Morocco has positioned itself as one of the most dynamic construction markets in North Africa. Large-scale infrastructure investments, expanding industrial zones, renewable energy projects, and growing logistics corridors are reshaping how facilities are planned and delivered. In this environment, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems are increasingly viewed as strategic construction methods rather than temporary alternatives. Decision-makers across public and private sectors are focusing on speed, cost control, and operational flexibility—criteria that align closely with modern modular and prefabricated solutions.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Morocco
Construction activity in Morocco spans industrial manufacturing, port expansions, logistics hubs, public infrastructure, and energy projects. One of the main drivers behind the growing demand for modular buildings is labor efficiency. Skilled construction labor costs are rising, particularly for projects located outside major urban centers. Modular systems reduce on-site labor requirements by shifting most production to controlled factory environments.
Another critical factor is construction time. Traditional building processes often face delays due to permitting, weather conditions, or site logistics. Modular buildings allow parallel workflows: site preparation and building production proceed simultaneously, shortening project timelines significantly. For investors and operators, this time advantage directly translates into faster project activation.
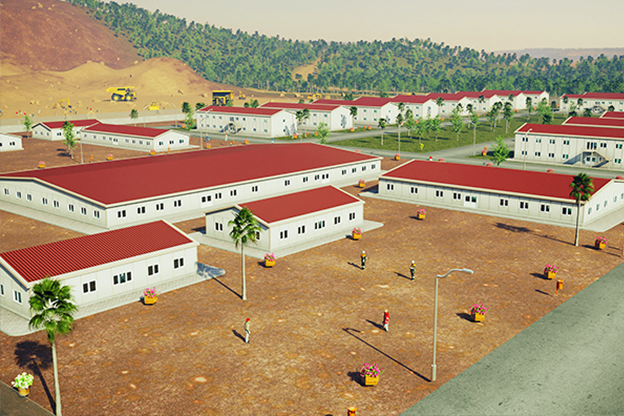
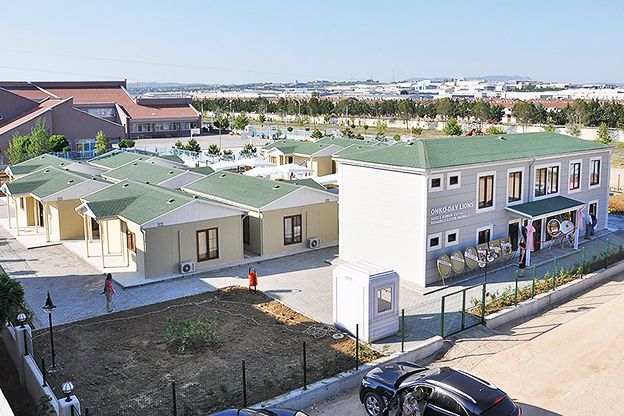
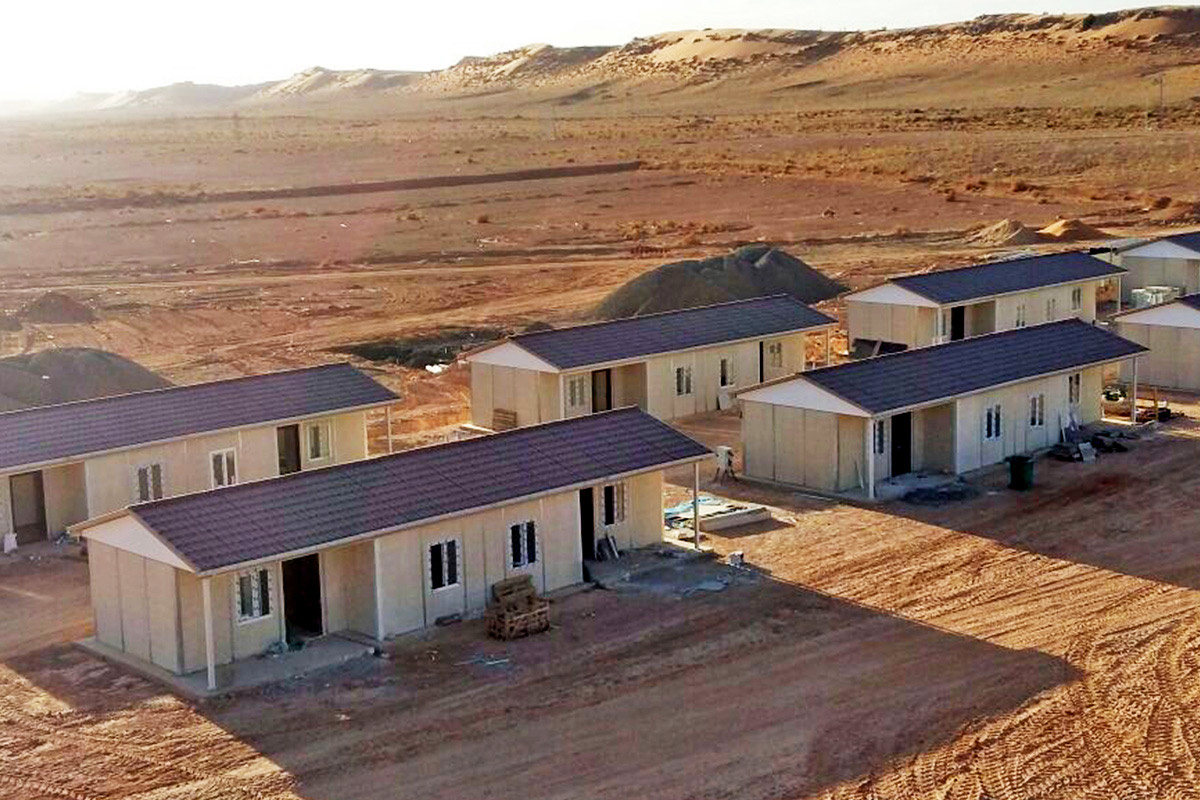
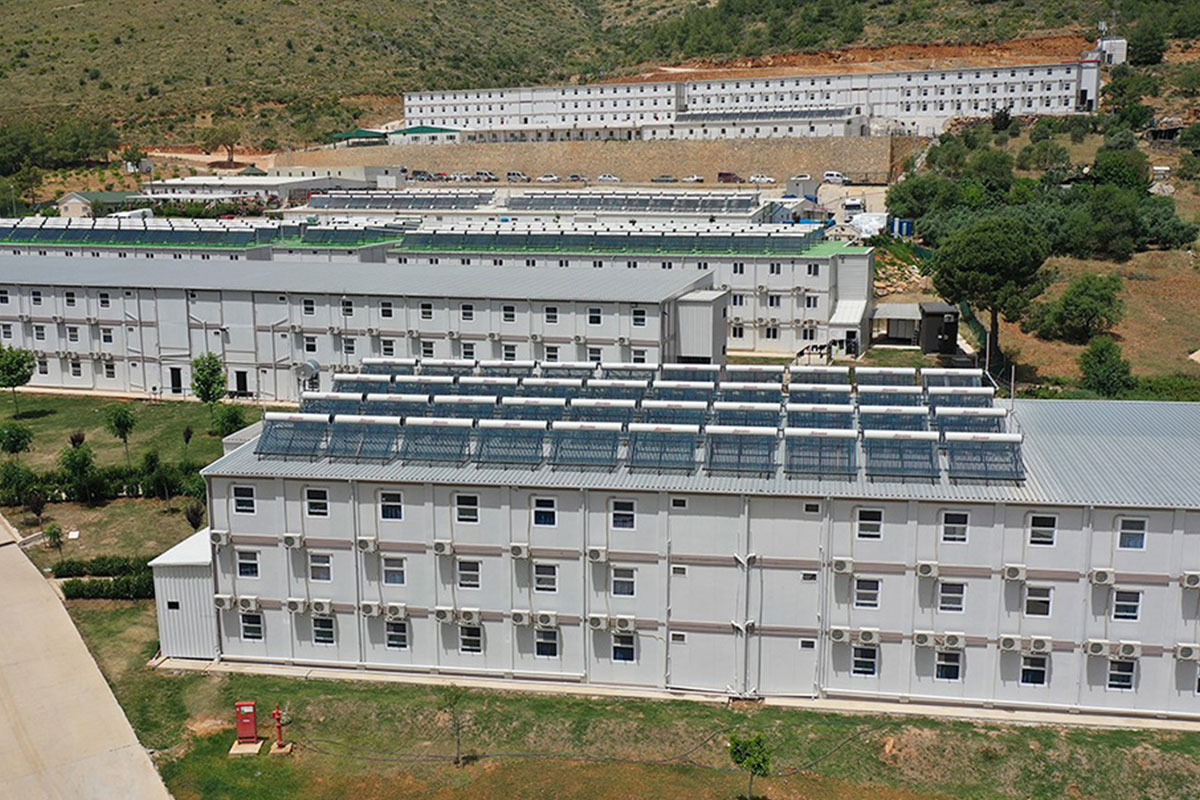
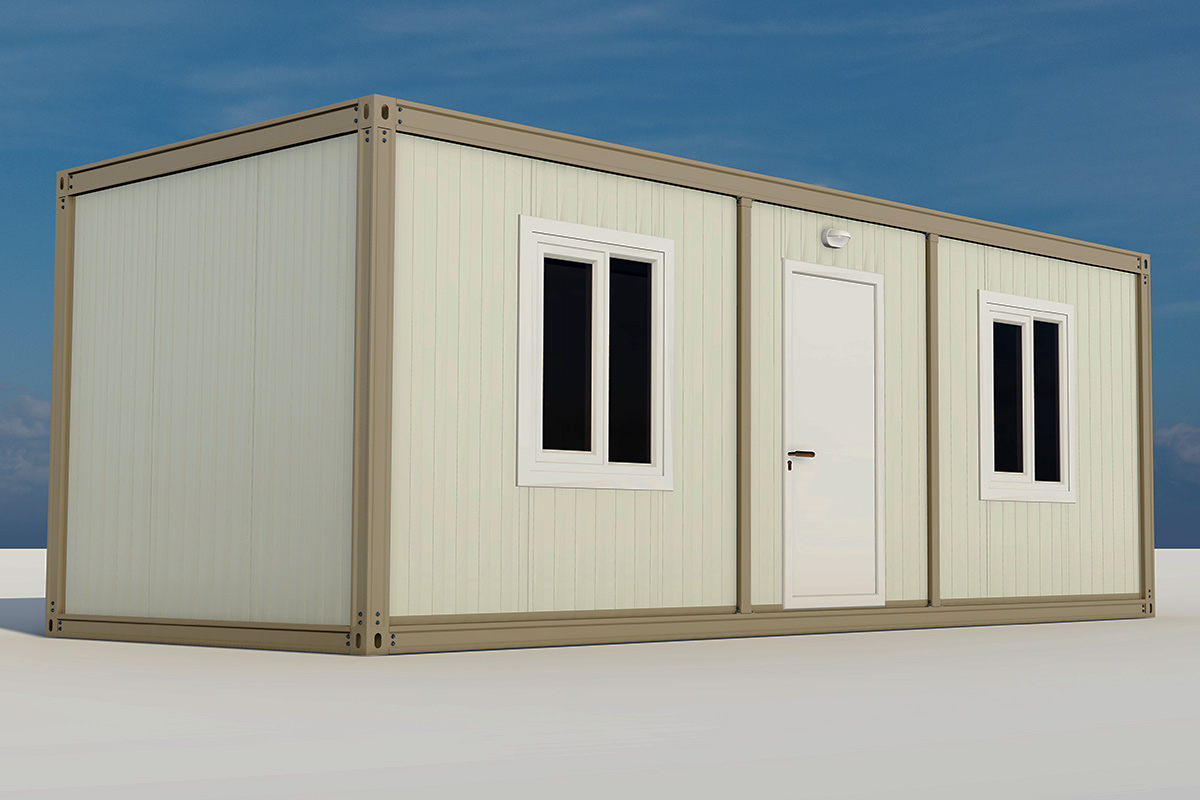
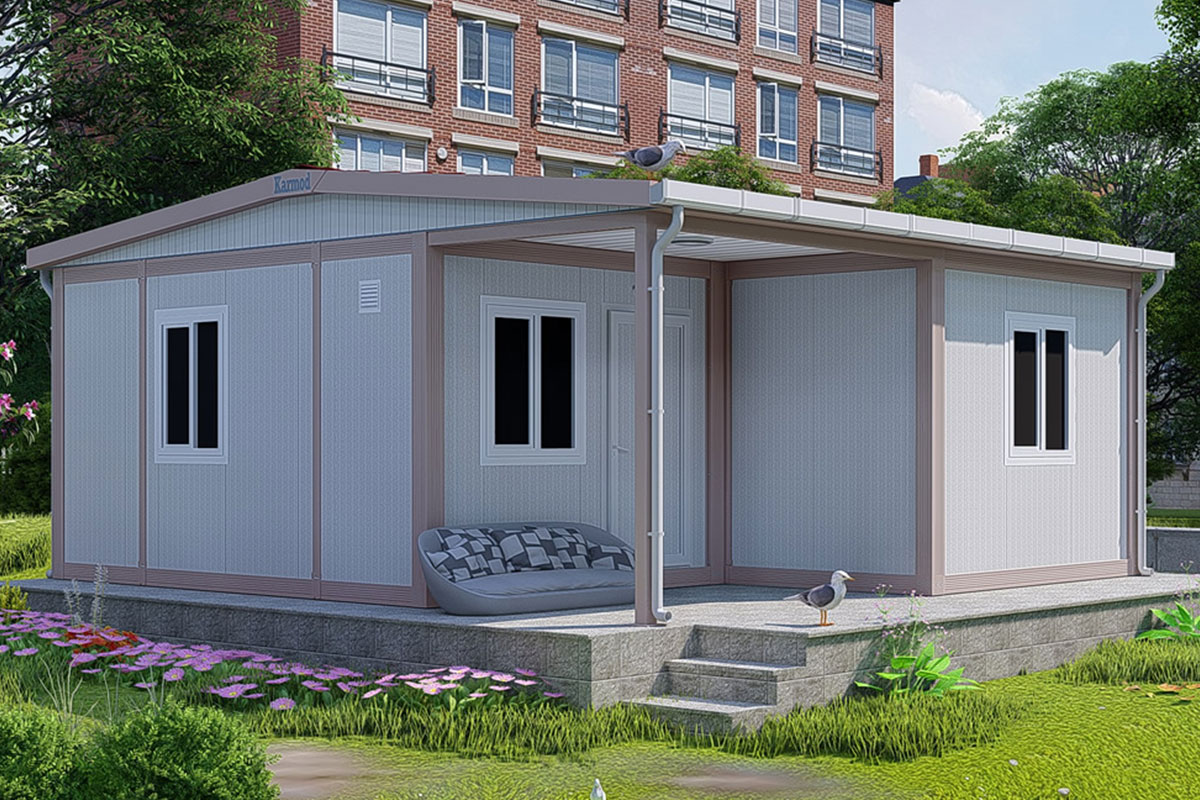
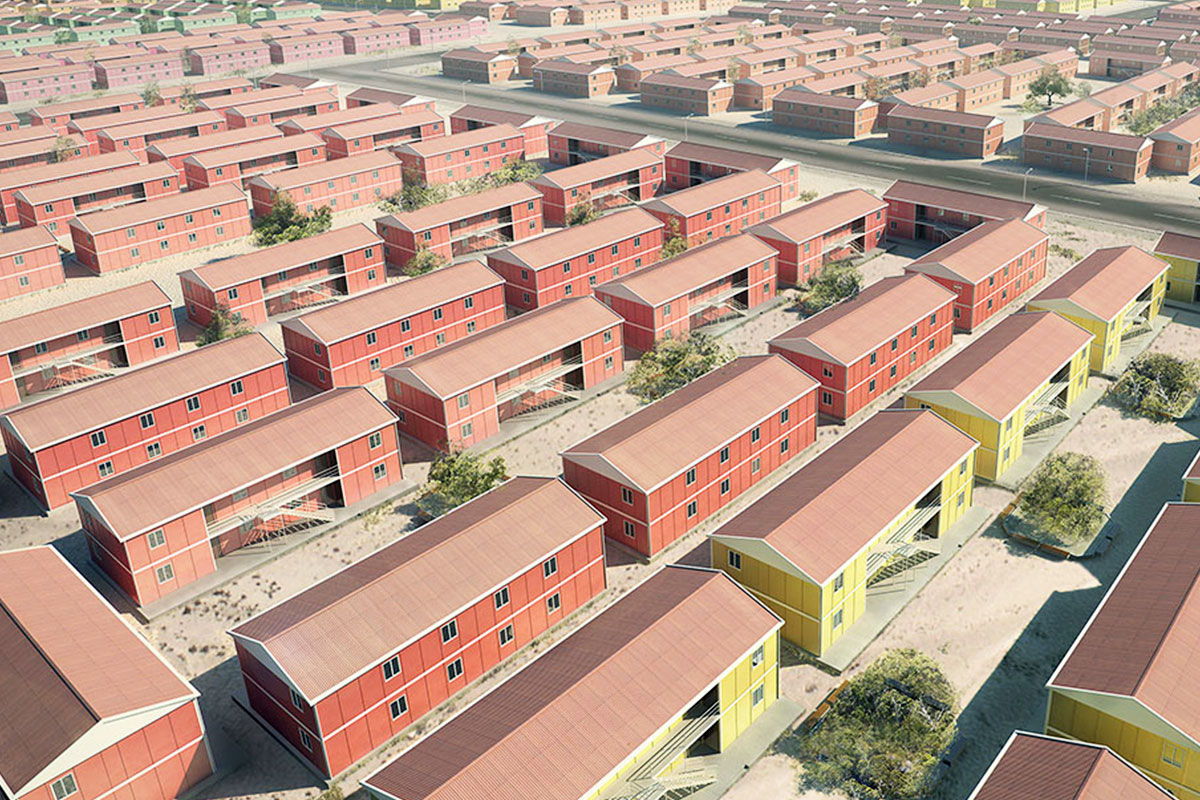
Morocco also has a strong need for both temporary and permanent structures. Industrial zones, mining operations, and renewable energy sites often require rapidly deployable offices, accommodation units, and technical facilities. At the same time, public institutions and private developers are adopting permanent prefabricated solutions for schools, healthcare units, and administrative buildings.
Sector-specific demand is another driver. Logistics and port operations along the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts rely on flexible facilities that can expand with trade volumes. Energy projects, particularly solar and wind installations, require modular site offices and control units in remote locations. Public-sector projects increasingly favor construction methods that ensure predictable costs and timelines.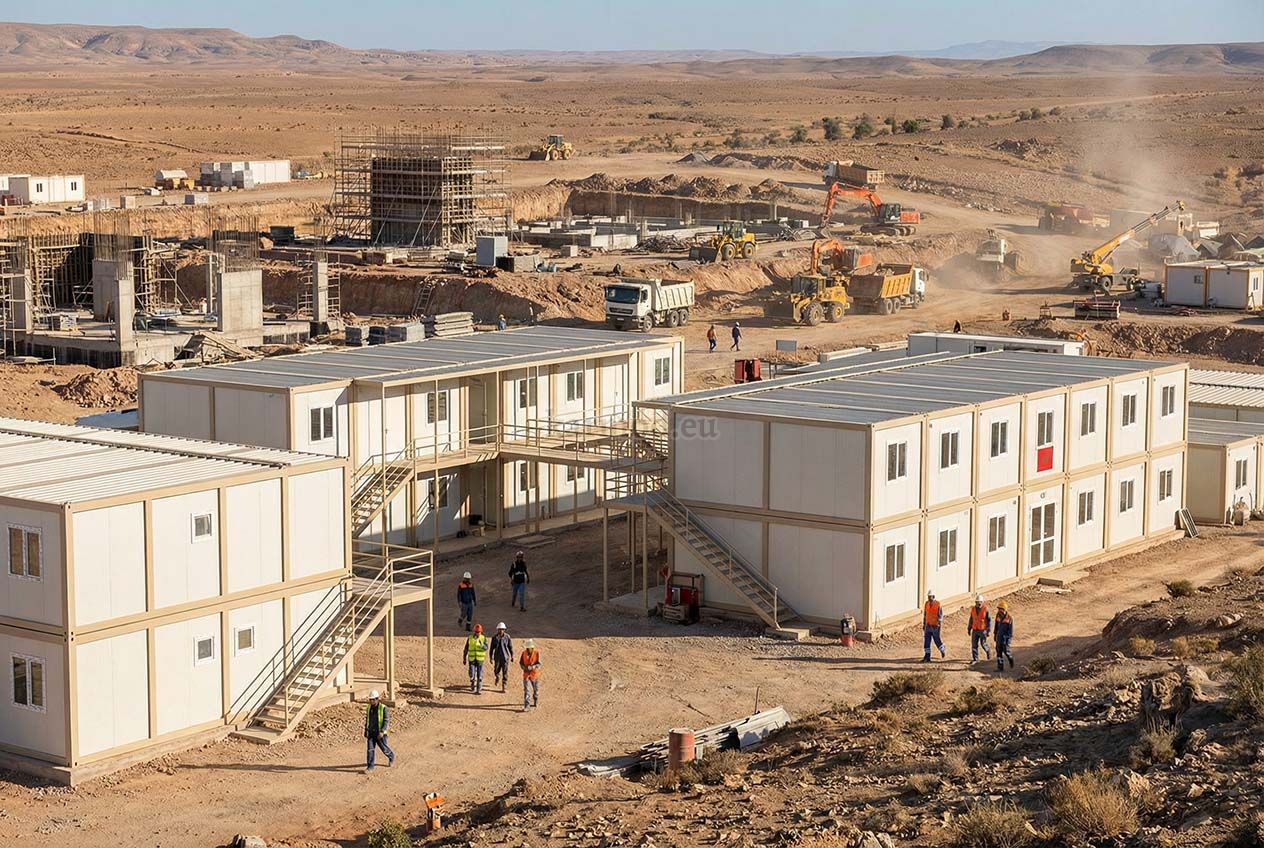
Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
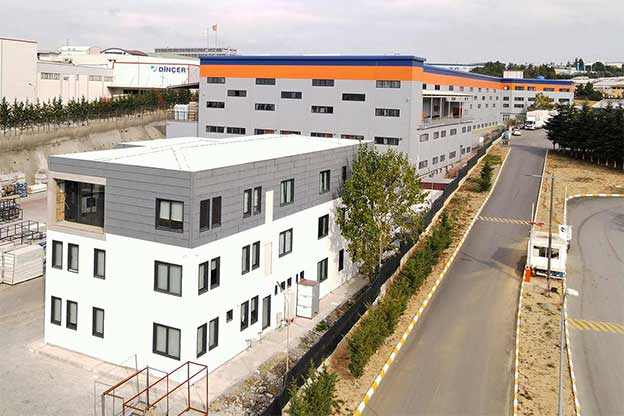
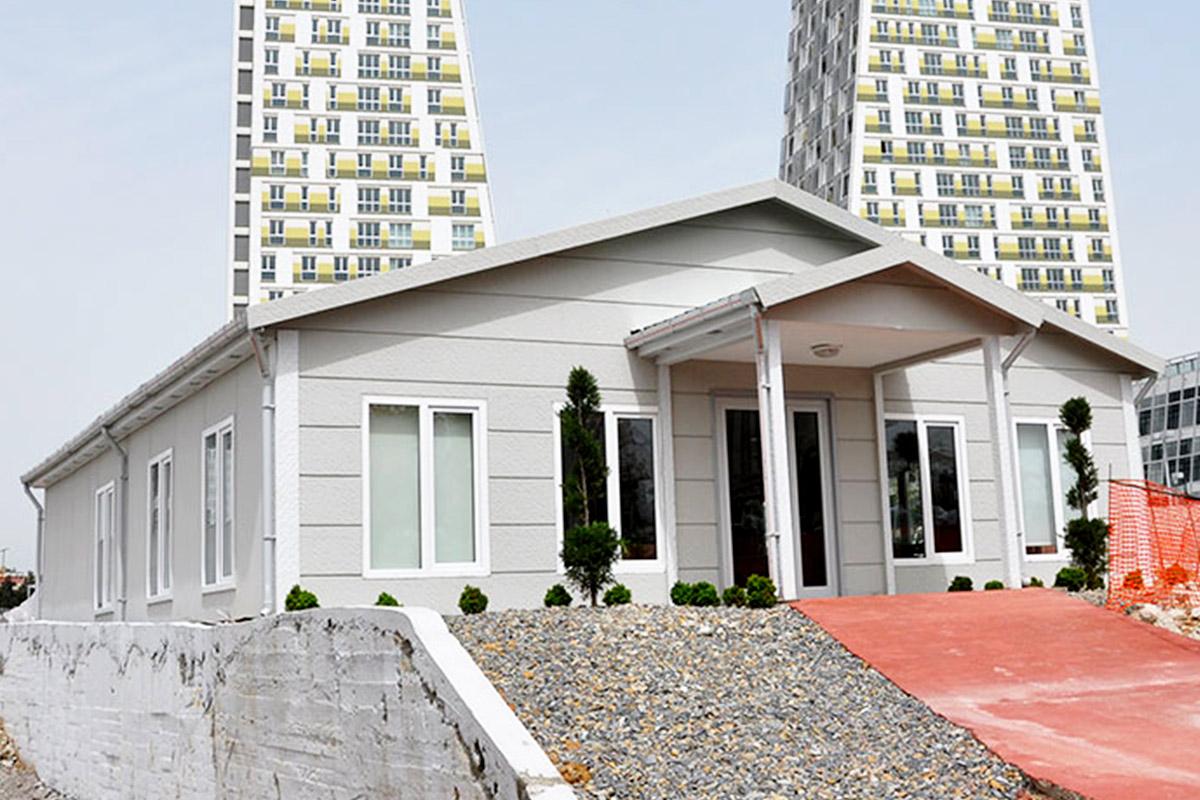
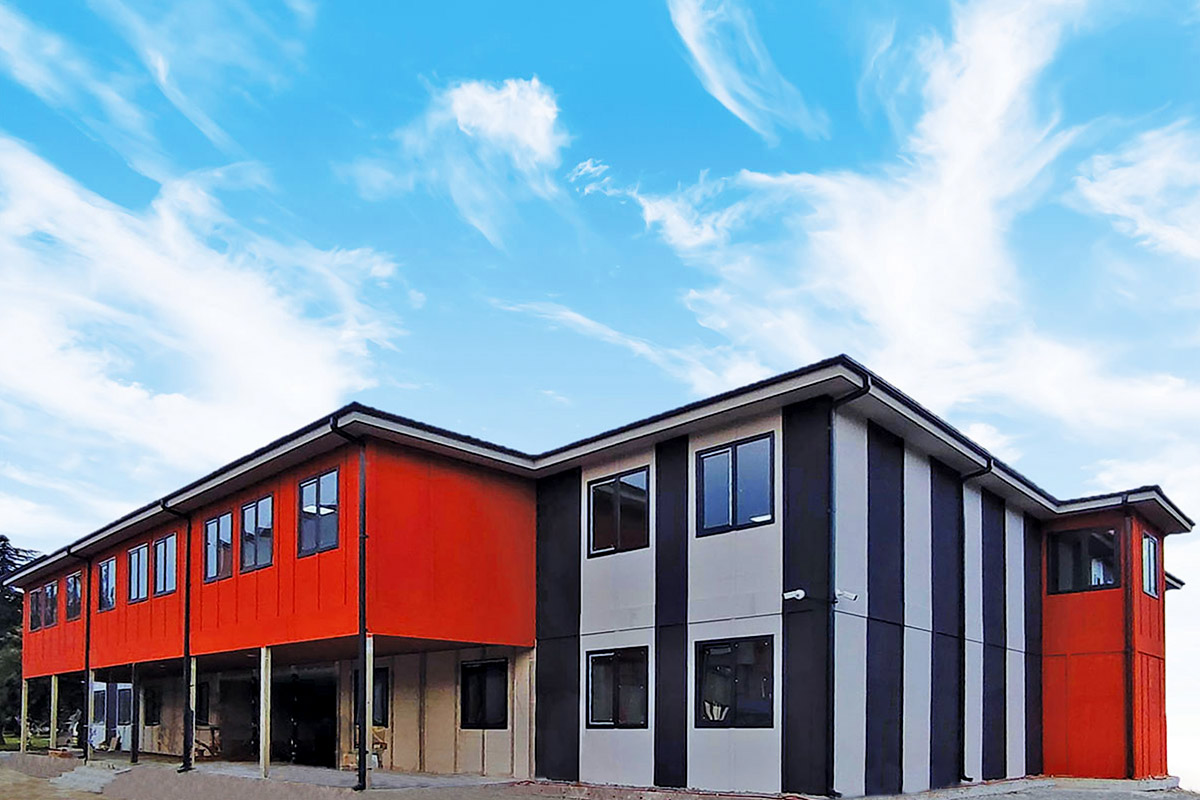
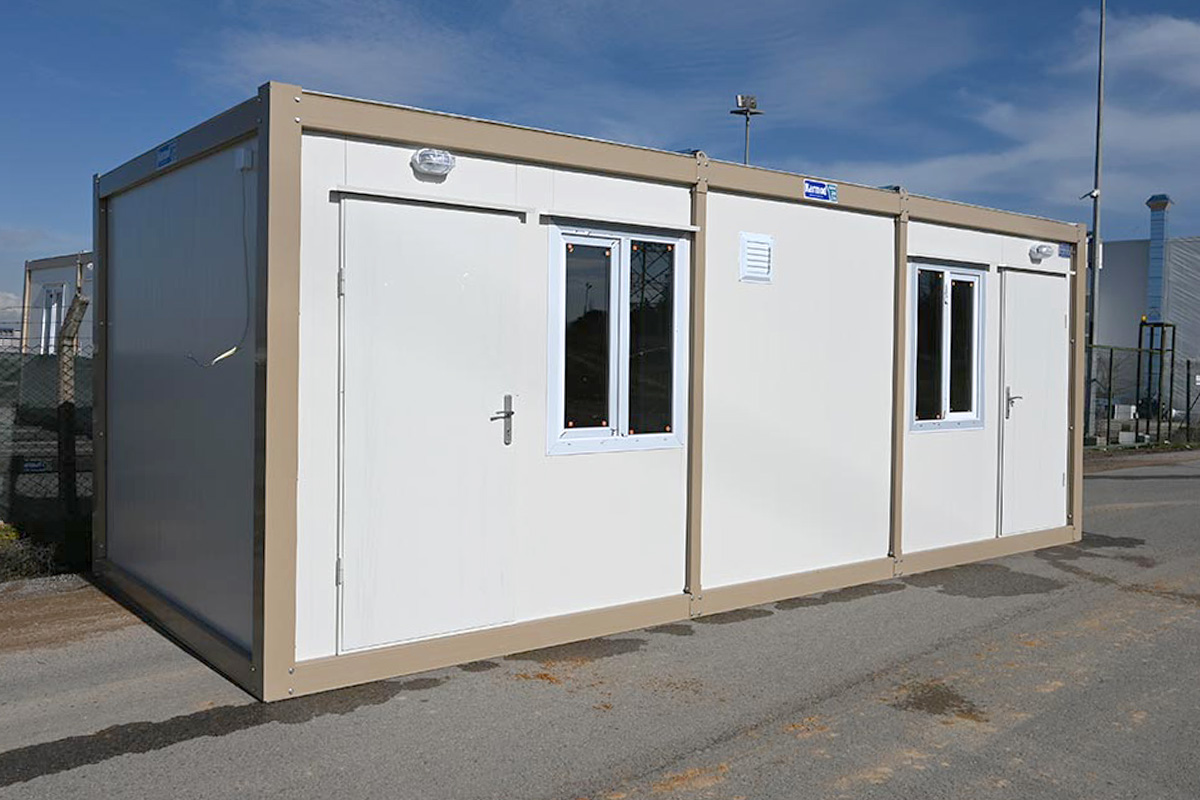
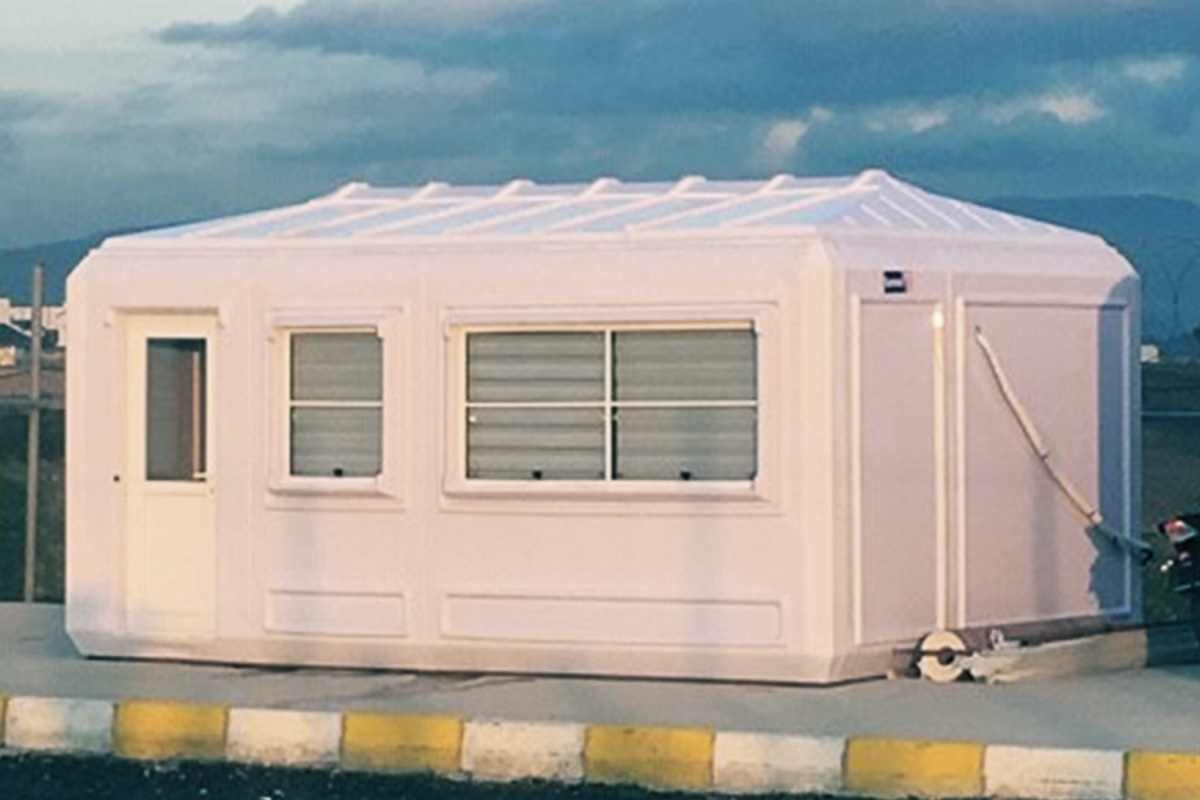
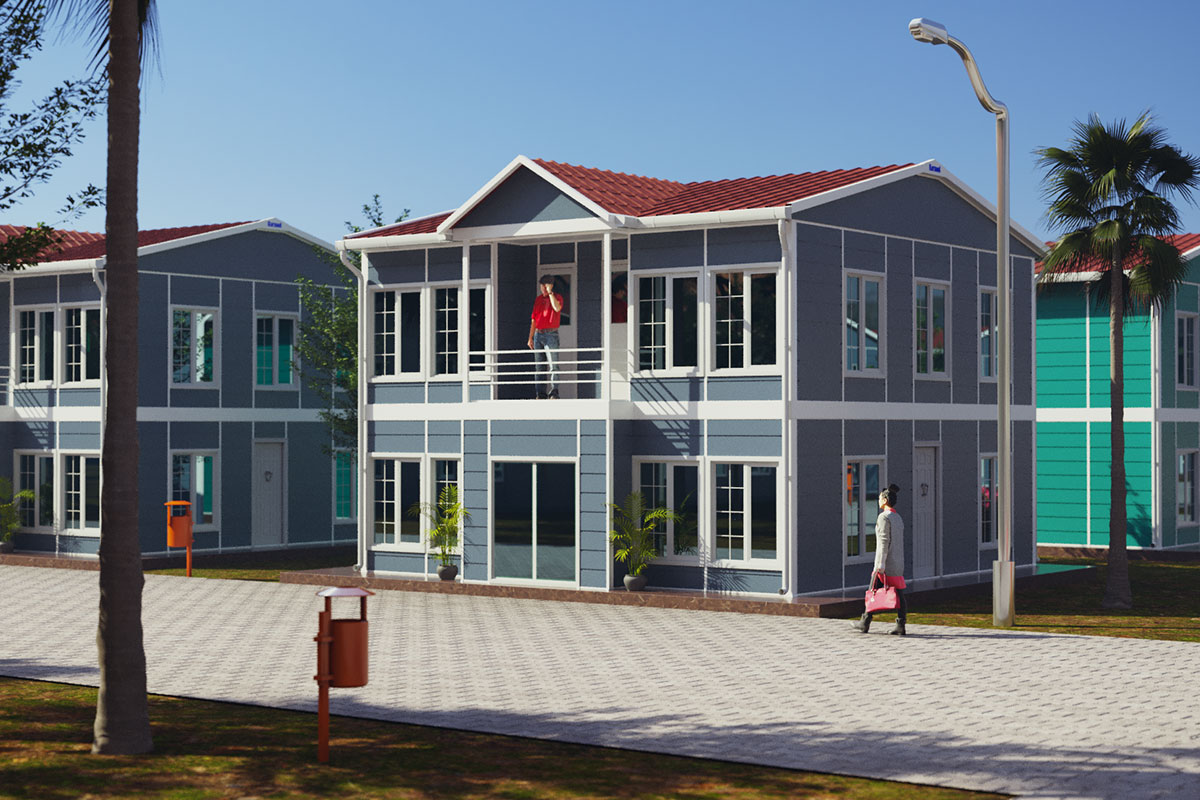
Although often discussed together, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve different strategic needs. Modular buildings are produced as complete volumetric modules. These modules are transportable, relocatable, and can be expanded by adding new units. This makes them particularly suitable for projects that may change location or scale over time, such as construction camps or temporary administrative facilities.
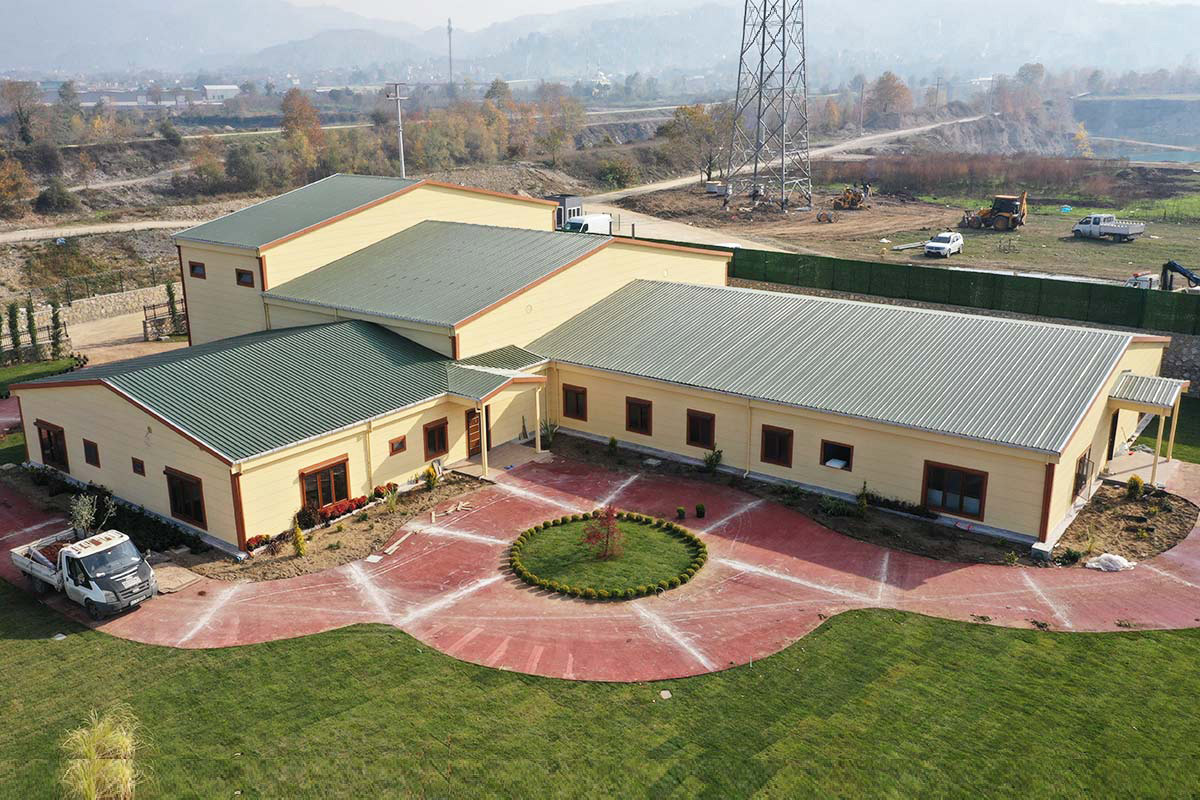
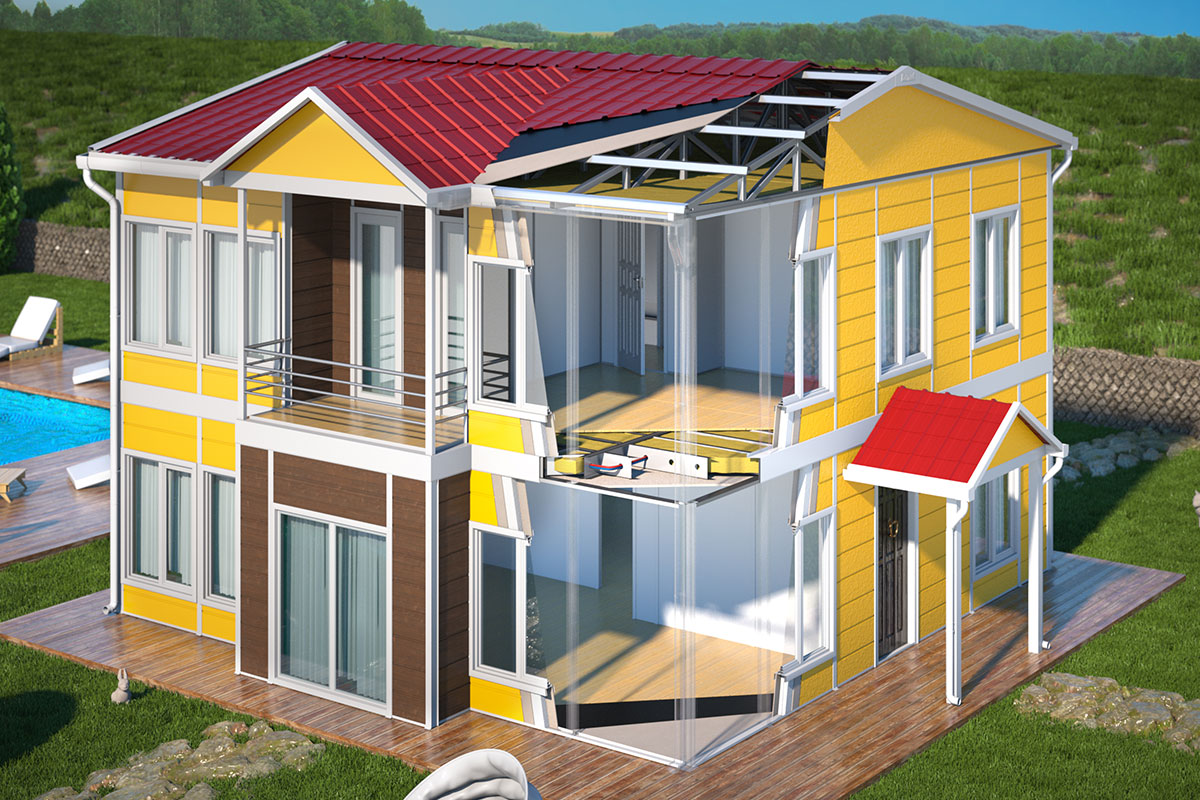
Prefabricated building systems, on the other hand, are based on panels or structural components manufactured off-site and assembled on location. These systems are typically chosen for permanent buildings where architectural integration, long-term use, and fixed layouts are priorities. A prefabricated building approach allows greater freedom in façade design and internal planning while still benefiting from industrialized production.
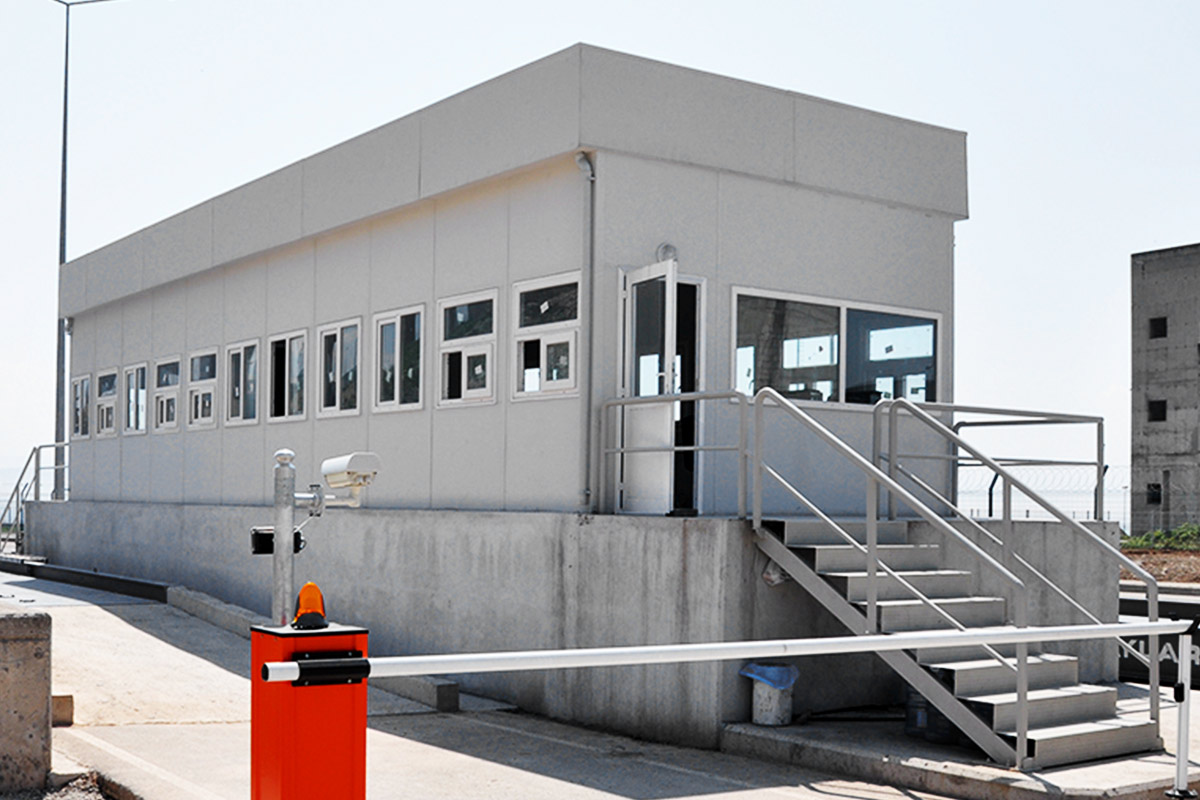
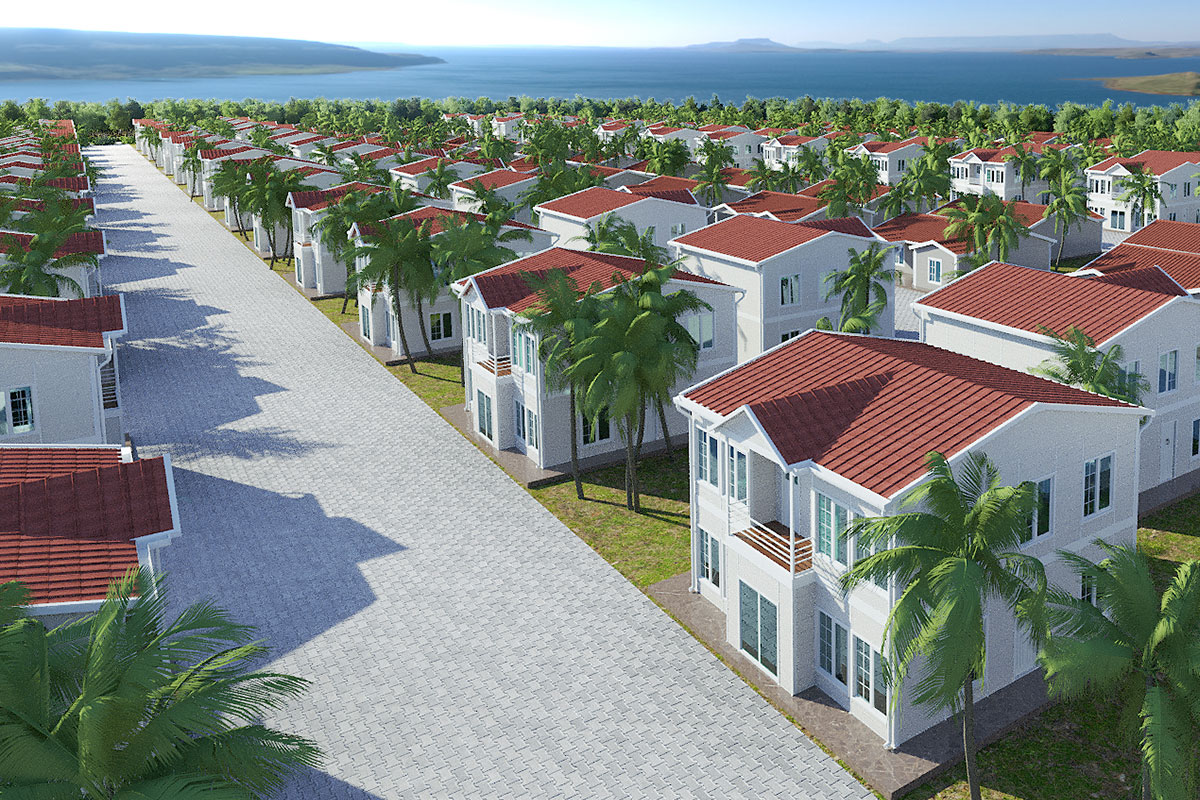
In Morocco, modular buildings are often preferred for industrial sites, logistics operations, and energy projects that require fast deployment and future adaptability. Prefabricated building systems are more commonly selected for permanent schools, healthcare units, and institutional buildings where long service life and architectural consistency are essential.
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Morocco
The versatility of these construction methods allows them to be applied across a wide range of sectors:
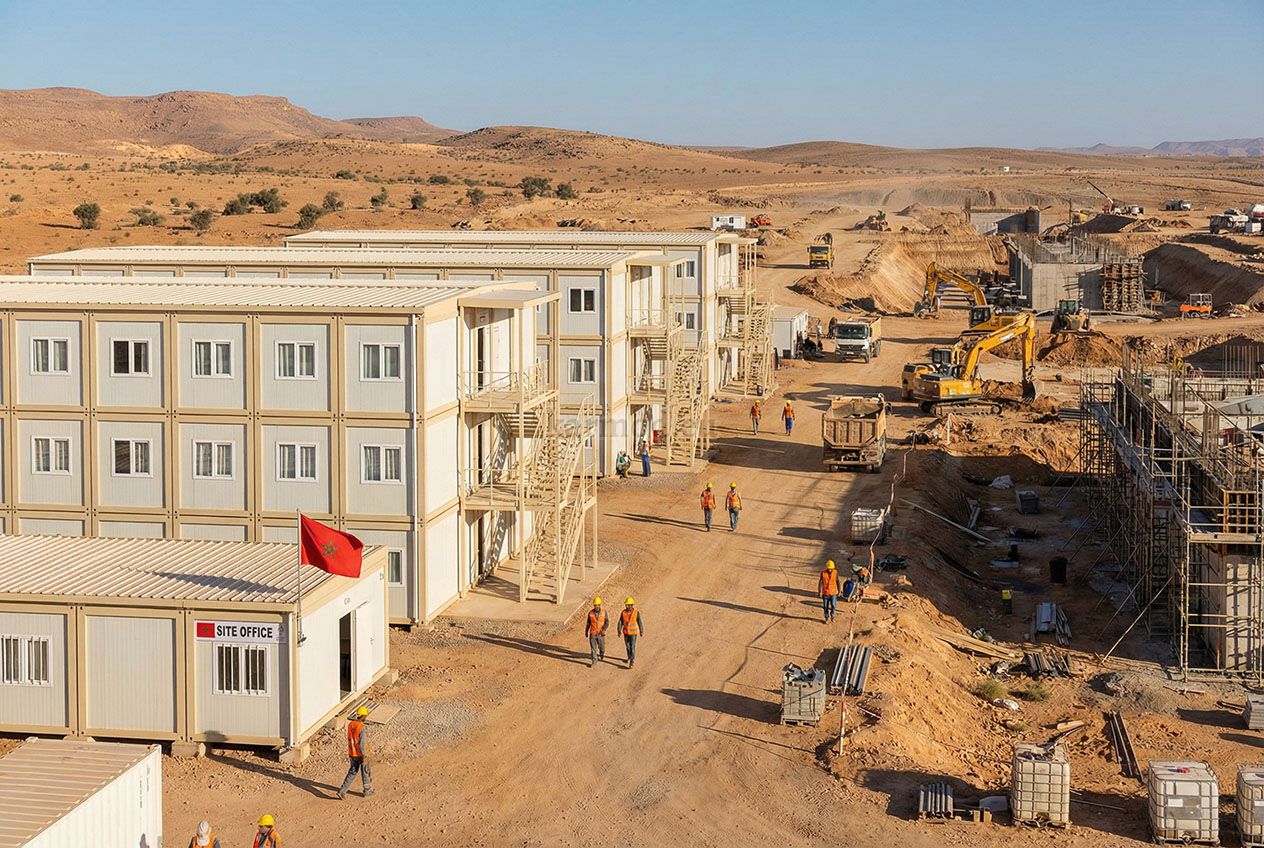
- Site offices & construction camps for infrastructure, port, and industrial projects
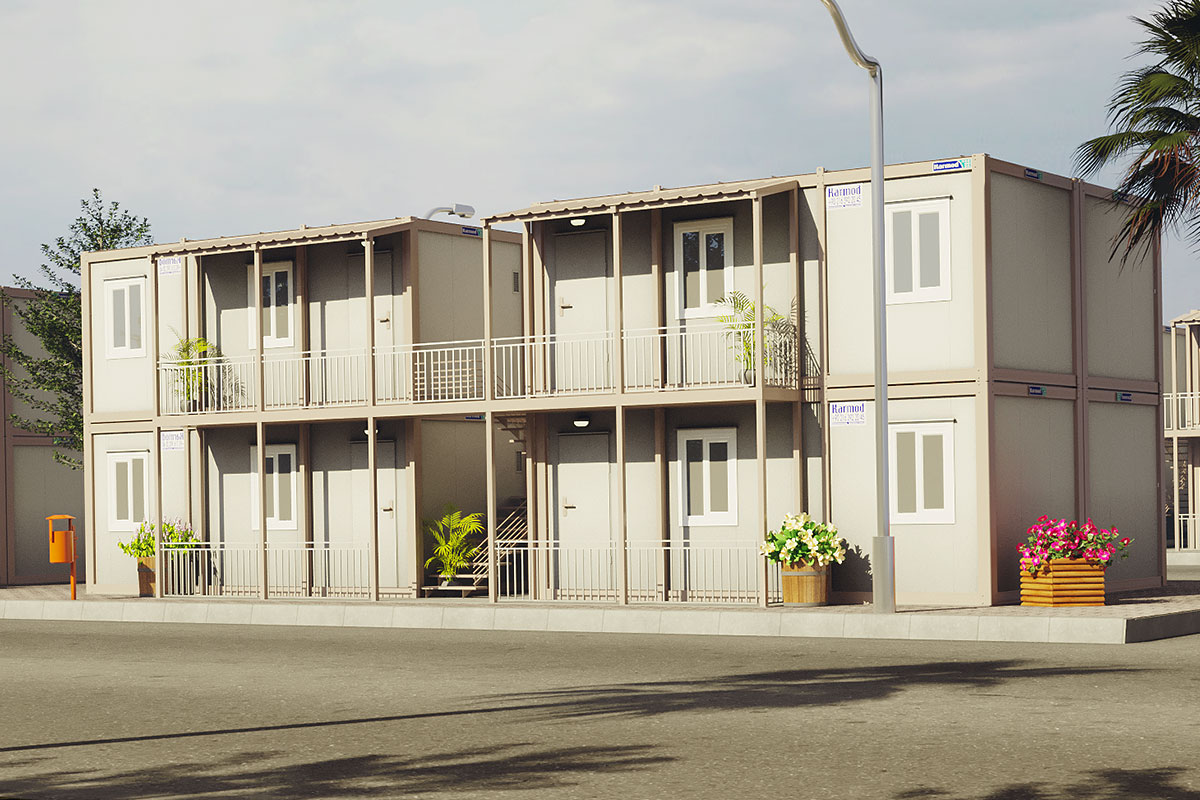
- Worker accommodation buildings for energy, mining, and large-scale construction sites
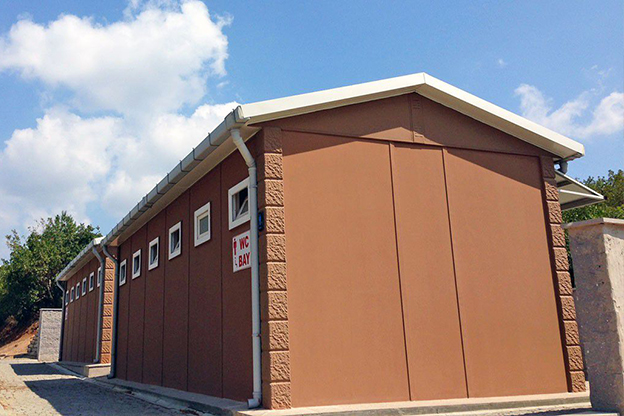
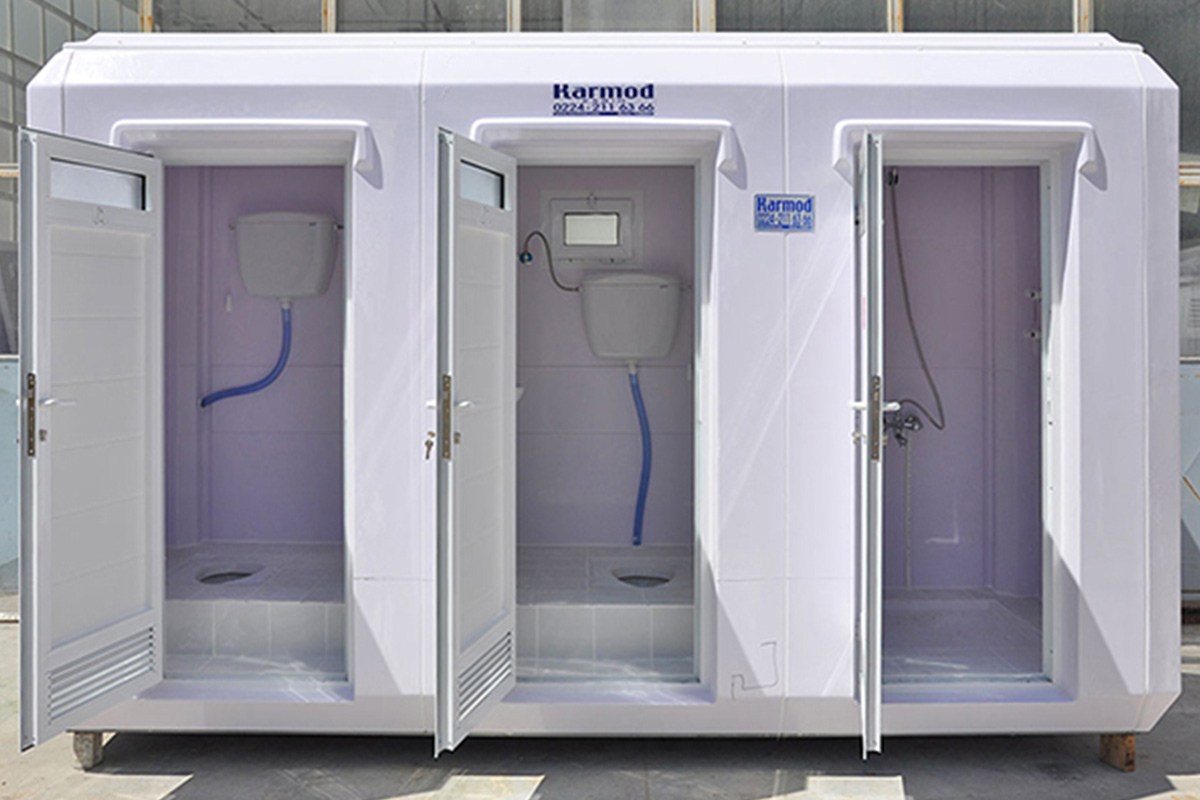
- Temporary schools & healthcare units to meet regional and emergency needs
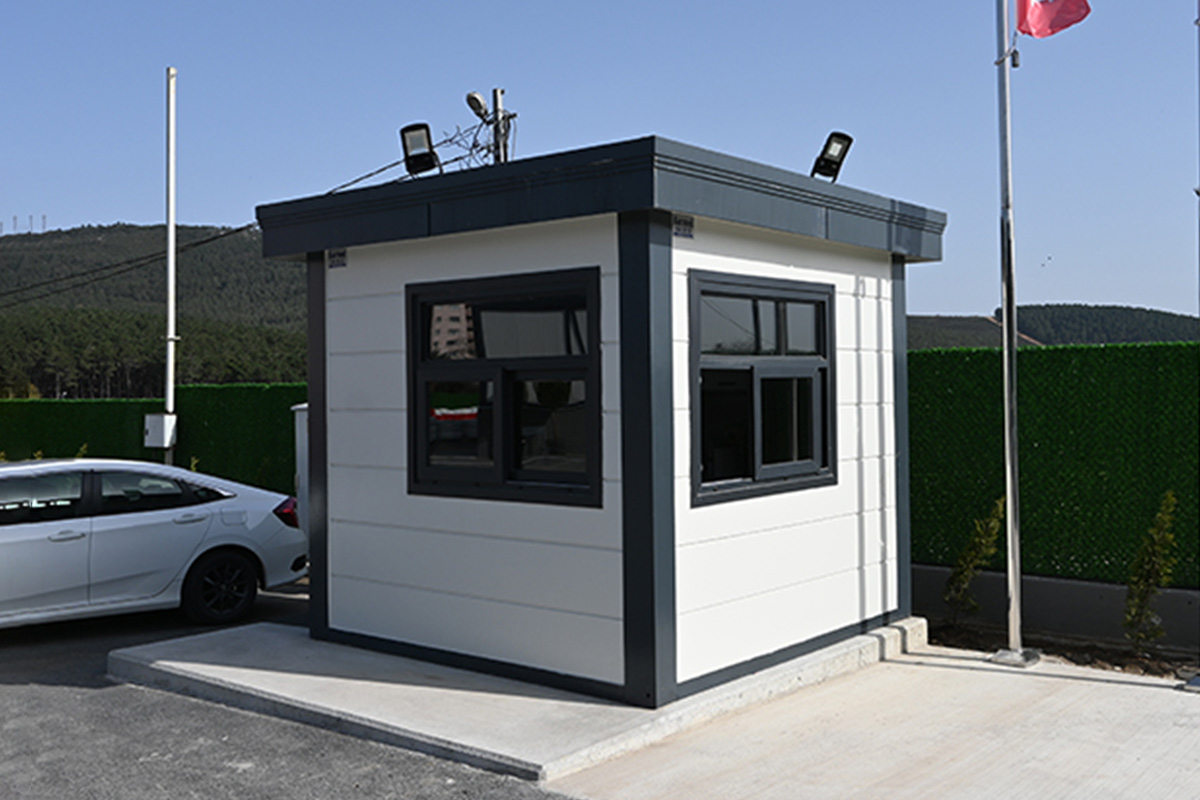
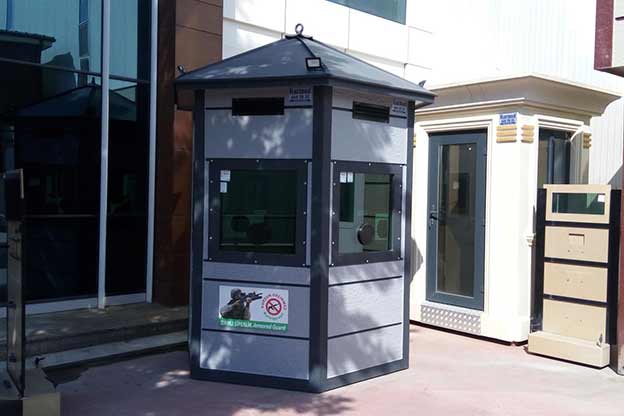
- Security buildings & technical units for controlled-access facilities and industrial zones
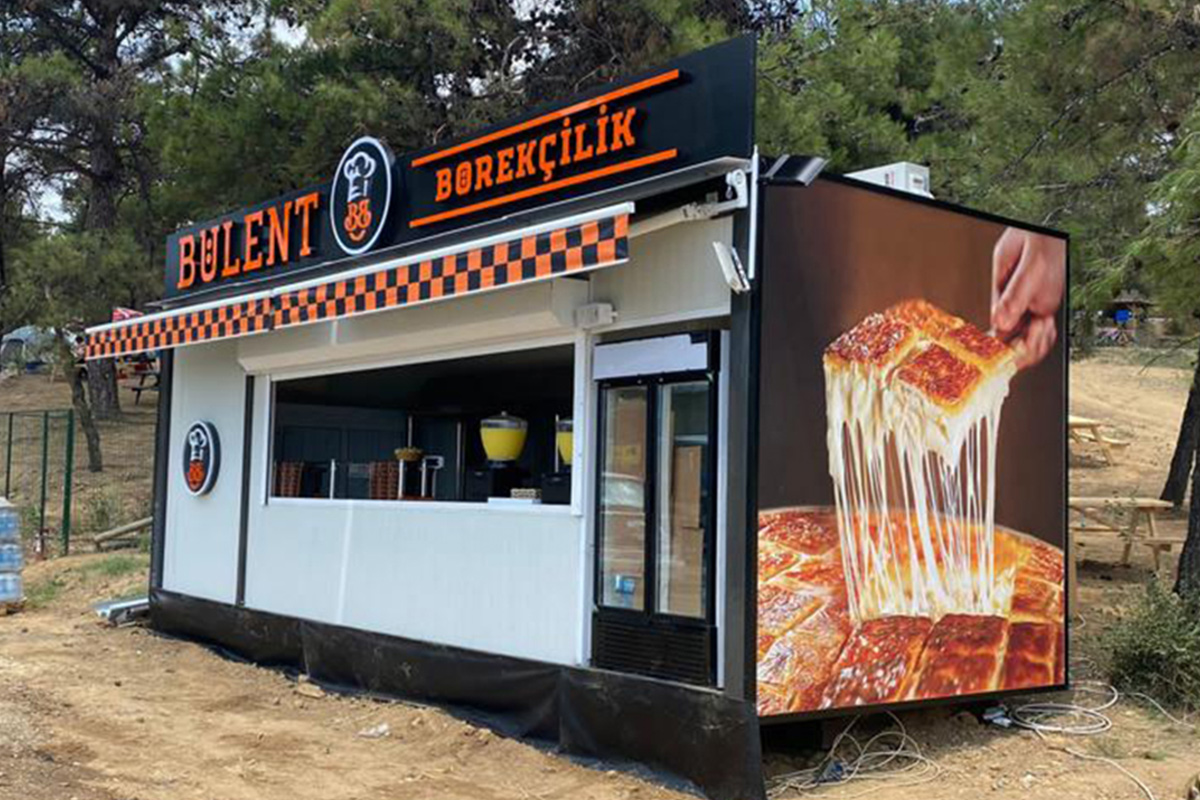
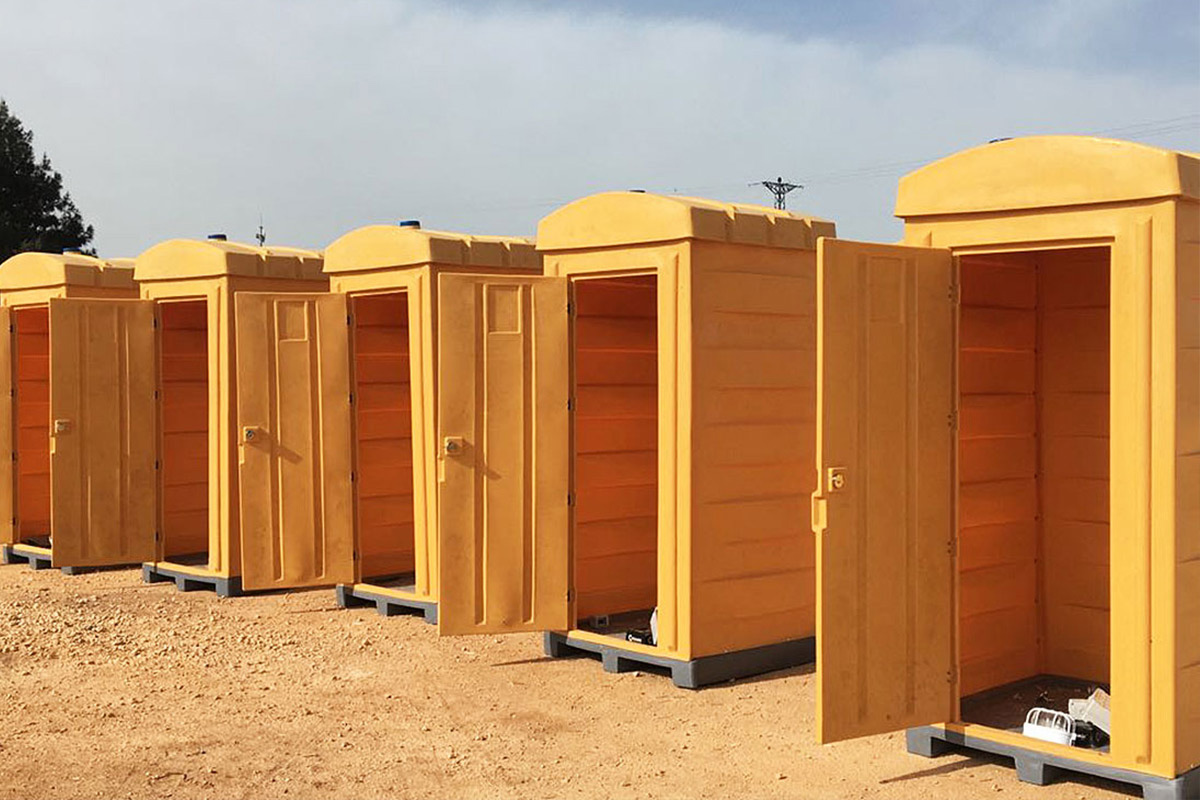
- Storage and logistics facilities supporting ports, free zones, and inland distribution centers
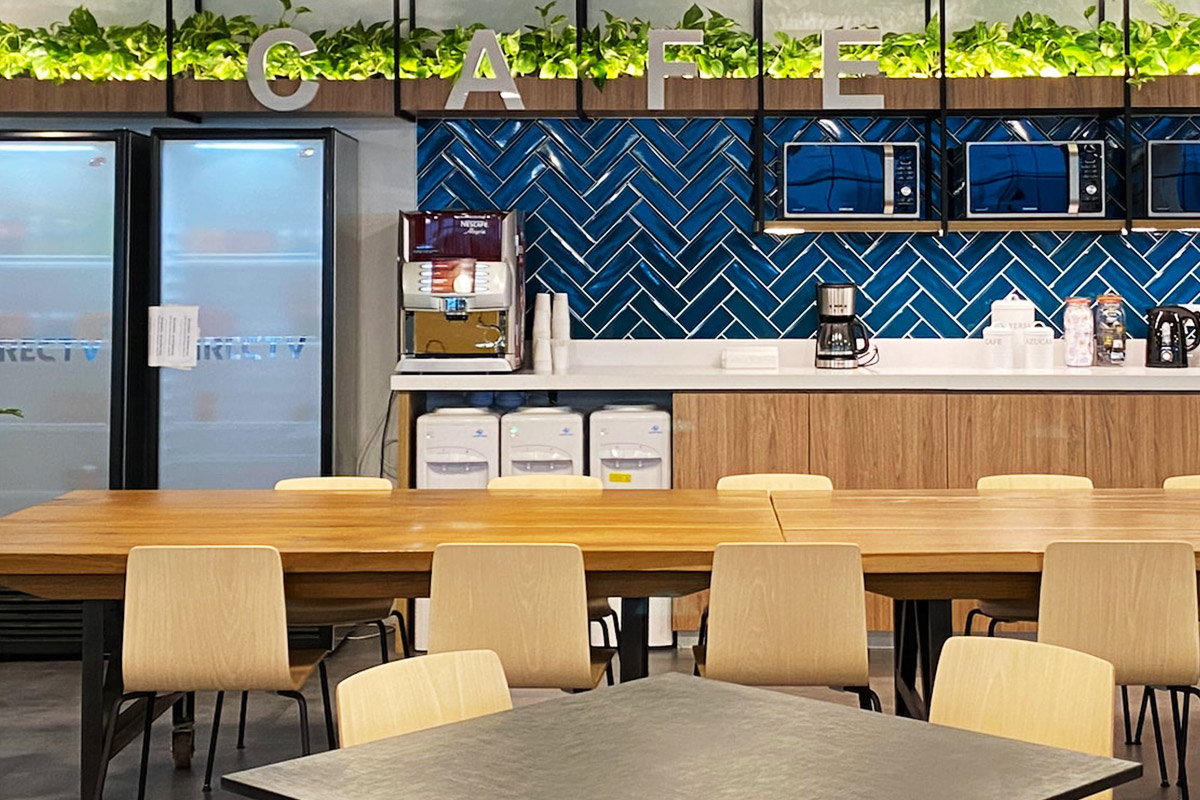
Each application benefits from reduced construction time, predictable quality, and controlled costs—key considerations for B2B decision-makers managing complex projects.
From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The implementation of modular and prefabricated buildings follows a structured and transparent process. It begins with project needs analysis, where operational requirements, capacity planning, and site conditions are evaluated in detail. This phase ensures that the building solution aligns with both functional and regulatory expectations.
Custom design and technical specifications follow. Layouts, insulation levels, fire safety requirements, and mechanical systems are defined according to Moroccan climate conditions and project-specific standards. Factory production then takes place under controlled conditions, ensuring consistent quality and minimizing material waste.
Once production is completed, units or components are prepared for delivery to Morocco. Logistics planning is a critical step, particularly for large or multi-module projects. On-site installation is typically completed within days rather than months, allowing facilities to become operational quickly and with minimal disruption to surrounding activities.
Companies such as Karmod approach this process with an emphasis on coordination and risk reduction. Drawing on experience from European and international projects, Karmod modular building solutions are designed to integrate smoothly into diverse project environments while maintaining consistent quality standards.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Morocco
Thermal insulation
Morocco’s climate varies significantly by region, from coastal humidity to inland heat. Proper thermal insulation is essential to ensure comfort, energy efficiency, and long-term performance.
Fire safety standards
Industrial and public projects must comply with strict fire safety requirements. Modular and prefabricated systems should incorporate certified materials and fire-resistant assemblies suitable for local regulations.
Climate suitability
Buildings must be designed to withstand temperature fluctuations, solar exposure, and, in some regions, high winds or sand conditions. Material selection and structural design play a decisive role here.
Custom layouts
No two projects are identical. The ability to customize layouts, expand facilities, or integrate technical systems is a major advantage of modular and prefabricated approaches.
With its long-standing focus on engineered building systems, Karmod supports projects that require both flexibility and durability. Rather than offering one-size-fits-all solutions, Karmod applies its international experience to adapt modular and prefabricated building concepts to local operational needs.
As Morocco continues to attract investment across infrastructure, energy, and logistics sectors, decision-makers are increasingly evaluating construction methods that reduce risk and accelerate returns. Modular buildings and prefabricated building systems offer a practical response to these expectations, providing scalable, efficient, and professionally delivered building solutions aligned with the country’s development trajectory.