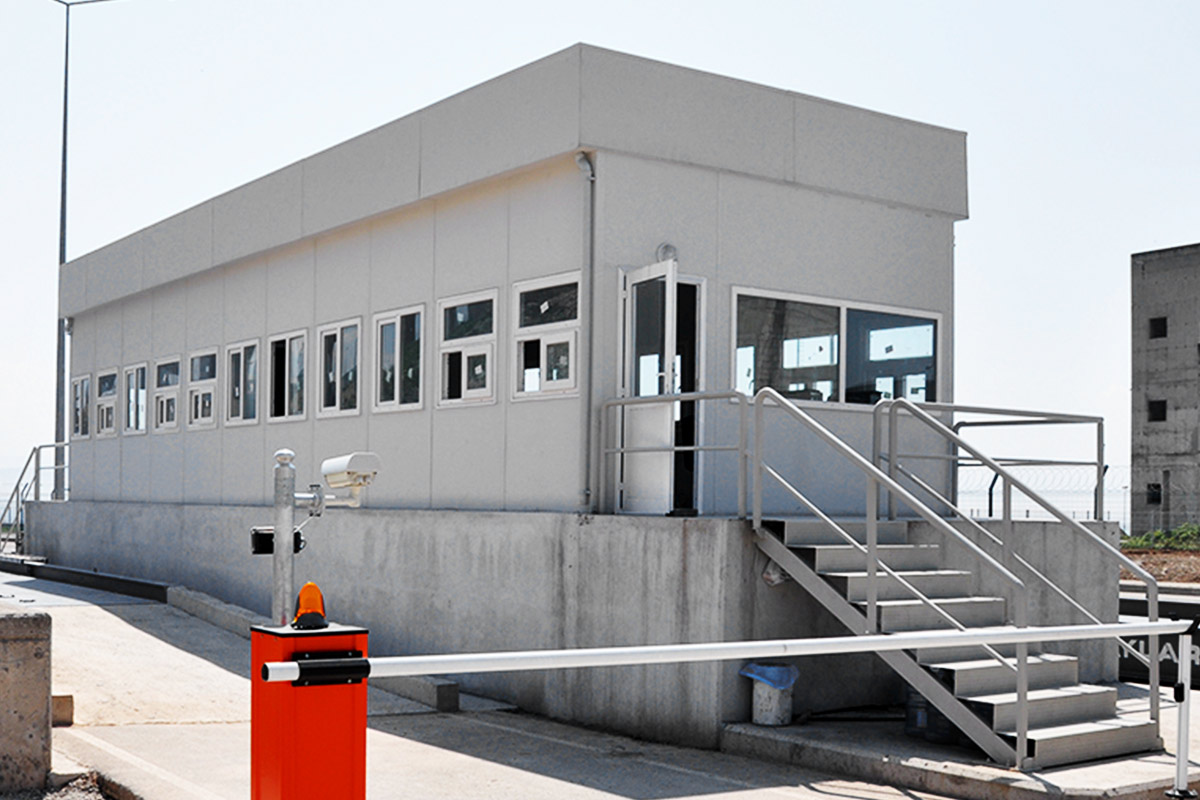
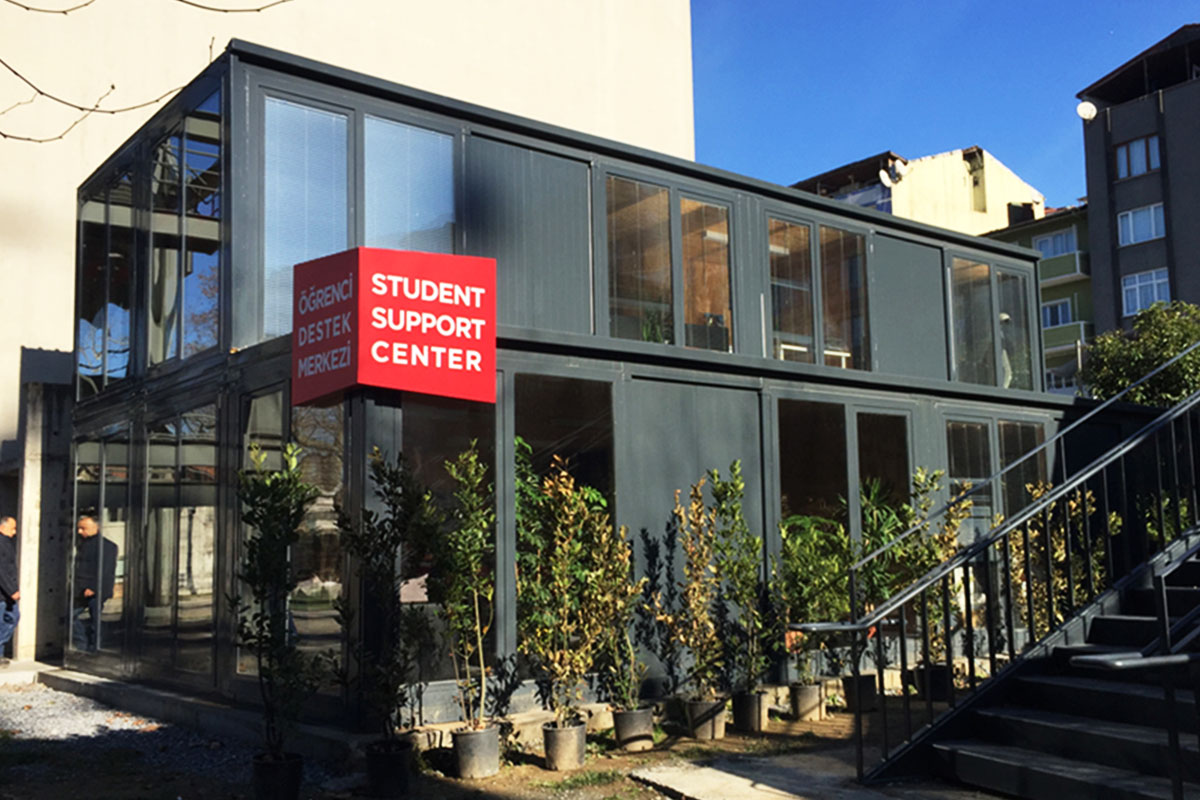
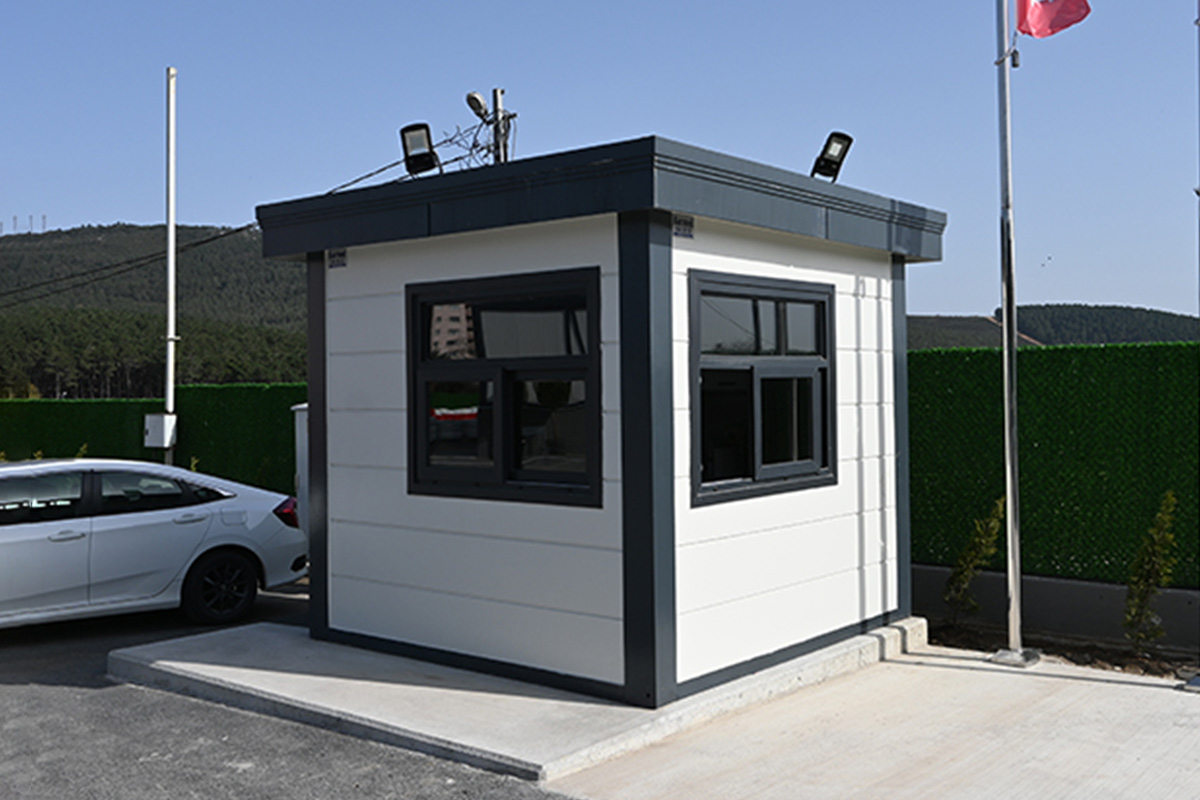
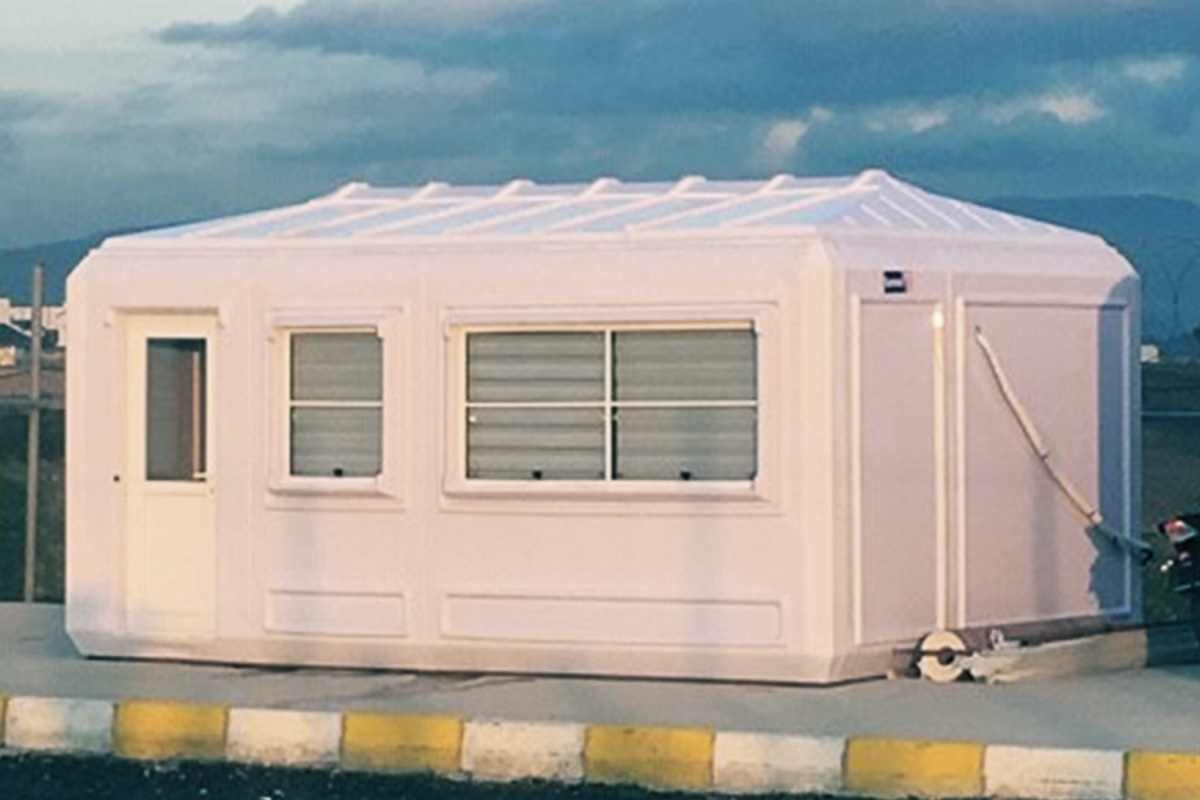
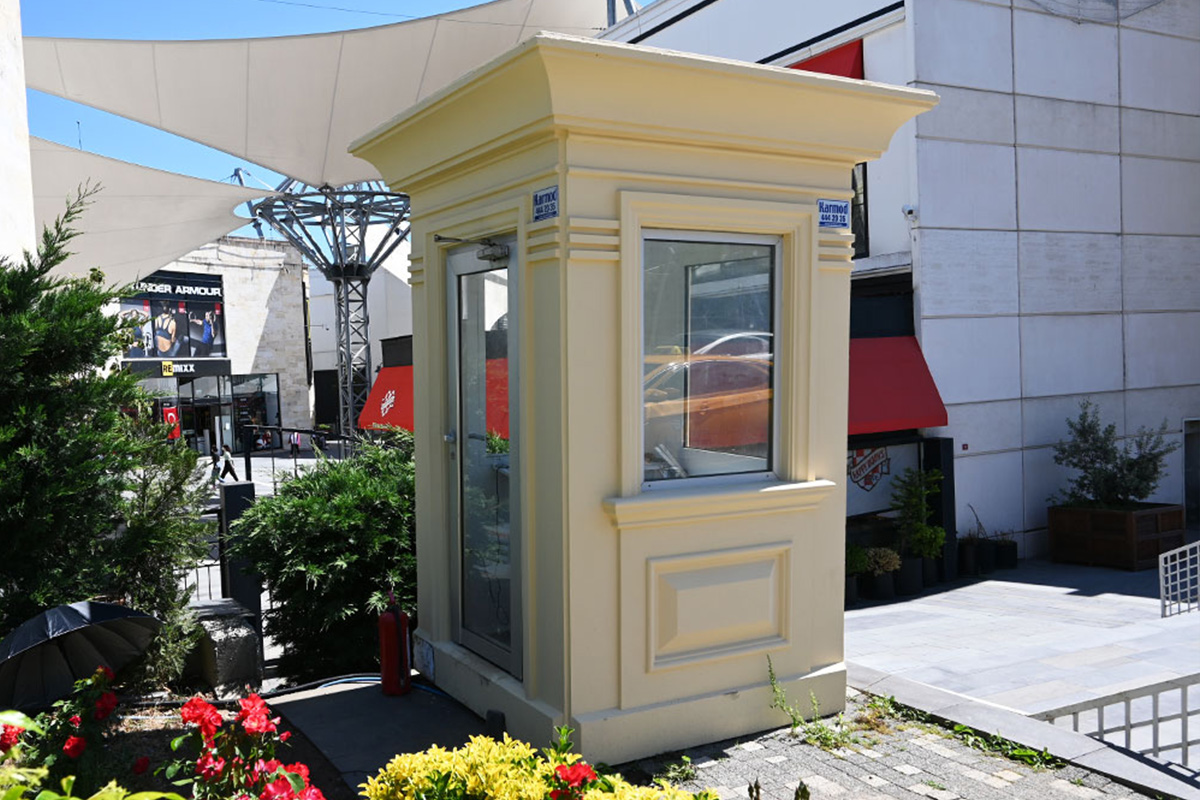
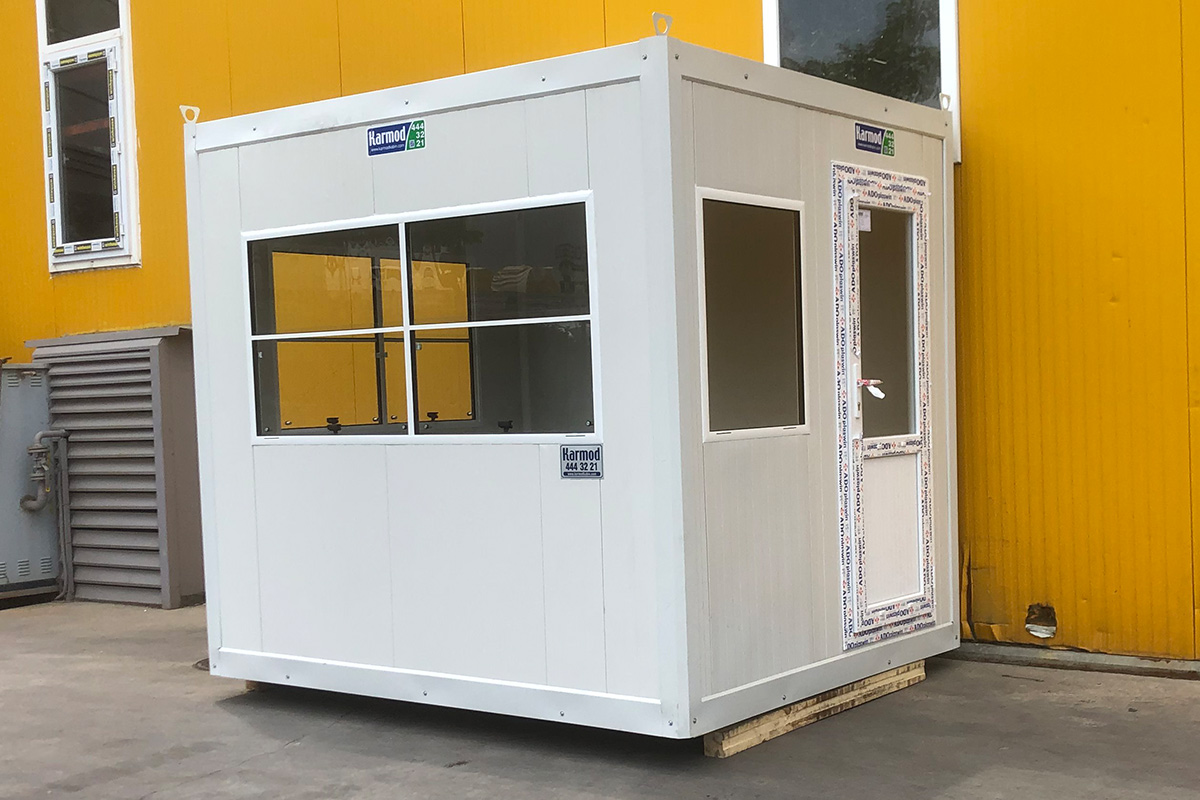
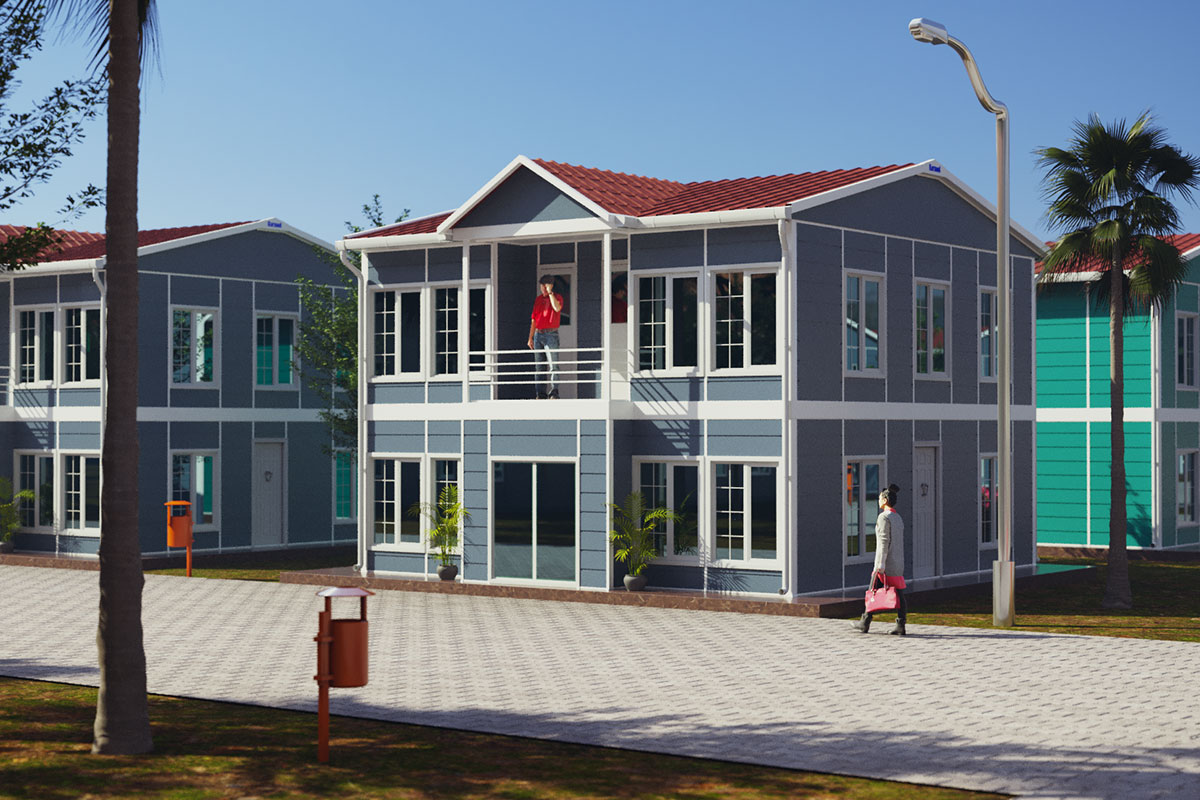
Modular buildings are manufactured as volumetric units, each forming a complete functional space. These modules can be transported, installed rapidly, expanded, or relocated as project requirements change. This makes modular buildings particularly suitable for logistics hubs, industrial facilities, and infrastructure projects where flexibility and scalability are essential.
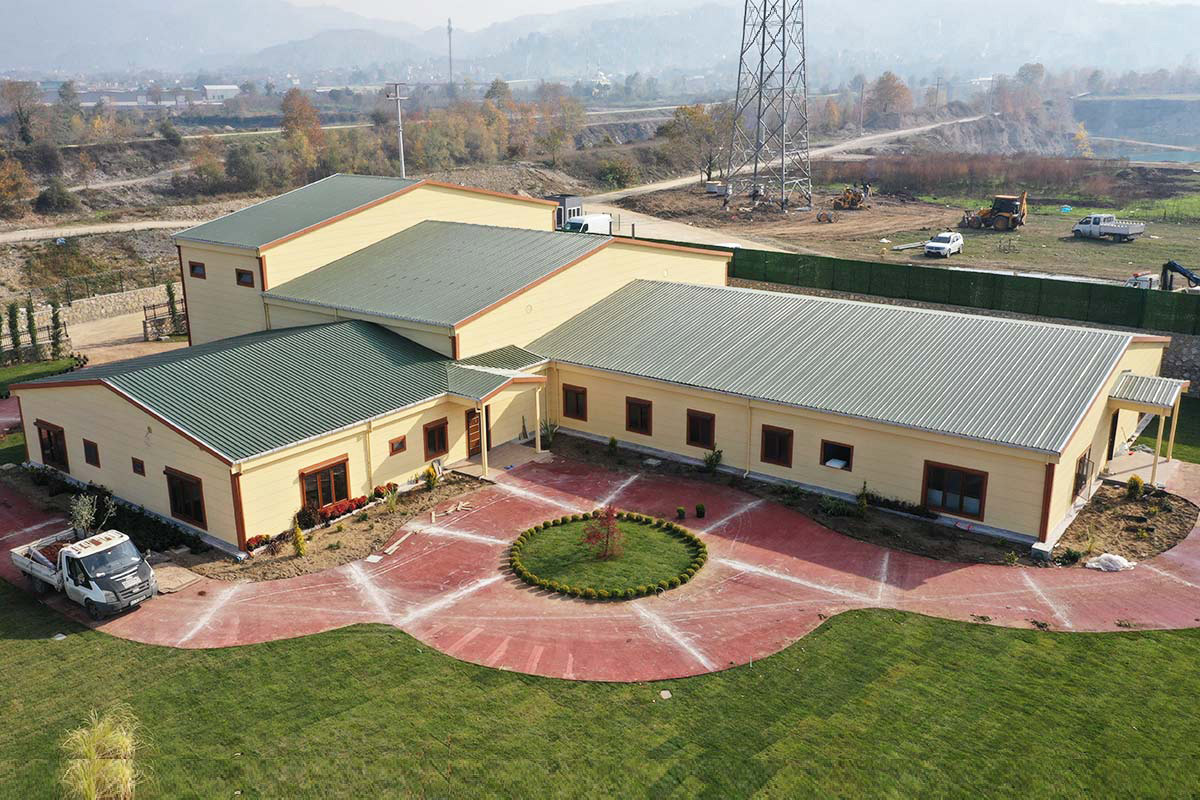
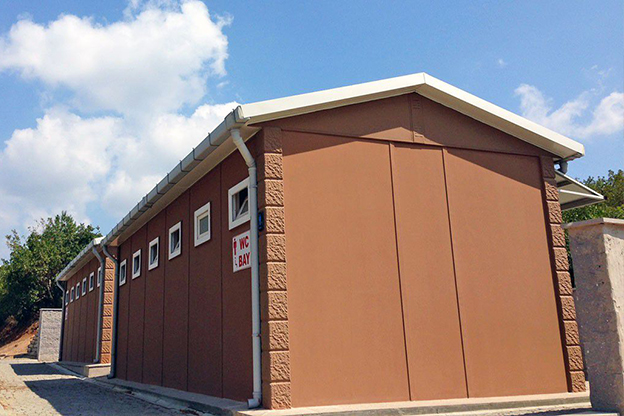
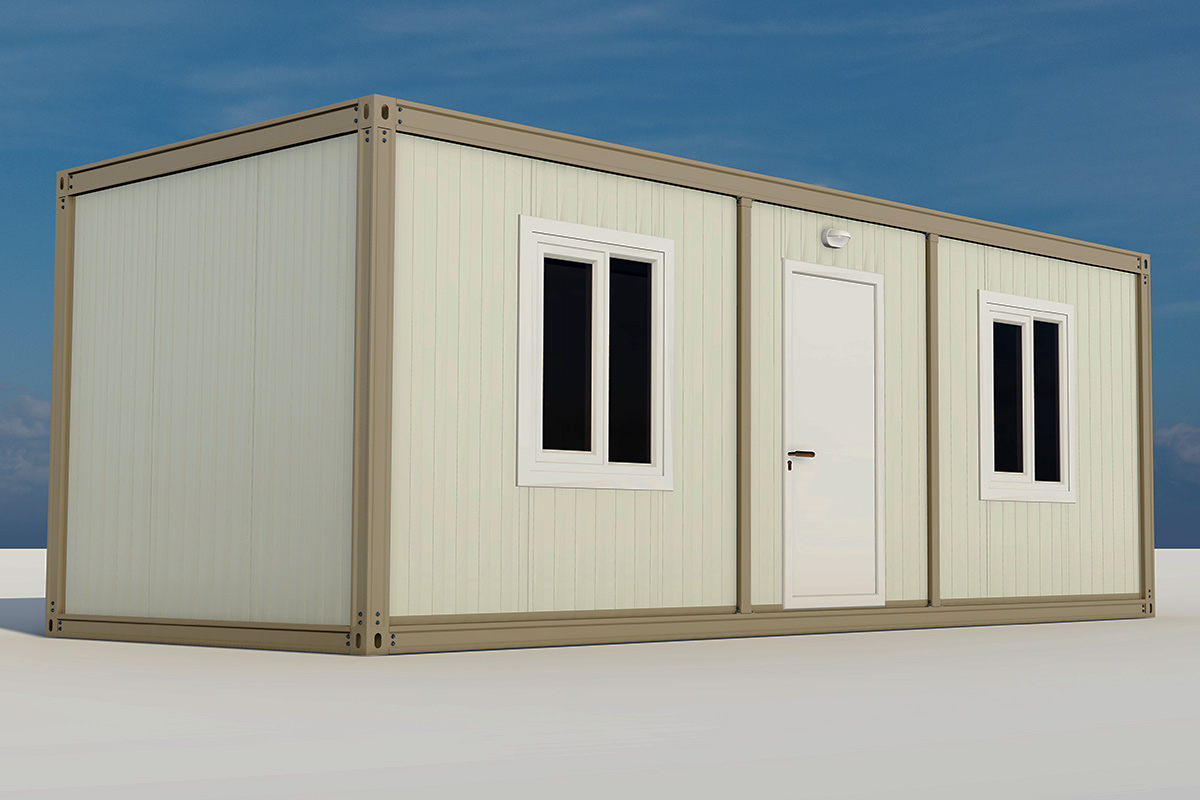
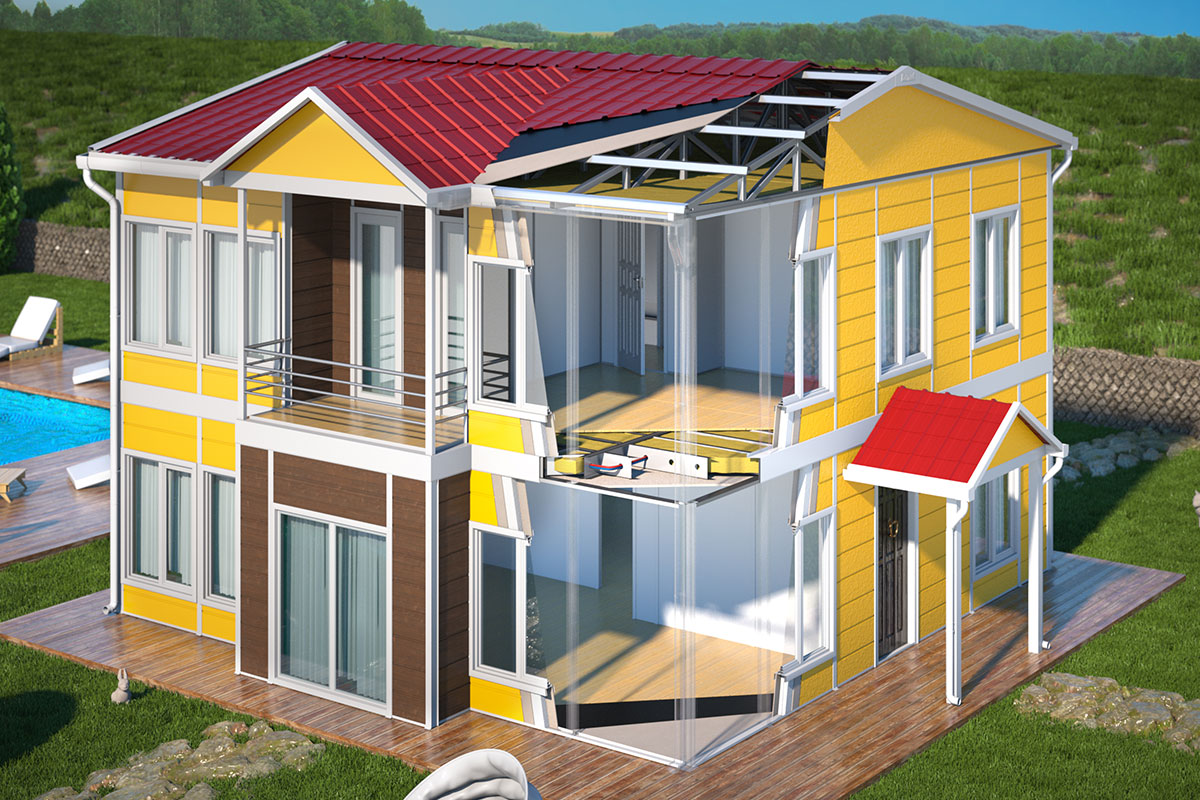
A prefabricated building, in contrast, is typically assembled on-site from panels or structural components produced in a factory. These systems are commonly selected for permanent structures where architectural integration, long-term occupancy, and site-specific design considerations take precedence.
In Malaysia, modular buildings are often favored for temporary facilities, site-based operations, and scalable industrial use, while prefabricated building systems are frequently chosen for permanent public buildings, warehouses, and administrative complexes. Selecting the right approach depends on factors such as building lifespan, mobility requirements, and long-term operational strategy rather than initial cost alone.
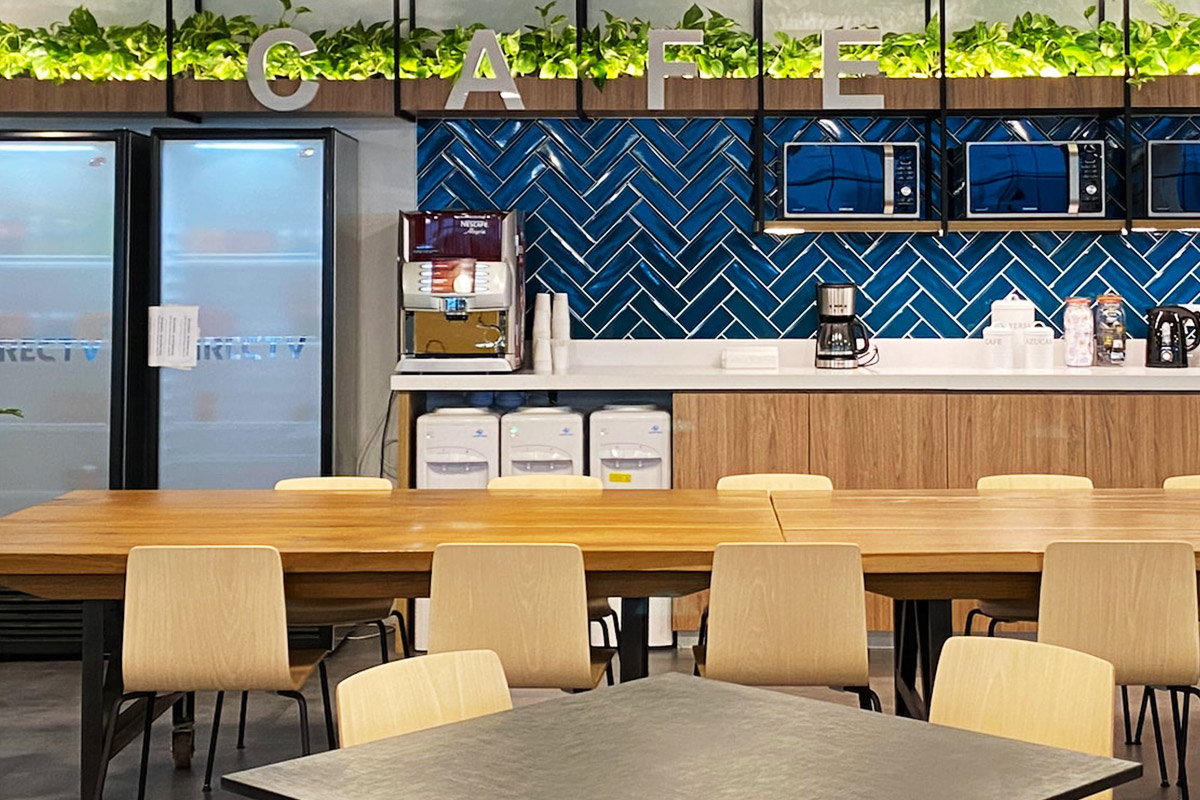
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Malaysia
Across Malaysia, modular and prefabricated solutions are used in a wide range of applications, including:
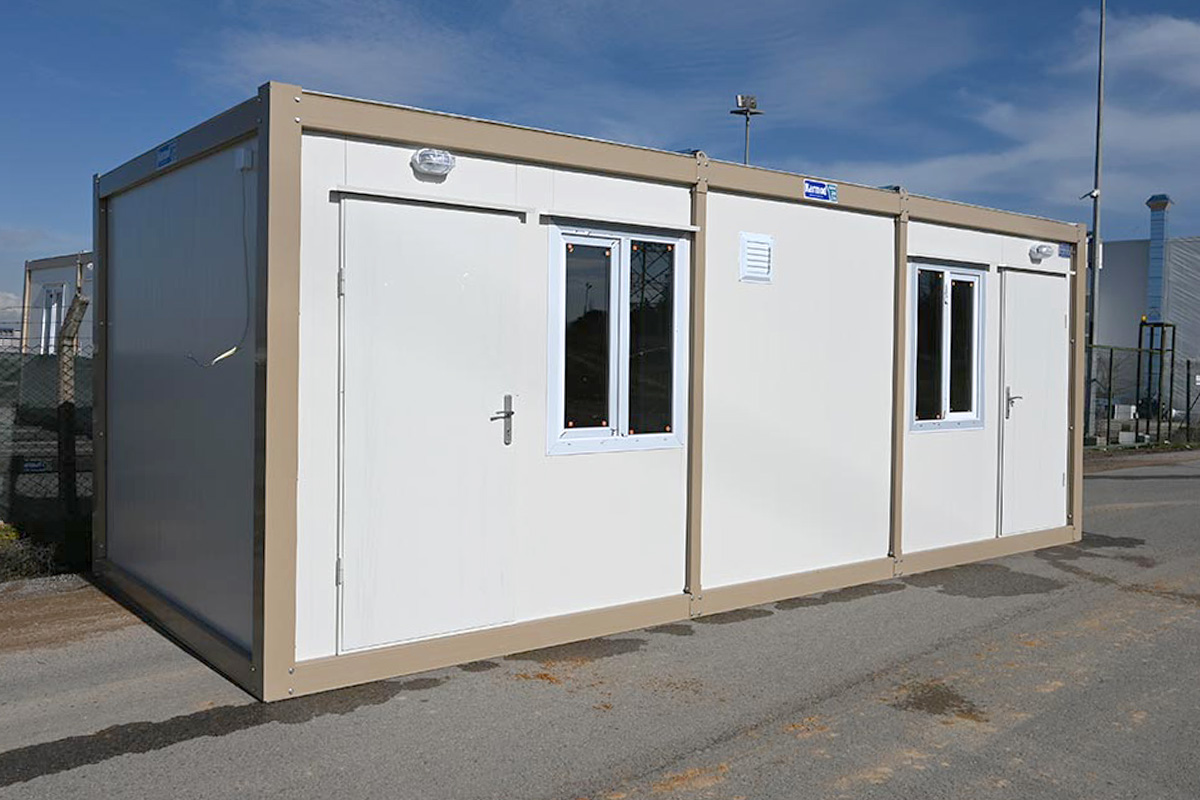
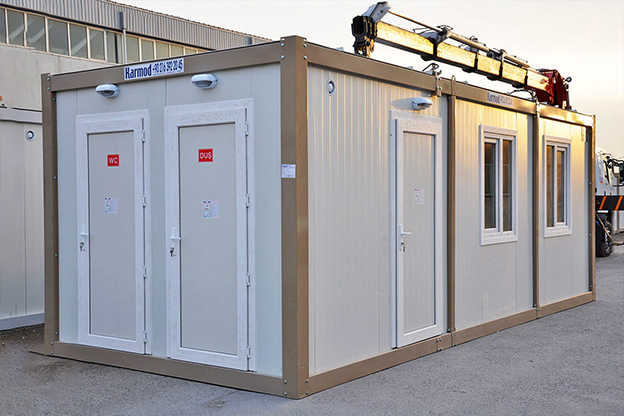
- Site offices & construction camps – Quick-to-install operational spaces for active projects
- Worker accommodation buildings – Housing solutions supporting industrial, infrastructure, and large-scale construction activities
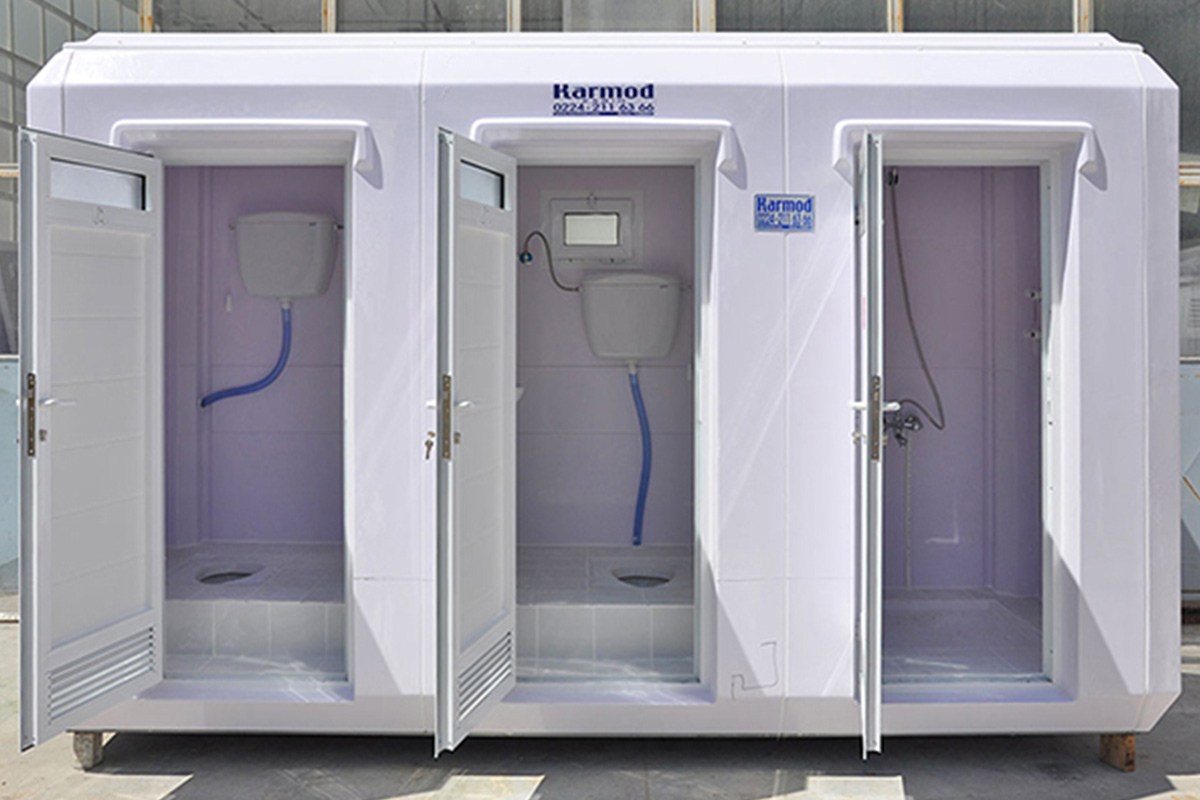
- Temporary schools & healthcare units – Facilities enabling public services to expand capacity efficiently
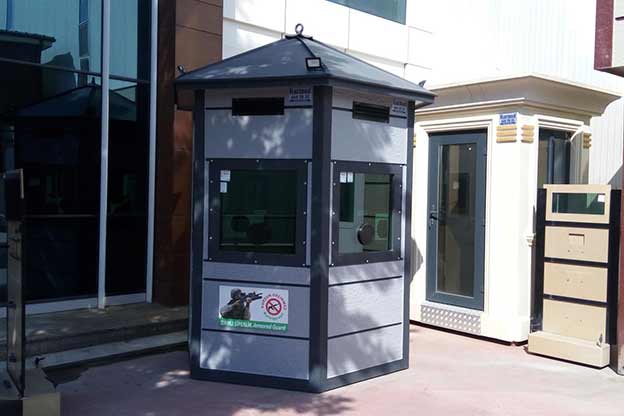
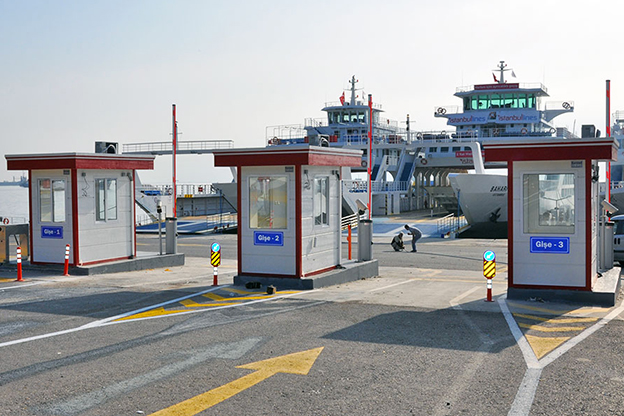
- Security buildings & technical units – Control and support buildings for industrial zones, logistics centers, and energy facilities
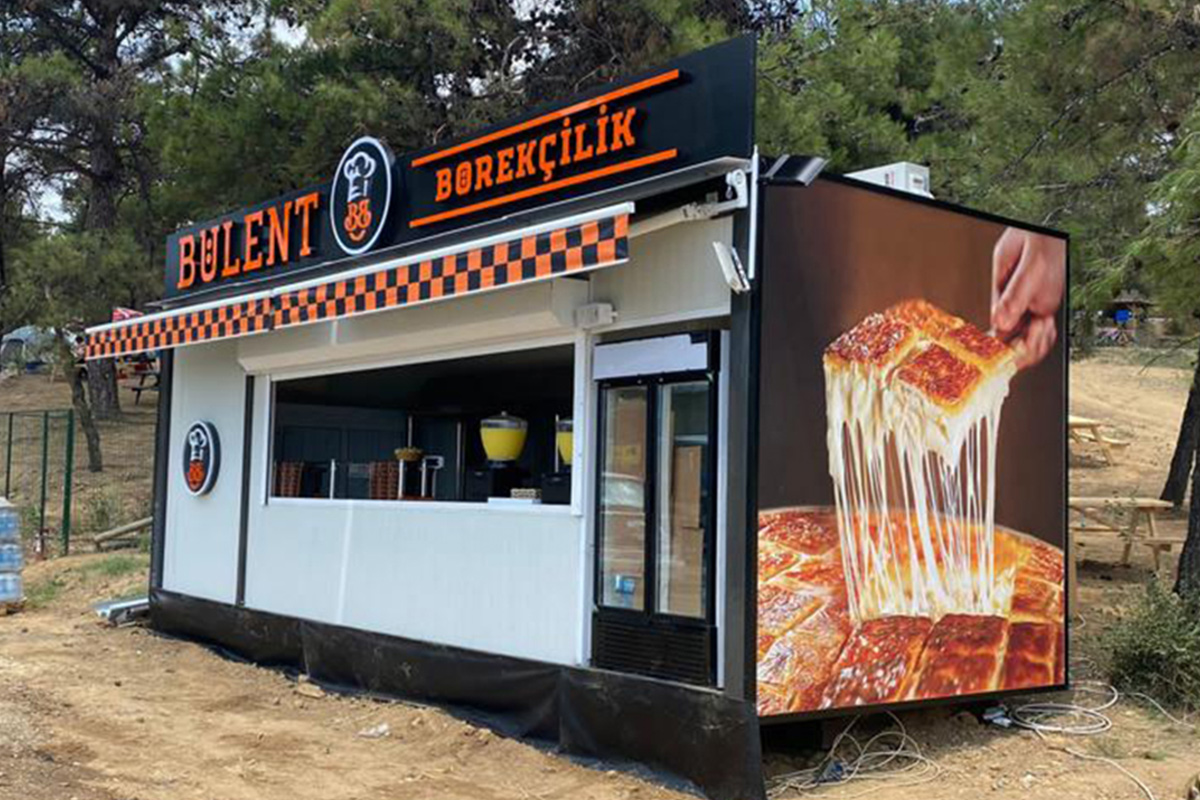
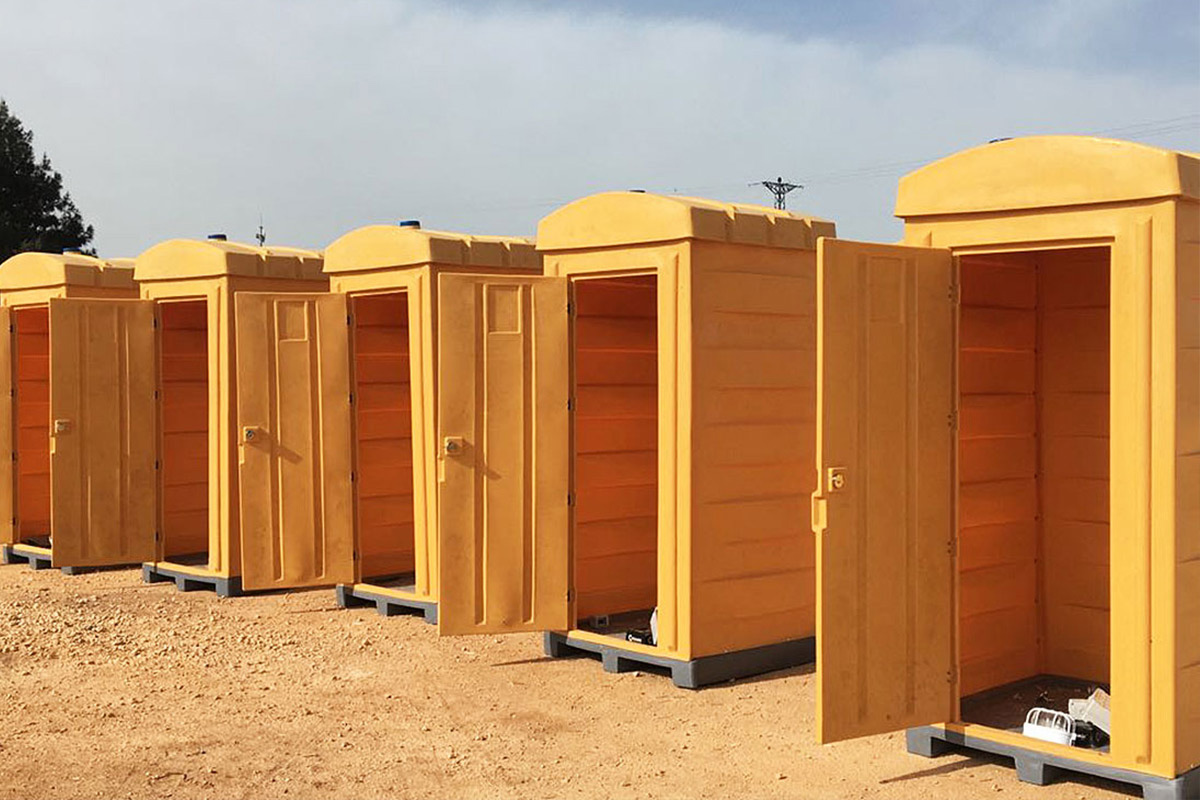
- Storage and logistics facilities – Fast-deployed buildings designed for future expansion
These use cases demonstrate how off-site construction methods support both immediate operational demands and longer-term development plans.

From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The delivery of modular buildings and prefabricated building systems follows a clear, step-by-step process designed to minimize uncertainty.
The process begins with project needs analysis, where functional requirements, capacity planning, and local regulations are evaluated. This stage is particularly important in Malaysia, where climate conditions and site constraints can vary significantly by region.
Custom design and technical specifications follow. Layouts, ventilation strategies, material selections, and safety requirements are tailored to the building’s intended use and environmental conditions.
Once designs are approved, factory production takes place. Manufacturing in controlled conditions ensures consistent quality and reduces exposure to weather-related delays.
Completed modules or components are then prepared for delivery to Malaysia, with logistics planning adapted to port access, road networks, and site accessibility.
The final step is on-site installation, which is typically completed in a short timeframe. Reduced on-site activity allows buildings to become operational quickly, supporting faster project handover.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Malaysia
Thermal insulation and ventilation: Essential for maintaining comfort and energy efficiency in Malaysia’s tropical climate.
Fire safety standards: Must comply with national regulations and sector-specific requirements, particularly for public and industrial facilities.
Climate suitability: Material selection and structural design must ensure durability under heat, humidity, and heavy rainfall.
Custom layouts: Flexible interior planning allows buildings to align with administrative, accommodation, or technical workflows.
Manufacturers such as Karmod integrate these considerations into a unified design and production approach. Drawing on extensive international experience, Karmod modular building solutions are engineered to perform reliably in diverse climates while meeting industry-specific requirements. This practical, standards-driven approach supports Malaysia’s evolving construction needs without sacrificing quality or adaptability.
By adopting modular buildings and prefabricated building systems, organizations in Malaysia can achieve faster delivery, improved cost control, and infrastructure that remains flexible as operational requirements evolve.