Romania has emerged as one of Eastern Europe’s most dynamic construction and investment markets. Rapid growth in logistics, manufacturing, energy infrastructure, and public projects has created a clear demand for building systems that are fast to deploy, cost-controlled, and reliable over the long term. In this environment, modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions are increasingly evaluated not as temporary alternatives, but as strategic construction methods aligned with modern project management and operational efficiency.
For international investors, EPC contractors, and public authorities operating in Romania, these systems offer a practical response to local market realities, including workforce availability, scheduling pressures, and evolving regulatory expectations.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Romania
Several structural factors explain why modular buildings have gained strong momentum across Romania.
Labor costs and workforce availability remain a decisive issue. While Romania continues to offer a competitive labor market compared to Western Europe, skilled construction labor has become more selective and less predictable. Modular construction reduces on-site labor dependency by shifting a significant portion of work to controlled factory environments.
Construction timelines are another key driver. Infrastructure upgrades, logistics hubs, and industrial zones often operate under strict delivery deadlines tied to financing, leasing agreements, or public tenders. Modular buildings allow parallel processes—site preparation and building production occurring simultaneously—helping projects reach operational readiness faster.
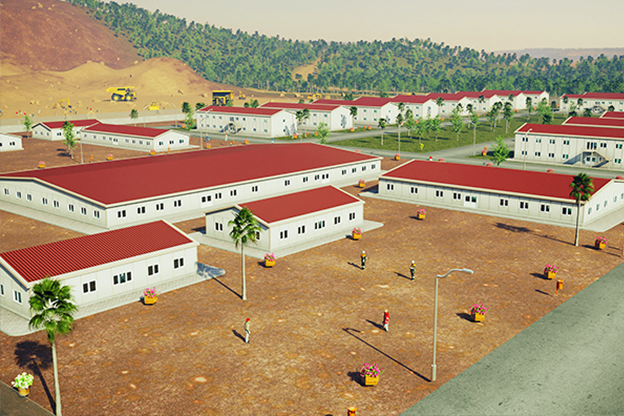
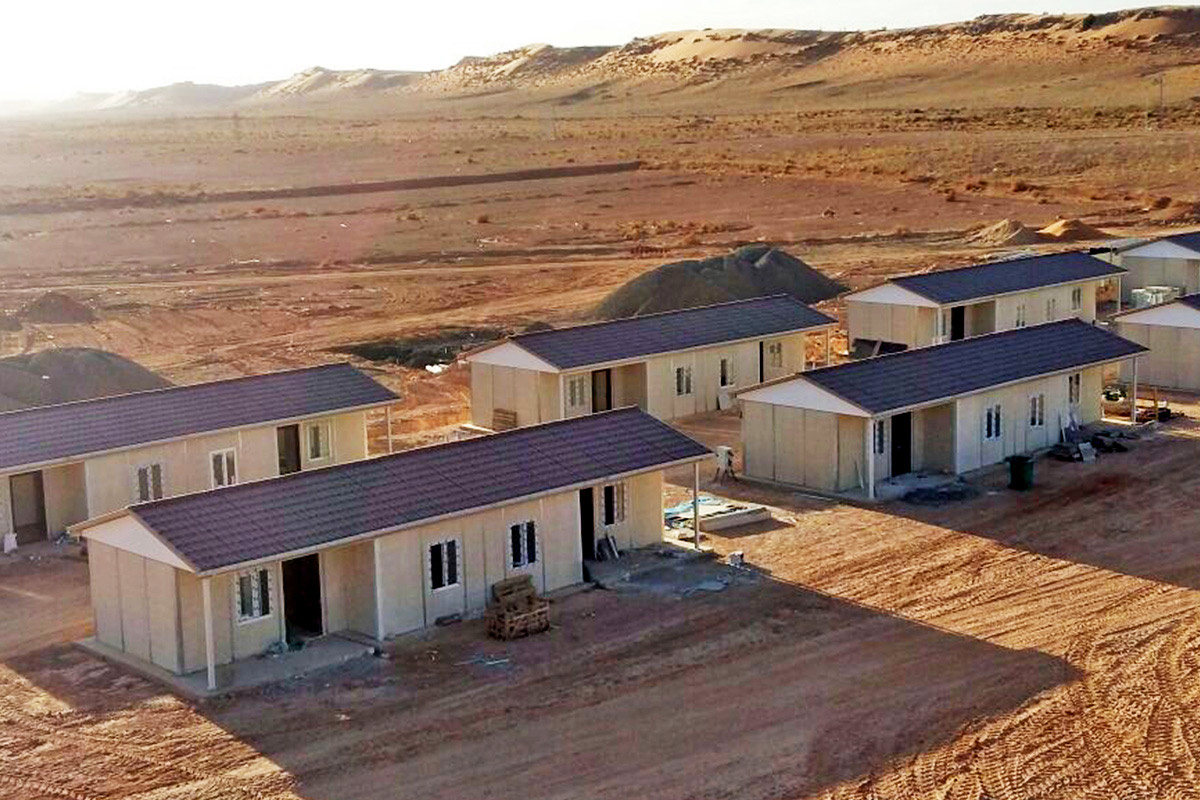
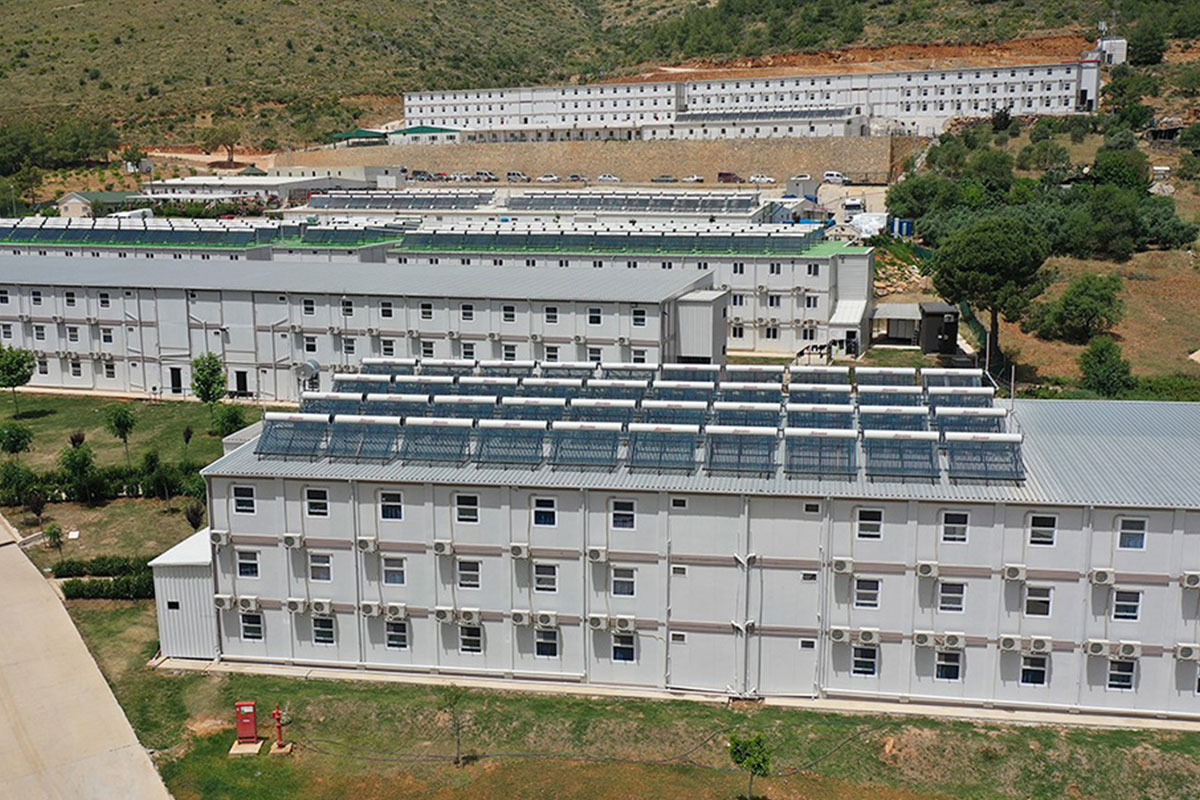
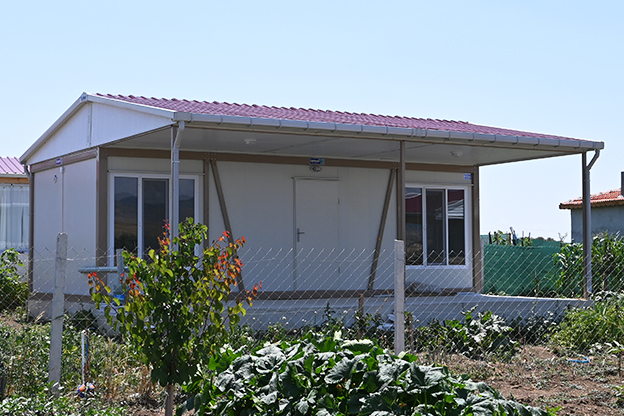
Romania also has a diverse need for both temporary and permanent structures. From short-term construction camps supporting highway and railway projects to long-term industrial facilities, decision-makers increasingly seek systems that can adapt to changing operational requirements.
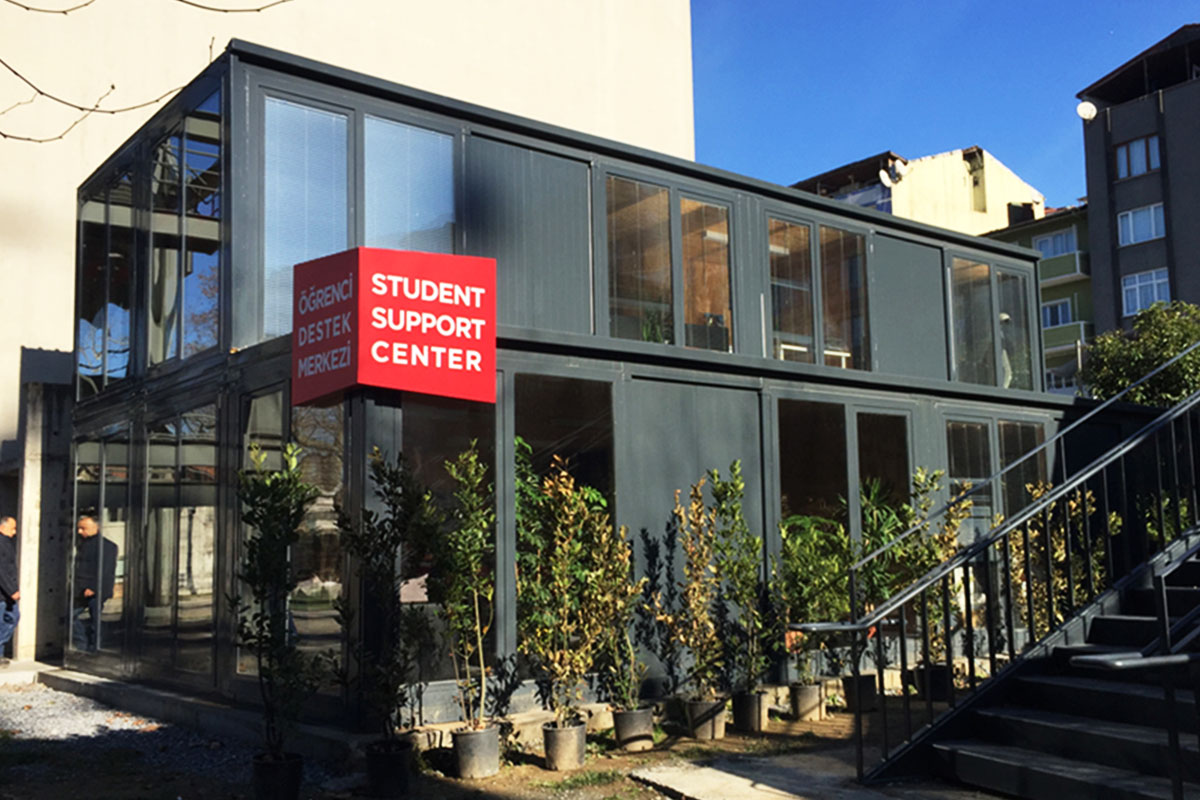
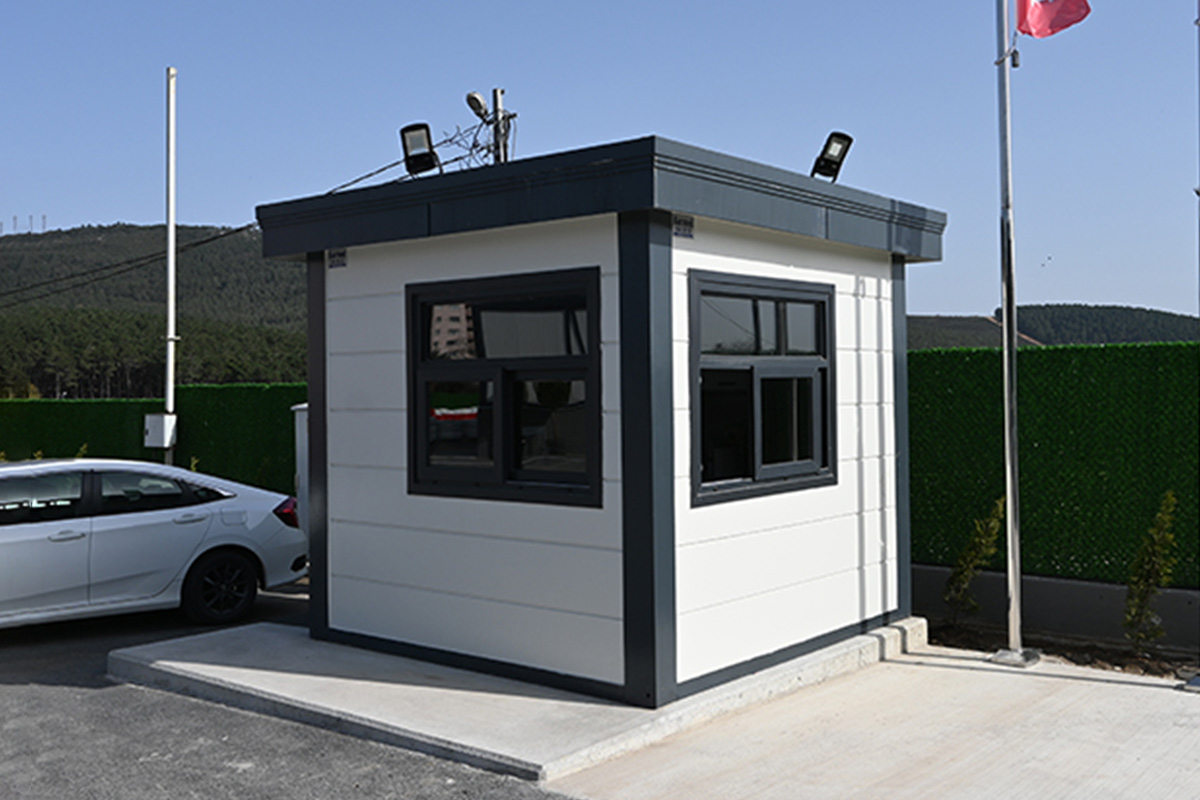
Sector-specific demand further reinforces this trend. Logistics and warehousing investments around Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, and Timișoara require scalable support buildings. Industrial manufacturing zones benefit from modular offices and technical units. Public sector projects, including education and healthcare, rely on fast-track solutions to respond to regional needs. Energy and infrastructure projects—particularly in renewables and transmission—require durable yet relocatable site facilities.
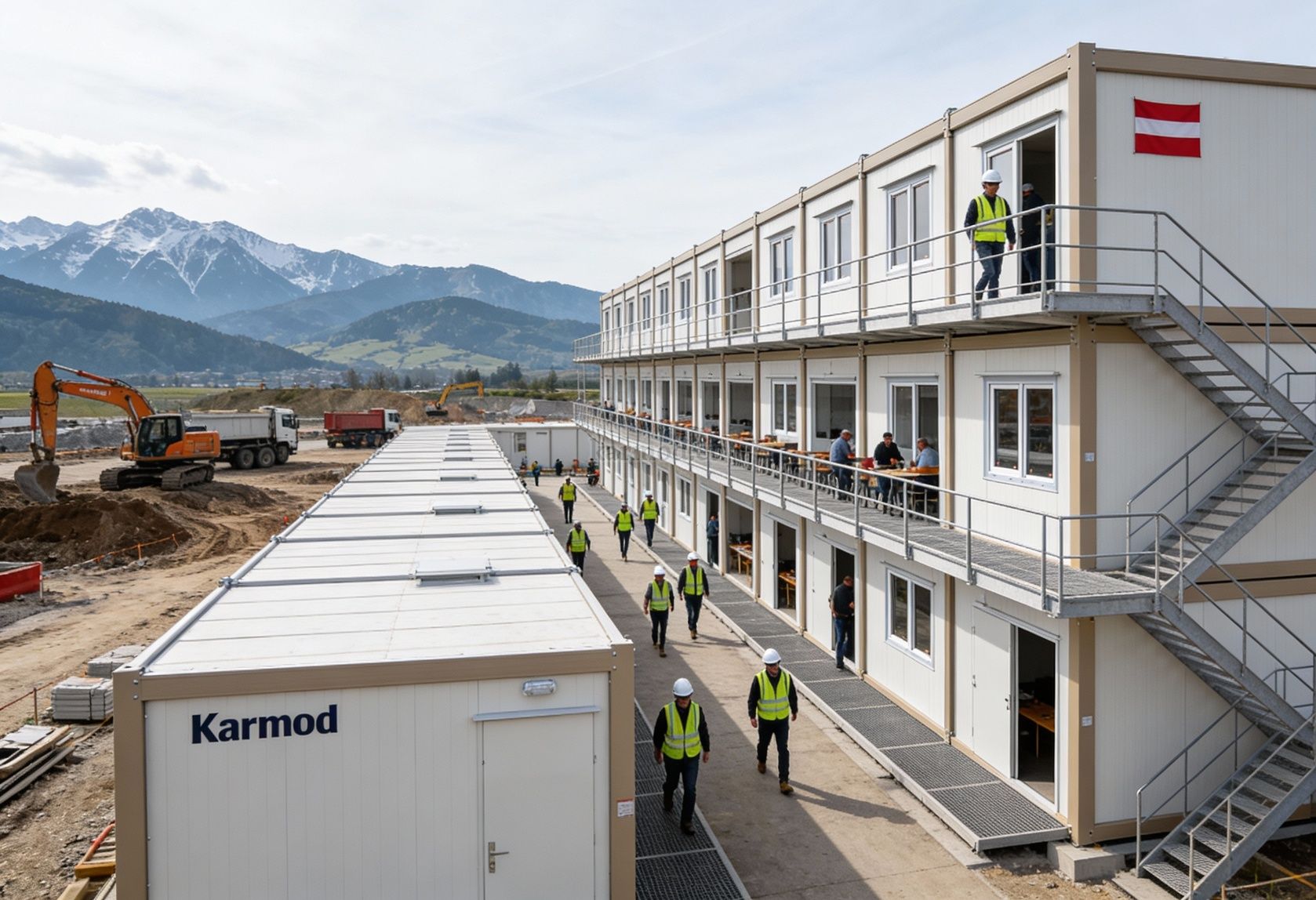

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
Although often discussed together, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve different functional priorities.
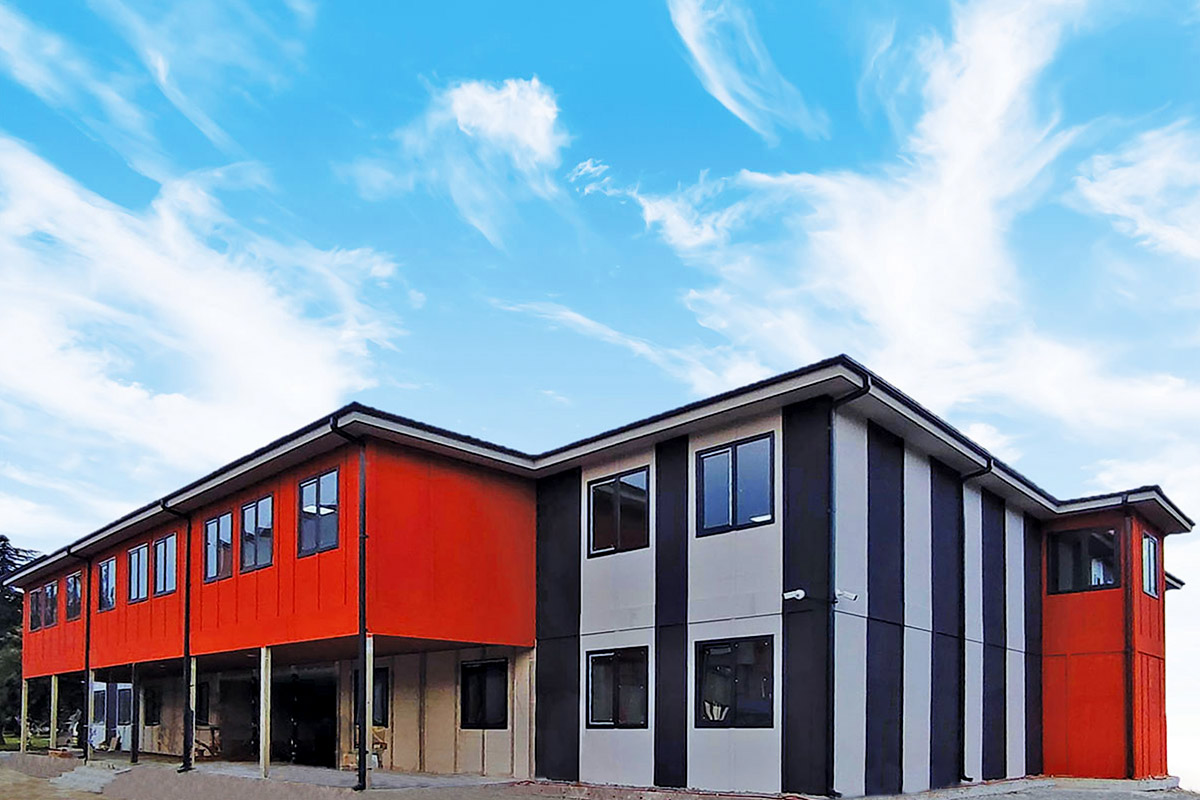
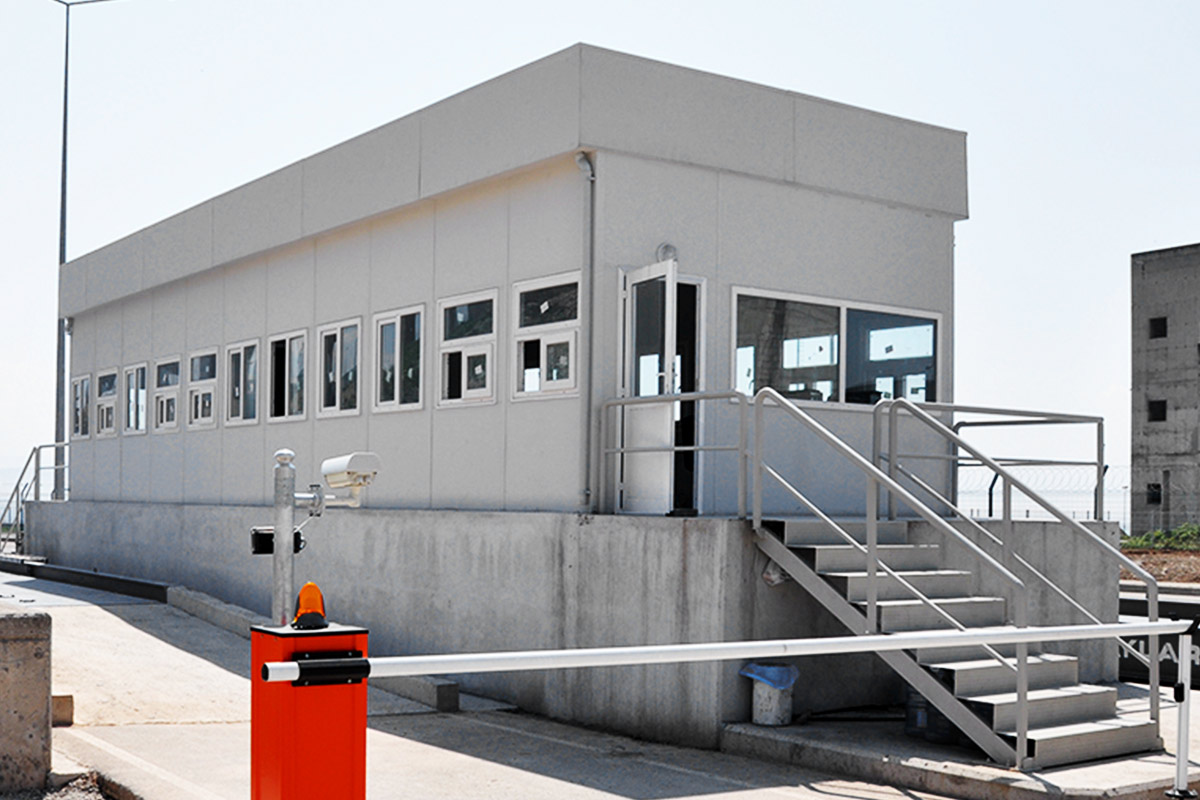
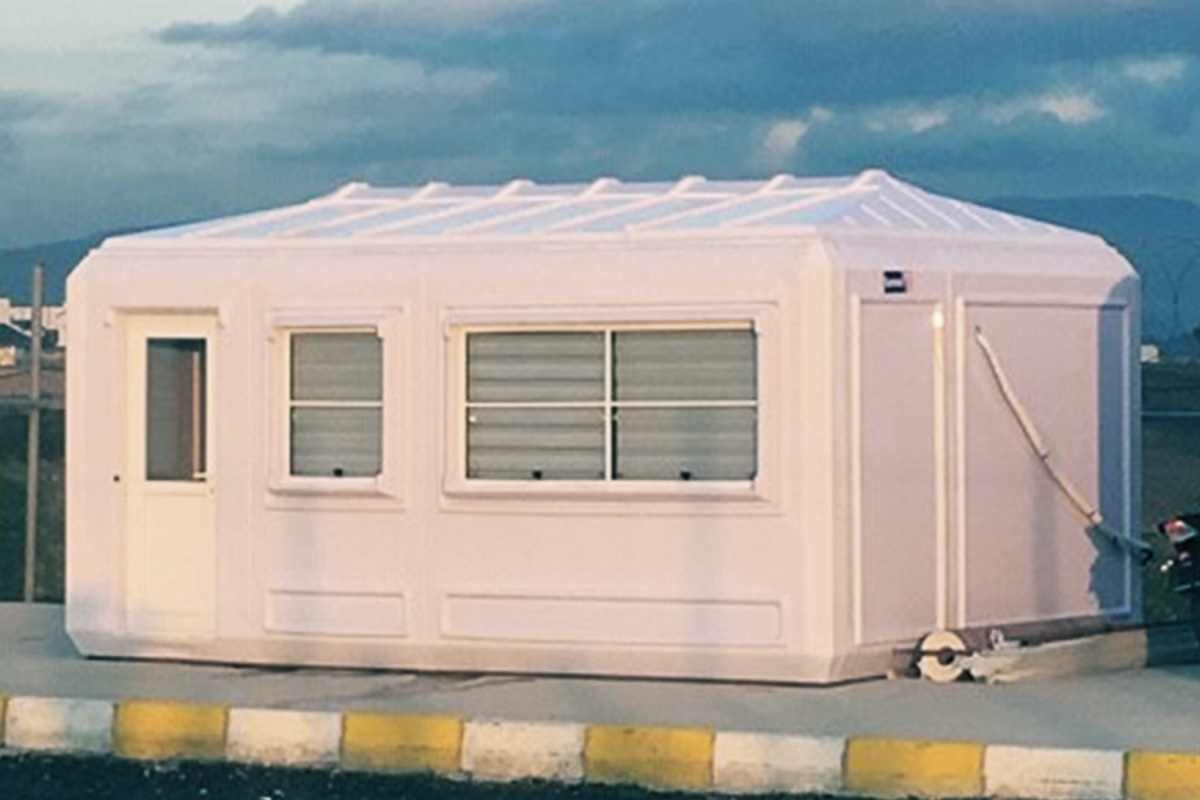
Modular buildings are based on volumetric modules produced in factories, transported to site, and assembled into complete structures. Their defining advantages include mobility, expandability, and flexibility. Units can be relocated, reconfigured, or expanded as operational needs evolve, making them suitable for projects with uncertain timelines or phased growth.
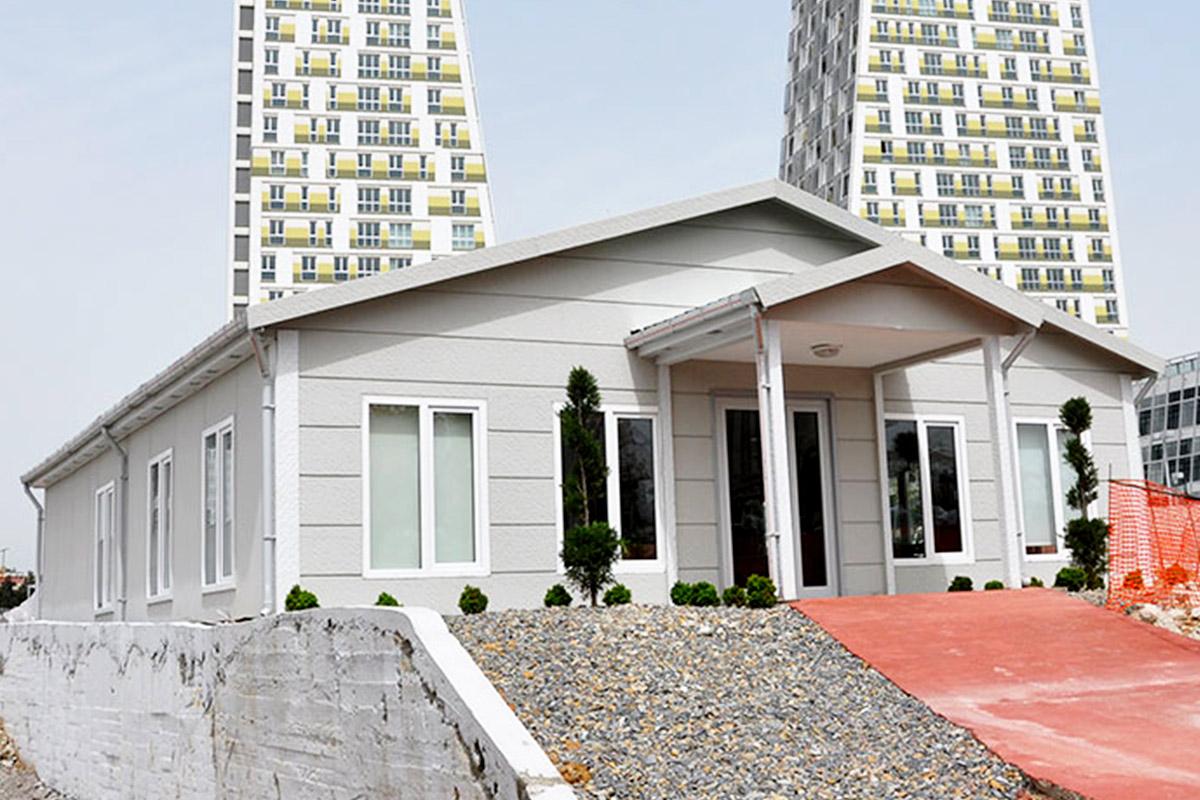
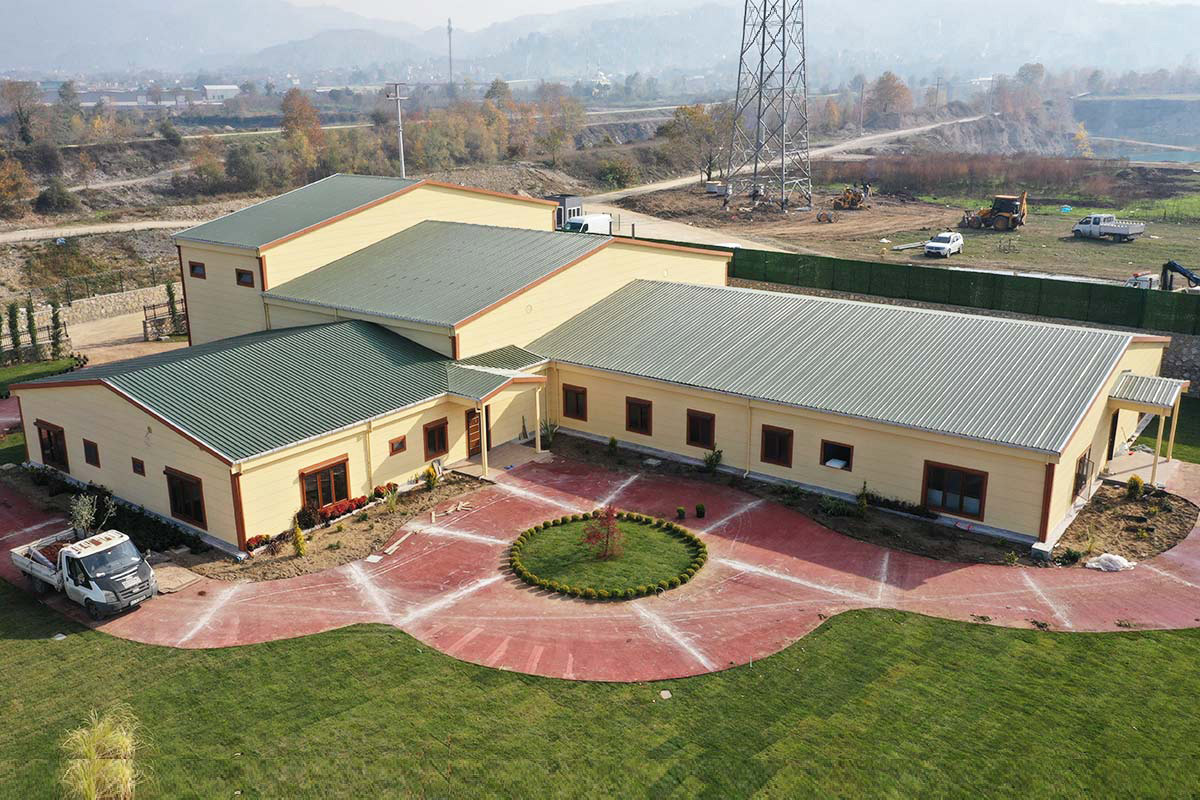
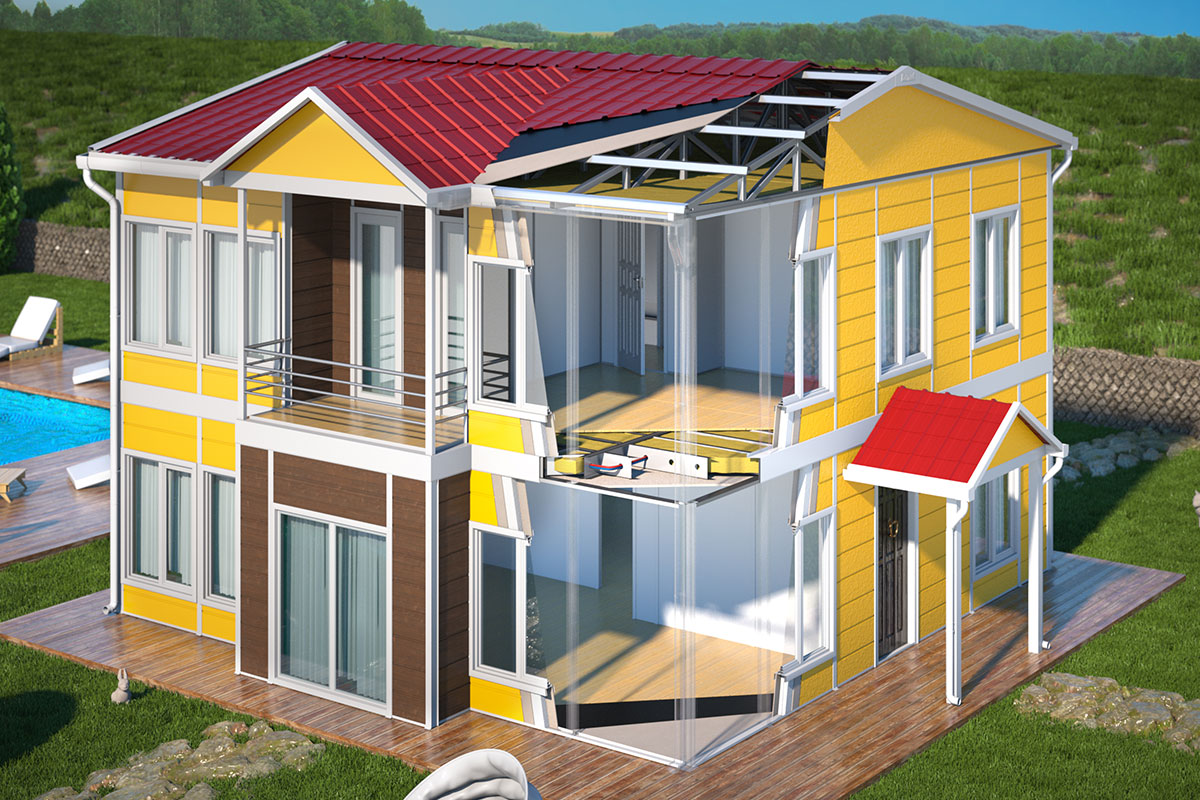
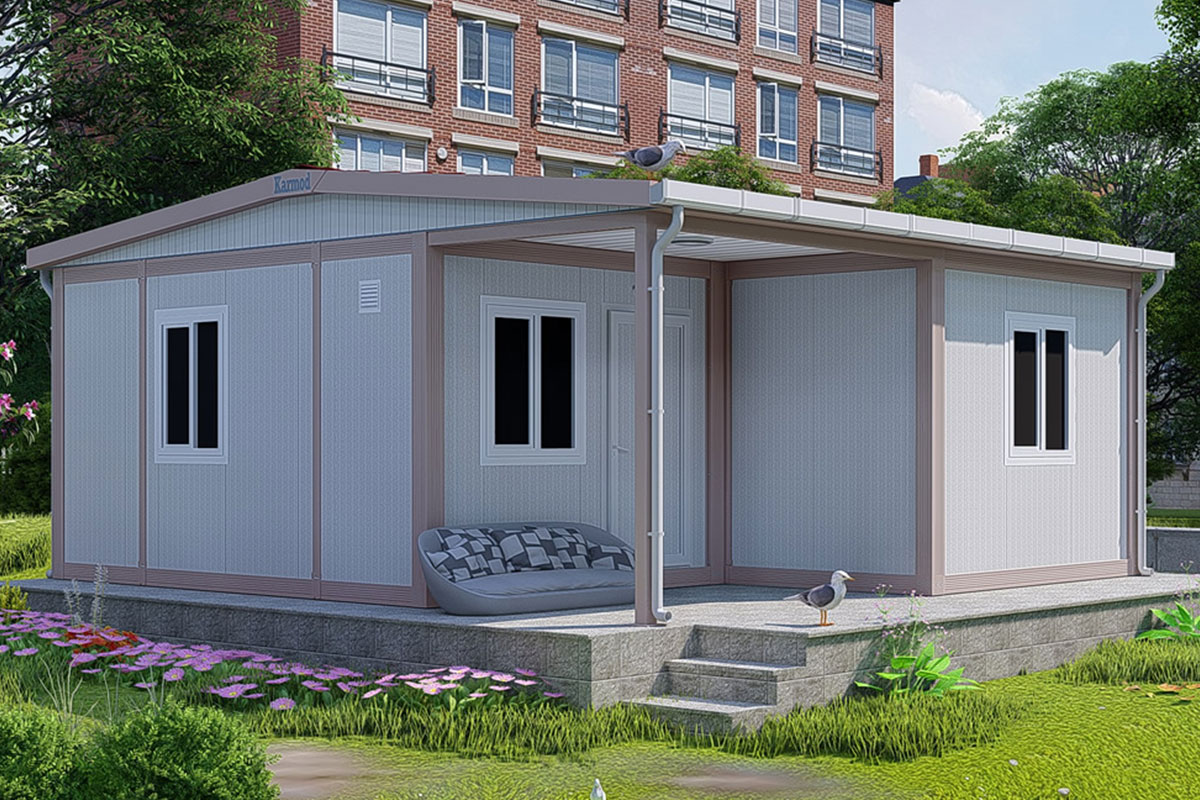
A prefabricated building, by contrast, is typically produced using panels or structural components that are assembled on site into a permanent structure. These systems are preferred when architectural continuity, long-term occupancy, and integration with existing infrastructure are the primary goals.
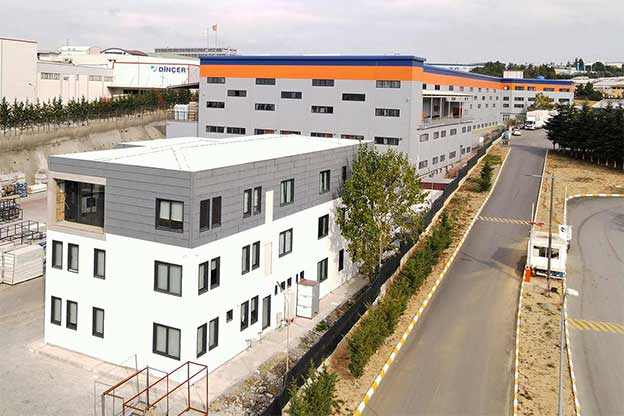
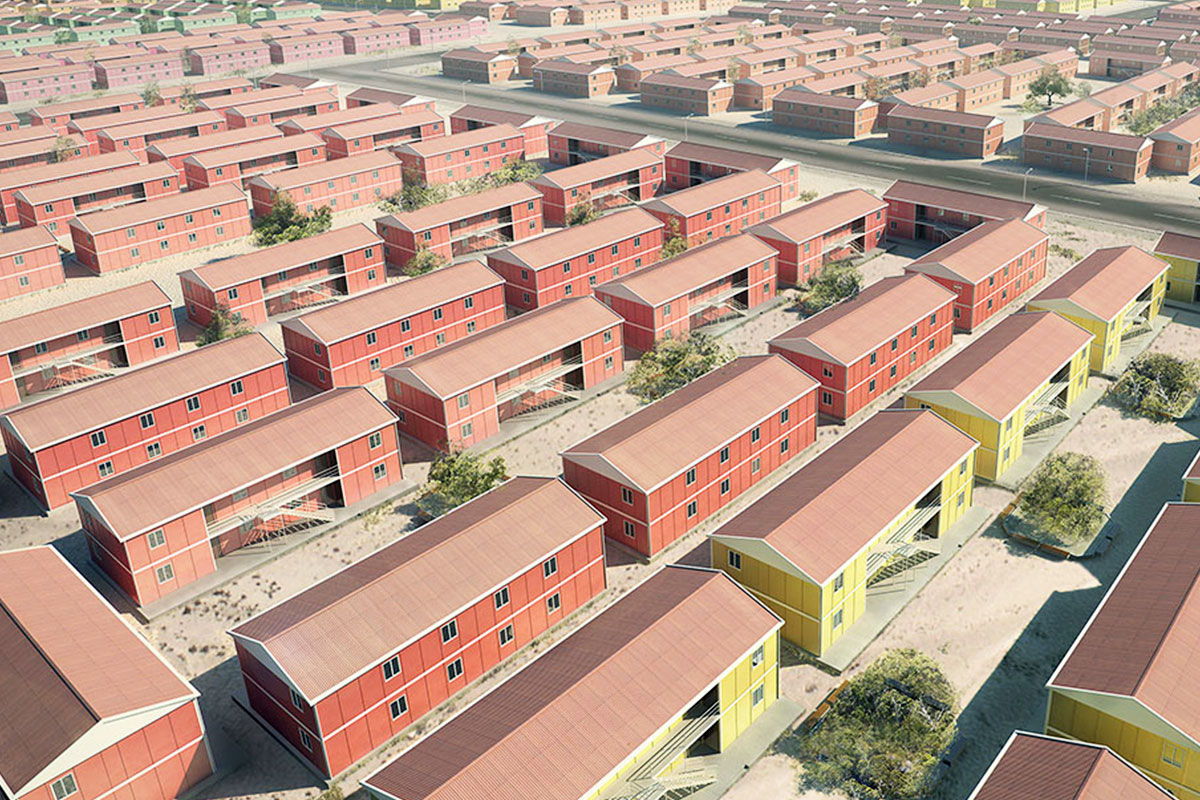
In Romania, modular buildings are often selected for logistics bases, construction projects, and energy sites where adaptability matters. Prefabricated building systems are more commonly used for permanent industrial facilities, schools, and administrative buildings where long-term use and architectural integration are essential.
Understanding this distinction allows project owners to align the building method with operational and financial objectives rather than treating both systems as interchangeable.
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Romania
Across Romania, these building systems are applied in a wide range of professional contexts:
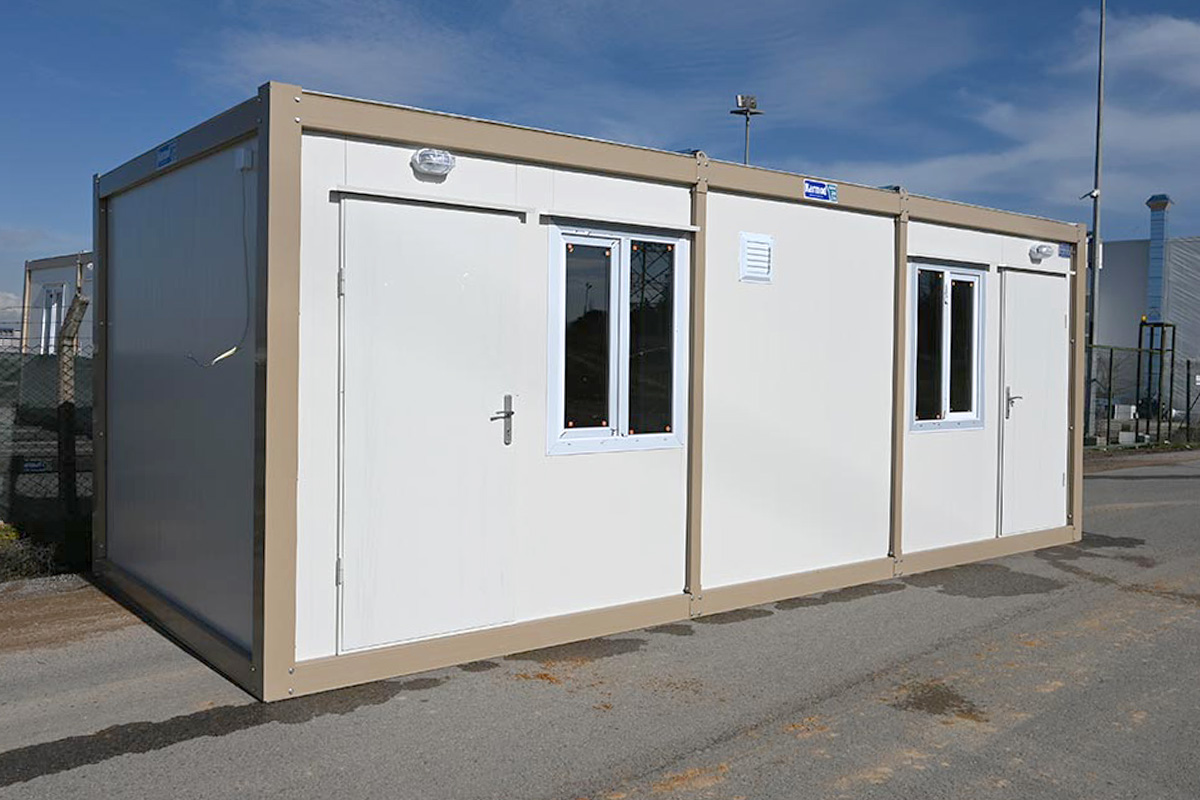
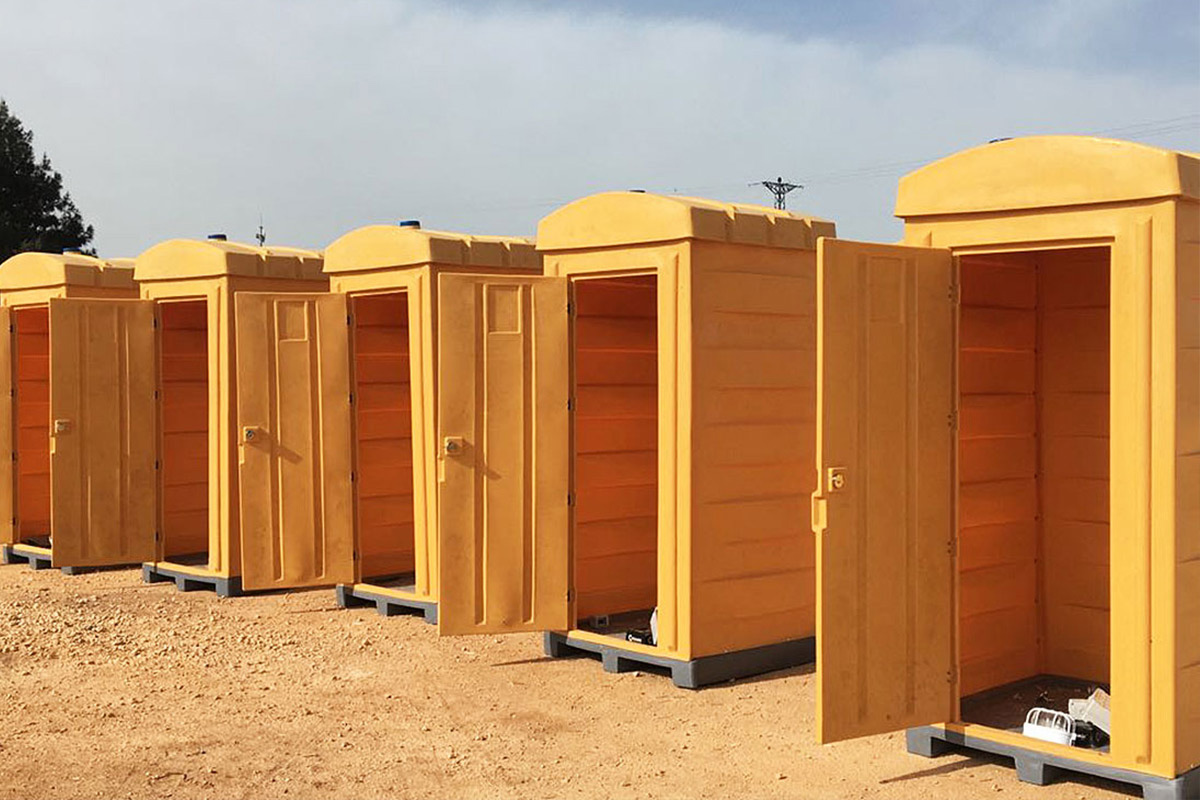
- Site offices and construction camps supporting infrastructure, road, and industrial developments
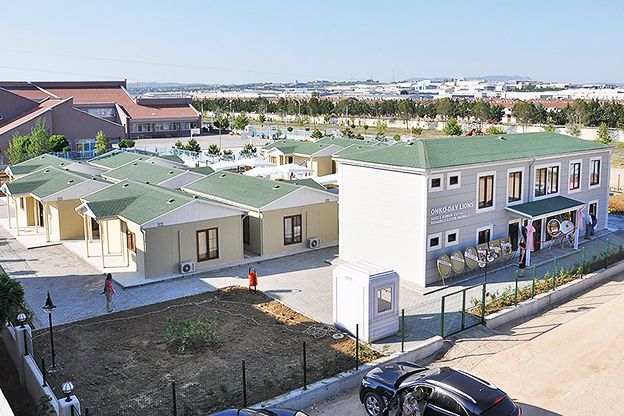
- Worker accommodation buildings designed for comfort, compliance, and efficient land use
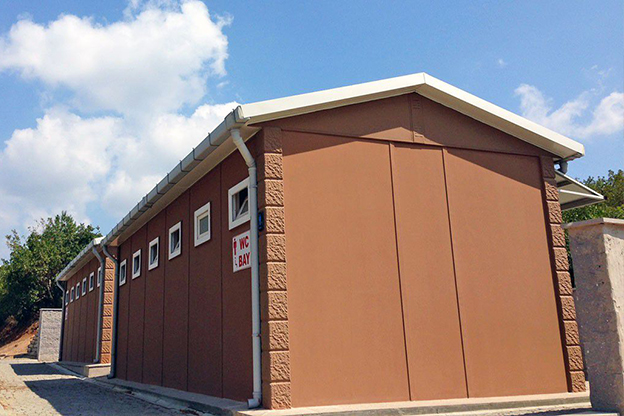
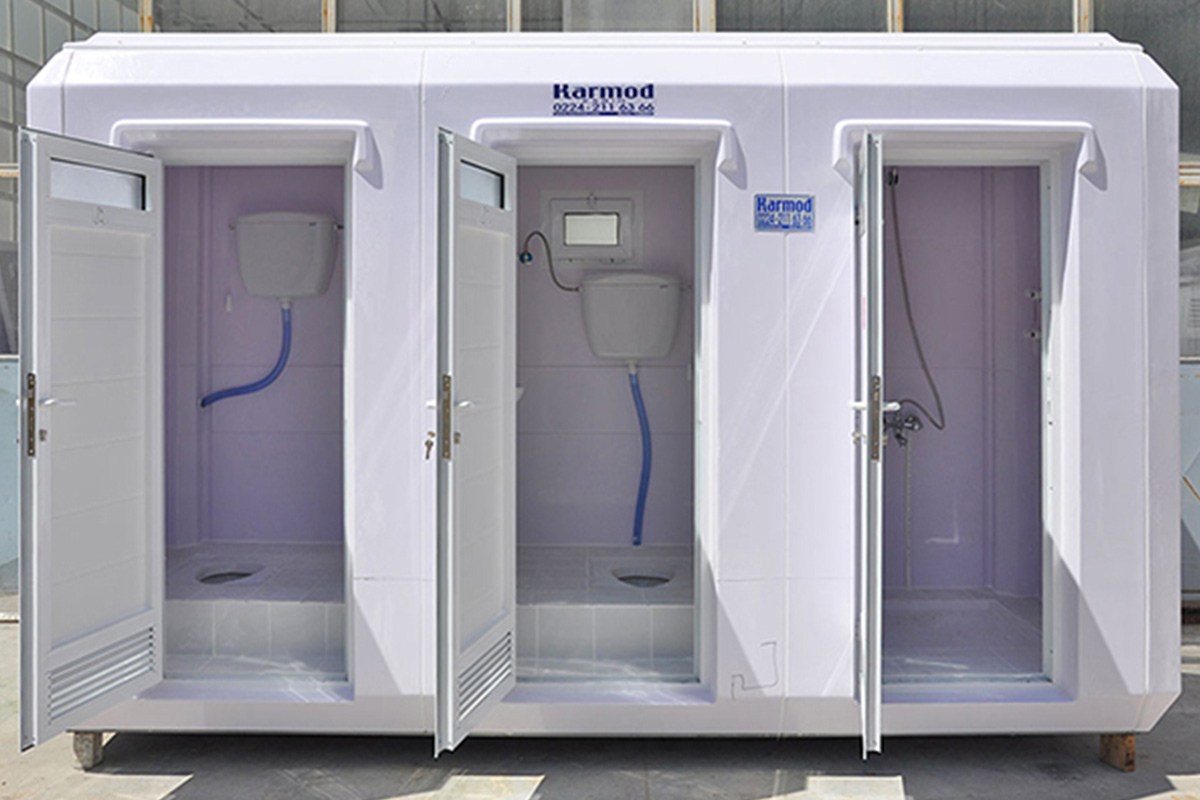
- Temporary schools and healthcare units addressing regional capacity needs
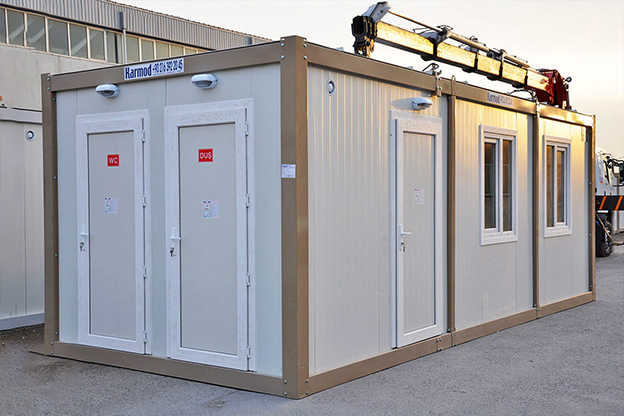
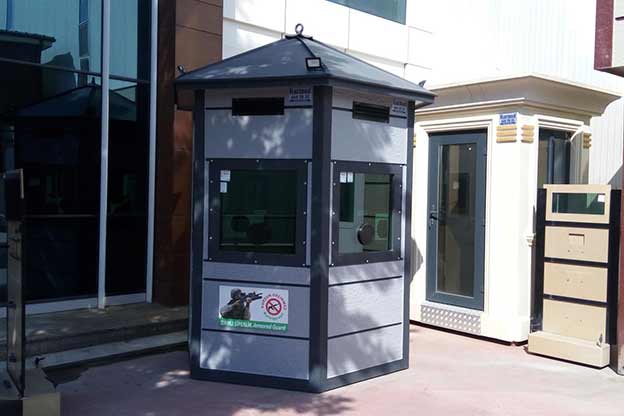
- Security buildings and technical units for controlled access, monitoring, and operations
- Storage and logistics facilities supporting distribution and industrial workflows
These applications demonstrate how modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions integrate into core business and public service operations rather than functioning as peripheral structures.
From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
A structured process is critical to achieving predictable outcomes in Romania’s regulatory and operational environment.
The process begins with project needs analysis, where operational requirements, occupancy levels, and technical standards are clearly defined. This stage ensures alignment with local regulations and site conditions.
Custom design and specifications follow, translating functional needs into layout plans, material selections, and compliance criteria. Climate considerations, insulation levels, and fire safety requirements are addressed at this stage.
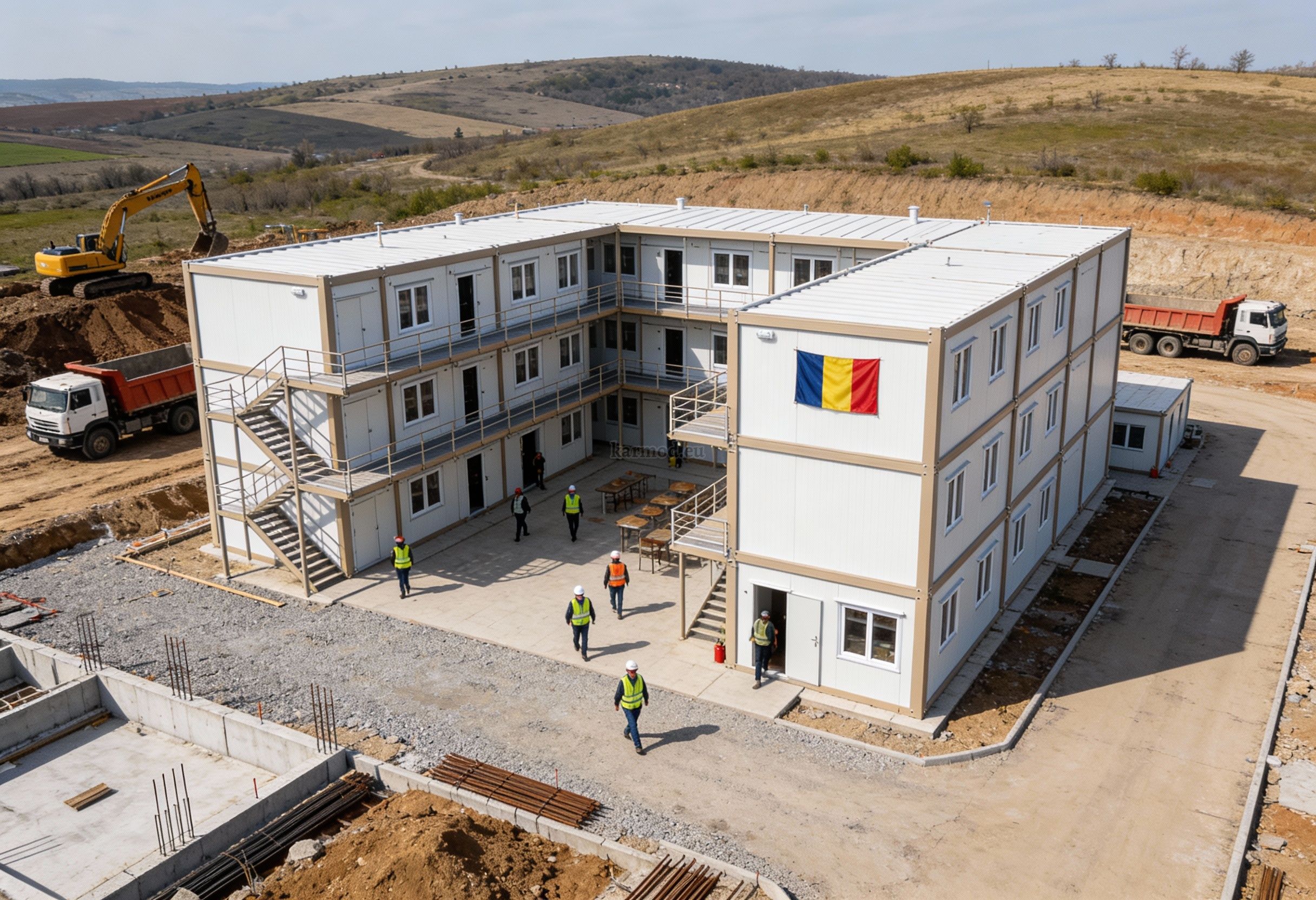
Factory production then takes place under controlled conditions, ensuring consistent quality and reduced material waste. This phase minimizes delays caused by weather or on-site constraints.
Delivery to Romania is coordinated with site readiness to avoid storage or handling inefficiencies. Logistics planning plays a critical role, particularly for large-scale modular deployments.
On-site installation completes the process. Assembly is typically fast and predictable, enabling buildings to become operational shortly after delivery.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Romania
Thermal insulation: Romania’s continental climate, with cold winters and warm summers, makes insulation performance a critical factor affecting energy efficiency and operating costs.
Fire safety standards: Compliance with national regulations and sector-specific requirements is essential, particularly for public and industrial buildings. Certified materials and documented compliance are required for approvals.
Climate suitability: Beyond insulation, roof design, moisture resistance, and ventilation strategies must be adapted to regional conditions.
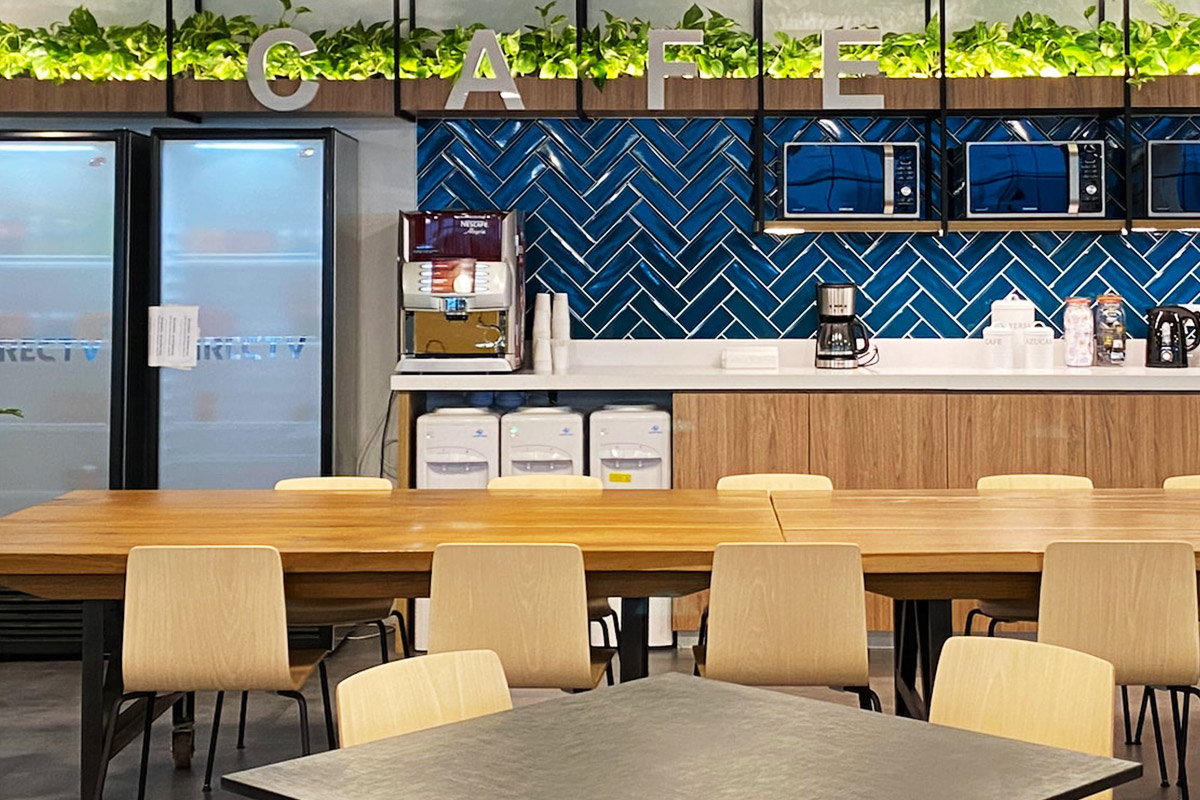
Custom layouts: Organizations increasingly demand buildings tailored to workflow efficiency rather than standardized templates. Flexible interior planning improves long-term usability.
In this context, Karmod has developed an approach shaped by extensive experience across Europe. Karmod modular building solutions are designed to meet diverse regulatory frameworks while maintaining consistent quality standards. Drawing on its European project background, Karmod supports clients in Romania with solutions that balance speed, durability, and functional clarity.
For decision-makers evaluating construction strategies in Romania, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems represent a practical alignment of time, cost, and performance. When applied with a clear understanding of local needs and professional execution, they become integral assets within modern project development frameworks.