The Philippines is experiencing sustained growth in infrastructure, industrial development, and urban expansion. Large public investments, private-sector construction, and disaster-resilient development programs are reshaping how buildings are planned and delivered across the country. Within this environment, modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions are increasingly preferred by organizations that require speed, reliability, and controlled project execution. For B2B decision-makers, these construction methods offer practical advantages that align with the Philippines’ geographic, climatic, and operational realities.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Philippines
Labor costs in the Philippines remain competitive compared to many regional markets, yet construction projects still face productivity challenges related to workforce availability, site coordination, and skill specialization. Modular buildings reduce on-site labor dependency by transferring a significant portion of construction activities to factory-controlled environments. This approach improves consistency, reduces rework, and allows companies to better forecast total project costs.
Construction timelines are a critical concern, particularly in urban centers such as Metro Manila and in regional infrastructure projects. Traditional construction methods are often affected by weather disruptions, congestion, and logistical constraints. Modular buildings allow site preparation and building production to run simultaneously, shortening overall project duration and enabling faster commissioning of facilities.
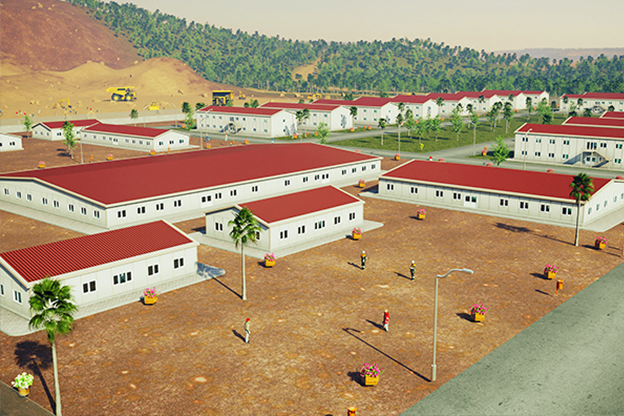
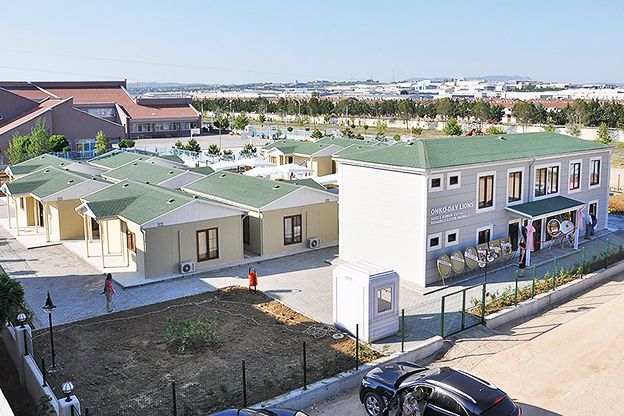
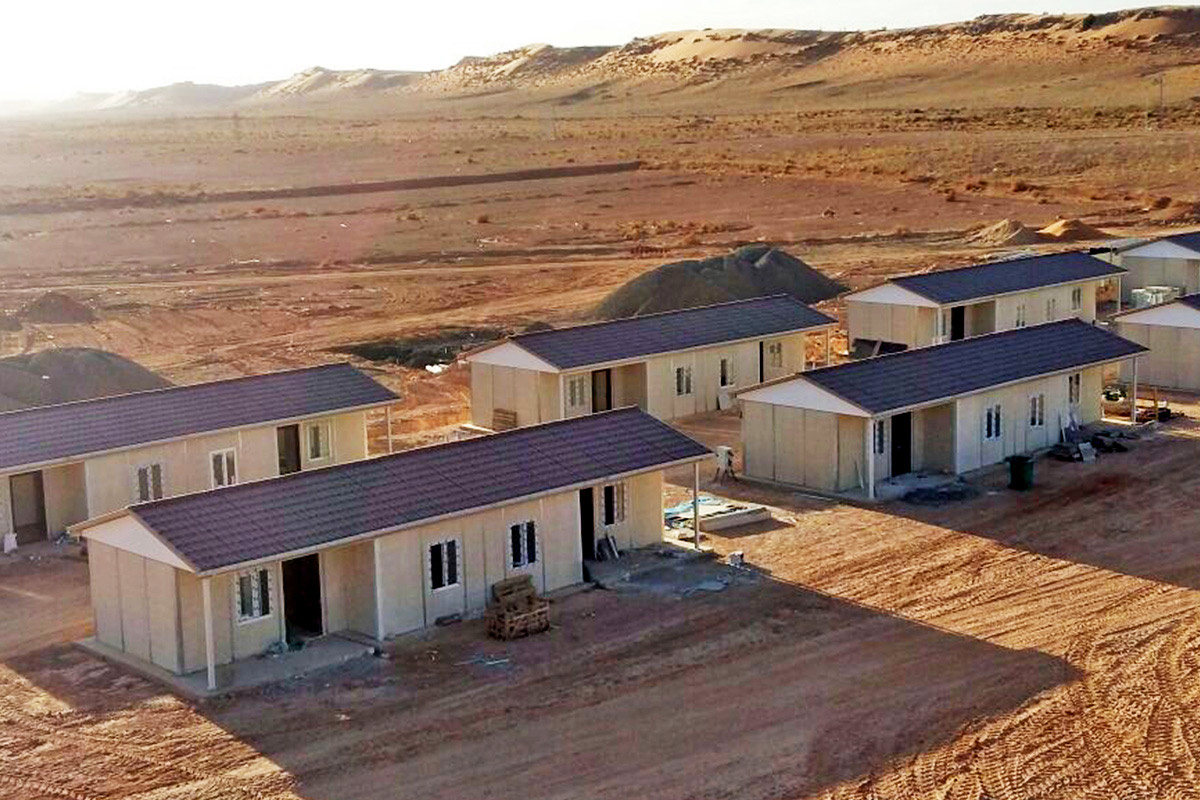
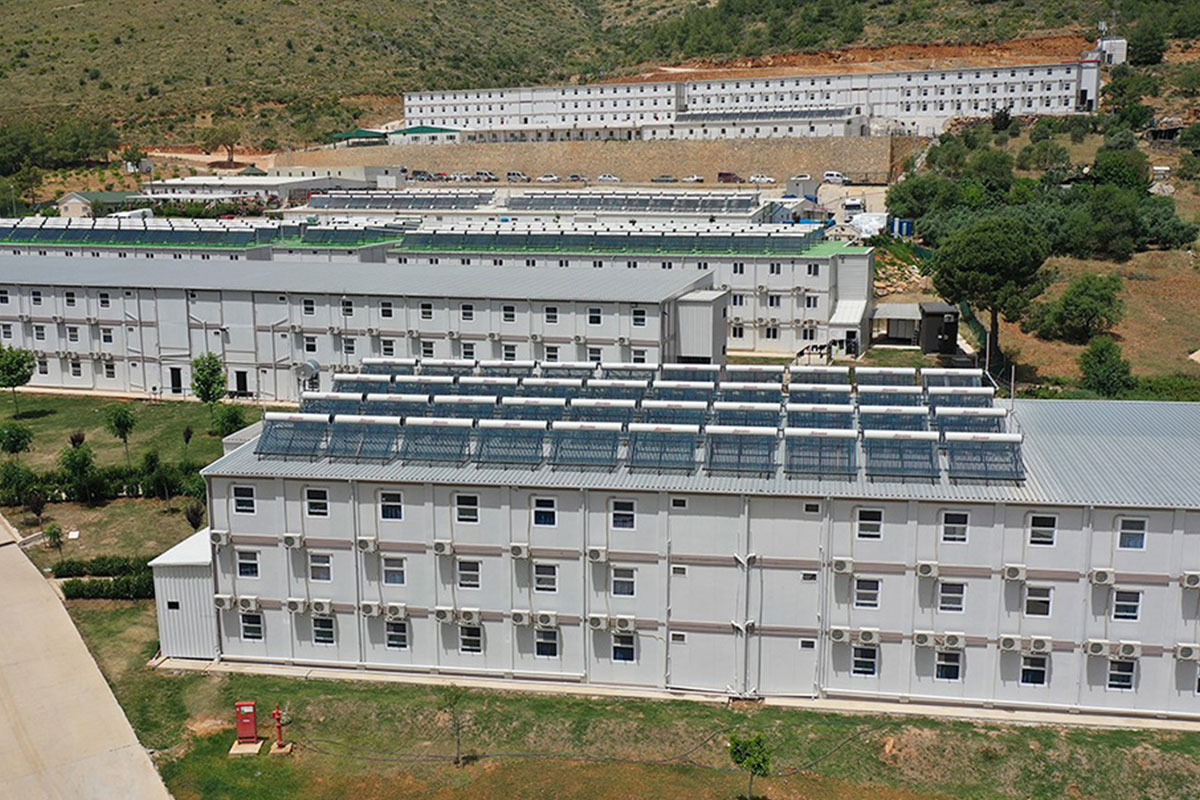
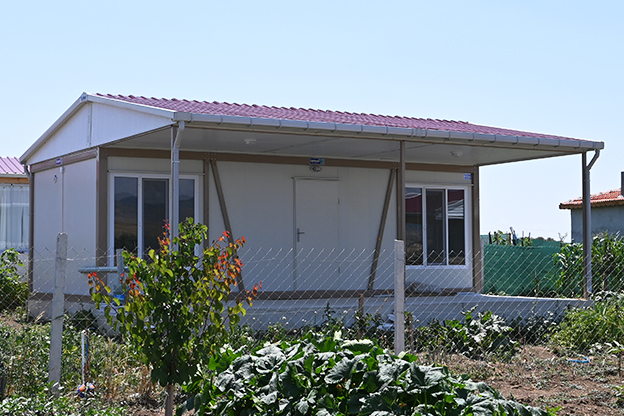
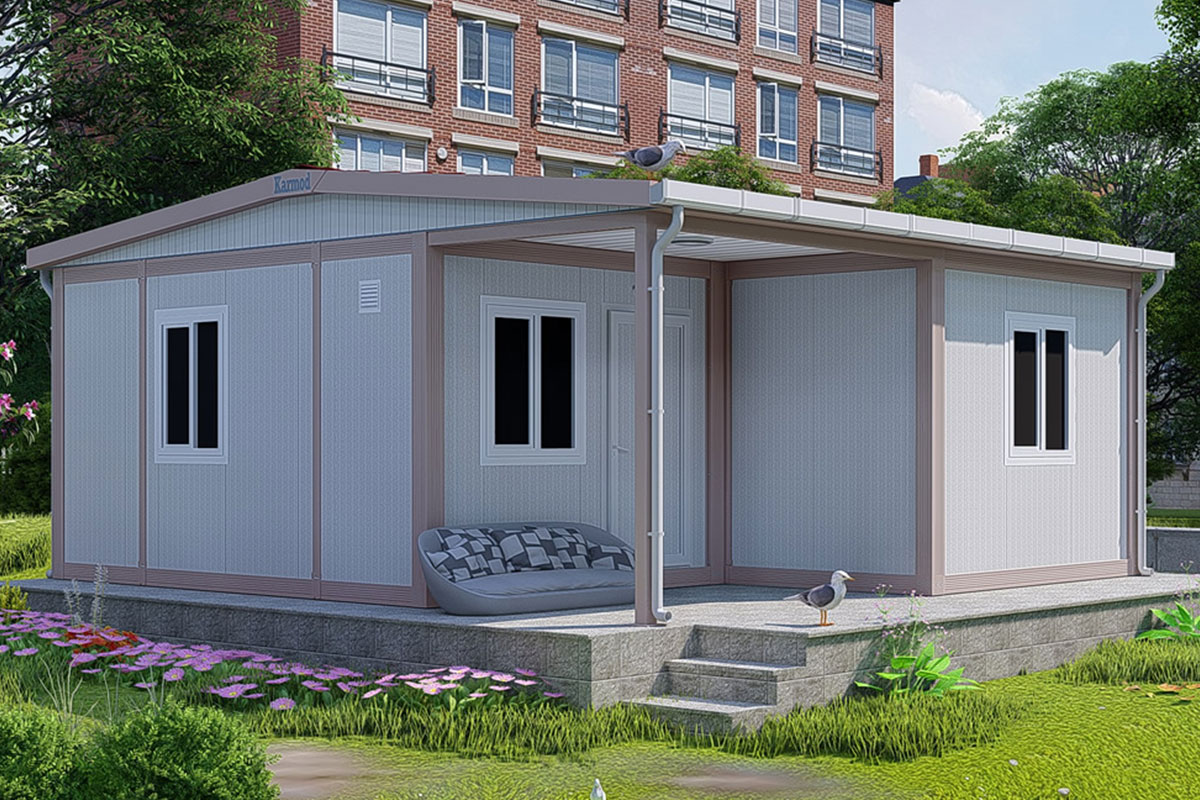
The balance between temporary and permanent building needs is especially relevant in the Philippines. Temporary facilities are frequently required for infrastructure projects, port developments, mining operations, and disaster response initiatives. At the same time, long-term demand exists for permanent schools, healthcare facilities, government buildings, and industrial plants. Modular systems address both needs by offering relocatable structures as well as long-lasting installations designed for extended use.
Sector-specific demand further drives adoption. Logistics and warehousing are expanding alongside port modernization and e-commerce growth. Industrial zones require quickly deployable offices and technical units. Public sector projects, including transportation, utilities, and education, often operate under fixed schedules where delayed building delivery can impact service continuity. In these contexts, modular buildings provide a predictable and scalable solution.
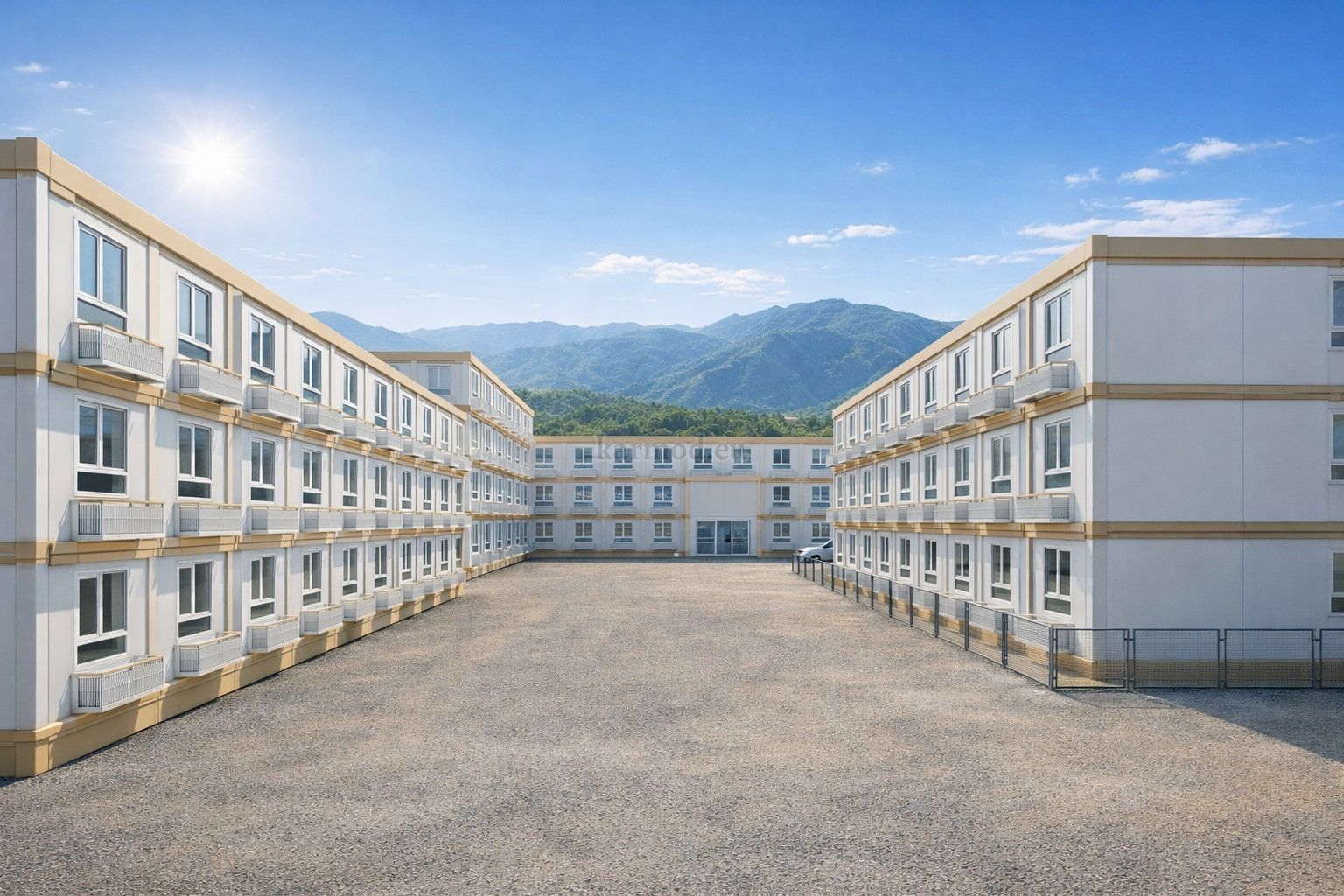

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
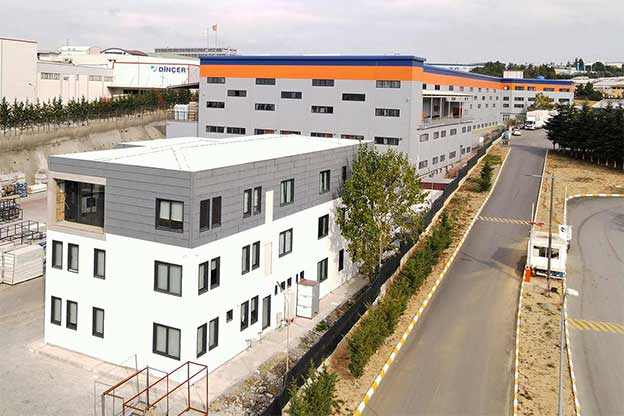
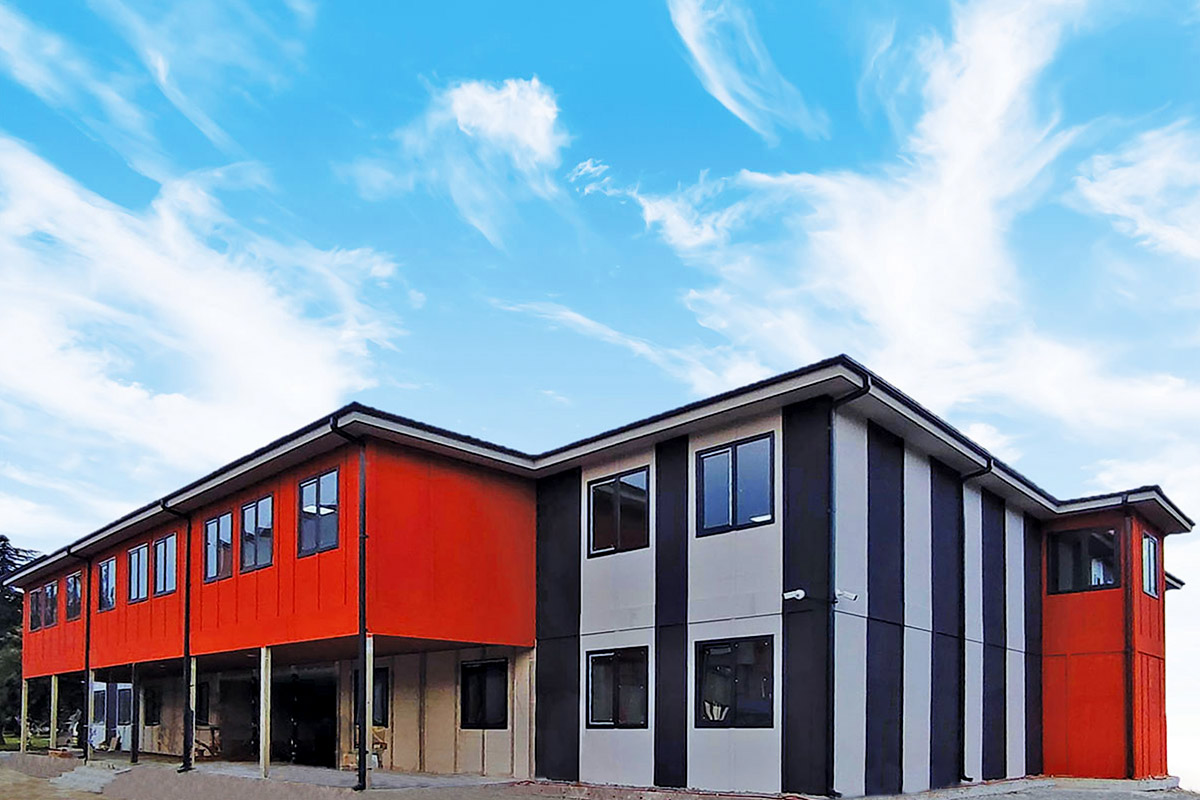
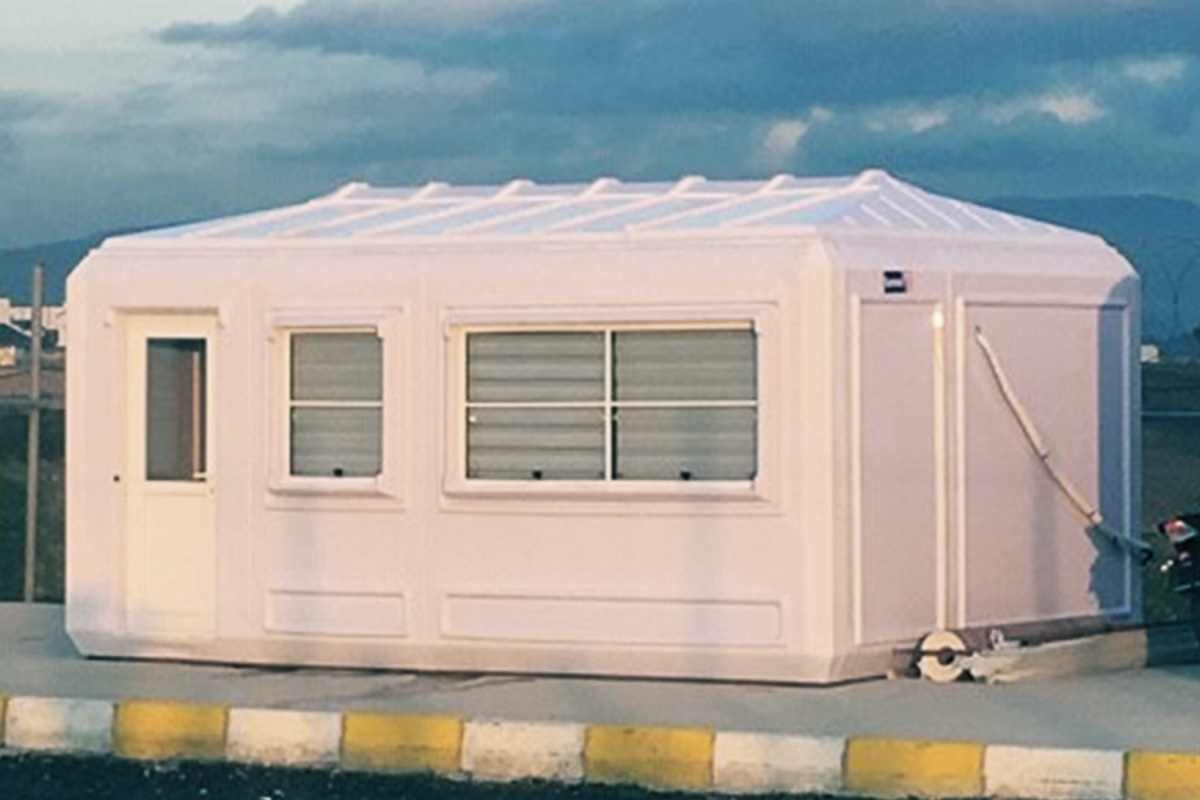
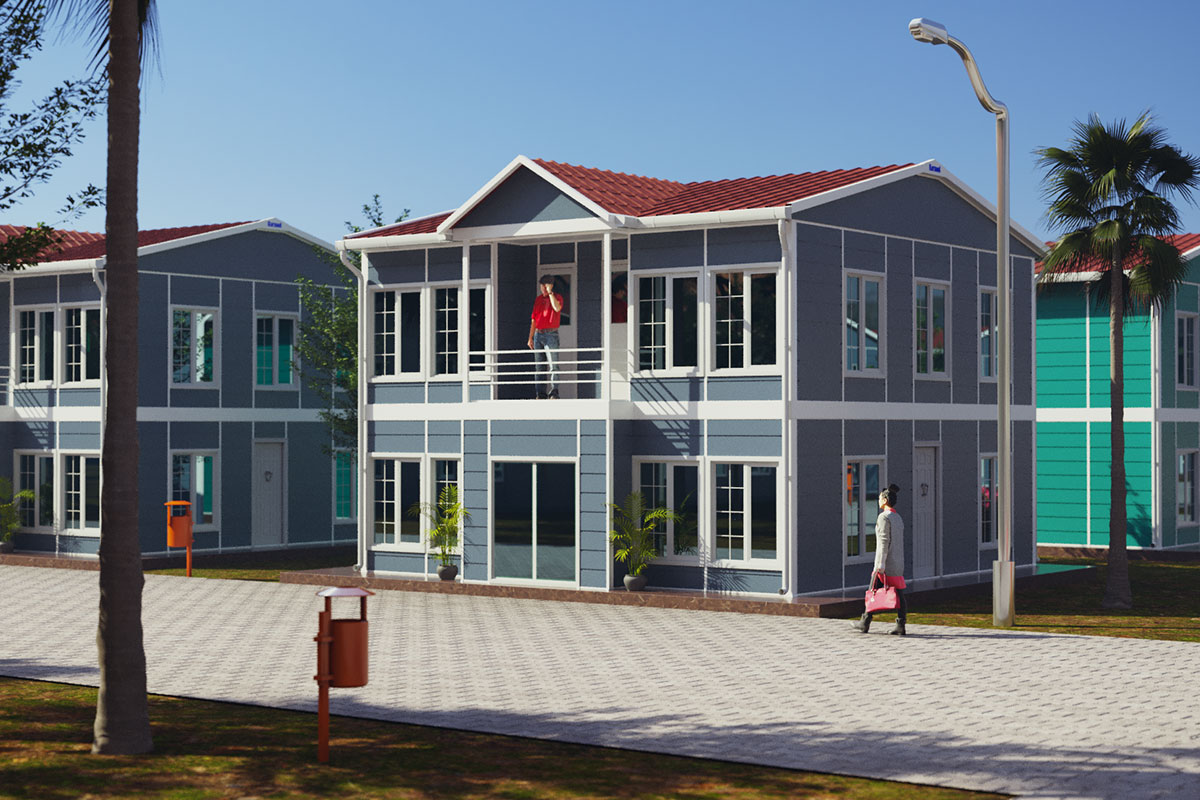
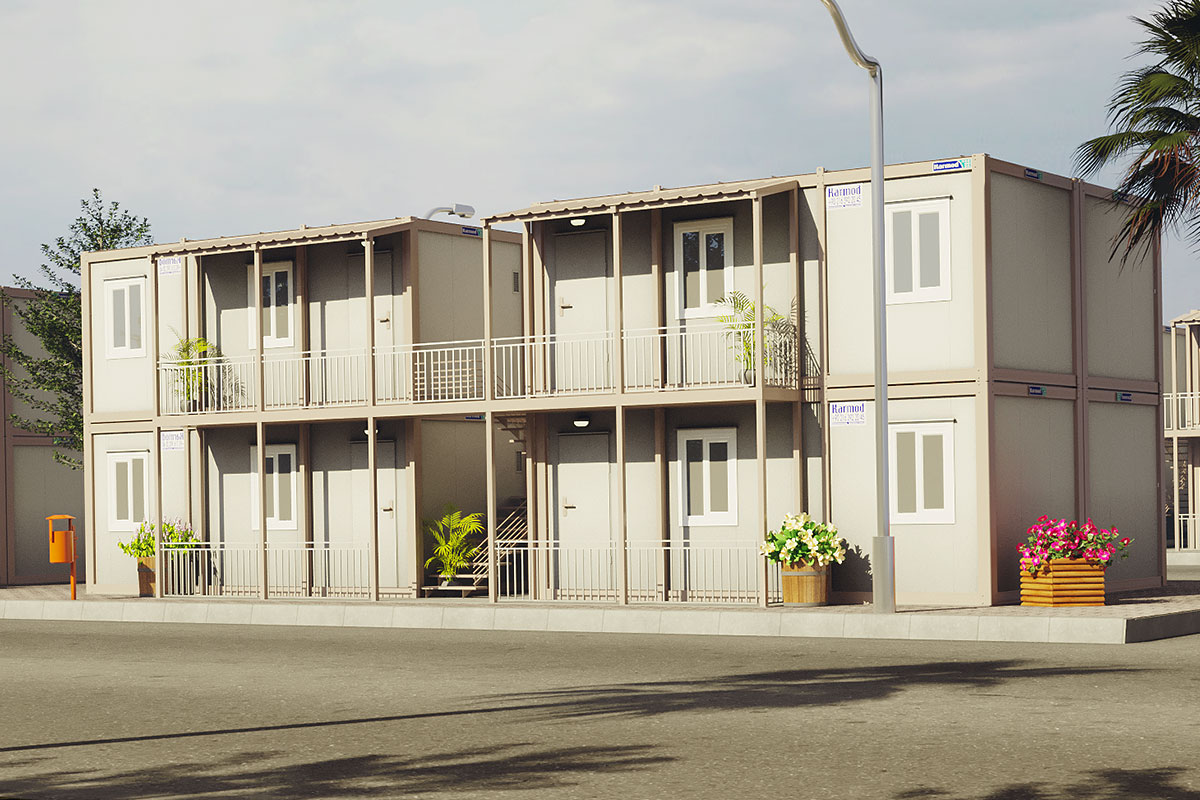
Although they share off-site production principles, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve different strategic purposes. Modular buildings are volumetric units manufactured as complete modules. These modules are transportable, can be installed rapidly, and allow for future expansion or relocation. This makes modular buildings well suited for projects that require flexibility, phased development, or temporary deployment.
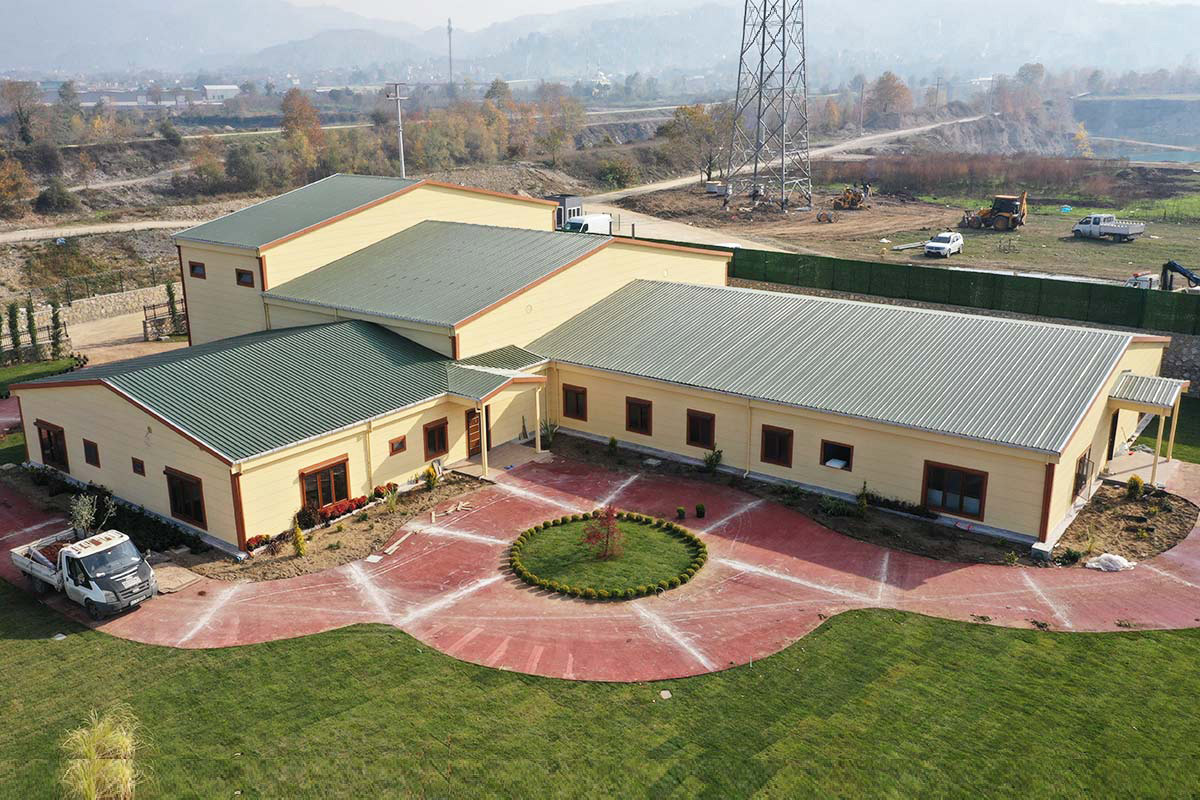
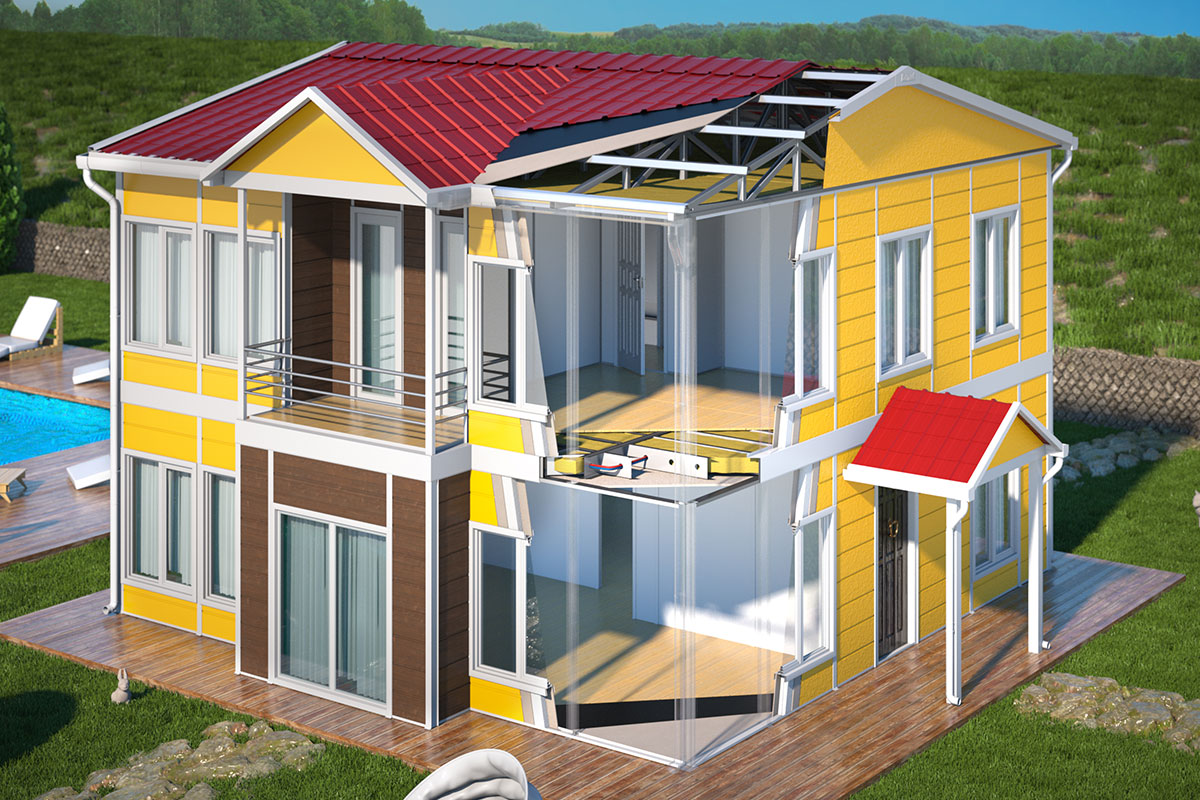
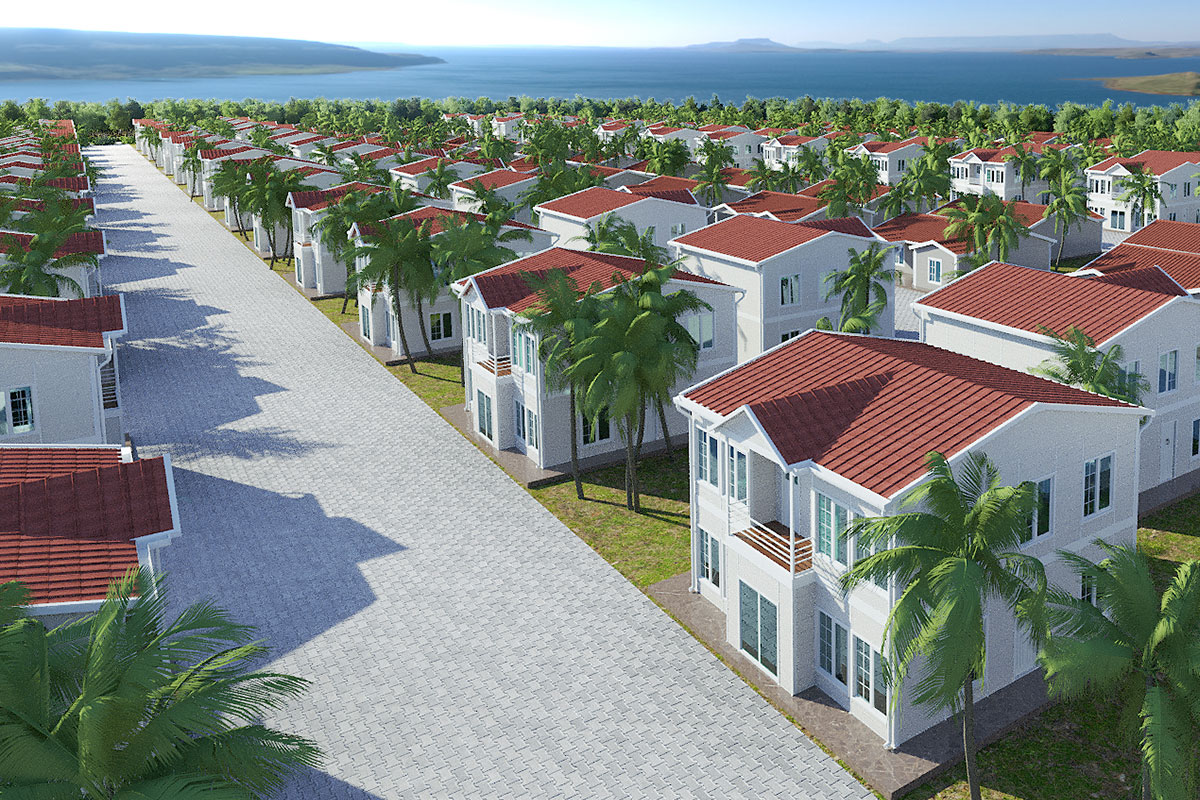
A prefabricated building, in contrast, is assembled from panels or structural components produced in factories and installed permanently on-site. These systems are typically chosen for long-term facilities where architectural integration and fixed layouts are important. Prefabricated building methods offer improved quality control compared to conventional construction while maintaining a permanent structural character.
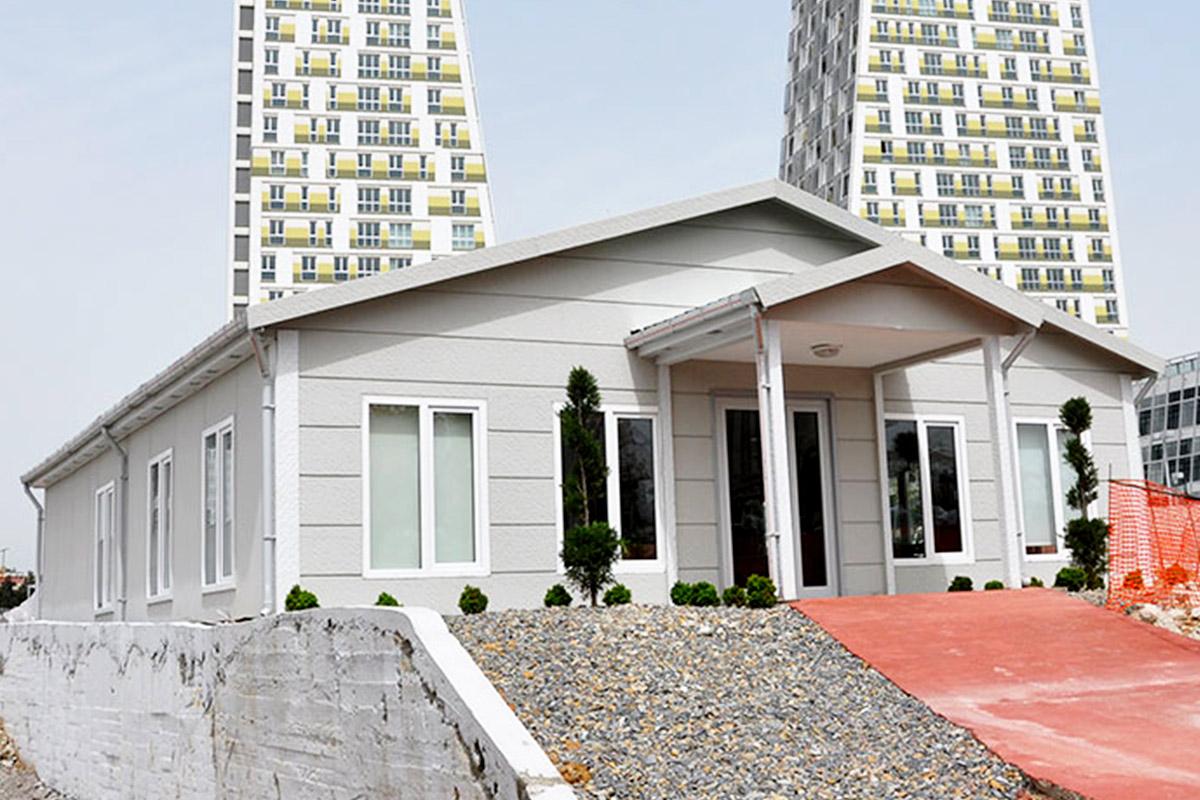
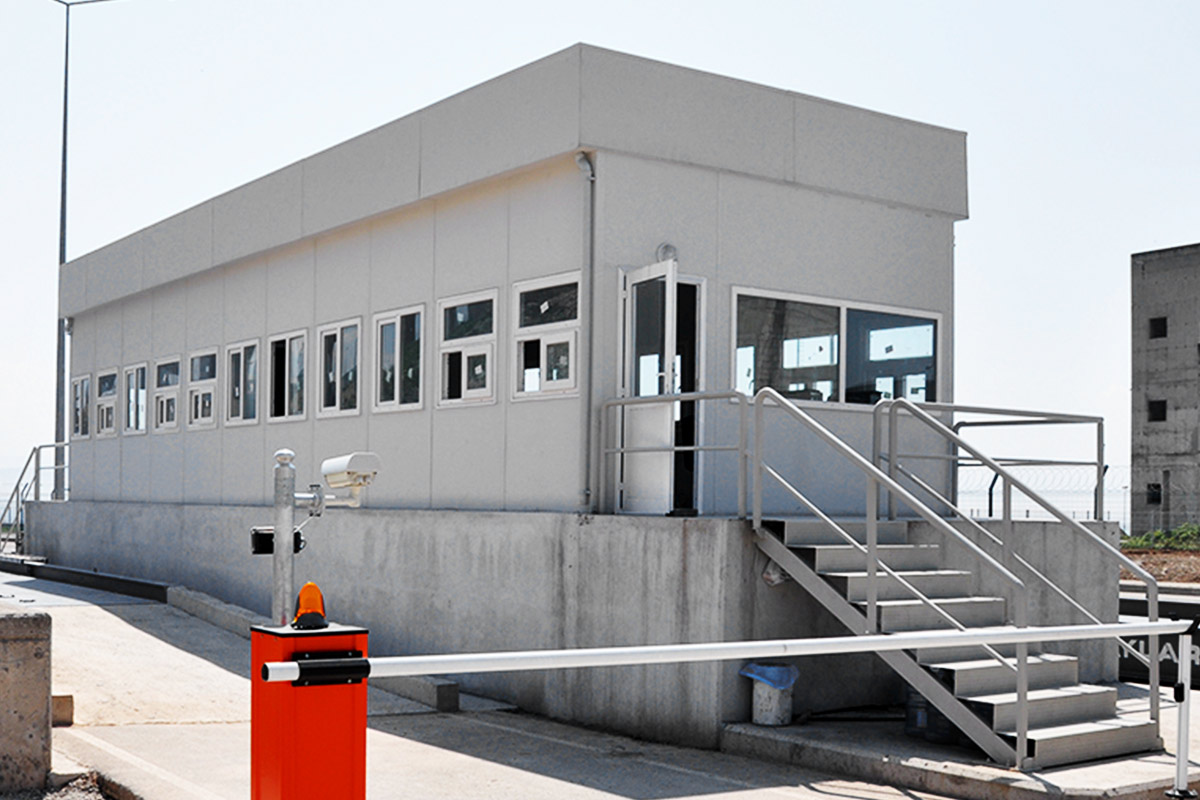
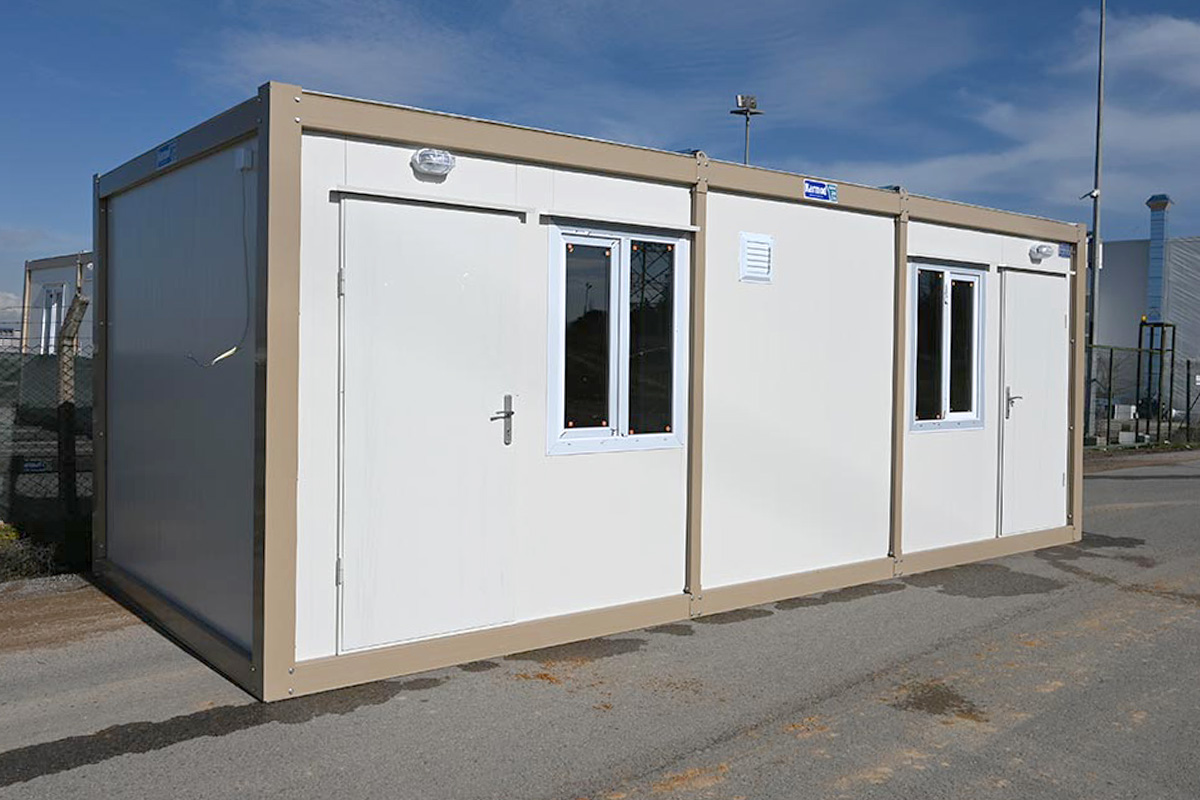
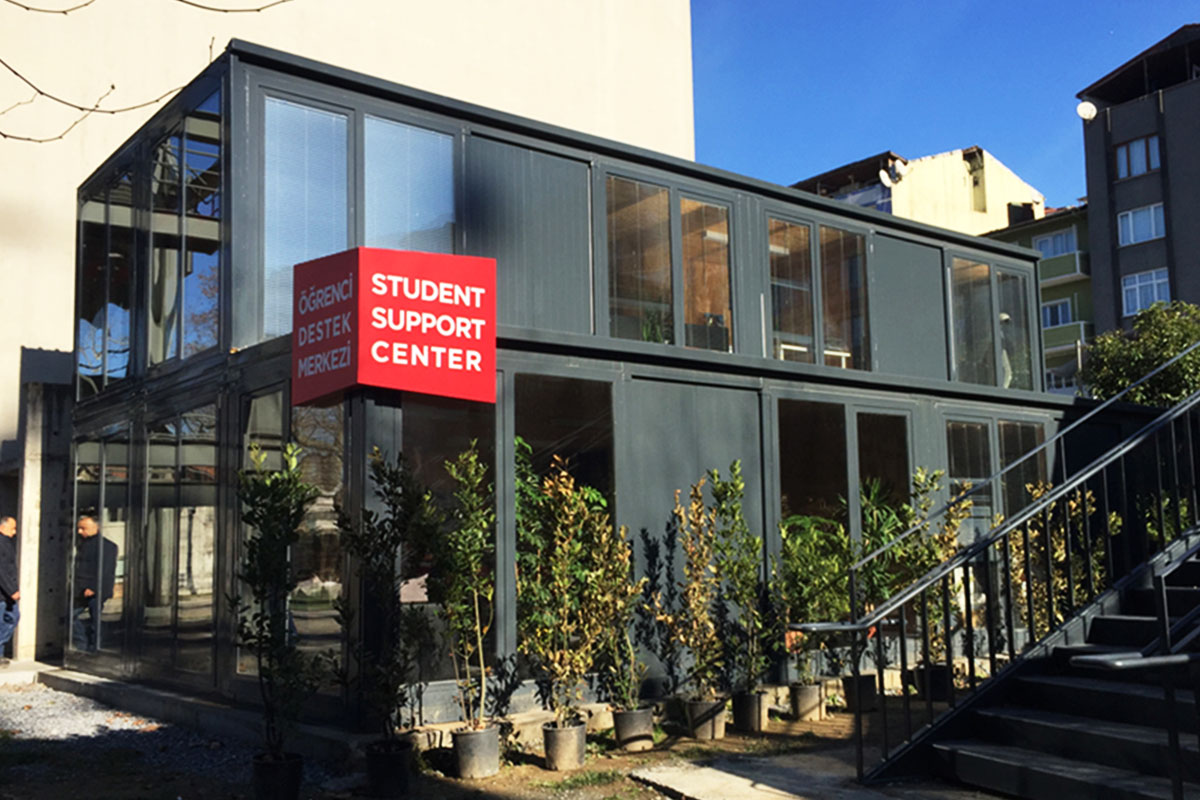
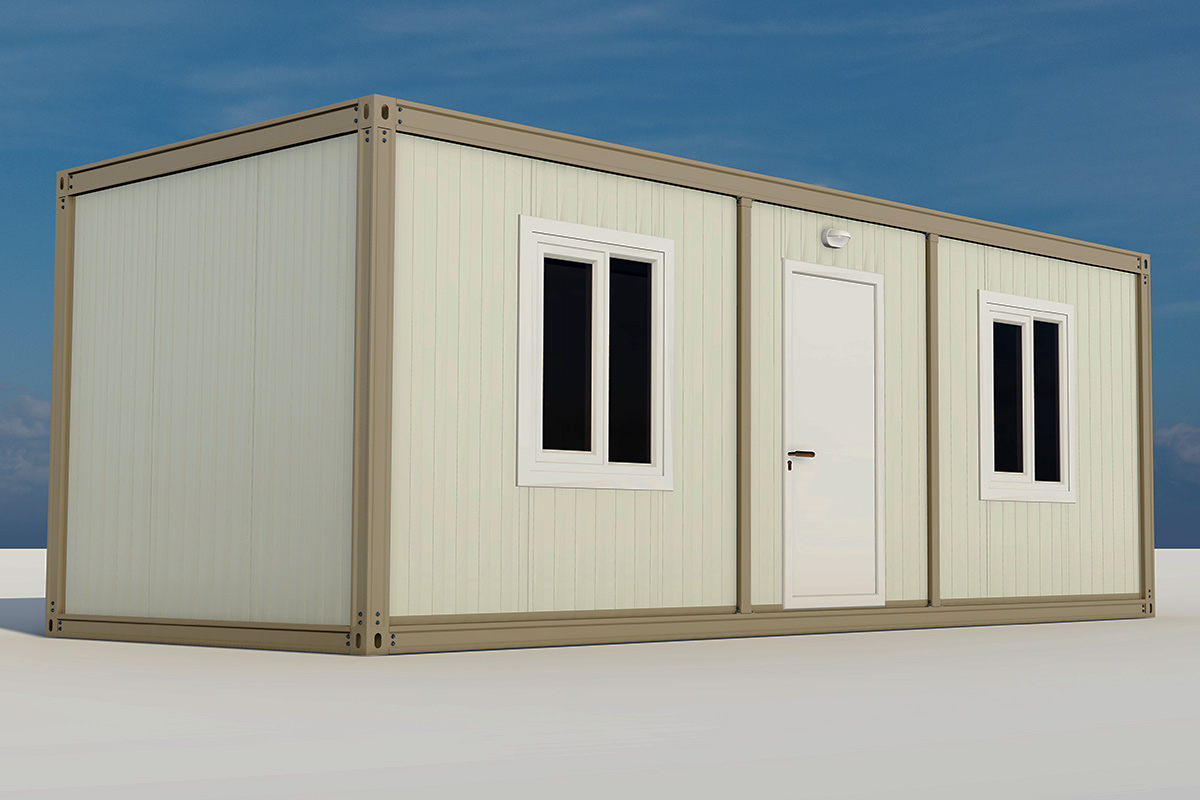
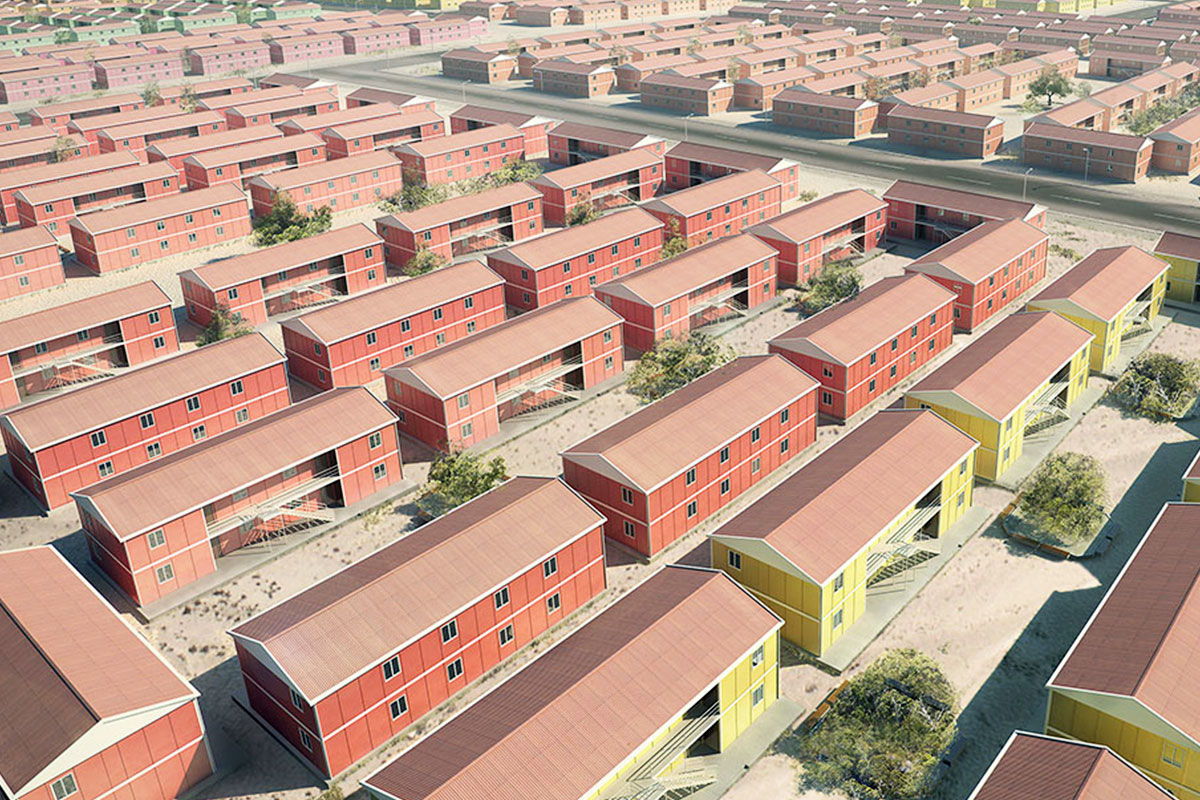
In the Philippines, modular buildings are often selected for site offices, worker accommodation, and technical facilities associated with infrastructure and industrial projects. Prefabricated building systems are more commonly used for permanent schools, hospitals, administrative buildings, and manufacturing facilities where durability and long service life are essential. Choosing between these systems depends on operational priorities rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Philippines
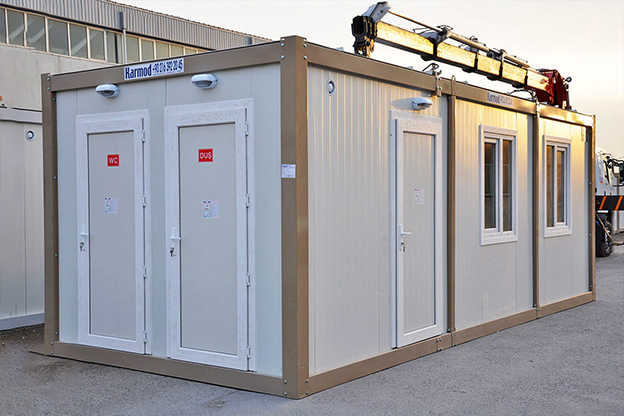
- Site offices & construction camps for infrastructure, port expansion, and large-scale commercial projects
- Worker accommodation buildings supporting industrial zones, mining activities, and energy developments
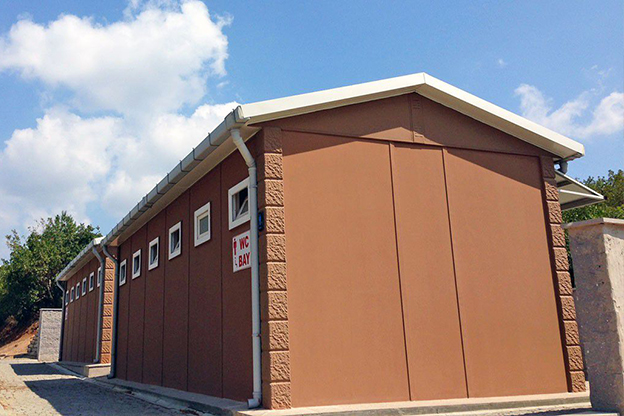
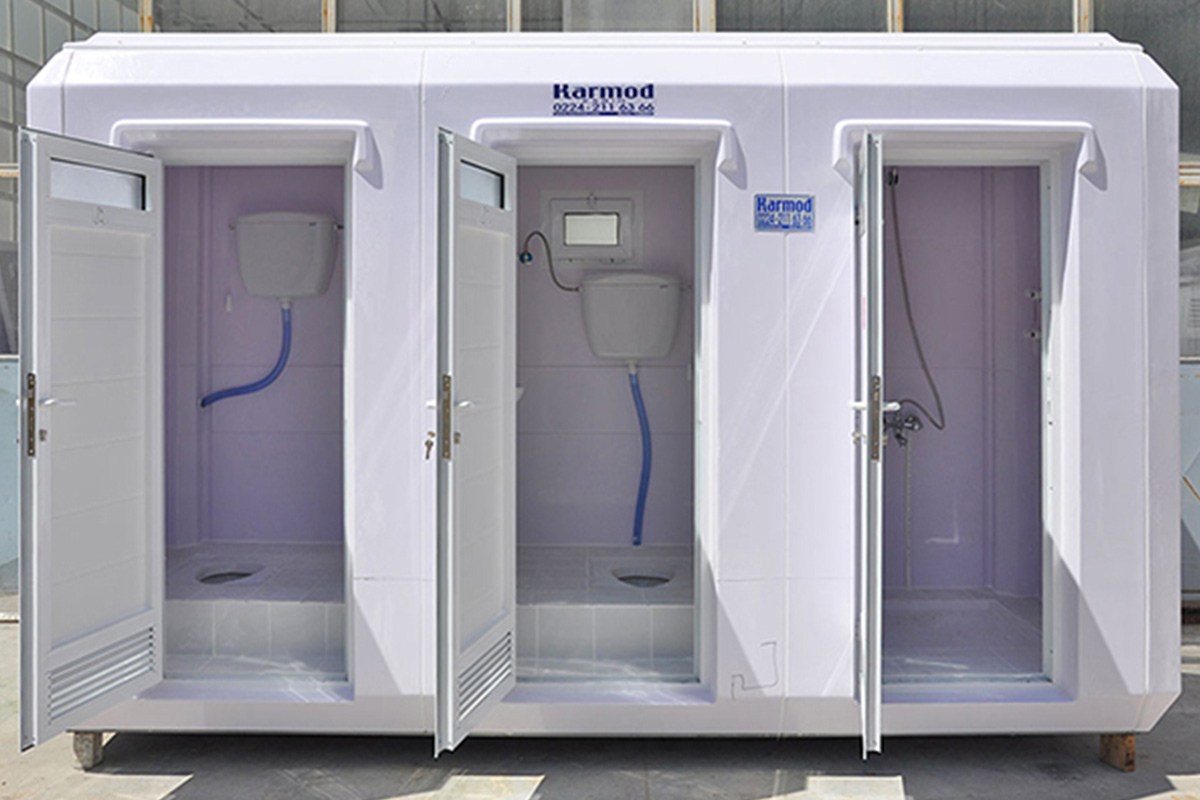
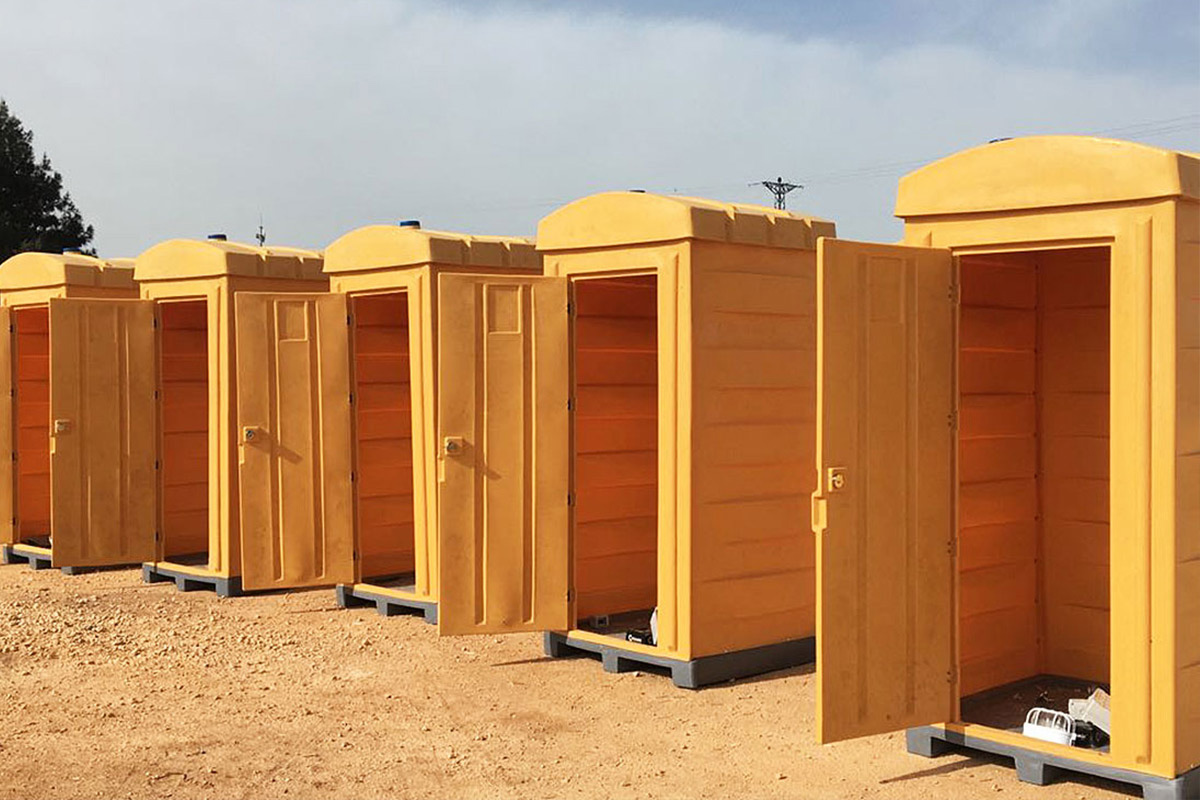
- Temporary schools & healthcare units addressing capacity needs during expansion phases or emergency situations
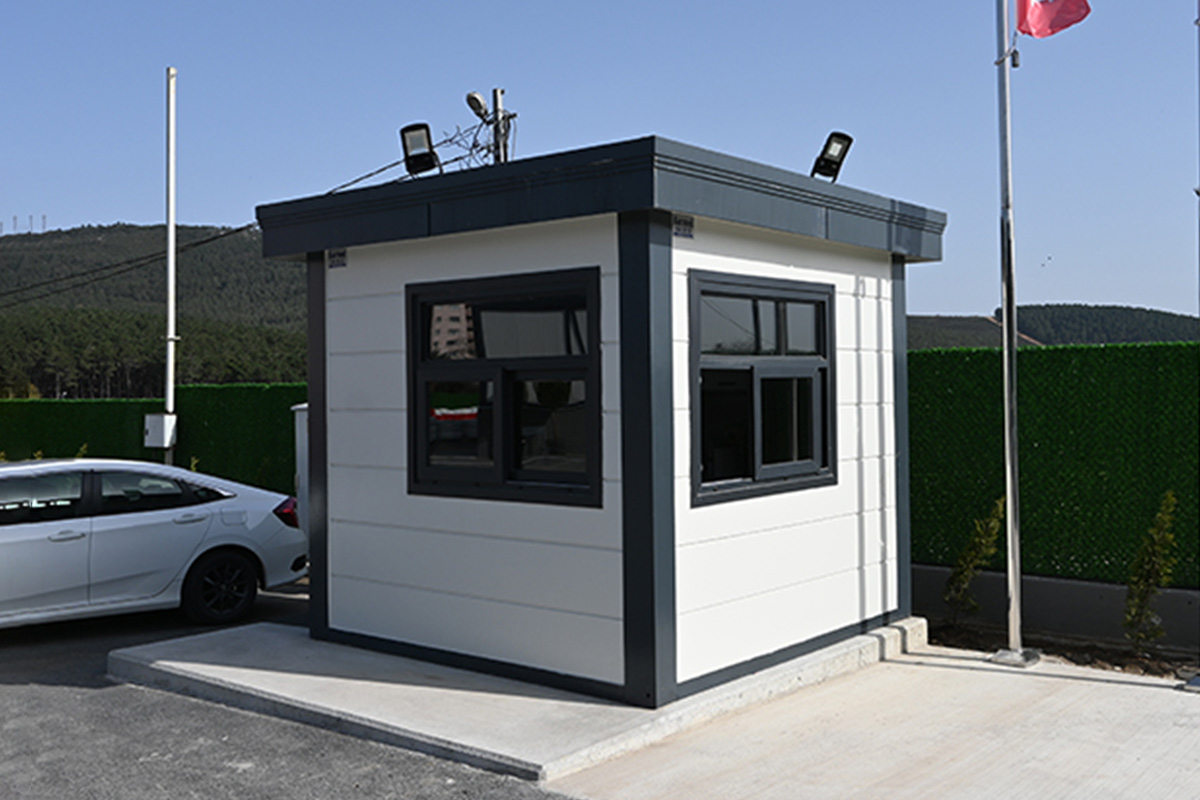
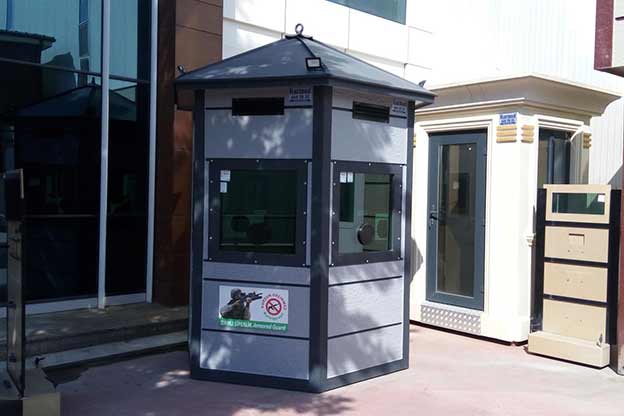
- Security buildings & technical units for access control, utilities, and critical infrastructure facilities
- Storage and logistics facilities near ports, industrial parks, and distribution corridors
These applications demonstrate how modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions integrate effectively into the Philippines’ diverse project environments.
From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The process begins with a comprehensive project needs analysis. This stage defines functional requirements, occupancy levels, compliance obligations, and site conditions specific to the Philippines. Clear planning at this point reduces risks and ensures alignment with operational goals.
Custom design and specification development follows. Layouts, structural details, insulation levels, and safety features are tailored to project requirements and local regulations. This phase ensures that buildings meet performance expectations while accommodating site-specific constraints.
Factory production is then carried out under controlled conditions. Whether producing complete modules or prefabricated components, this stage delivers consistent quality, minimizes material waste, and limits weather-related delays.
Once production is complete, units are delivered to the Philippines using coordinated logistics planning. On-site installation is performed efficiently, often within a short timeframe, enabling facilities to become operational with minimal disruption to surrounding activities.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Philippines
Thermal insulation plays an important role due to the country’s tropical climate. Proper insulation design supports indoor comfort and energy efficiency, particularly in high-temperature and high-humidity environments.
Fire safety standards must be integrated from the earliest design stage. Compliance with applicable local codes and project-specific safety requirements is essential for both temporary and permanent buildings.
Climate suitability extends beyond temperature. Resistance to heavy rainfall, strong winds, and coastal conditions influences material selection and structural engineering decisions, especially for long-term installations.
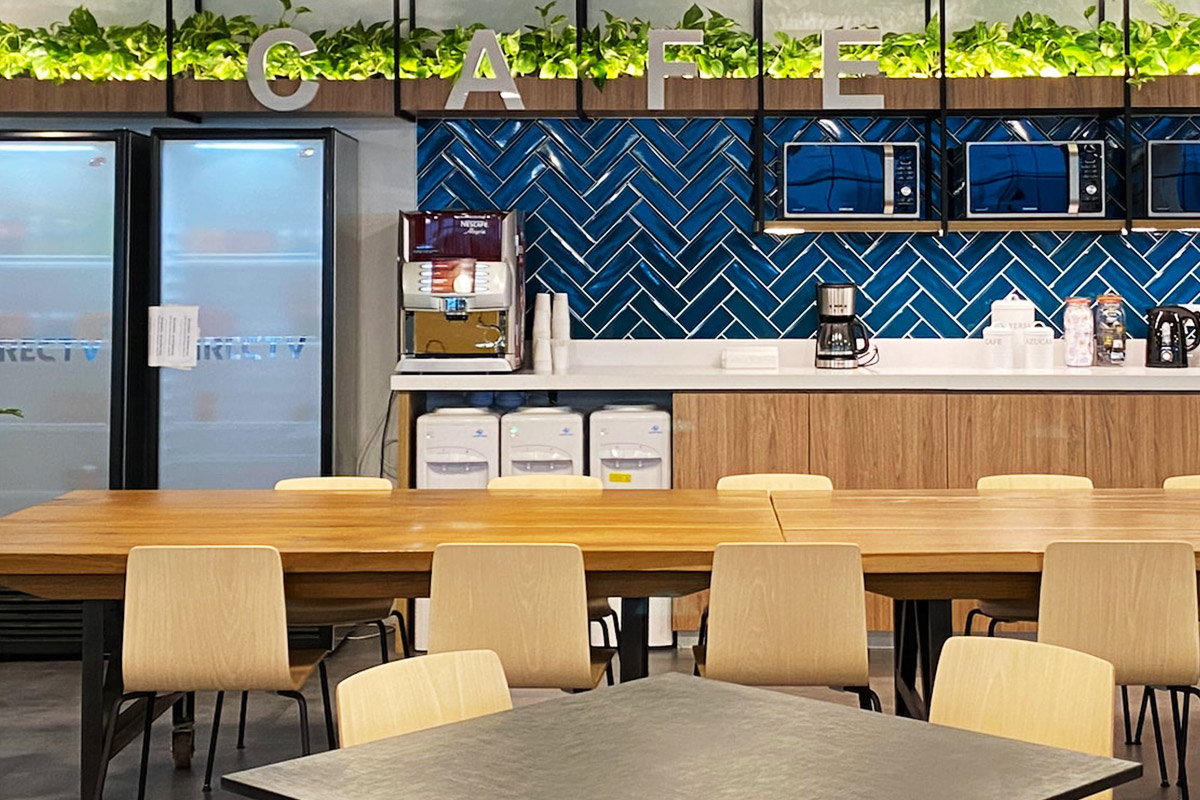
Custom layouts allow organizations to adapt buildings to operational workflows. Flexible interior planning ensures that offices, accommodation units, and technical spaces support productivity and efficient use of space.
With experience gained across multiple international markets, Karmod brings a practical understanding of how modular buildings and prefabricated building systems should be adapted to regional conditions. Drawing on its European project experience, Karmod develops modular building solutions that balance durability, speed, and functional efficiency while addressing the environmental and operational demands of the Philippines. This background provides confidence for organizations seeking reliable building solutions aligned with long-term planning rather than short-term construction constraints.