Nepal’s construction landscape is shaped by challenging geography, diverse climate zones, and a growing need for fast, reliable infrastructure. From rapidly expanding urban areas like Kathmandu Valley to remote regions requiring accessible building solutions, decision-makers increasingly look for construction methods that reduce risk, control costs, and shorten project timelines. In this context, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems are gaining strong traction across both public and private sectors, offering predictable quality and scalable deployment without the delays of conventional construction.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Nepal
Several structural factors are driving interest in modular construction across Nepal. One of the most significant is labor cost volatility. Skilled construction labor can be difficult to source consistently, especially outside major cities. Modular buildings reduce on-site labor requirements by shifting most of the work to controlled factory environments, where productivity and quality can be managed more efficiently.
Construction timelines are another critical factor. Infrastructure projects in Nepal often face delays due to weather conditions, terrain limitations, or logistical constraints. Modular systems allow parallel progress: while site preparation continues locally, building modules are produced off-site. This overlap significantly shortens total project duration, which is especially valuable for time-sensitive developments.
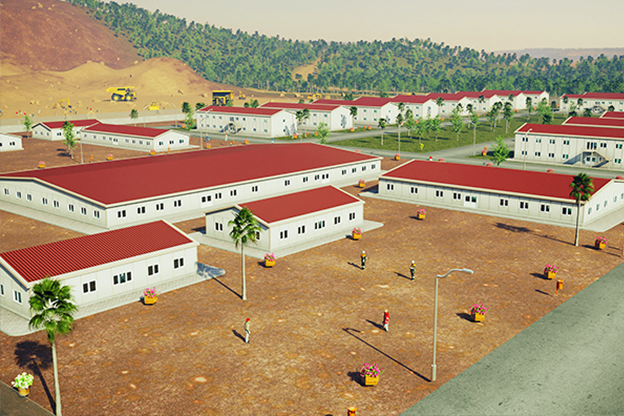
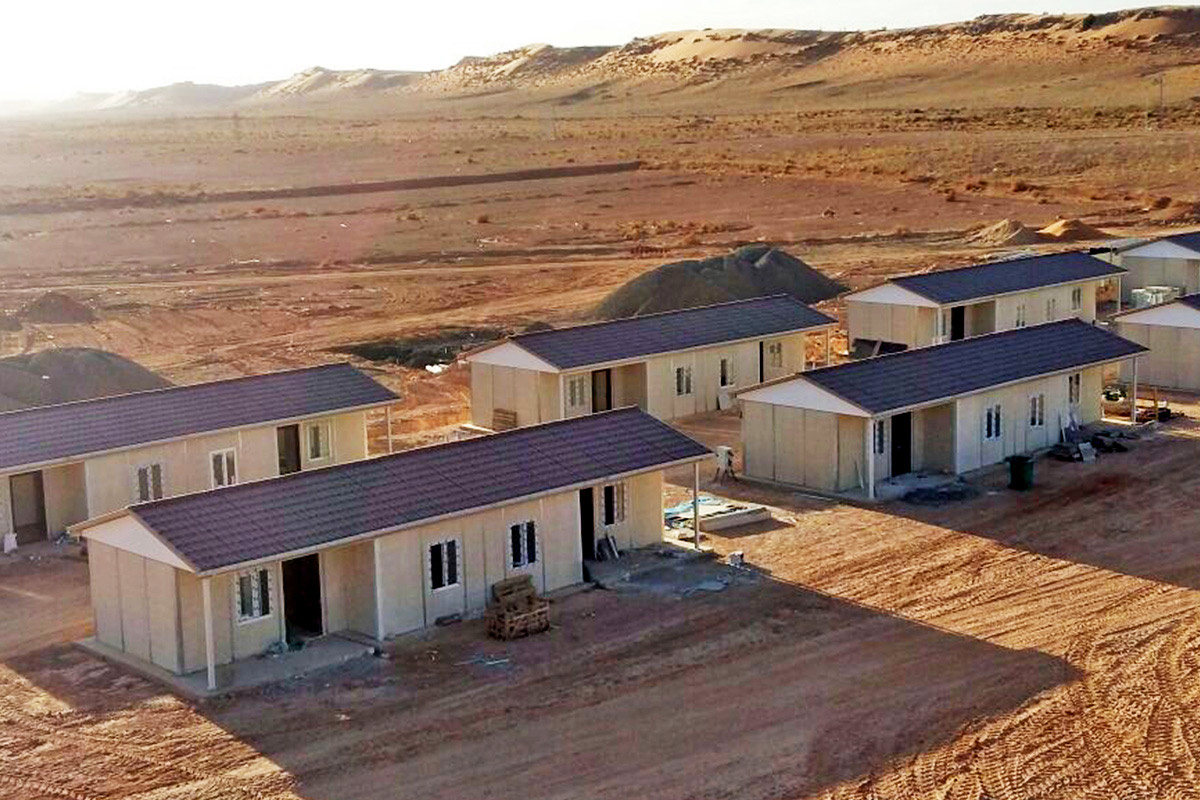
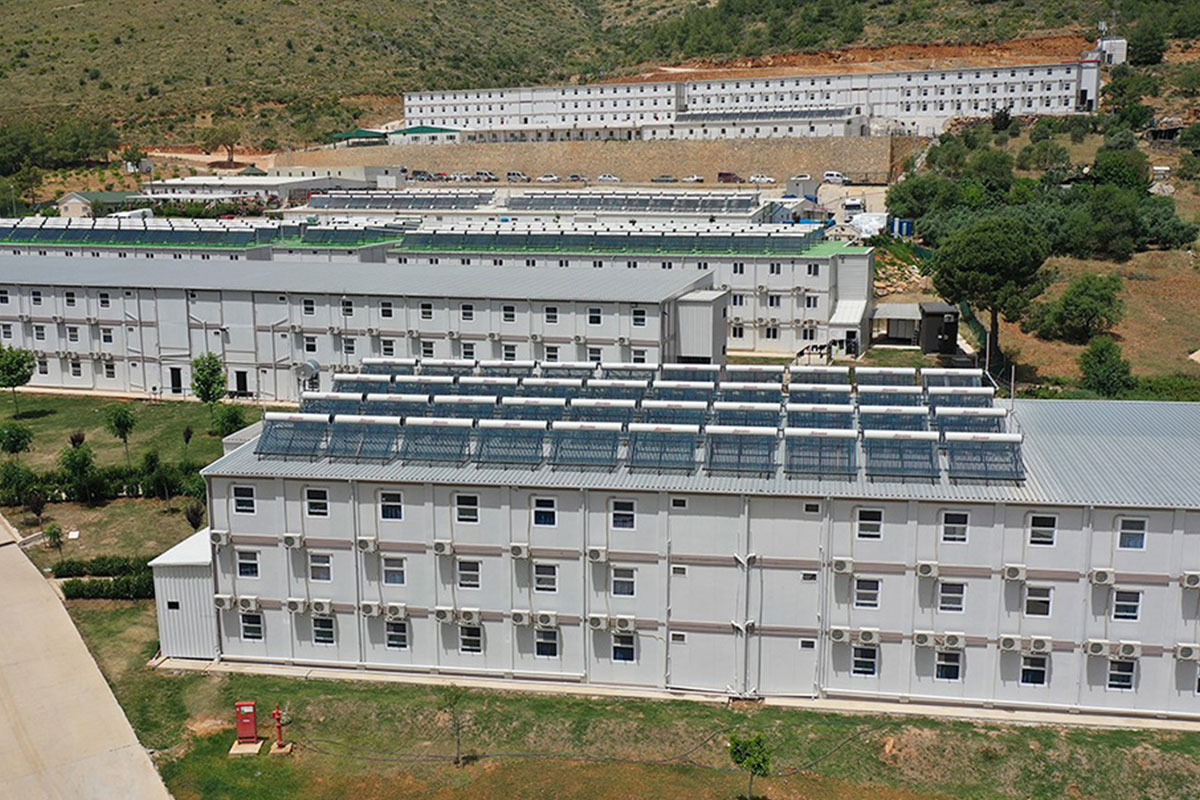
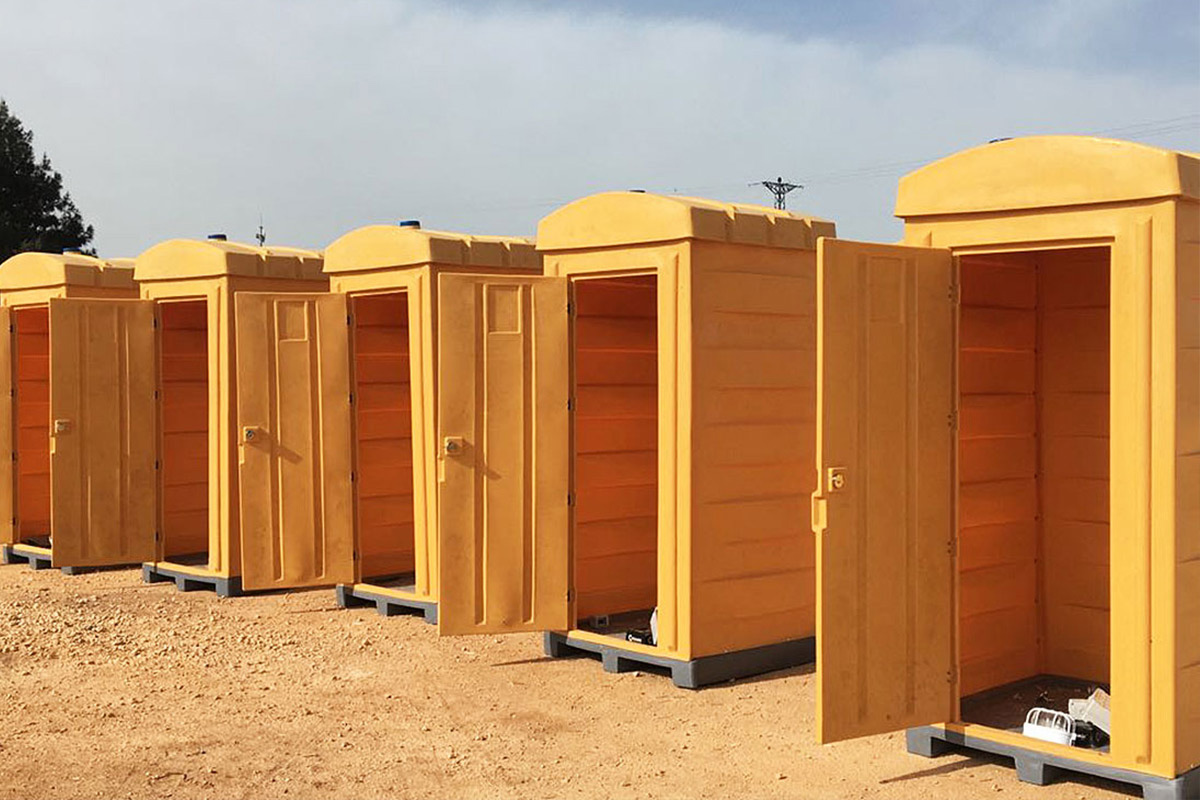
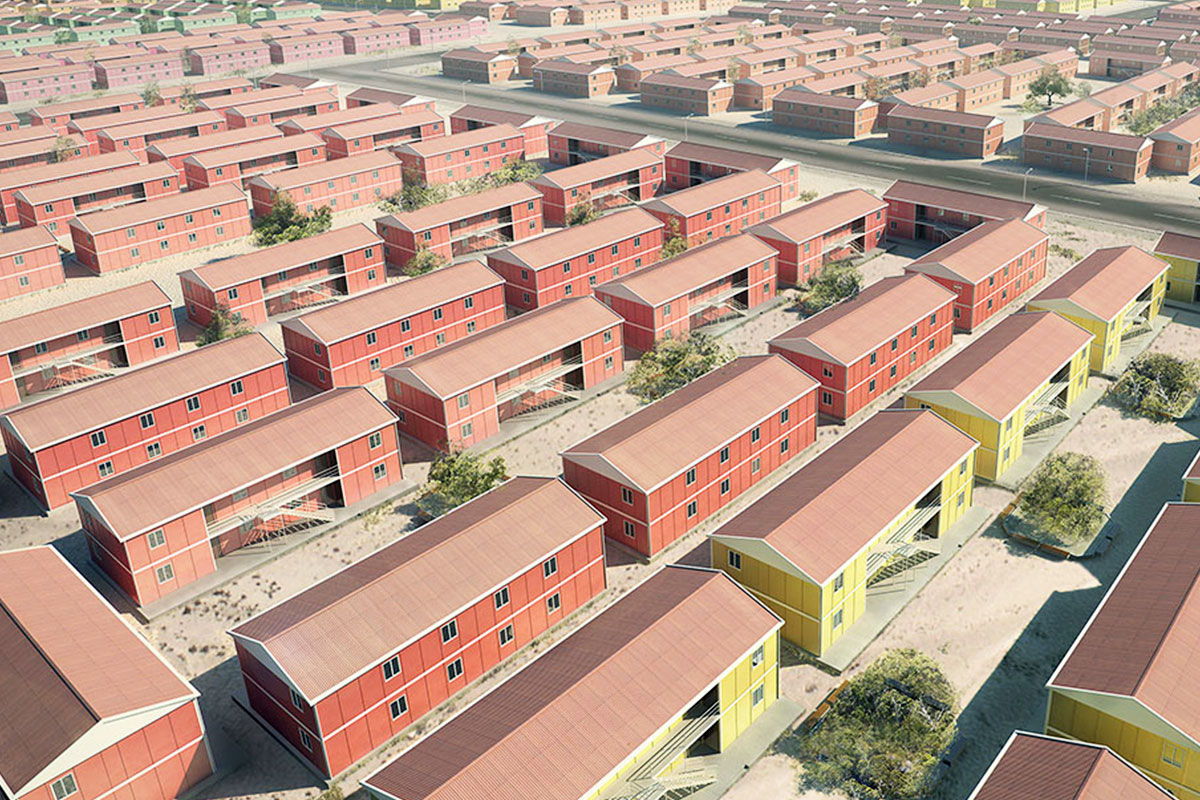
Nepal also has a strong need for both temporary and permanent structures. Temporary facilities are essential for hydropower projects, road construction, and post-disaster response, while permanent buildings are required for education, healthcare, administration, and industrial operations. Modular buildings address both needs with the same core system, enabling relocation or long-term use depending on project goals.
Sector-specific demand further reinforces this trend. Energy projects, particularly hydropower plants, require worker camps and technical units in remote areas. Public institutions need schools and healthcare units that can be deployed quickly. Logistics and industrial operators seek functional facilities that can adapt as operations expand. These realities make modular construction highly compatible with Nepal’s development priorities.
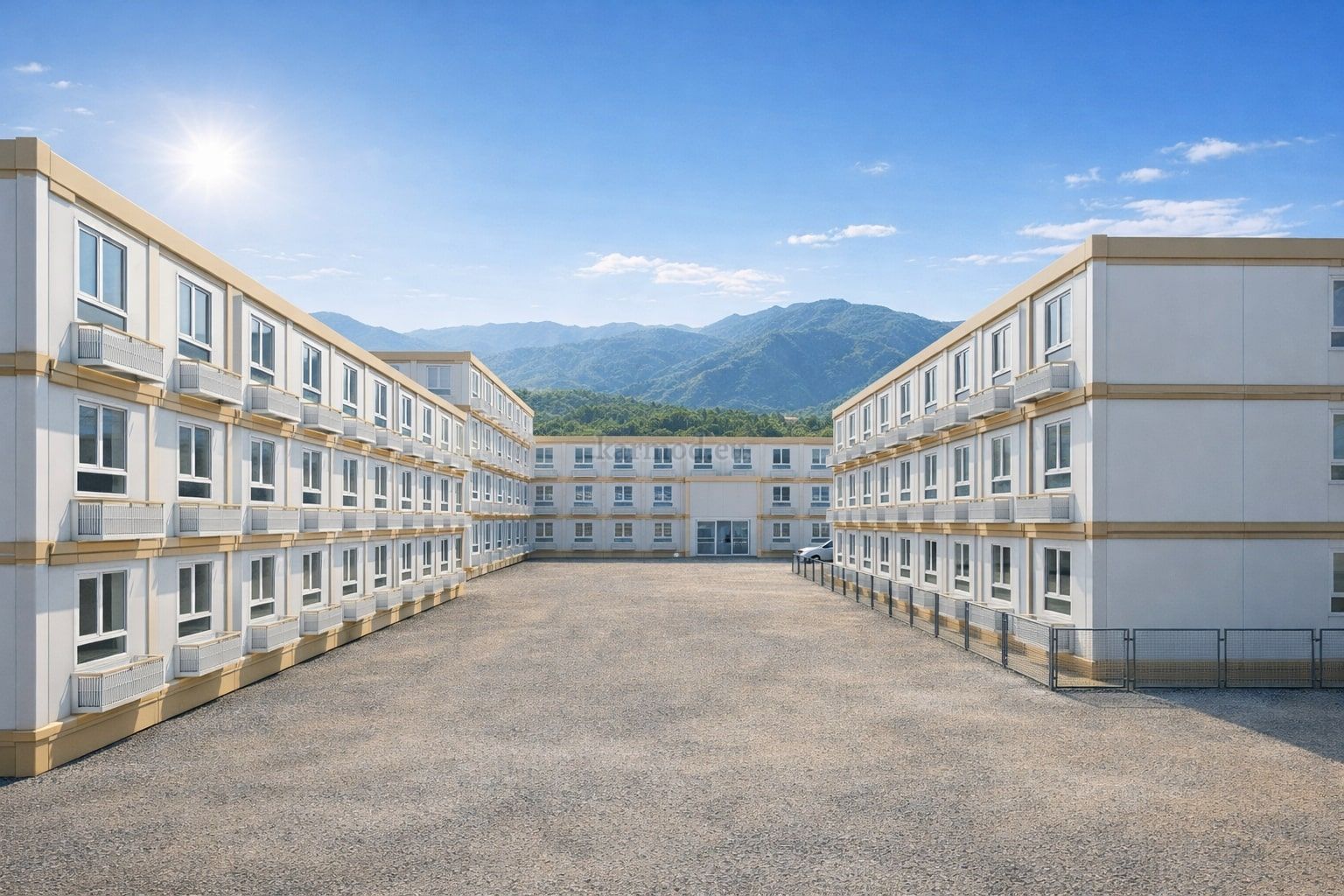

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
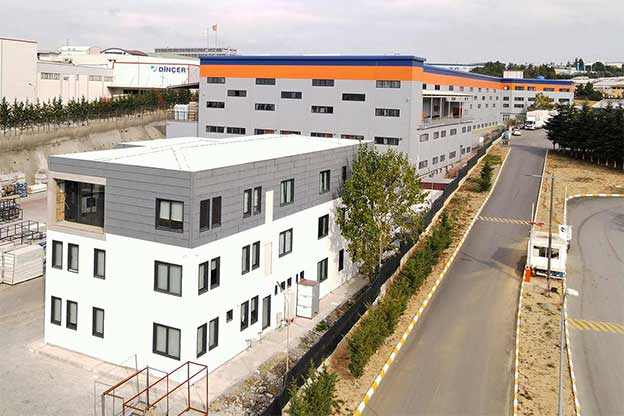
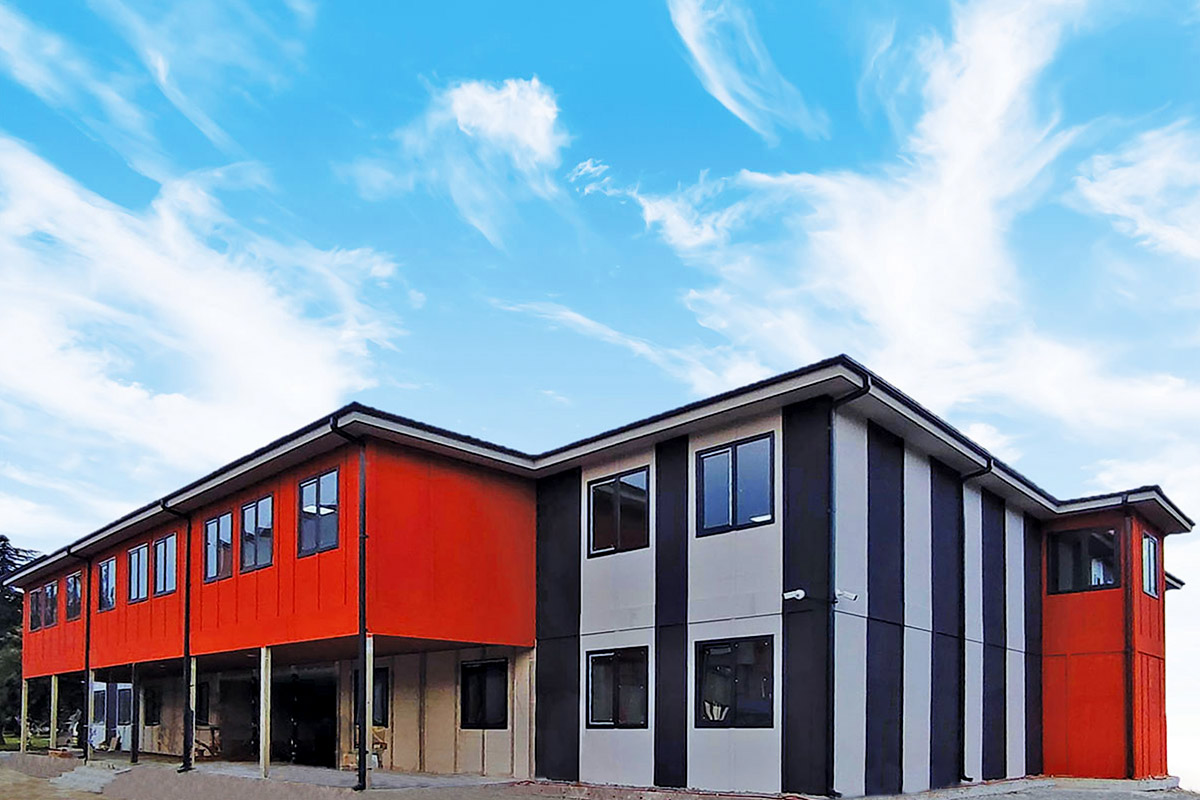
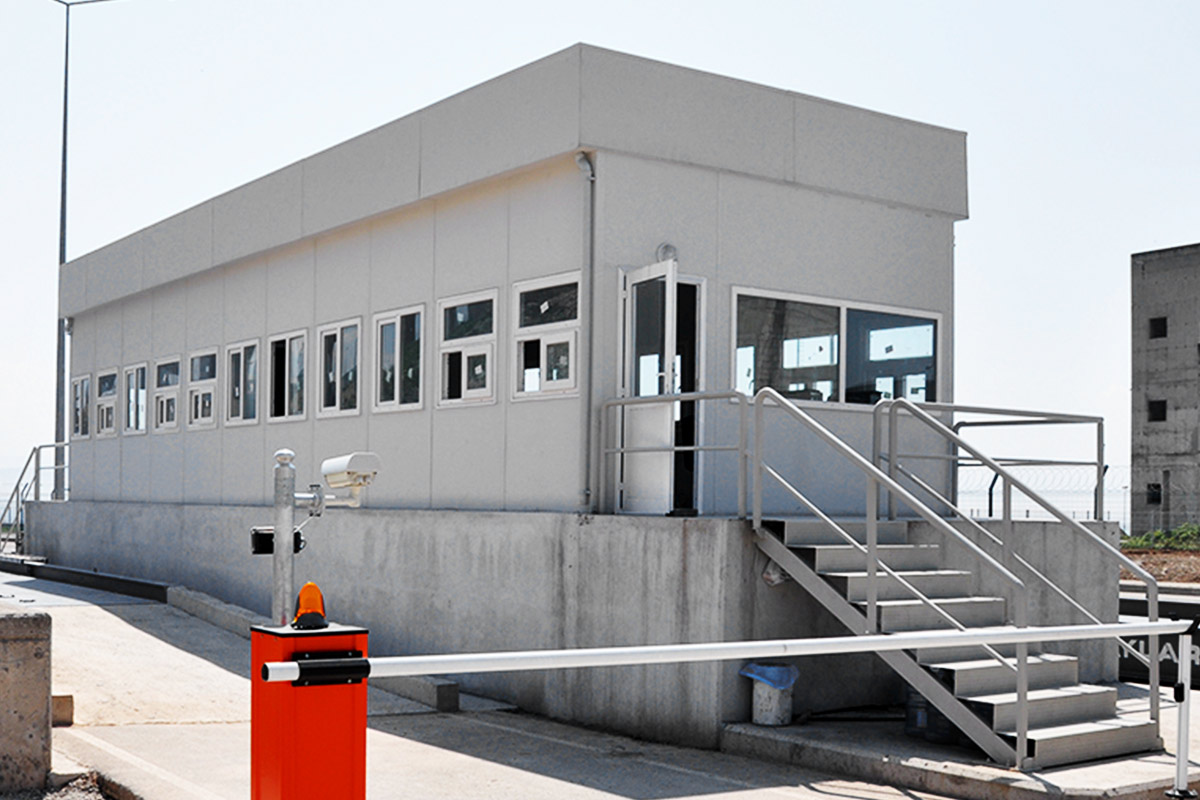
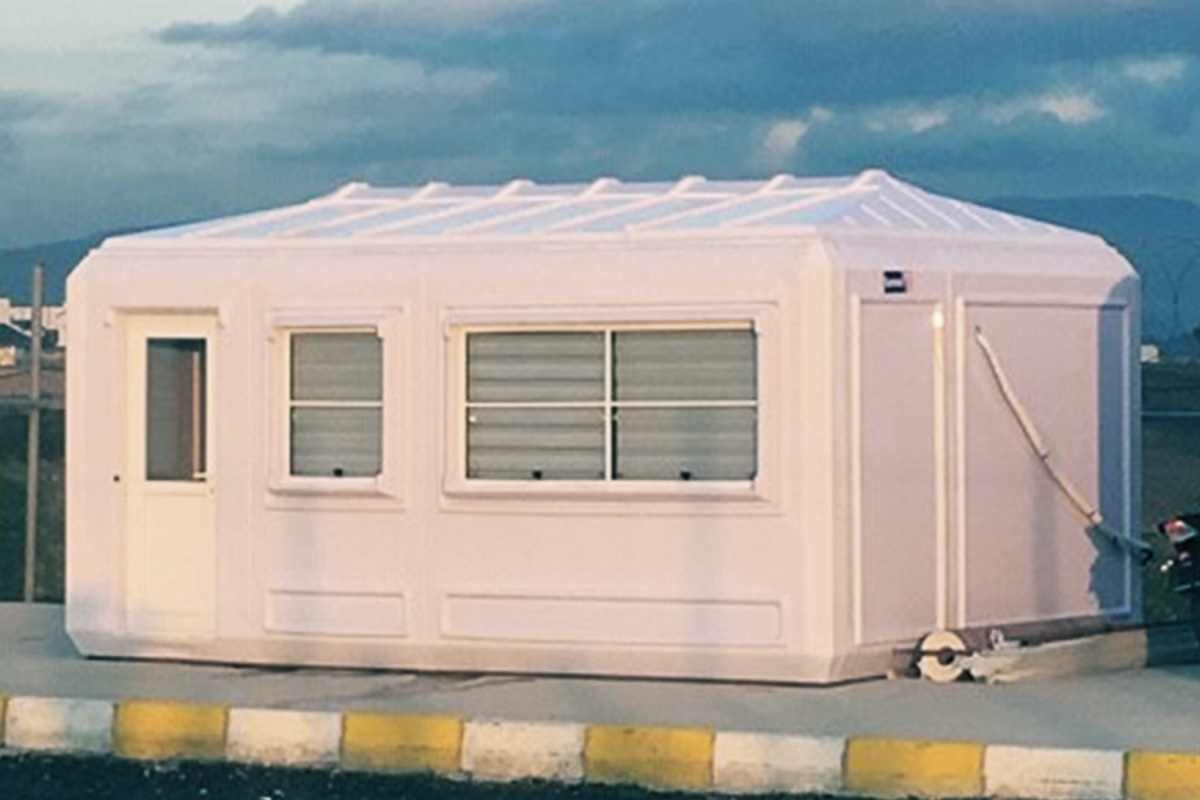
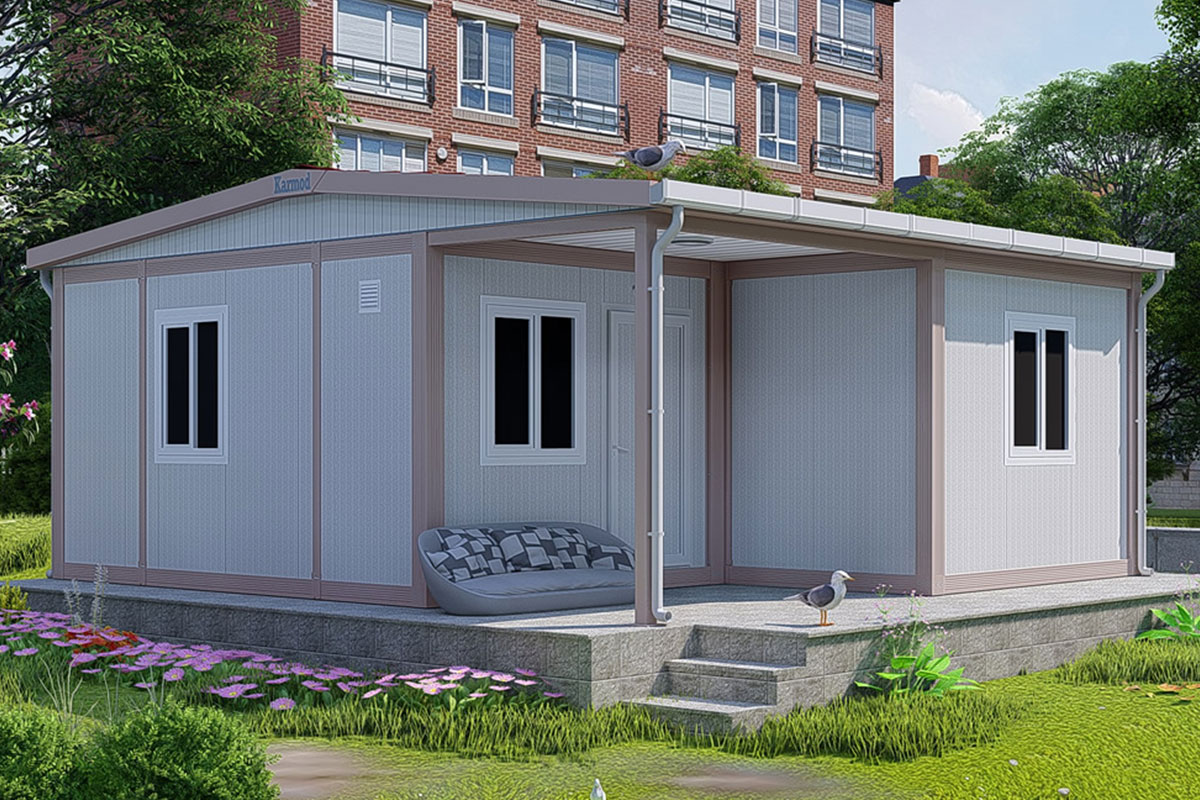
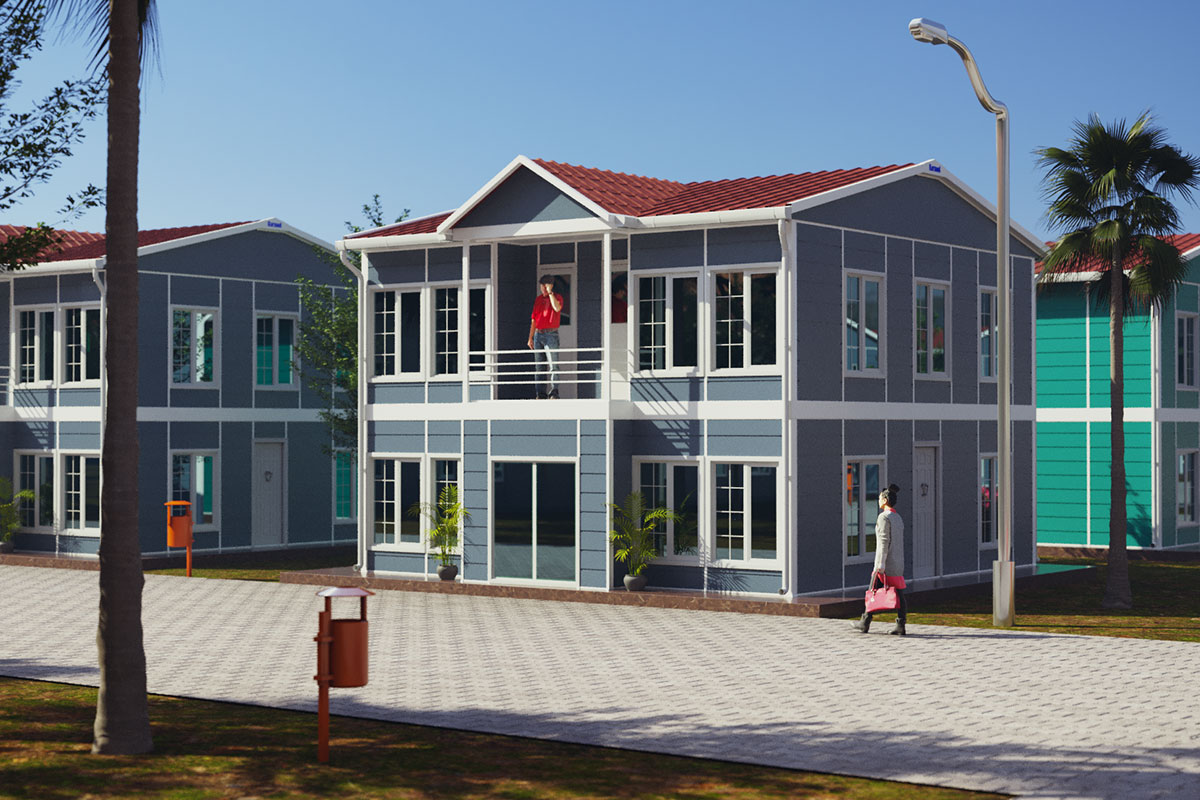
Although often mentioned together, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve different strategic purposes. Modular buildings are produced as complete volumetric units. Each module can function independently or be combined with others, making them easy to transport, relocate, or expand. This flexibility is particularly valuable in Nepal, where project scopes can change due to terrain, access, or regulatory adjustments.
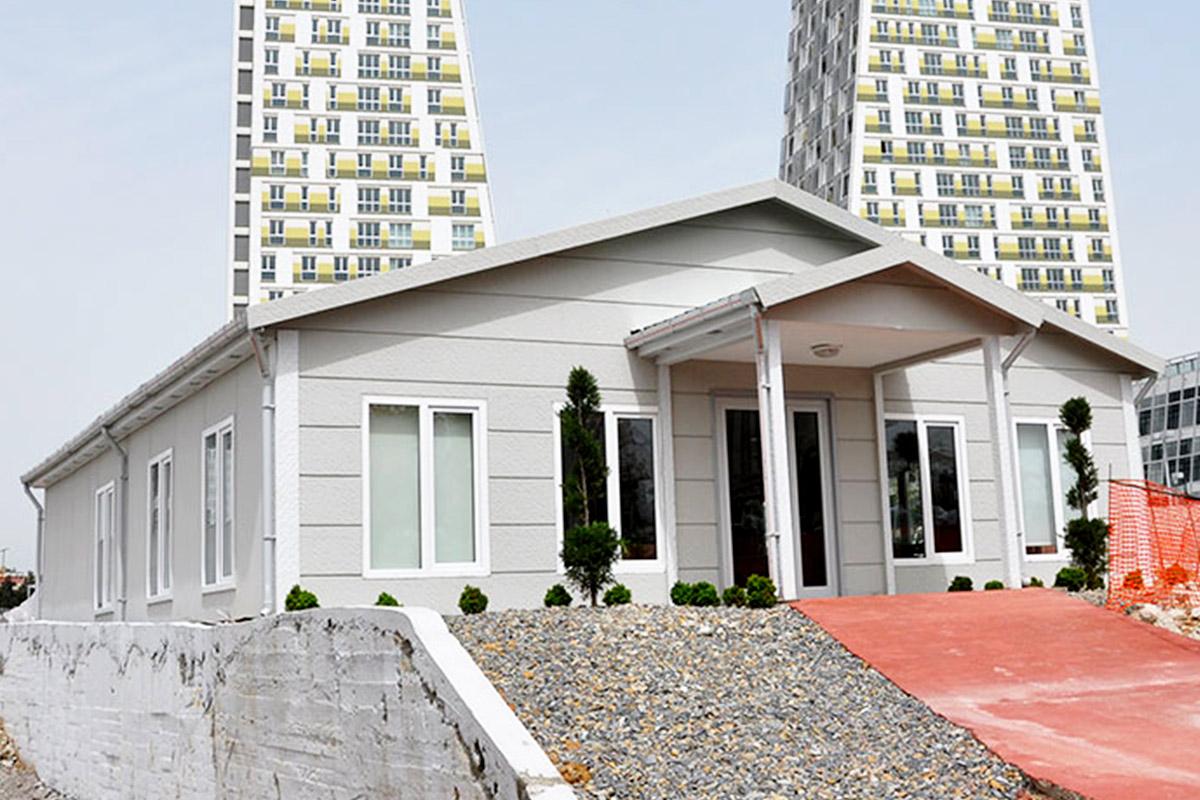
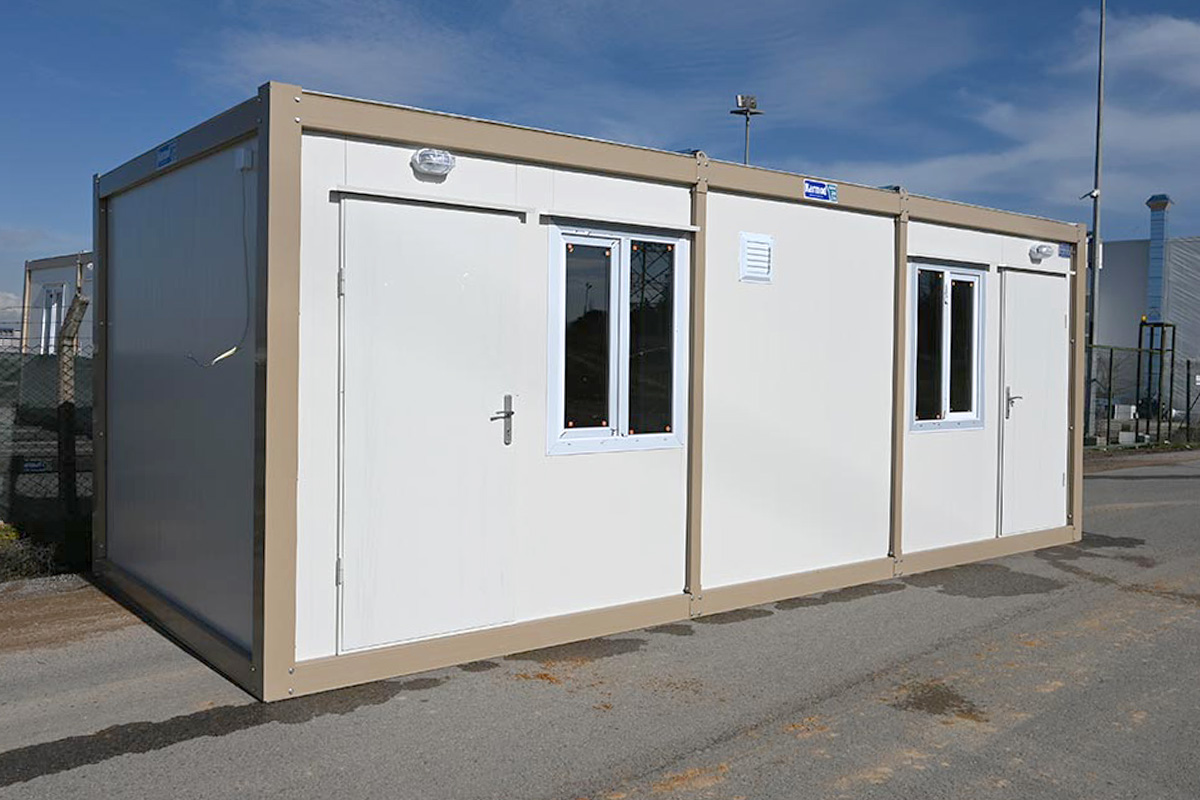
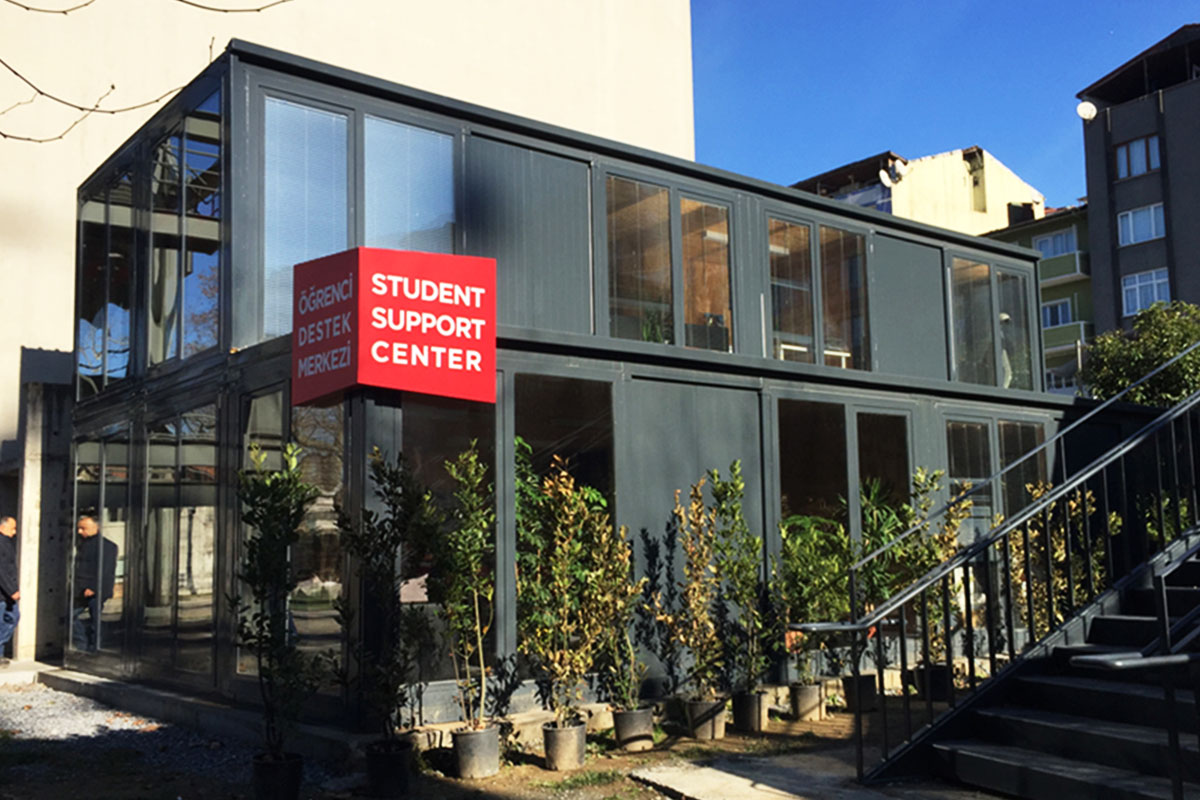
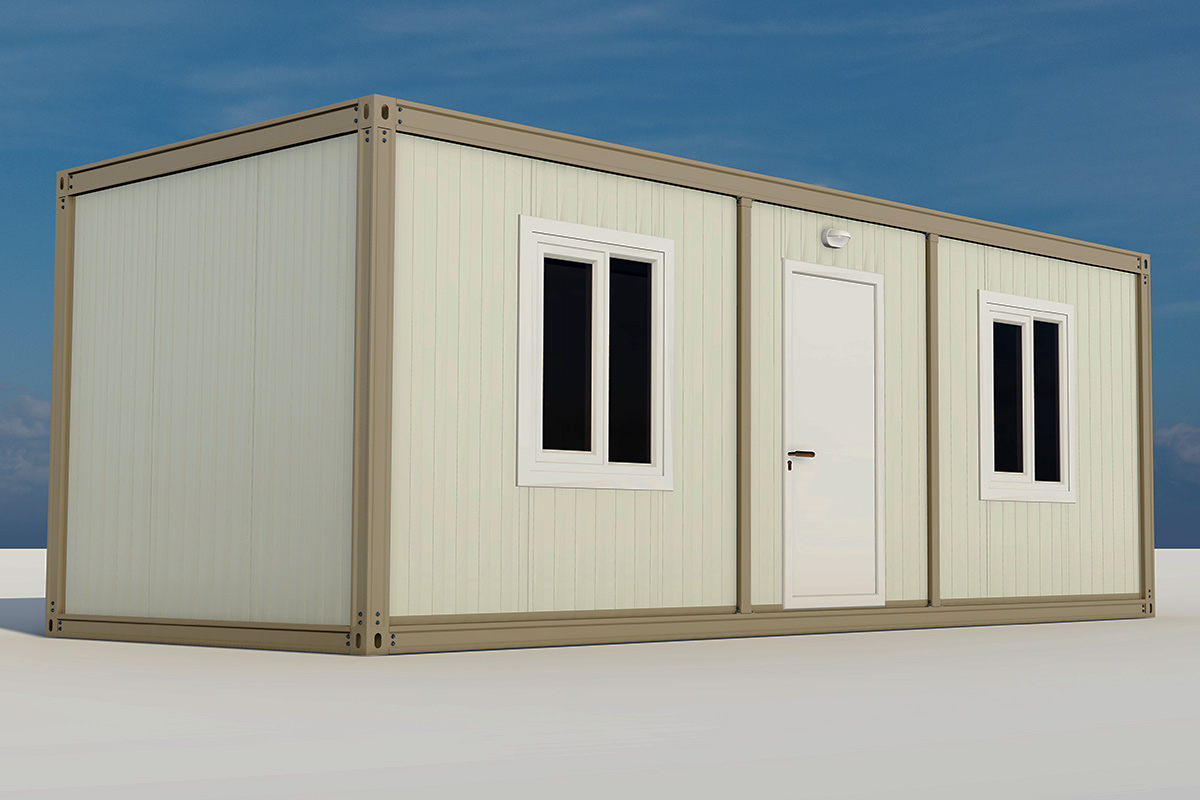
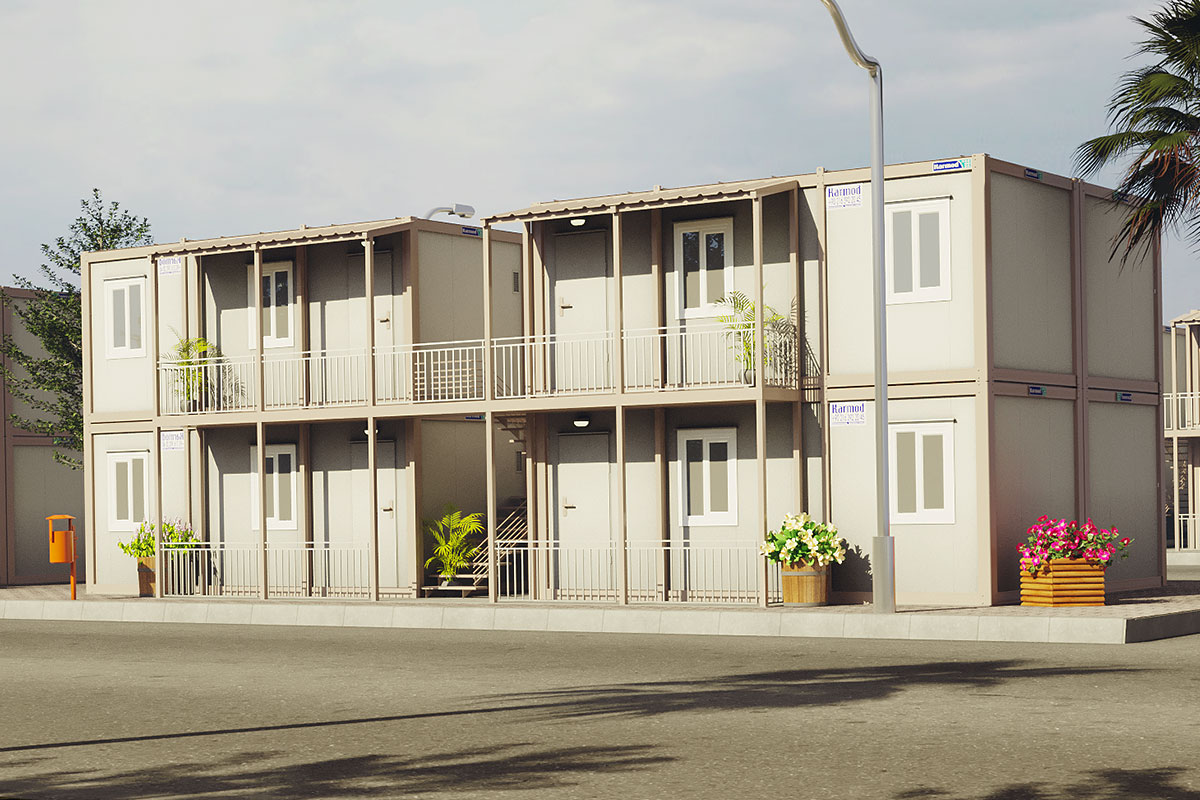
A prefabricated building, by contrast, is typically assembled from panels or structural components produced in a factory and then installed on-site as a fixed structure. These systems are well suited for long-term facilities where relocation is not expected. They provide architectural consistency and strong structural performance for permanent use.
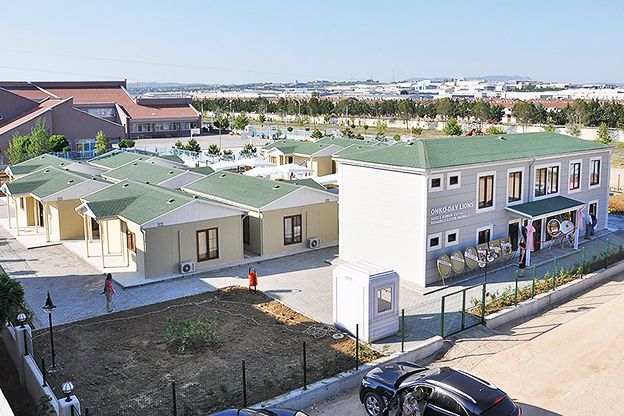
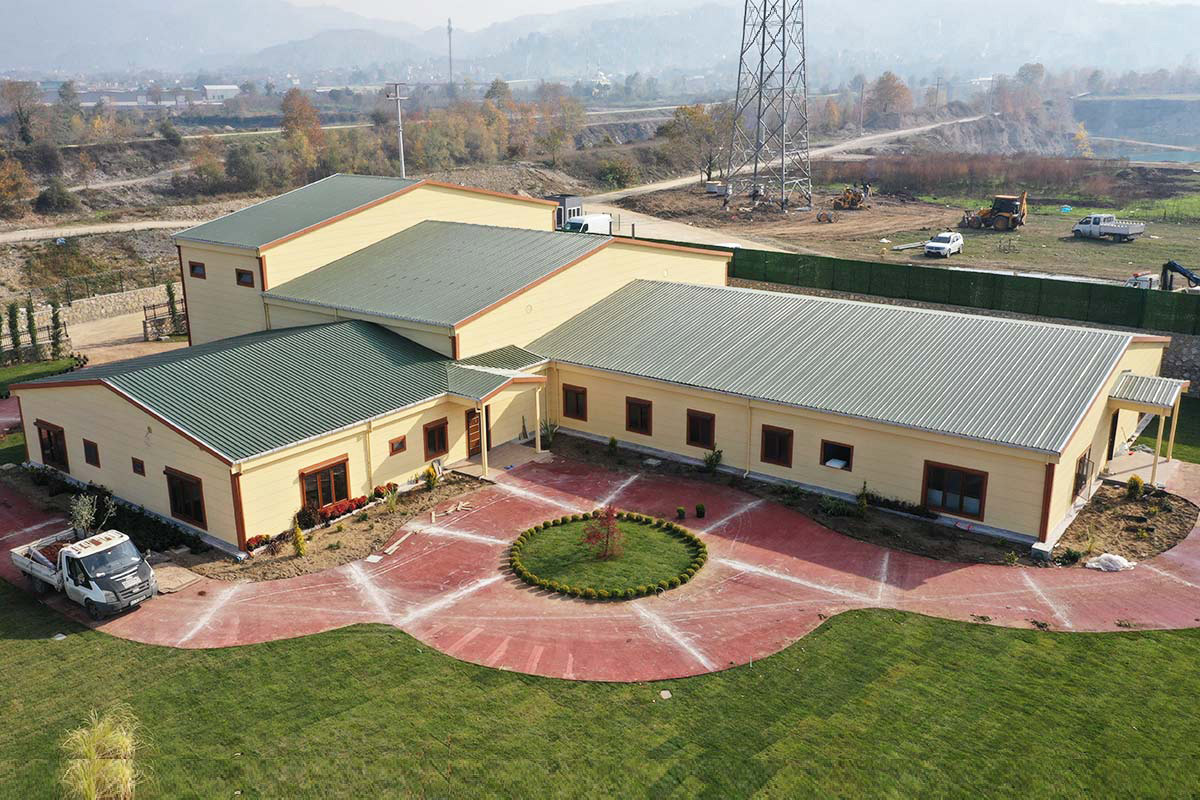
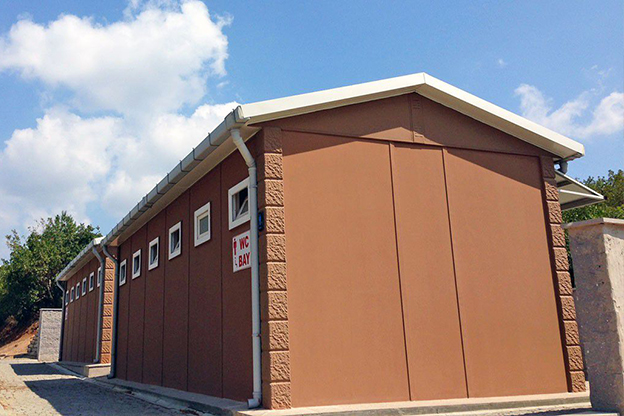
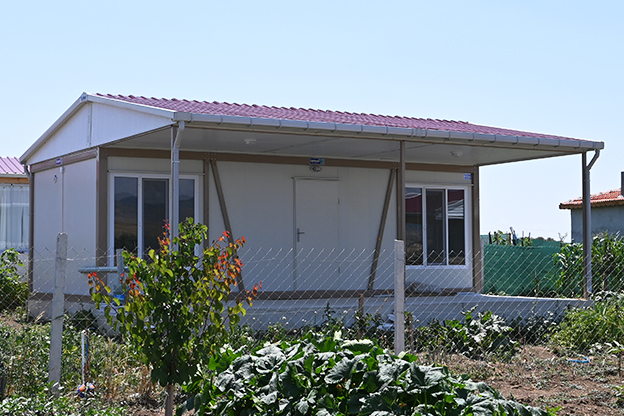
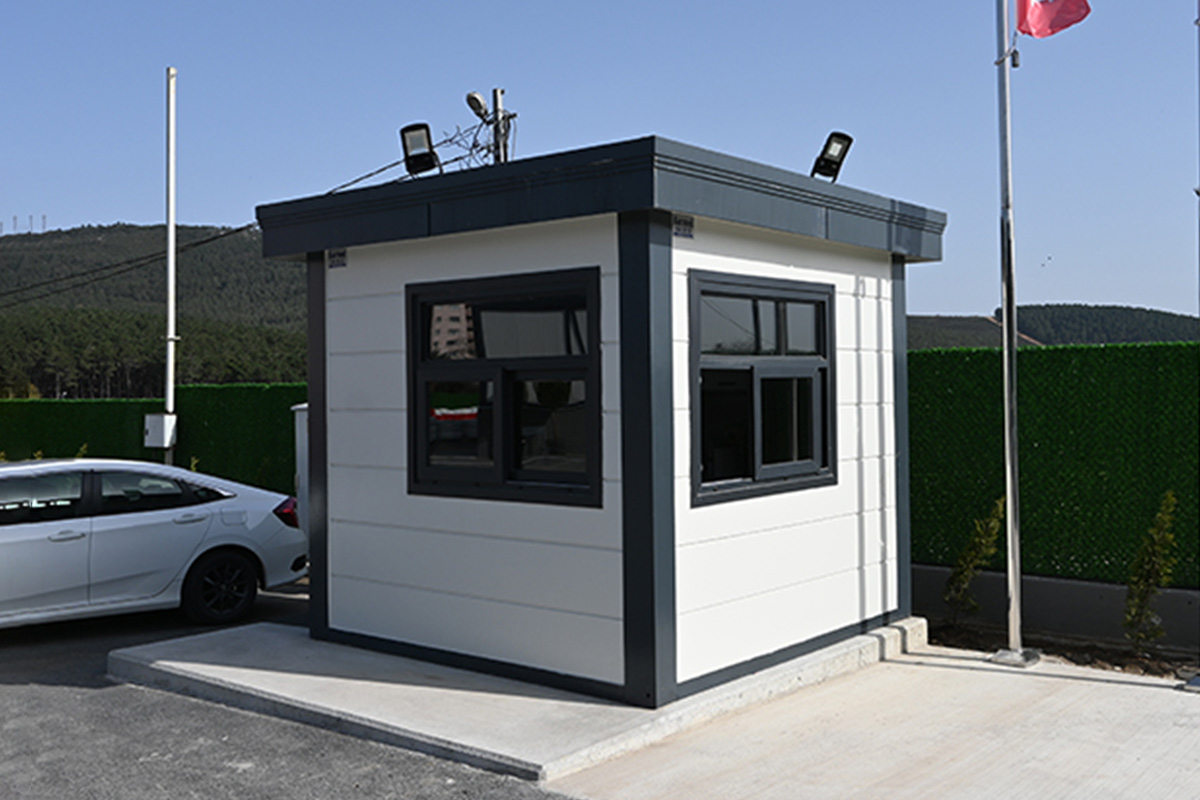
In Nepal, modular buildings are often preferred for construction camps, temporary offices, and remote worker accommodation, where mobility and speed are priorities. Prefabricated building solutions are more commonly selected for permanent schools, healthcare centers, and administrative buildings that require long service life and minimal future modification.
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Nepal
Across Nepal, modular and prefabricated solutions are applied in a wide range of functional contexts:
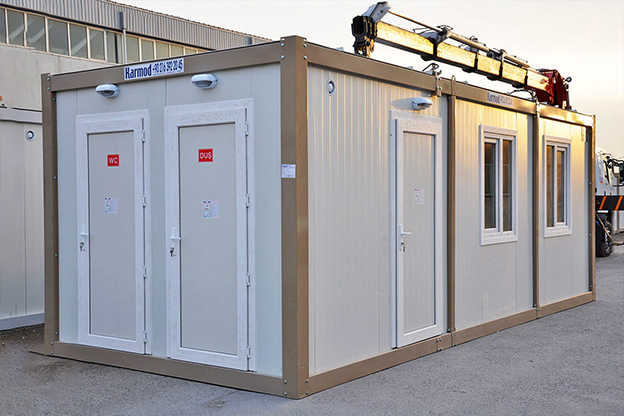
- Site offices & construction camps supporting infrastructure, road, and hydropower projects
- Worker accommodation buildings in remote or high-altitude locations
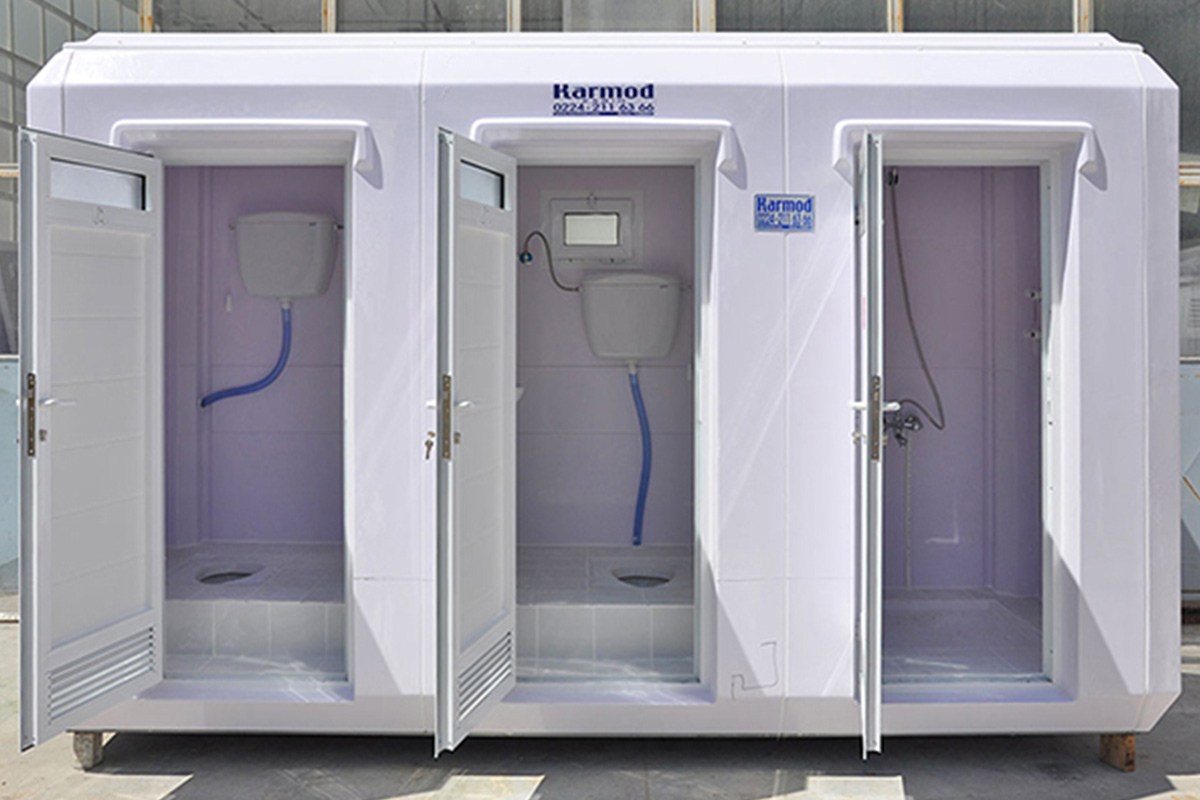
- Temporary schools & healthcare units for rapidly growing or underserved communities
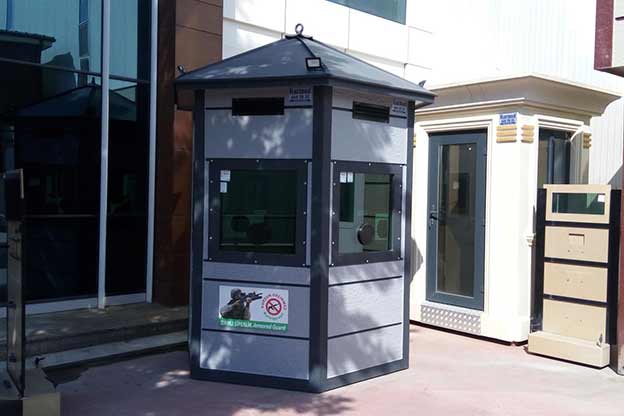
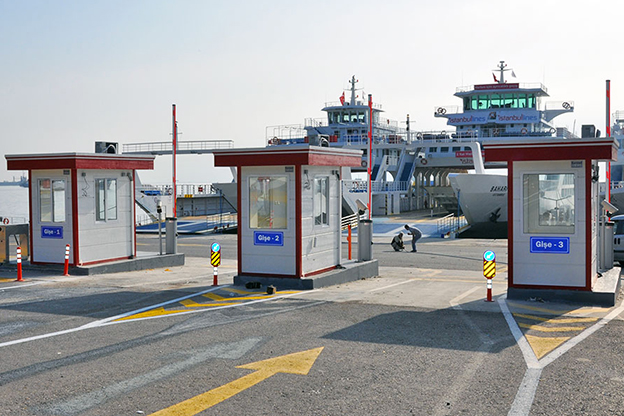
- Security buildings & technical units at energy facilities, borders, and industrial sites
- Storage and logistics facilities for industrial supply chains and public services
These applications demonstrate how adaptable off-site construction methods can support both economic development and public needs without excessive on-site complexity.

From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
A successful modular or prefabricated project follows a structured process designed to minimize uncertainty. It begins with project needs analysis, where functional requirements, capacity, location, and regulatory considerations are defined. This stage is essential for aligning building design with Nepal’s local conditions.
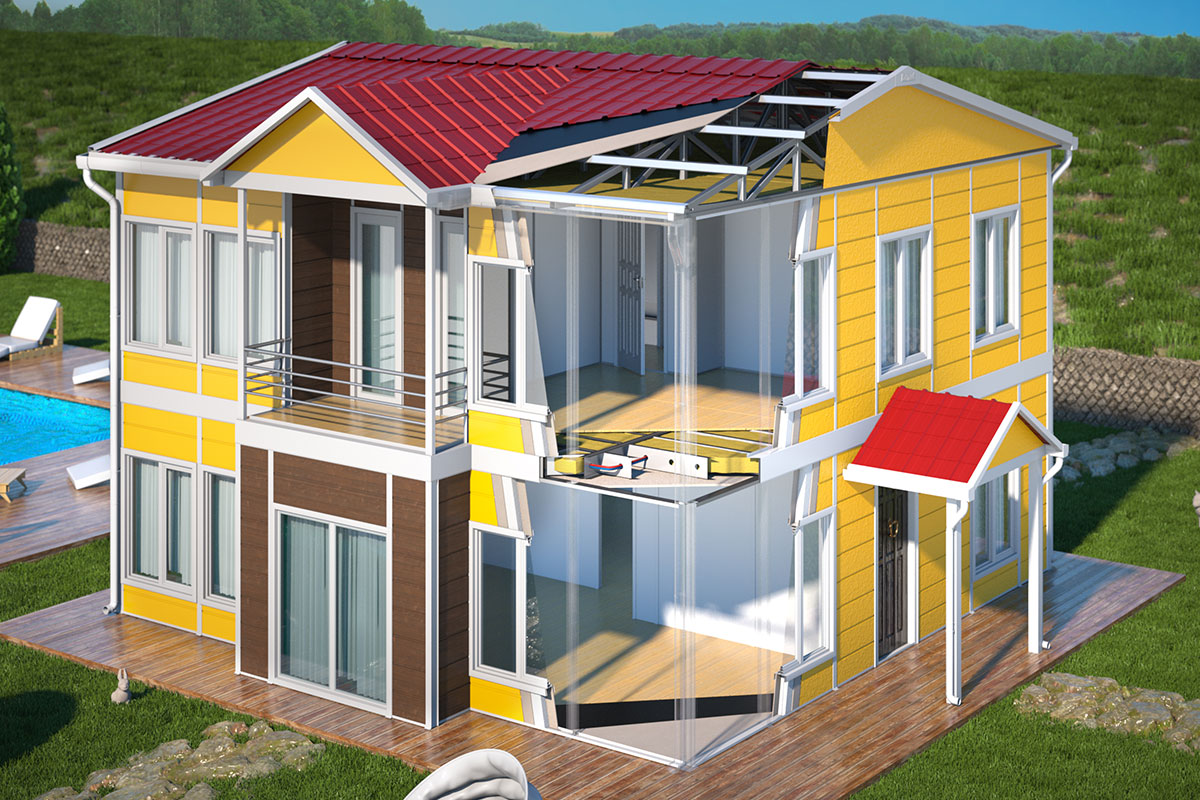
Next comes custom design and technical specifications. Layouts, insulation levels, fire safety features, and technical systems are tailored to the project’s intended use and climate zone. Once designs are approved, factory production starts under controlled conditions, ensuring consistent quality and precise tolerances.
After production, units are prepared for delivery to Nepal, with logistics planned to account for road access, terrain, and site constraints. The final phase is on-site installation, which is typically completed in a fraction of the time required for traditional construction, allowing facilities to become operational quickly.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Nepal
Thermal insulation is essential due to temperature variations between regions and seasons. Proper insulation improves energy efficiency and occupant comfort, especially in mountainous areas.
Fire safety standards must be addressed carefully. Industrial and public projects require materials and systems that comply with international fire performance criteria while aligning with local regulations.
Climate suitability is another key issue. Buildings must be designed to handle monsoon rains, humidity, and, in some regions, seismic considerations. Structural detailing and material selection play a decisive role in long-term performance.
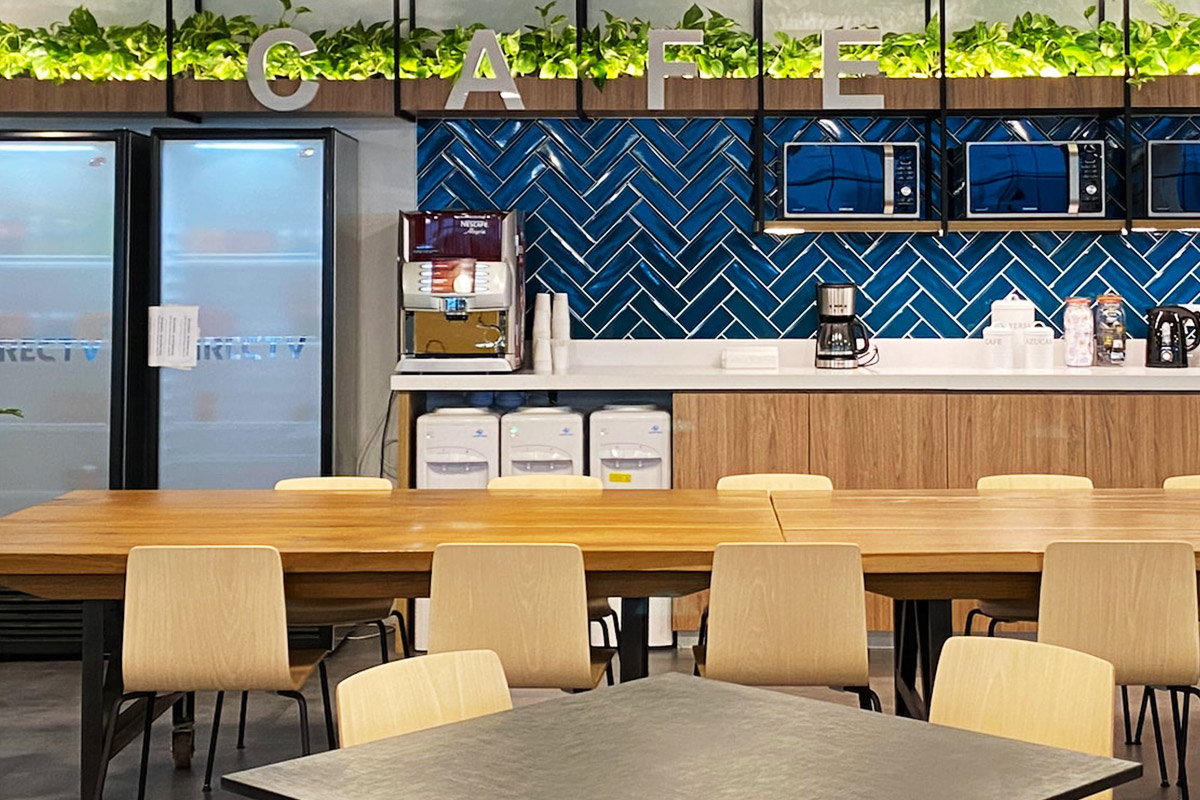
Custom layouts play a major role in usability. Modular systems allow interior configurations to be adapted for offices, accommodation, medical use, or technical operations without compromising structural integrity.
With decades of experience in off-site construction, Karmod applies proven manufacturing and project management practices to projects in Nepal. Drawing on European market experience and adapting solutions to challenging geographies, Karmod modular building solutions are designed to balance durability, transport efficiency, and functional flexibility. This approach supports organizations seeking reliable building systems that perform consistently under demanding conditions.
For decision-makers in Nepal evaluating construction strategies, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems offer a practical path forward. They reduce exposure to delays, provide predictable quality, and support scalable growth—key advantages in a market where efficiency and reliability directly influence project success.