Sierra Leone is experiencing a gradual but steady transformation in its construction and infrastructure landscape. Public investment programs, international development projects, mining activities, logistics corridors, and energy initiatives are creating a consistent demand for fast, reliable, and cost-controlled building solutions. In this environment, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems are increasingly viewed as practical tools for delivering facilities without the delays and uncertainties of conventional construction.
For project owners, contractors, and institutional decision-makers in Sierra Leone, the priority is clear: structures that can be delivered on time, perform reliably under local climate conditions, and adapt to both temporary and long-term operational needs. Modular and prefabricated approaches align well with these expectations, particularly in regions where logistics planning and workforce availability play a decisive role.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Sierra Leone
One of the main drivers behind the adoption of modular buildings in Sierra Leone is workforce cost optimization. Skilled construction labor is often limited outside major urban centers, and mobilizing large teams to remote sites can significantly increase project expenses. Modular systems reduce on-site labor requirements by shifting most of the production process to controlled factory environments.
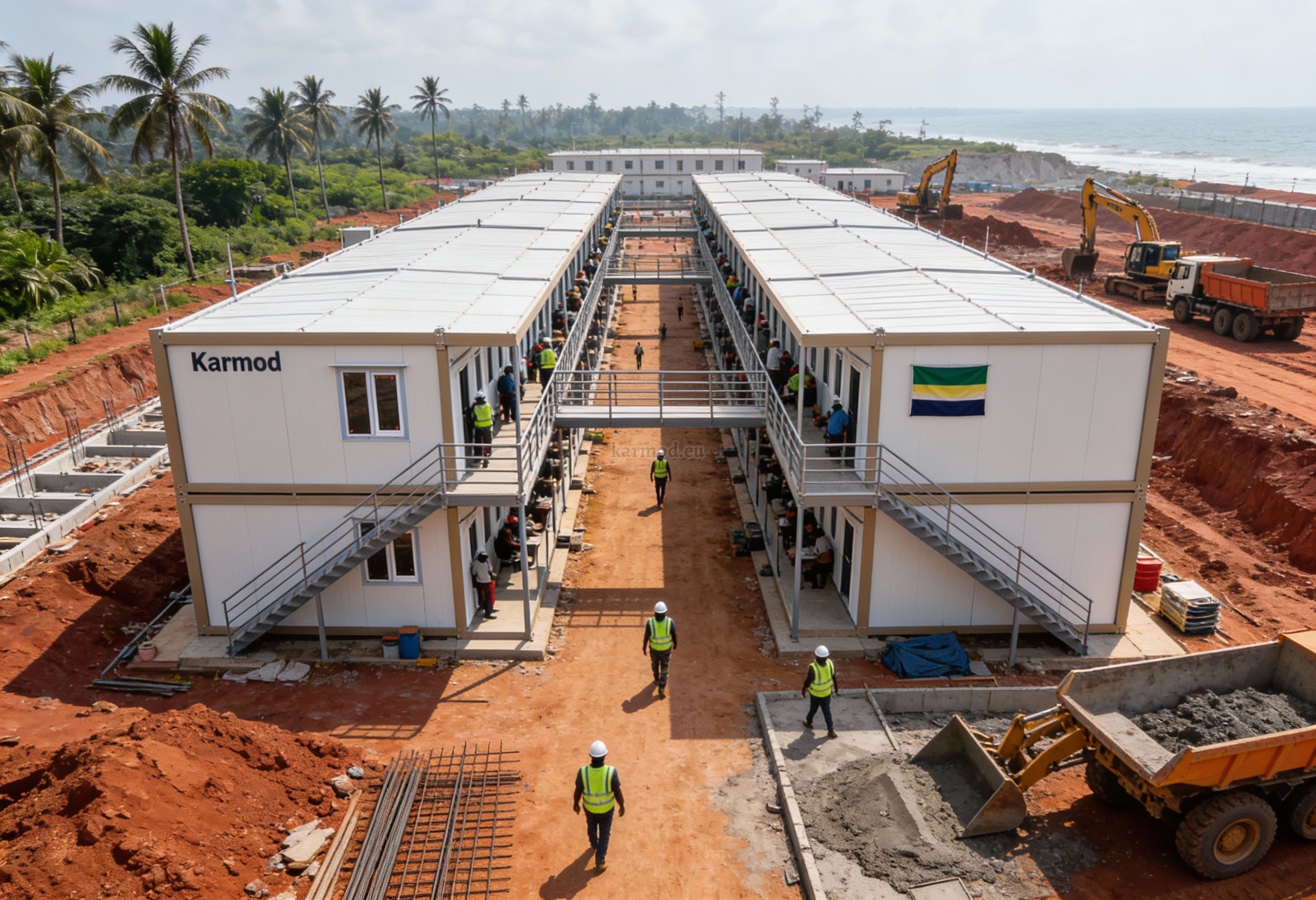
Construction timelines are another critical factor. Traditional building methods can be slowed by weather conditions, material supply disruptions, or site accessibility challenges. Modular buildings shorten project schedules by allowing parallel processes: while site preparation is underway, building modules are manufactured off-site. This approach is particularly valuable for projects linked to mining operations, energy facilities, and logistics hubs, where delays directly affect operational continuity.
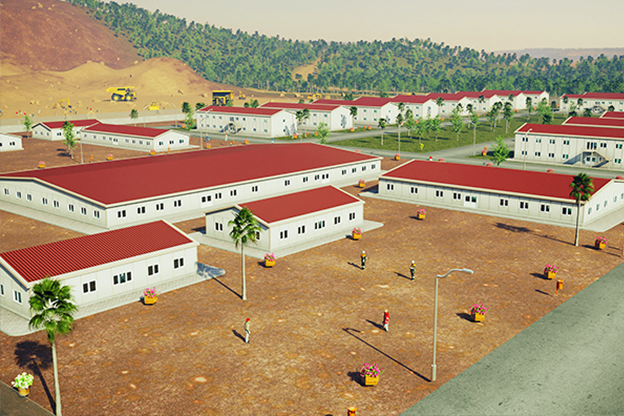
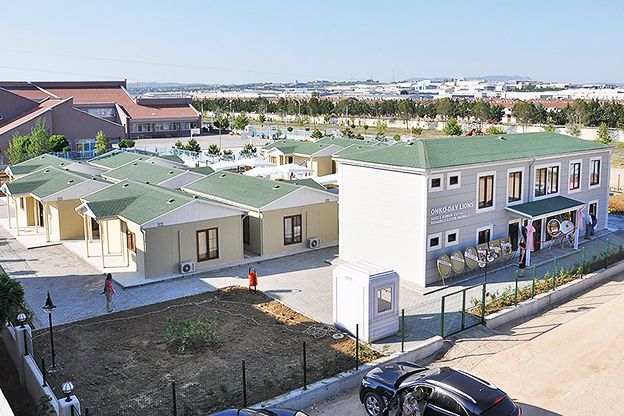
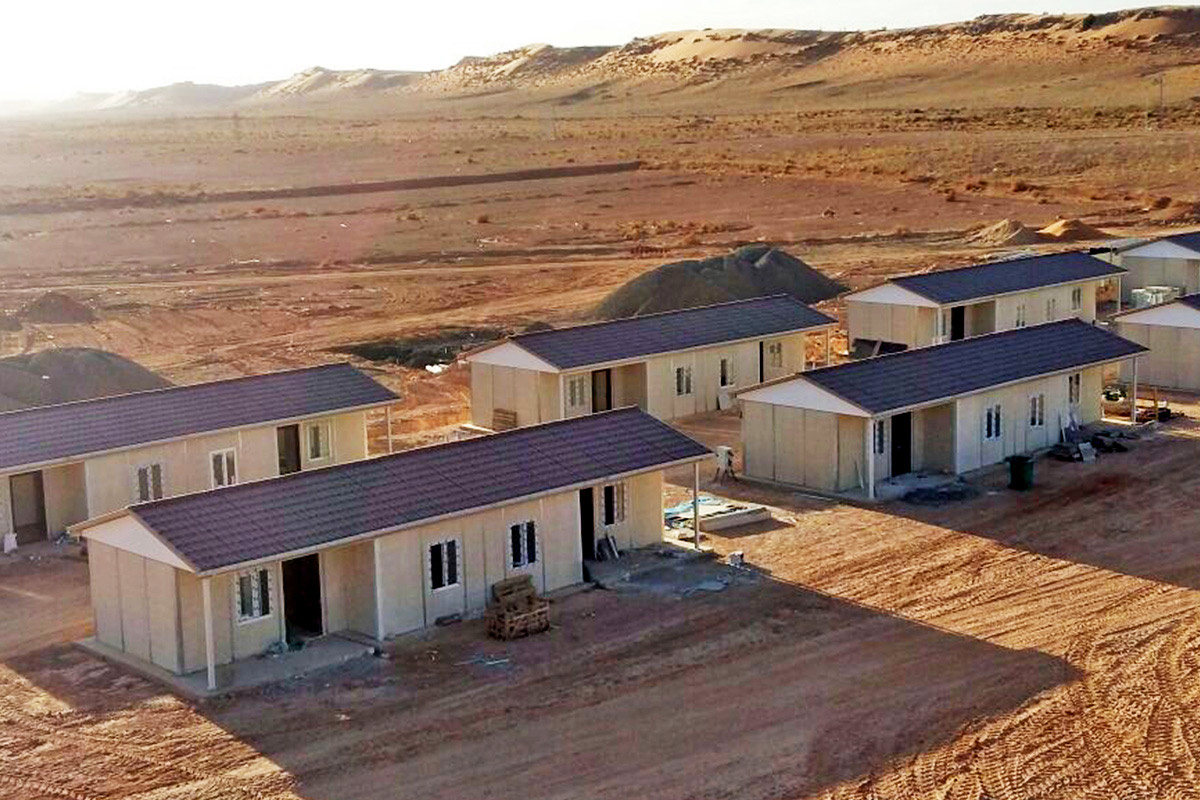
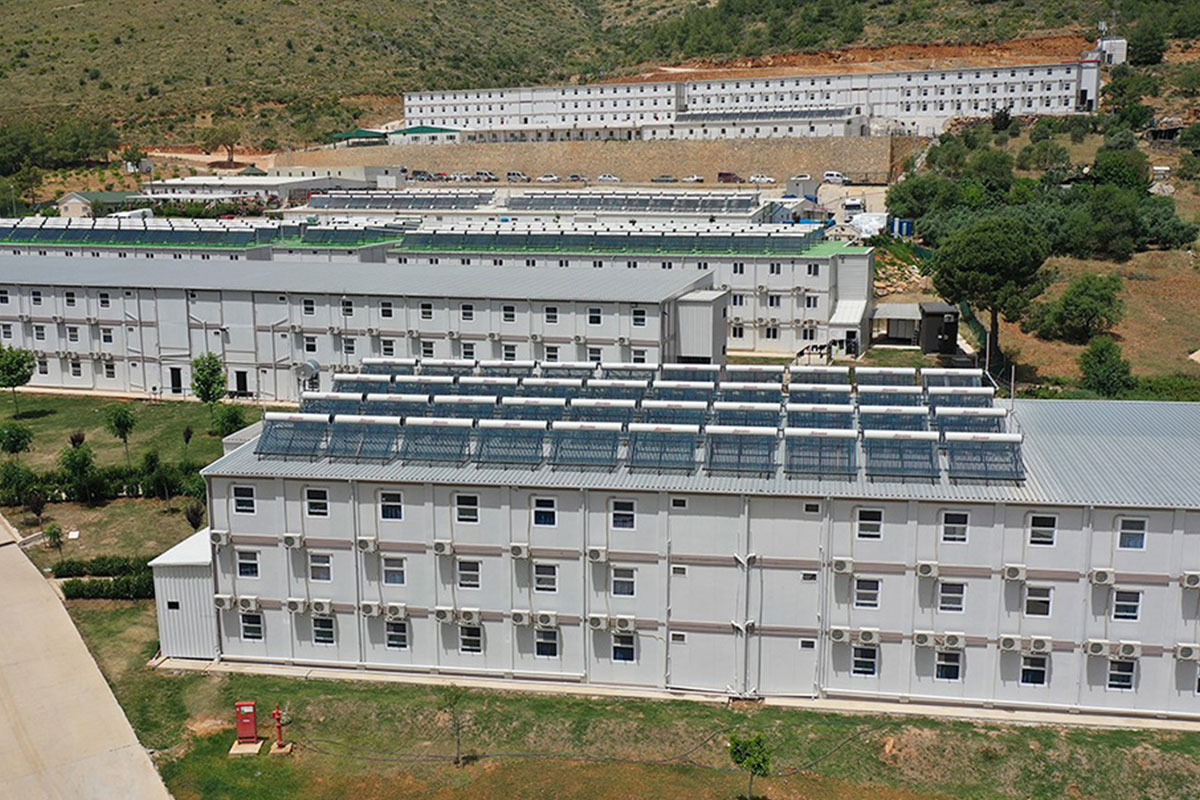
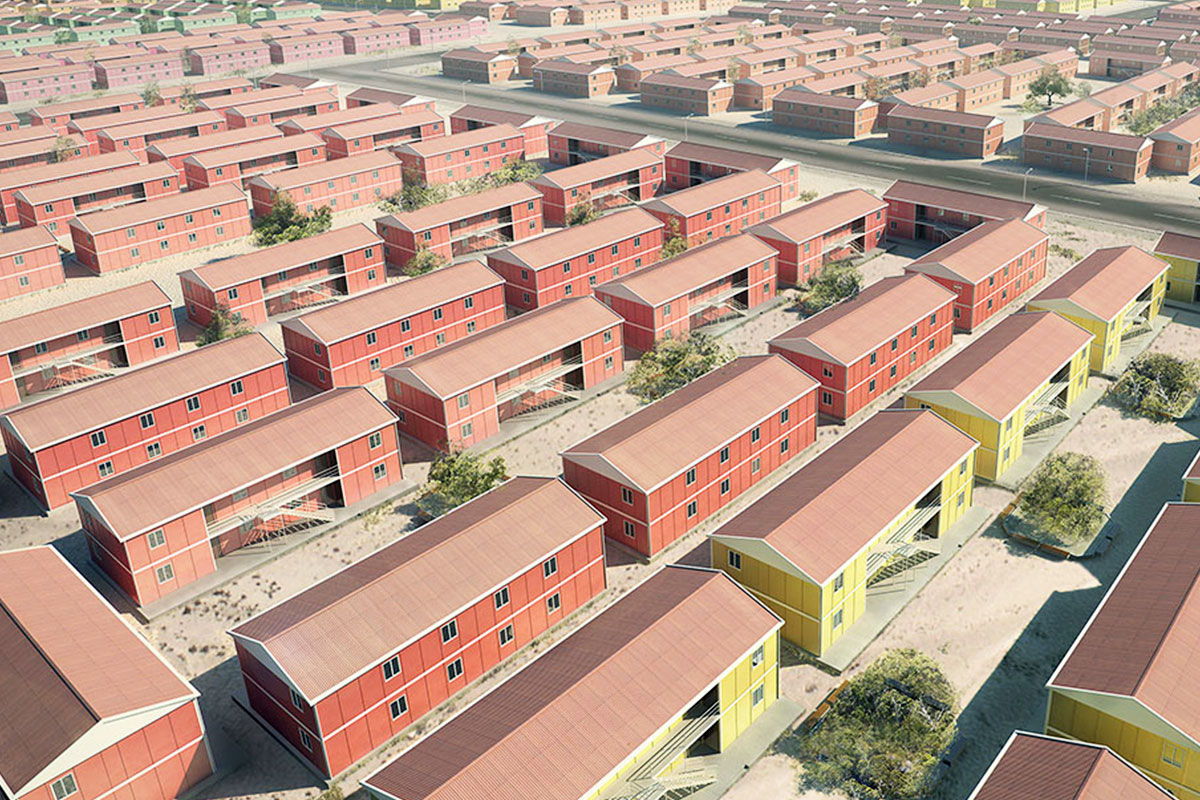
The need for both temporary and permanent structures is also shaping demand. Sierra Leone hosts numerous projects that require rapid deployment of site offices, worker accommodation, and technical units during construction phases, followed by long-term facilities once operations are stabilized. Modular buildings support this transition, as units can be relocated, expanded, or reconfigured as project requirements evolve.
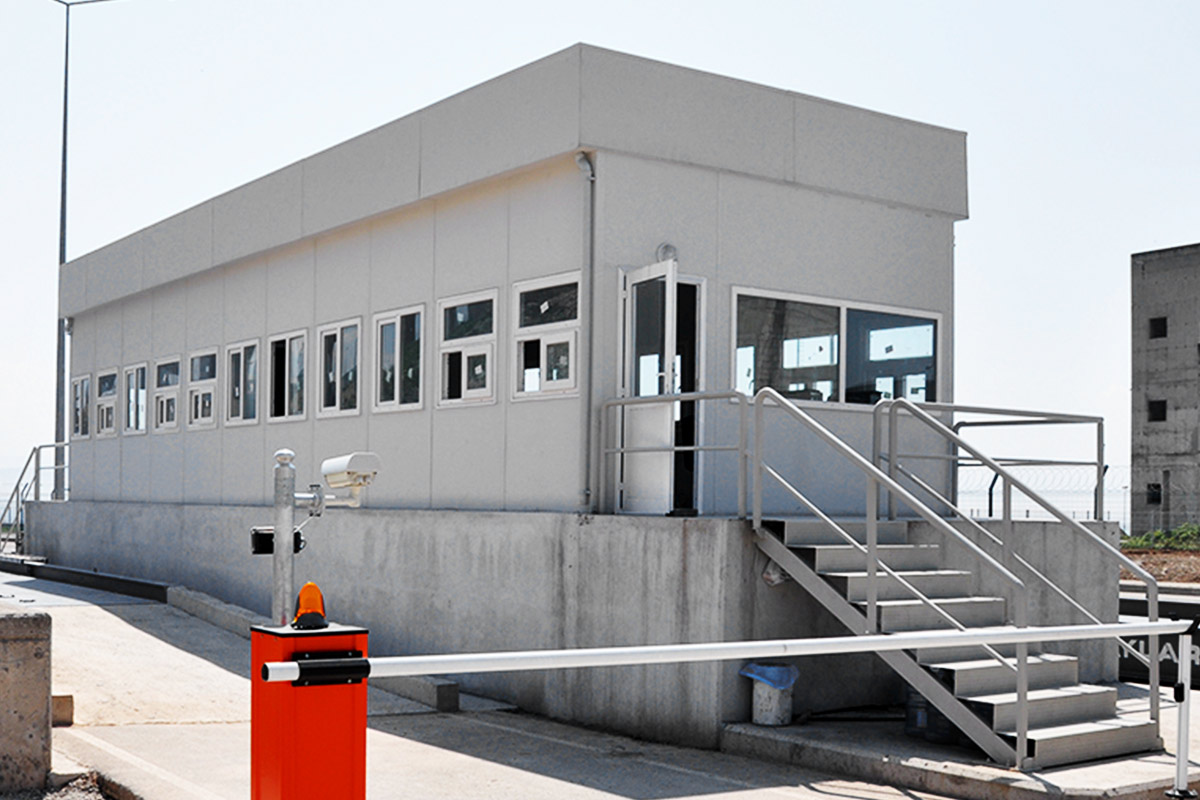
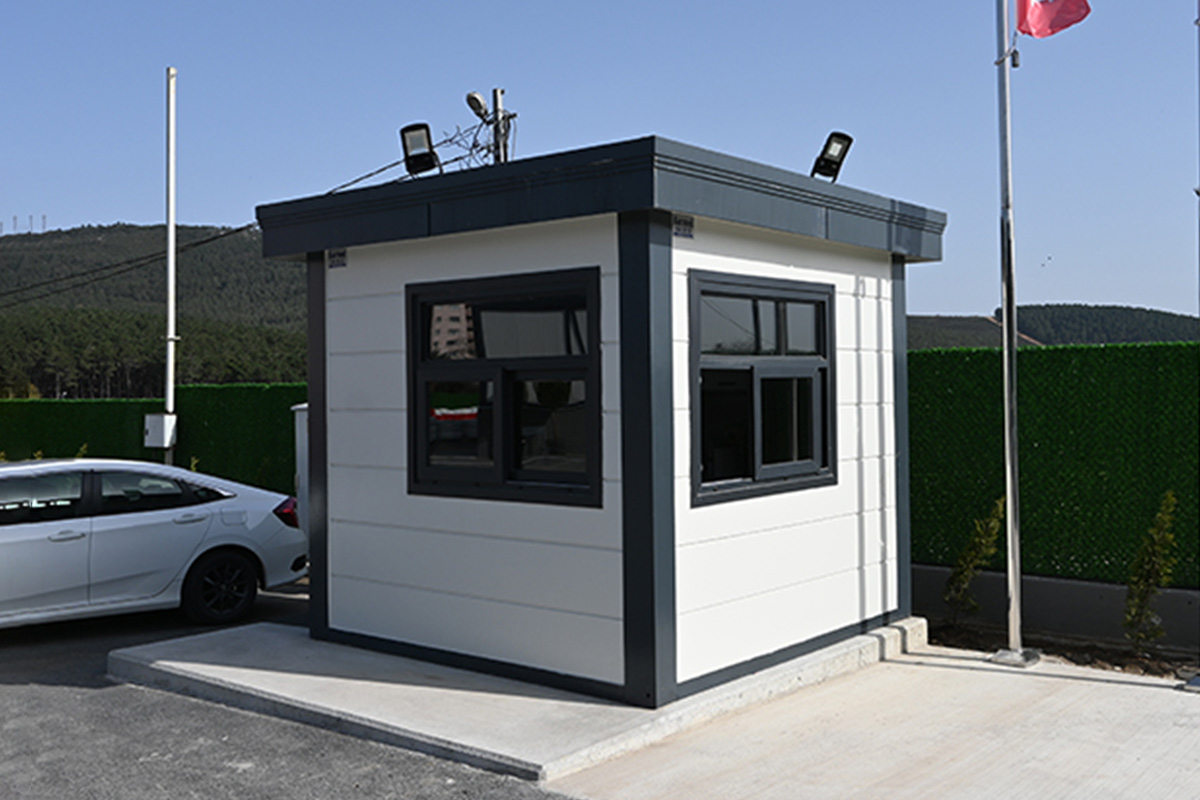
Sector-specific demand further reinforces this trend. Mining and mineral processing projects require robust accommodation and operational buildings near extraction zones. Public-sector initiatives in healthcare and education often need facilities that can be deployed quickly in underserved regions. Energy and infrastructure projects depend on technical buildings that meet safety and performance standards while remaining flexible. In these contexts, modular construction provides a balanced solution.
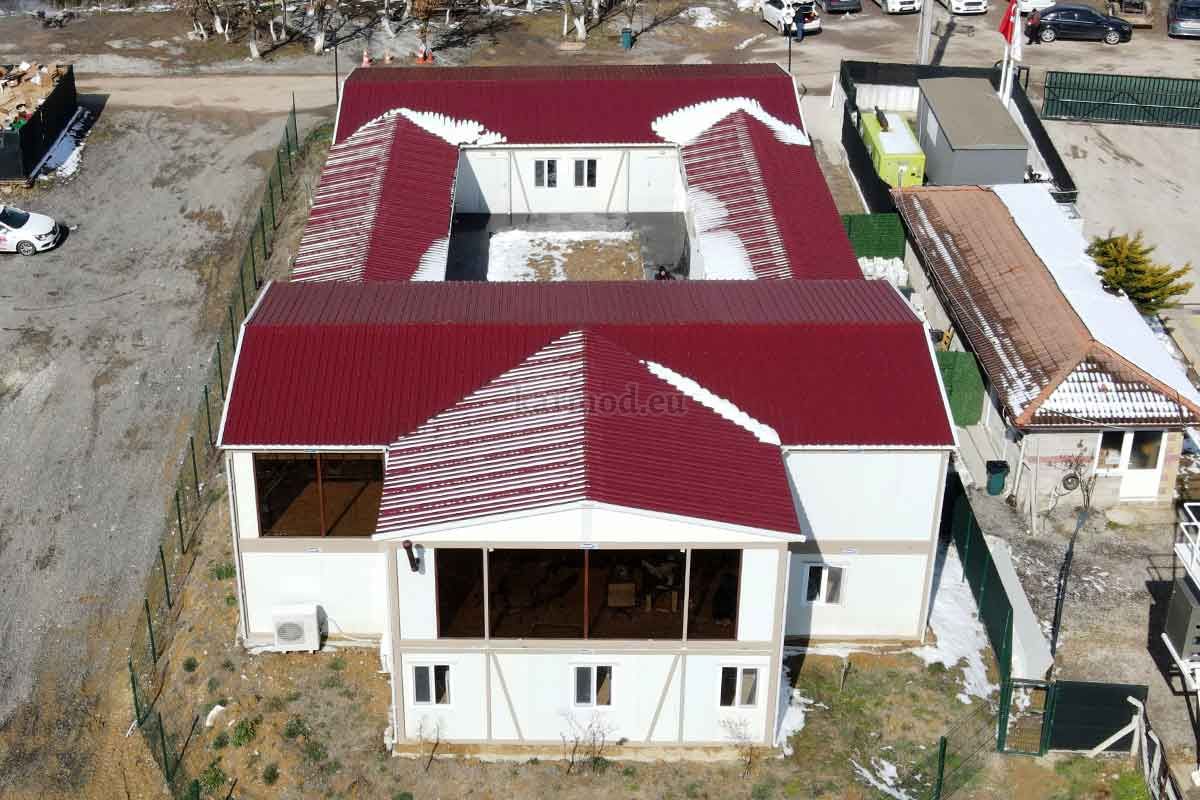

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
While modular buildings and prefabricated building systems are often mentioned together, they serve different functional priorities and project scenarios.
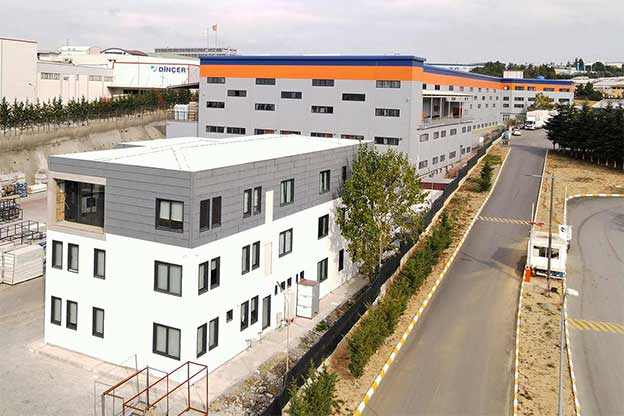
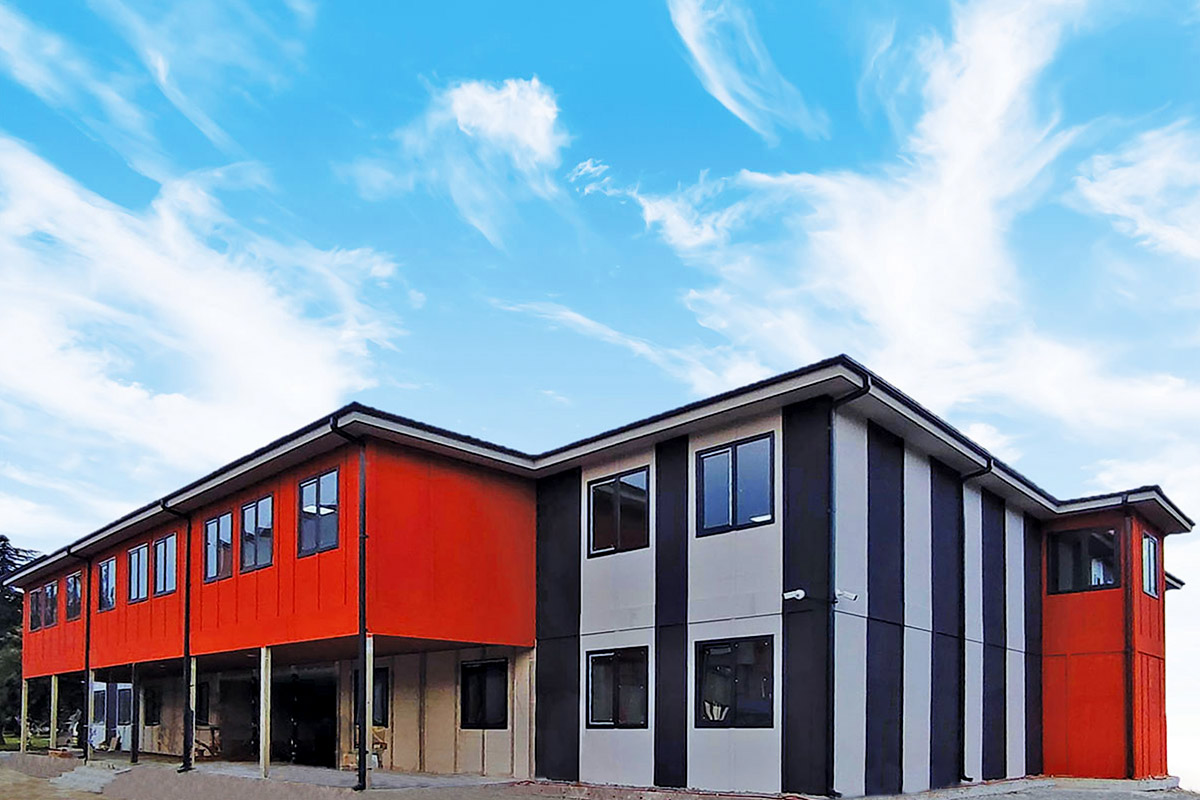
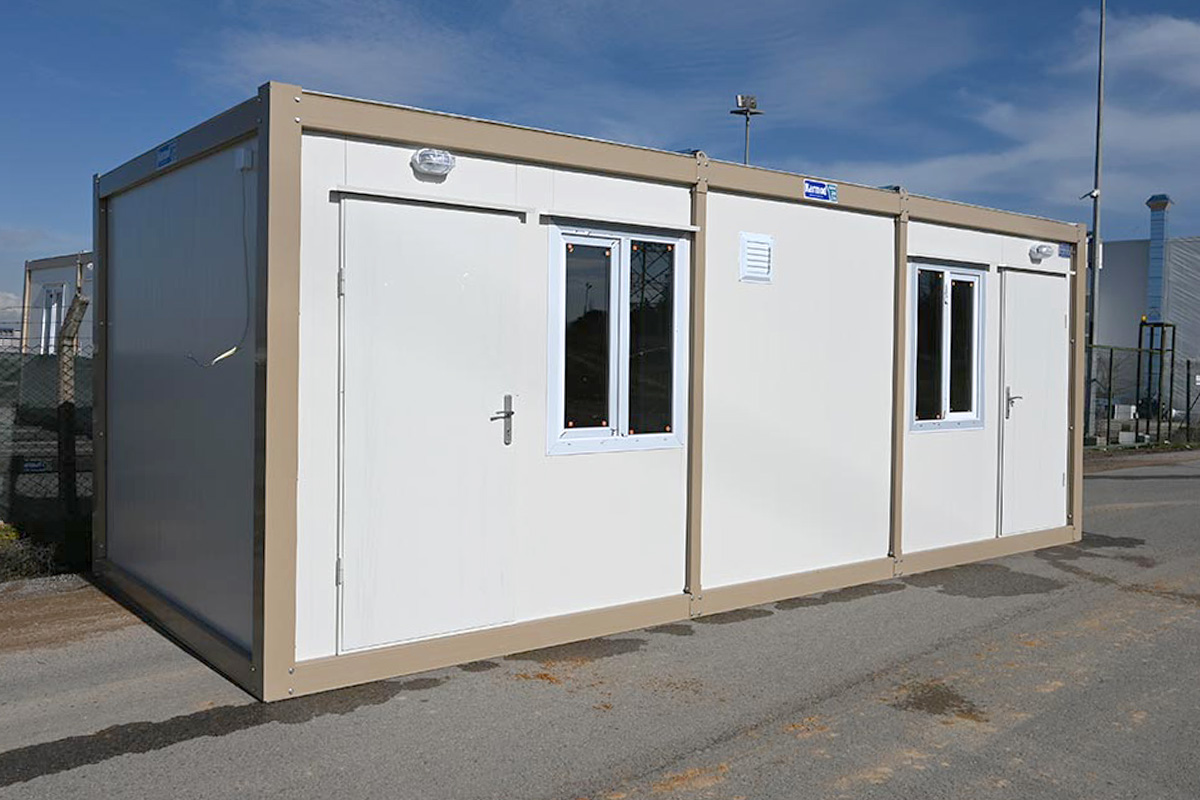
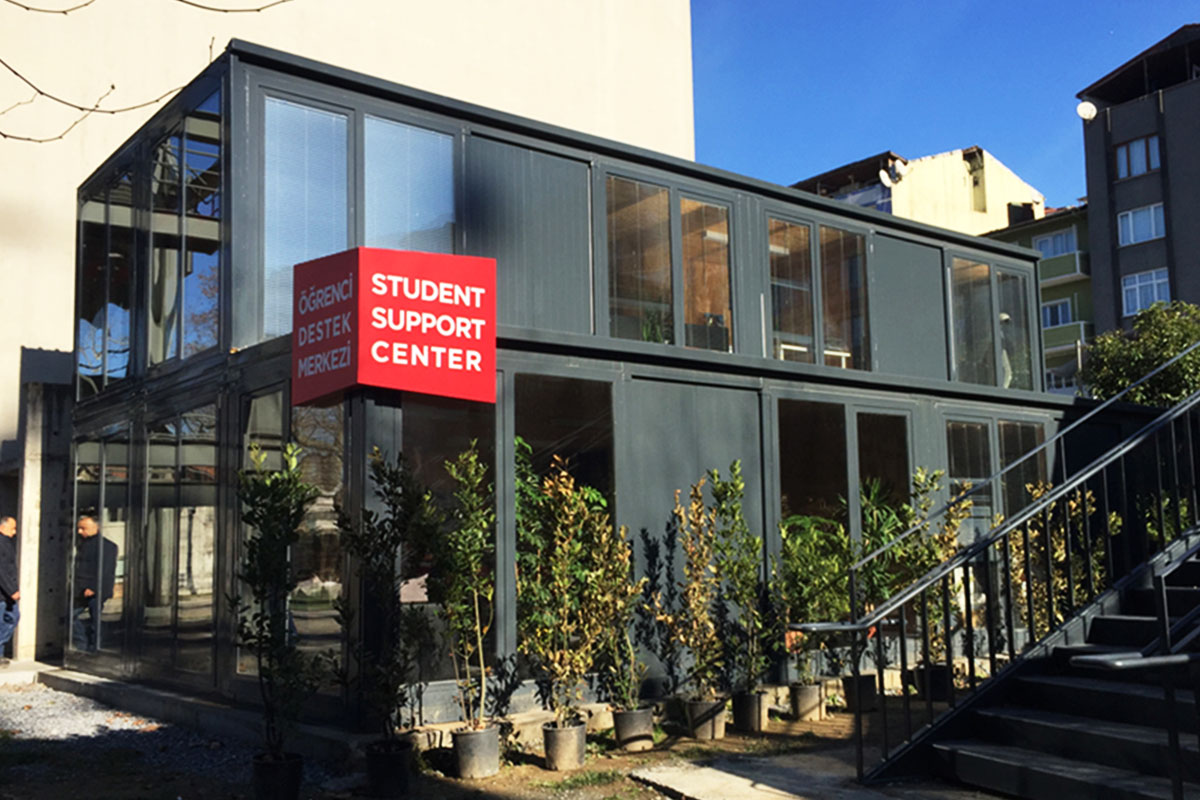
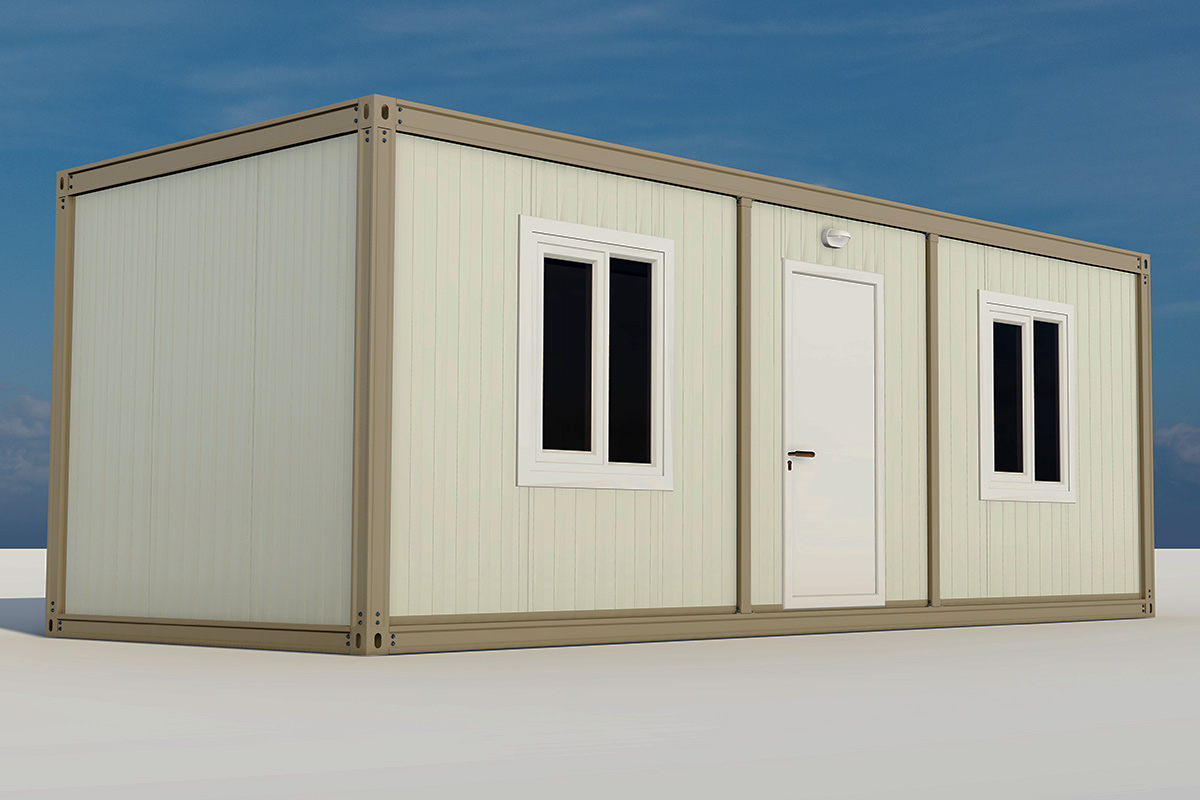
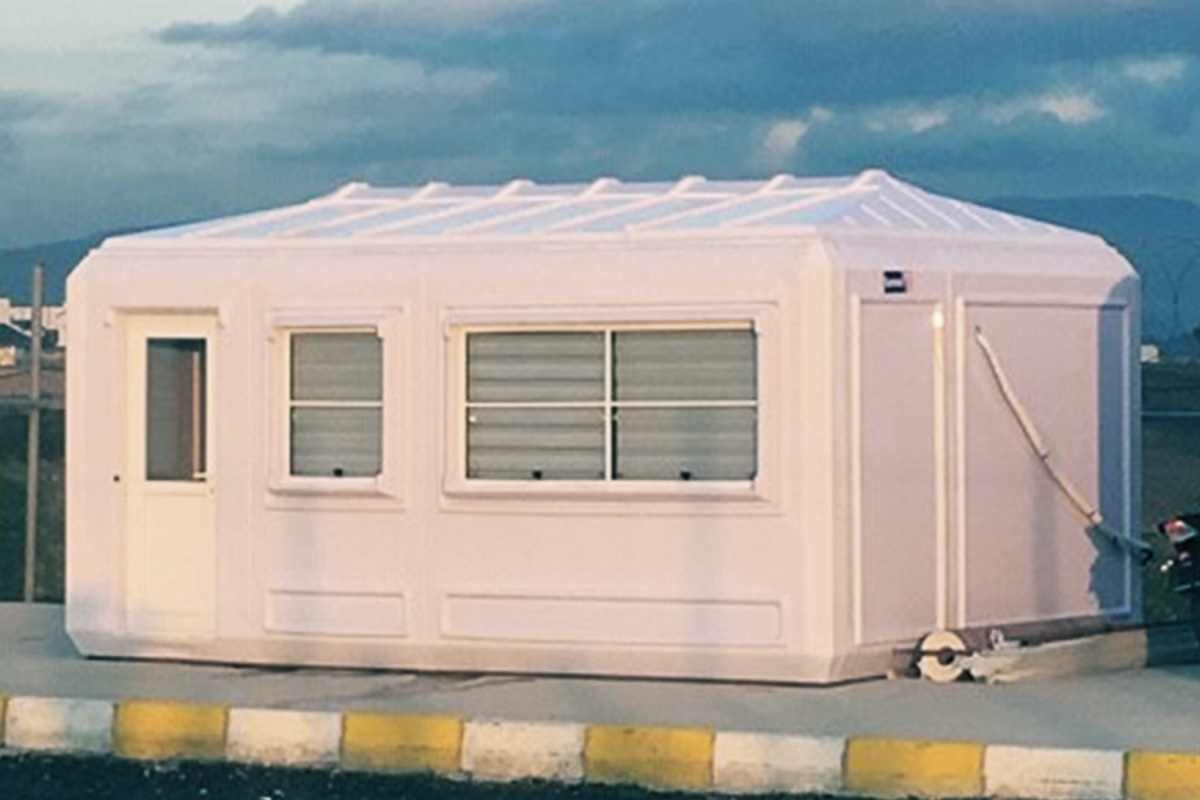
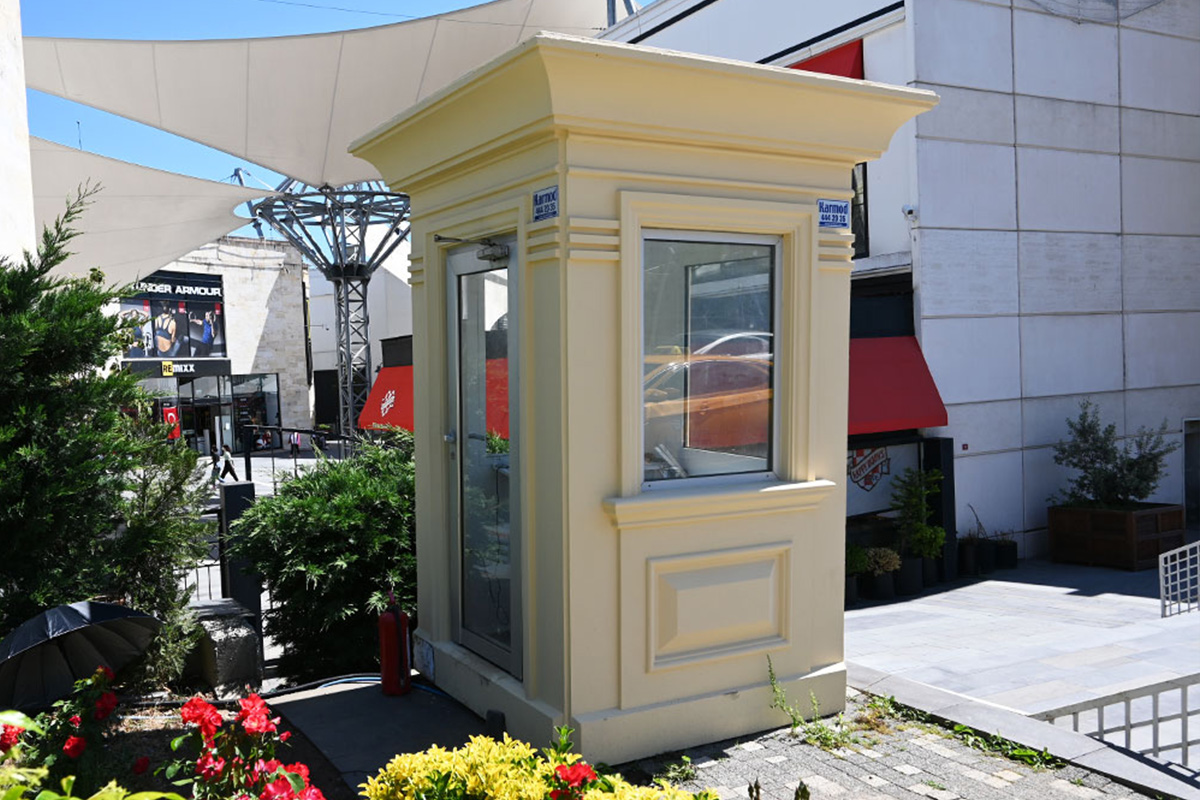
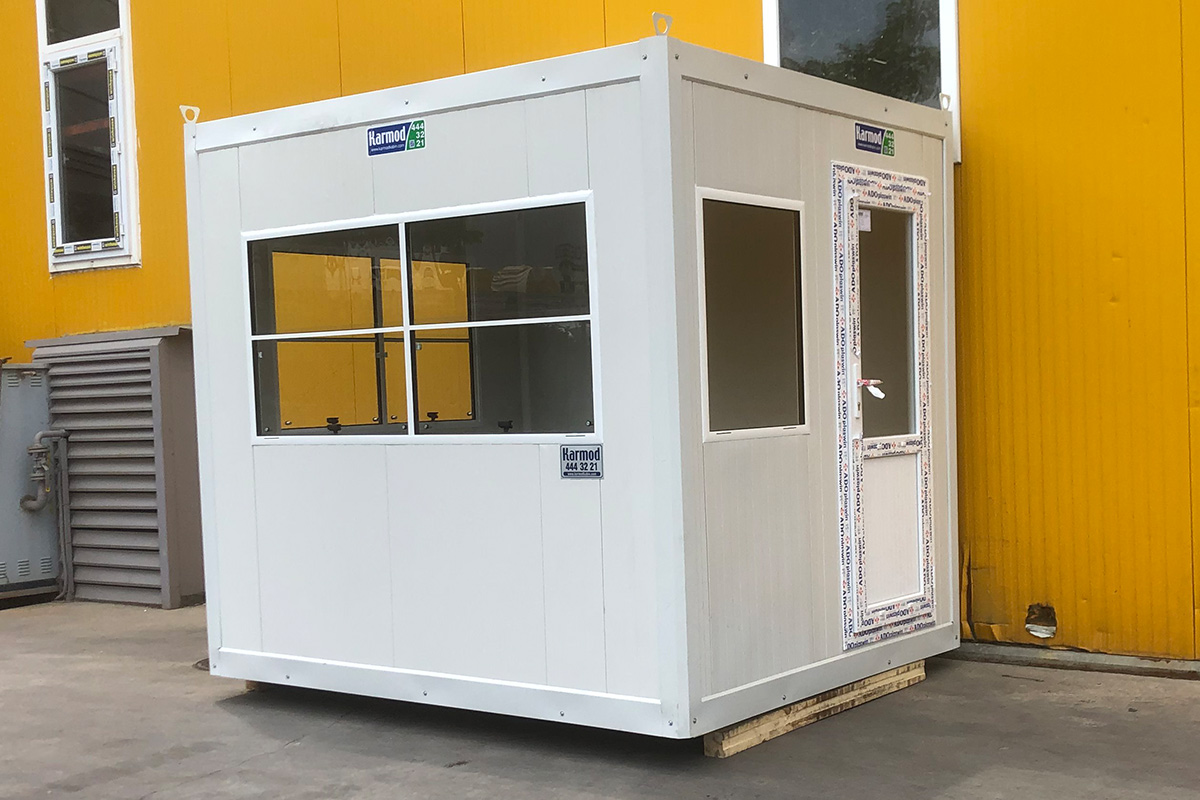
Modular buildings are based on volumetric modules that are fully or partially completed in the factory. These modules are transported to site and assembled into complete structures. This method emphasizes portability, scalability, and adaptability. In Sierra Leone, modular buildings are frequently preferred for site offices, worker camps, and facilities that may need to be relocated once a project phase is completed.
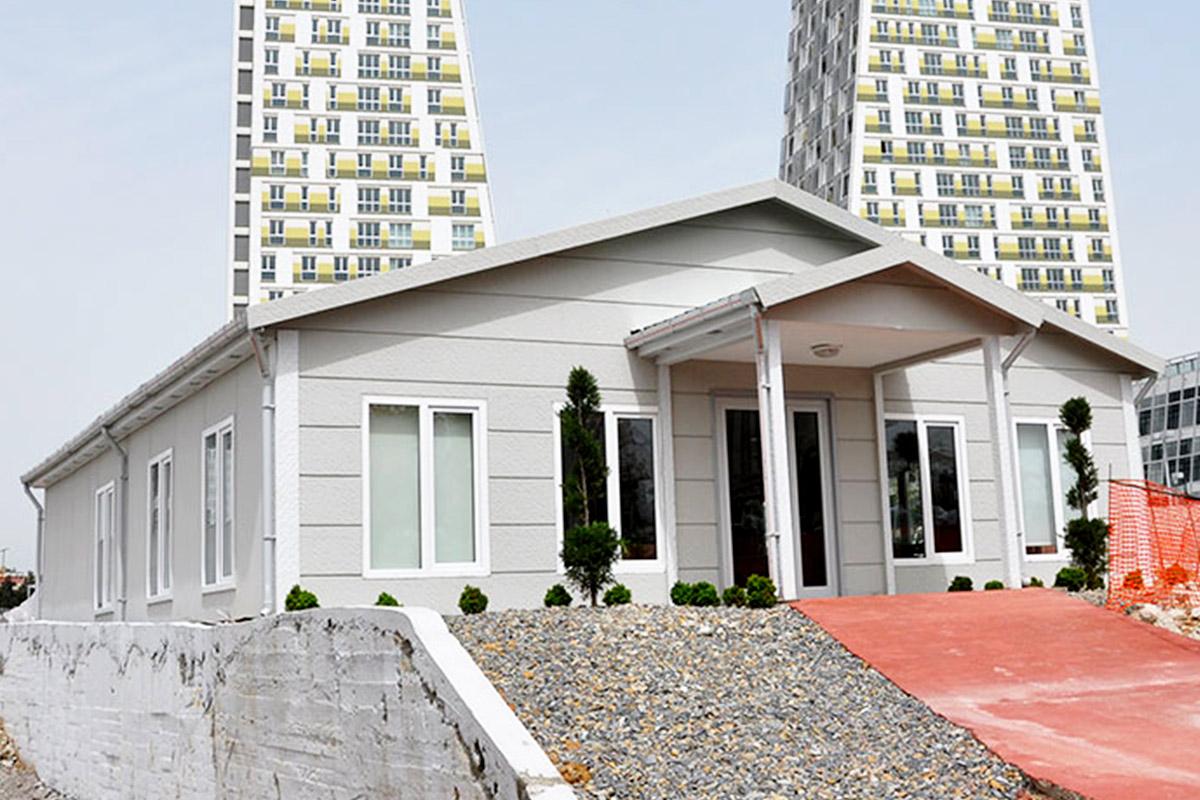
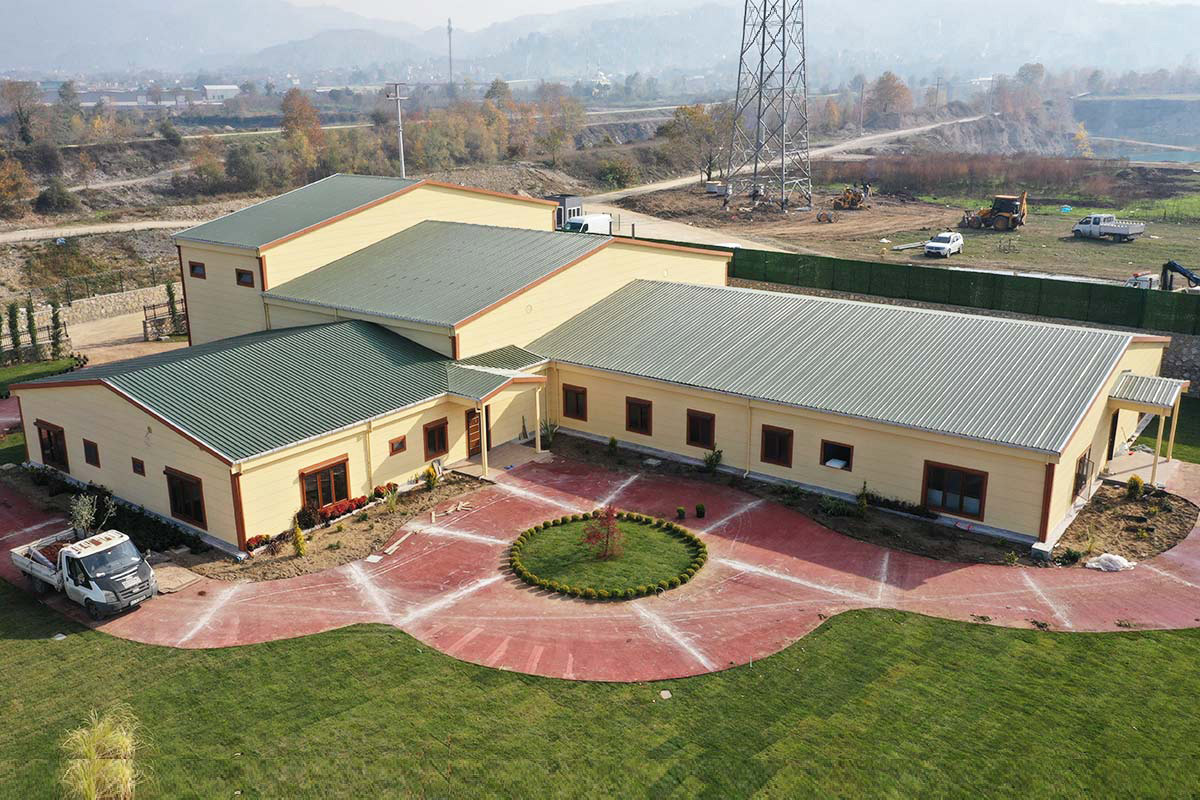
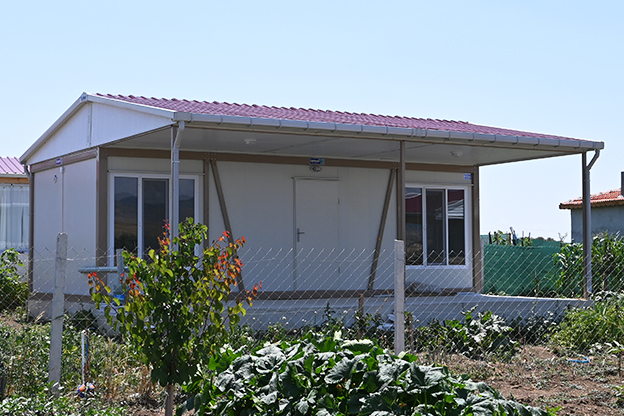
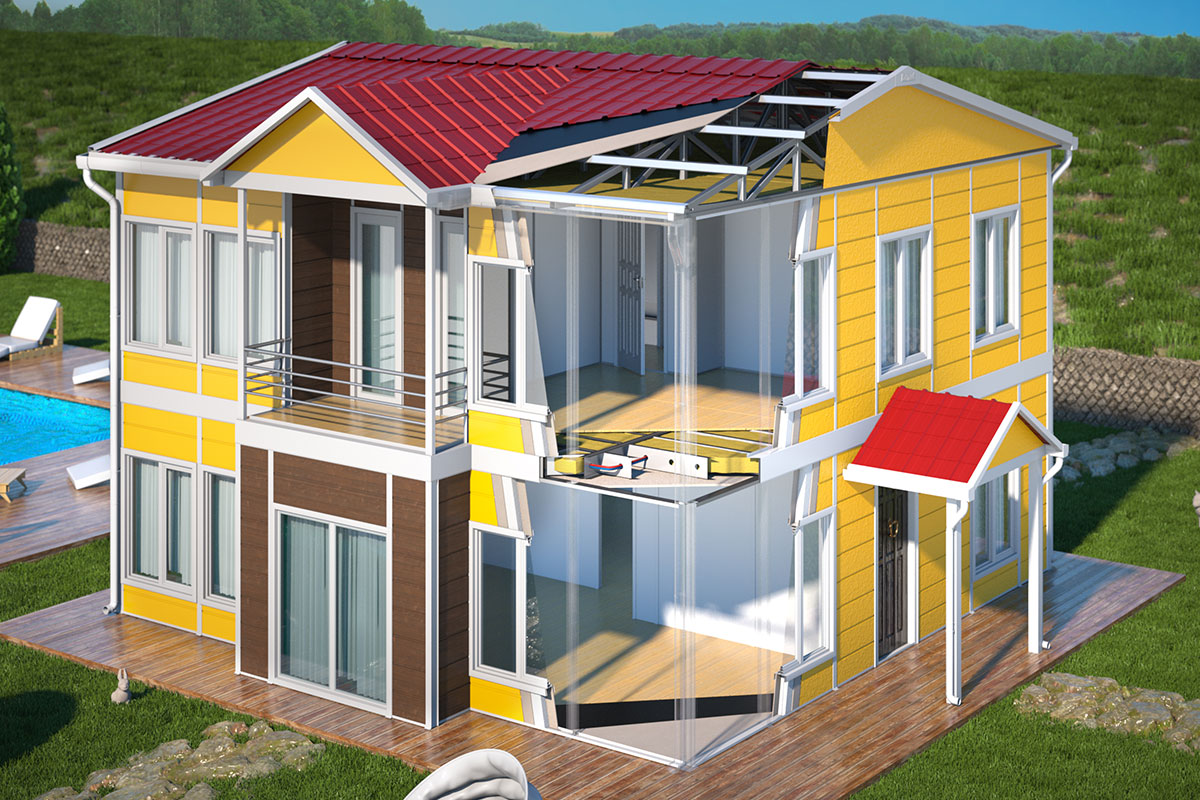
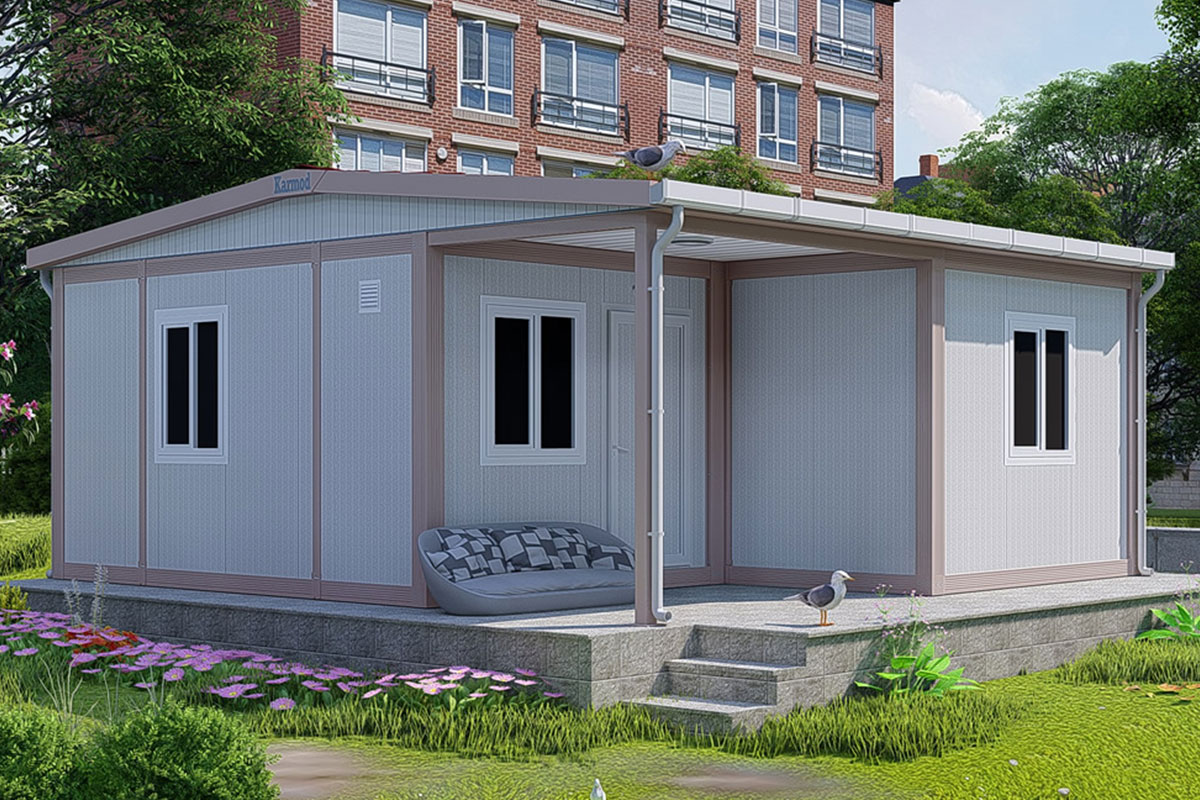
Prefabricated building systems, by contrast, rely on panels and structural components produced off-site and assembled on location. These systems are typically used for more permanent buildings where relocation is not anticipated. A prefabricated building approach is often selected for schools, clinics, administrative buildings, and long-term housing projects that require durable, fixed layouts.
Project context determines which system is more suitable. For short- to medium-term industrial projects or remote operations, modular buildings offer logistical and operational flexibility. For permanent public or institutional facilities, prefabricated building systems provide long-term stability while still benefiting from factory-controlled quality and reduced construction time.
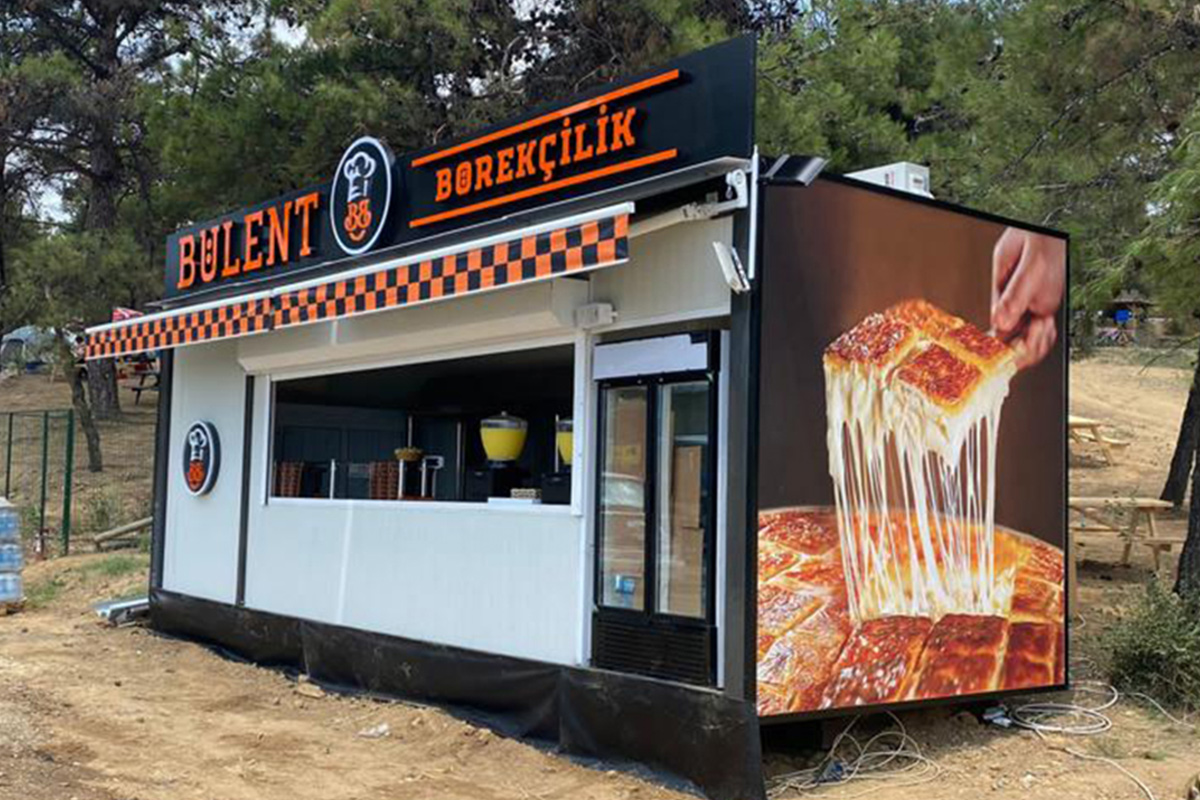
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Sierra Leone
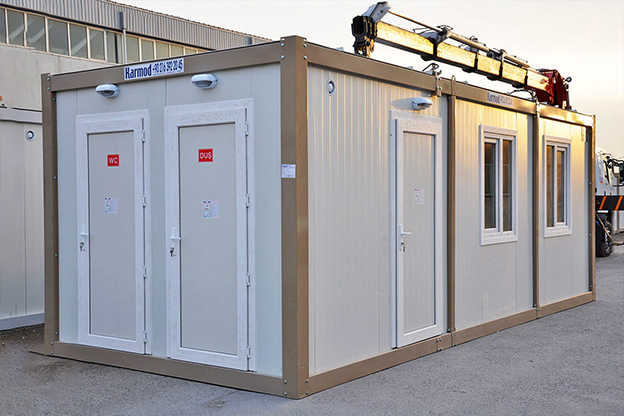
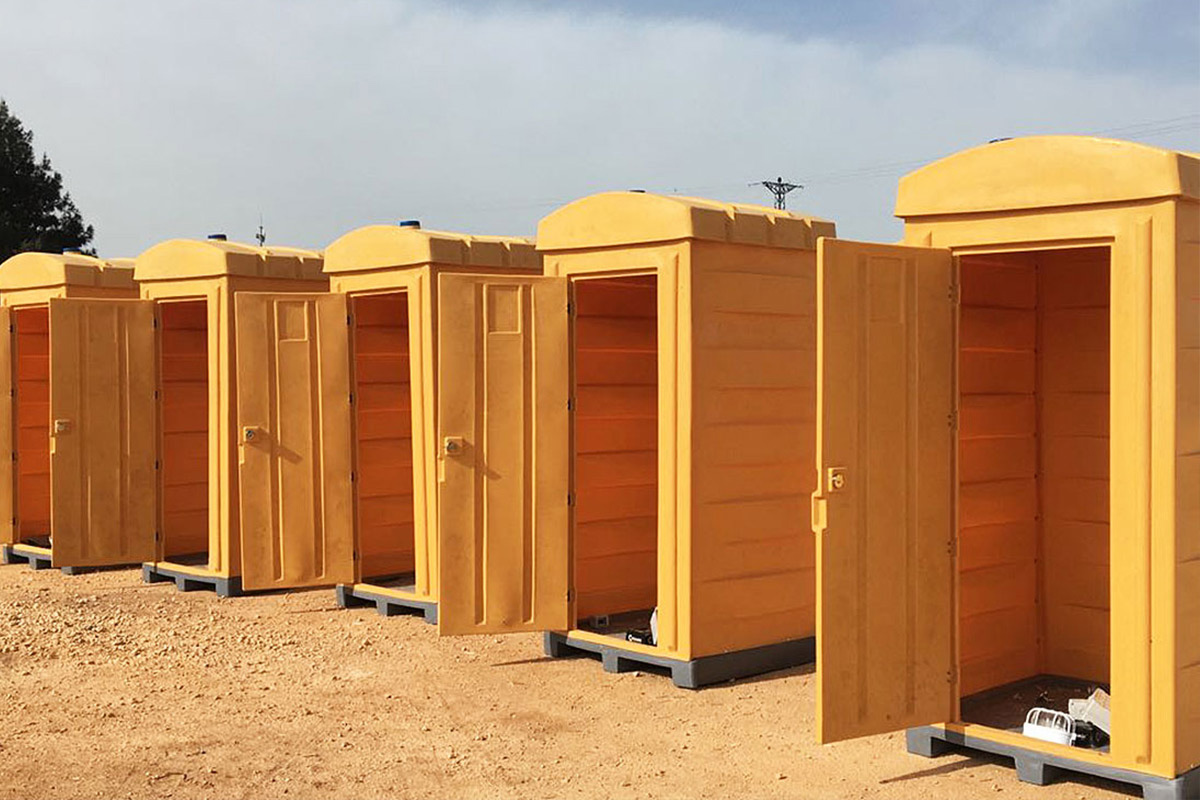
- Site offices & construction camps supporting project management, engineering teams, and on-site administration
- Worker accommodation buildings designed for mining, energy, and infrastructure personnel in remote locations
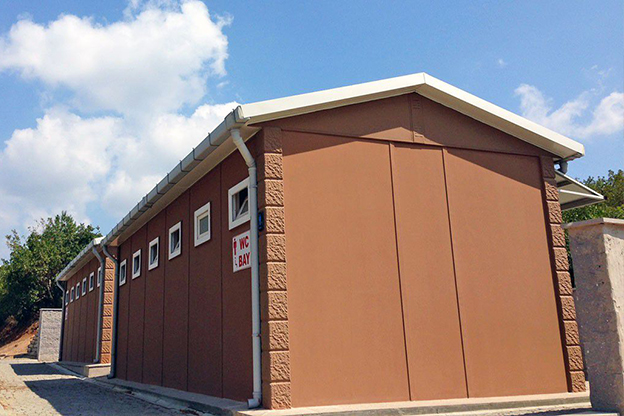
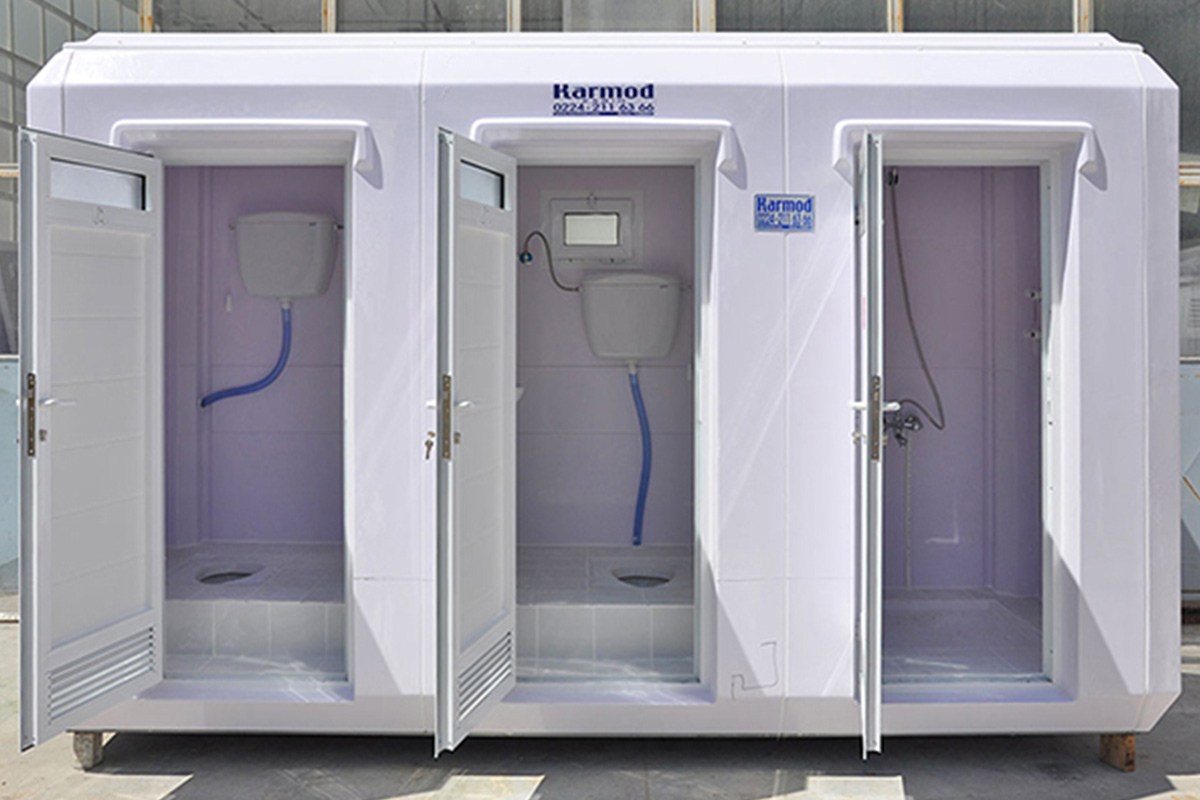
- Temporary schools & healthcare units providing rapid-response solutions in underserved regions
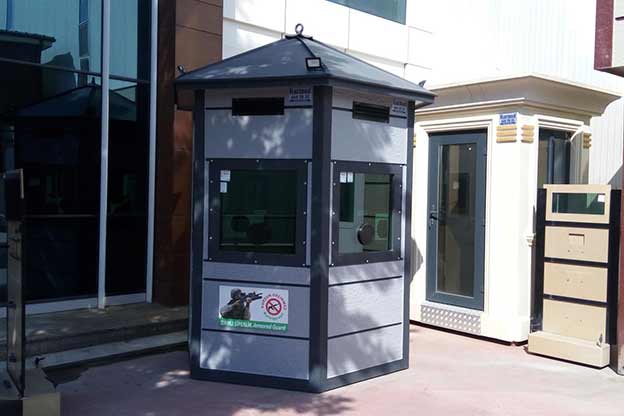
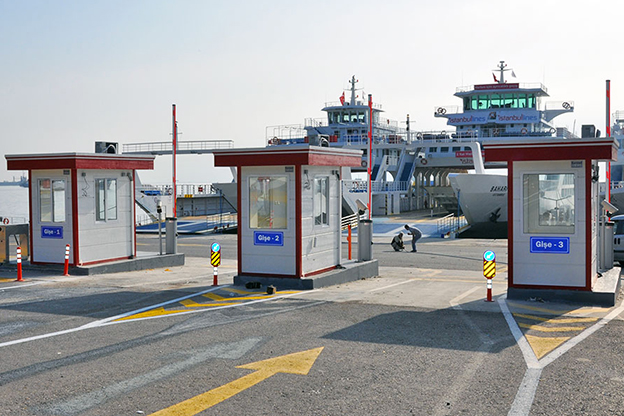
- Security buildings & technical units for access control, monitoring, and operational management
- Storage and logistics facilities improving material handling and supply chain efficiency
These applications demonstrate how modular and prefabricated systems address both immediate operational requirements and longer-term development objectives across Sierra Leone.
From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The process begins with a detailed project needs analysis. Operational requirements, capacity expectations, site conditions, and regulatory considerations specific to Sierra Leone are evaluated to ensure alignment with real-world use.
This is followed by custom design and technical specifications. Layouts, structural systems, insulation levels, and interior configurations are adapted to local climate conditions and functional demands. At this stage, experienced manufacturers such as Karmod translate operational needs into practical and compliant building solutions.
Factory production then takes place under controlled conditions, ensuring consistent quality, precise detailing, and reduced material waste. This stage also minimizes exposure to weather-related delays.
Once production is complete, units are prepared for delivery to Sierra Leone. Logistics planning is critical, particularly for projects located outside major ports or urban centers. Efficient transport coordination helps ensure timely and reliable delivery.
On-site installation completes the process. Modular units are assembled quickly with minimal disruption, allowing facilities to become operational far sooner than with conventional construction methods.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Sierra Leone
Thermal insulation: High temperatures and humidity levels require effective insulation solutions to maintain indoor comfort and reduce energy consumption.
Fire safety standards: Industrial and public-sector projects must comply with relevant fire safety requirements, making certified materials and tested systems essential.
Climate suitability: Buildings must withstand heavy rainfall, high humidity, and variable soil conditions common across different regions of Sierra Leone.
Custom layouts: Flexible interior planning allows buildings to be adapted for administrative, residential, or technical functions without compromising efficiency.
Karmod modular building solutions are designed to address these considerations through proven engineering, adaptable layouts, and materials selected for demanding environments. Drawing on experience across multiple international markets, Karmod applies a solution-oriented approach that supports both operational efficiency and long-term reliability.
For decision-makers in Sierra Leone seeking building systems that balance speed, quality, and adaptability, modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions offer a clear strategic advantage. When implemented with proper planning and experienced partners, these systems help projects move forward with confidence, predictability, and operational readiness.