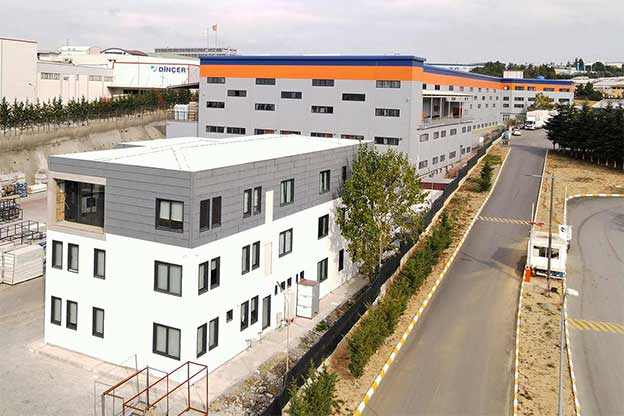
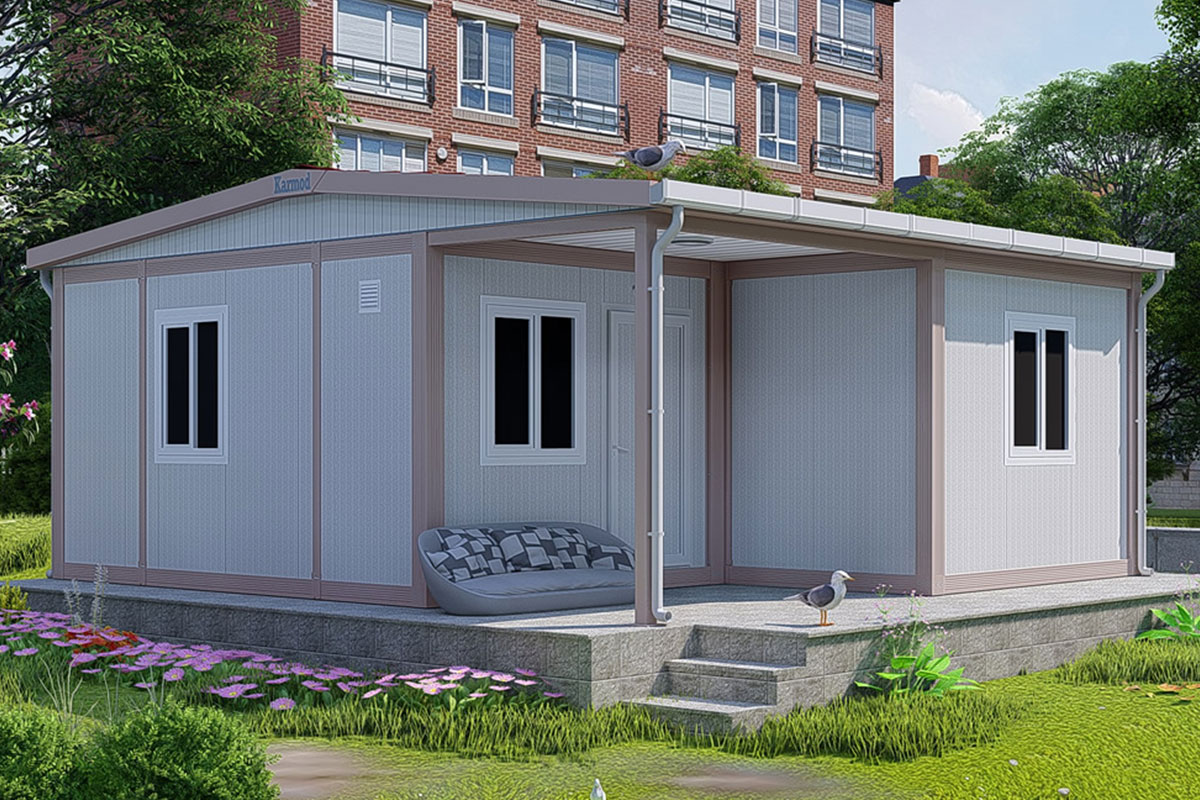
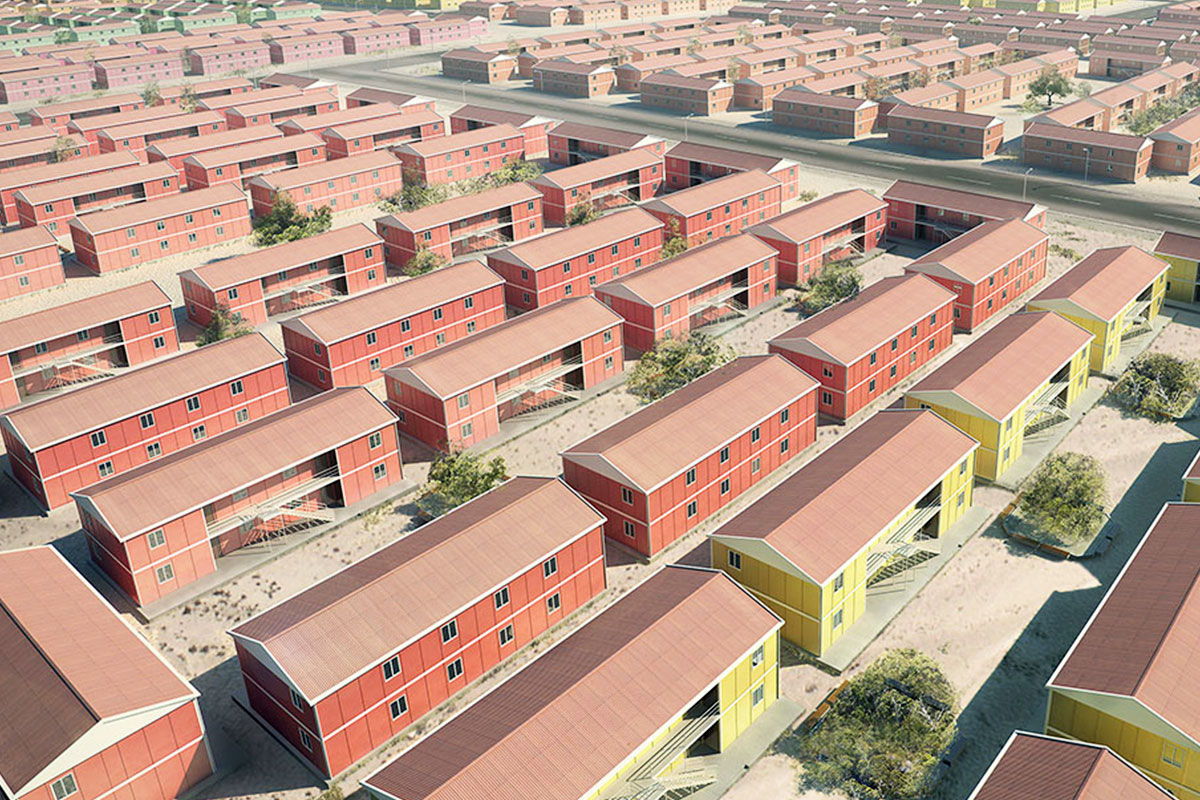
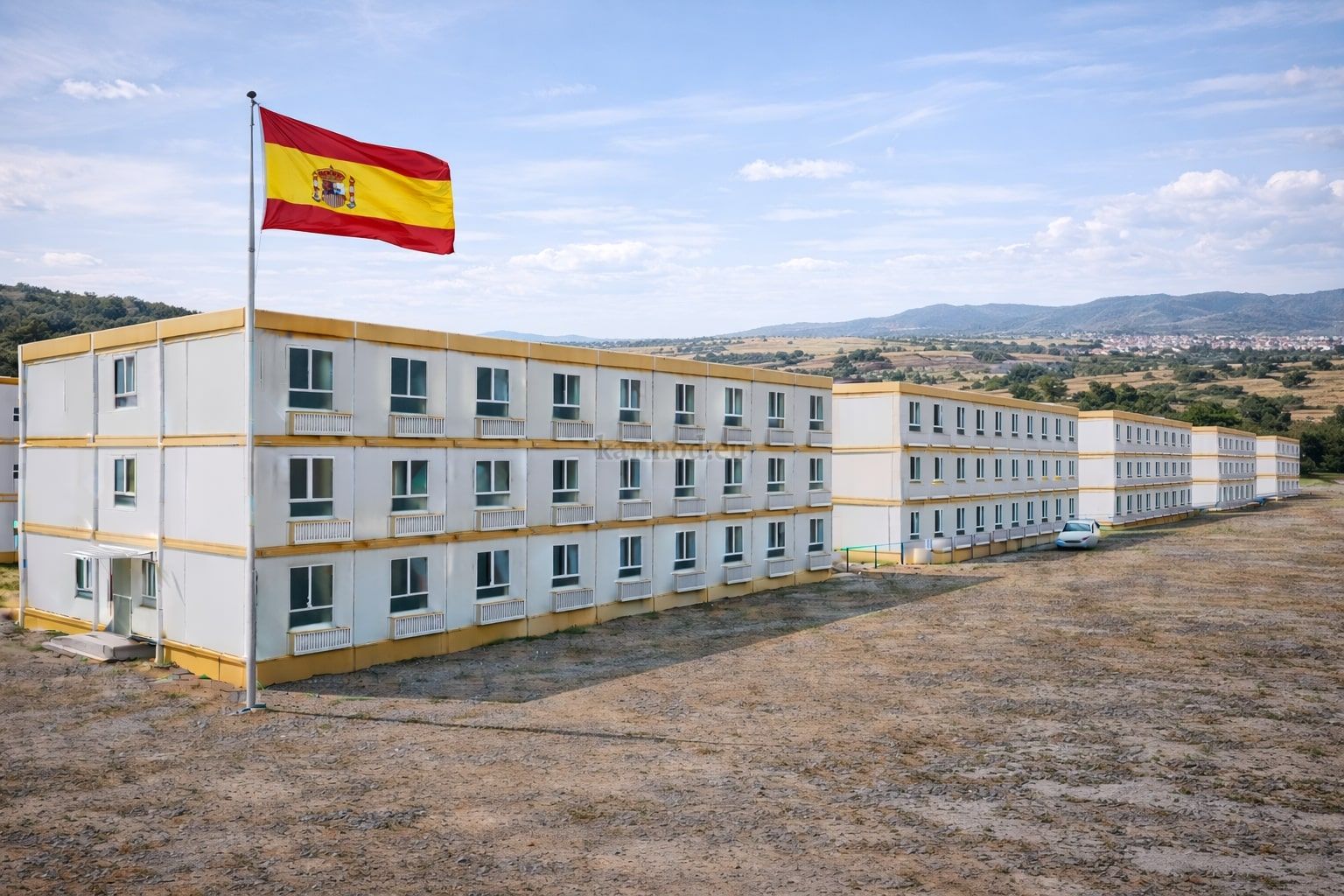
Across Spain, construction and infrastructure decision-makers are rethinking how facilities are delivered. Rising labor costs, tighter project timelines, and the need for both temporary and permanent structures are driving interest toward modular buildings and prefabricated building solutions. These systems are no longer niche alternatives; they are increasingly part of mainstream planning for logistics hubs, industrial zones, energy projects, and public infrastructure across the country.
For organizations operating in Spain’s diverse regions—from major ports to inland industrial corridors—the ability to deploy buildings faster, with predictable quality and cost control, has become a strategic advantage rather than a technical detail.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Spain
Several structural factors explain why modular construction methods are gaining momentum in Spain.
Labor costs and workforce availability continue to challenge conventional construction. Skilled labor shortages in certain regions make on-site, labor-intensive building models harder to sustain. Modular production shifts much of this work to controlled factory environments, reducing dependency on fluctuating site labor conditions.
Construction timelines are under constant pressure. Logistics operators, renewable energy developers, and public authorities often work with fixed commissioning dates. Modular buildings allow parallel processes—site preparation and factory production—cutting total project duration significantly.
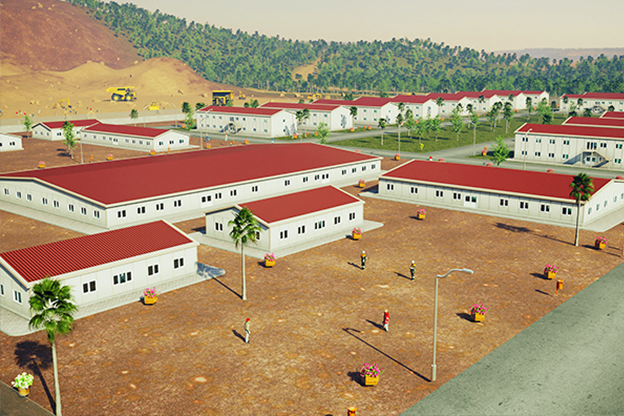
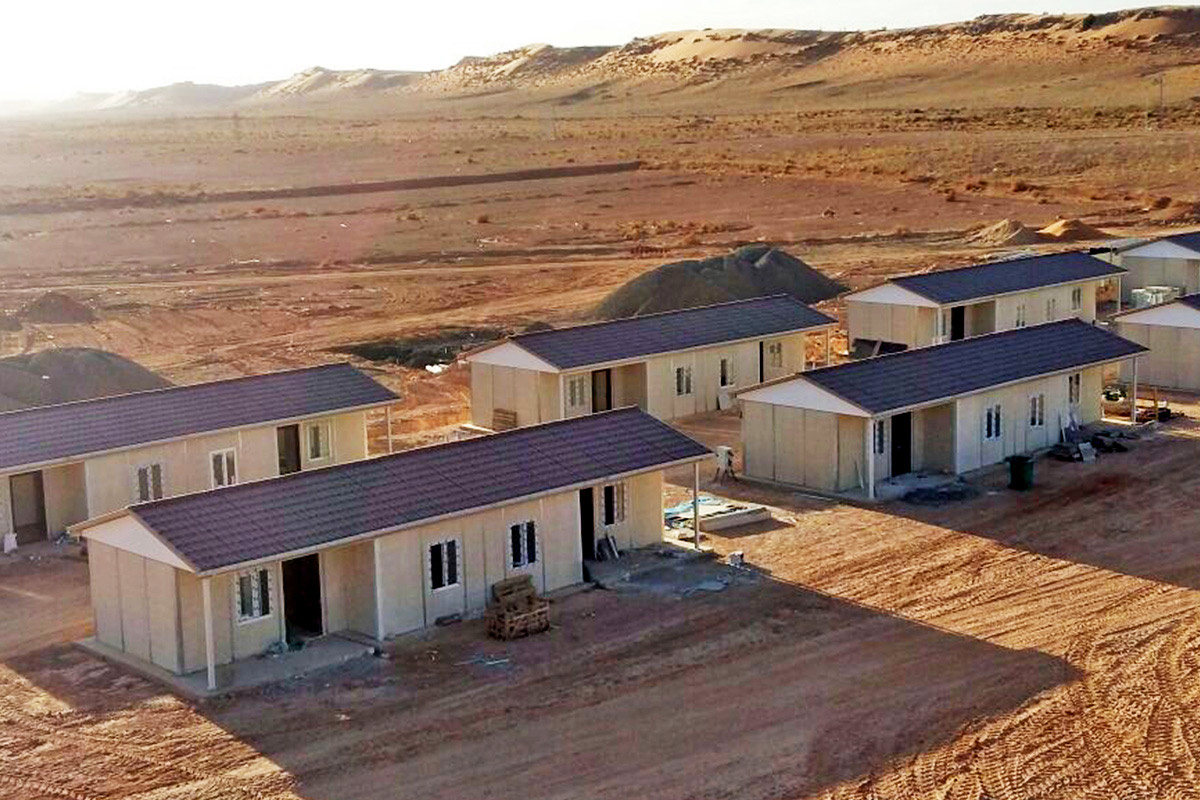
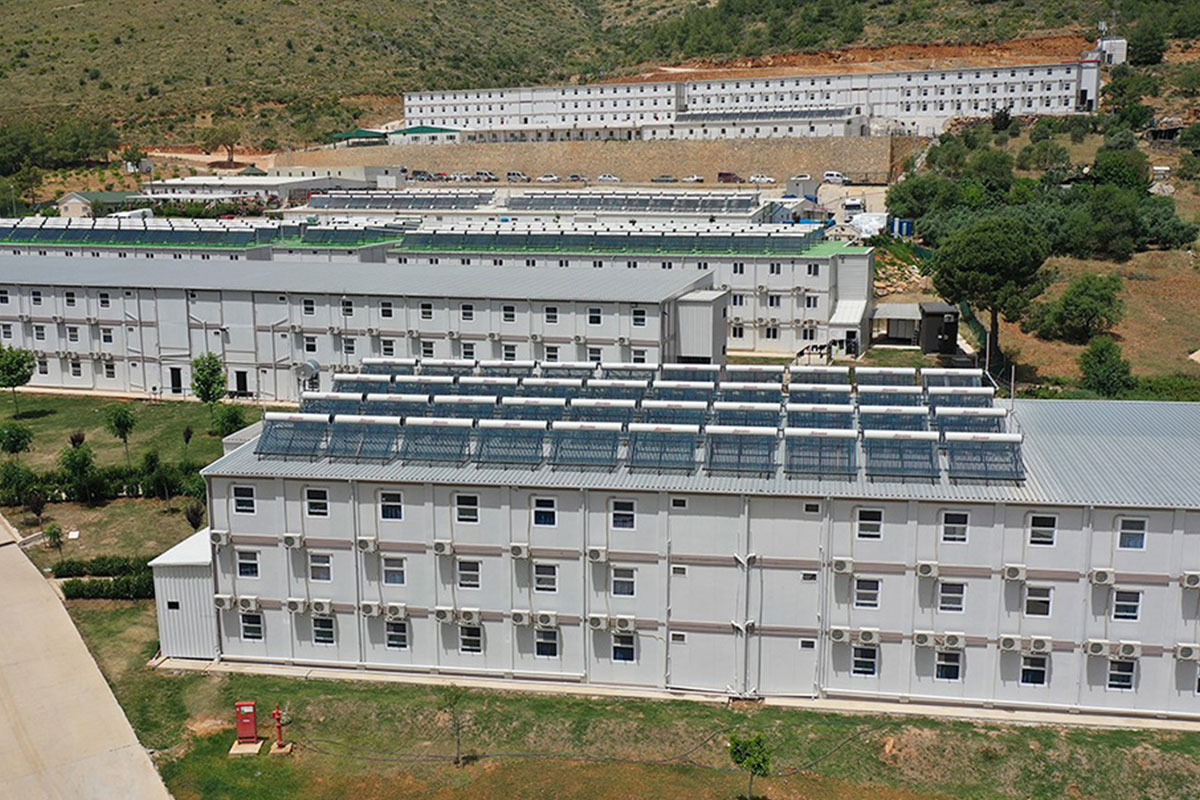
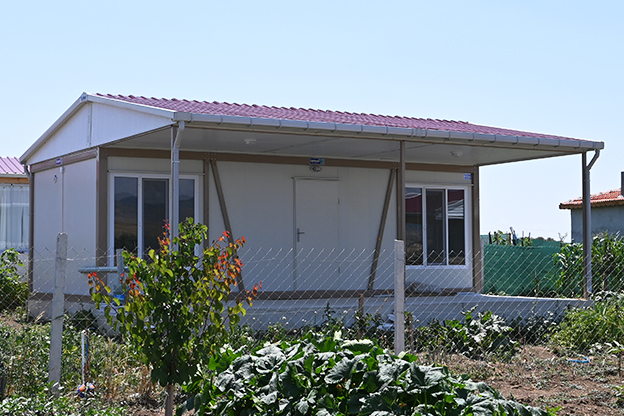
Spain’s market increasingly requires a mix of temporary and permanent building solutions. Temporary site offices for infrastructure projects, seasonal worker accommodation in agriculture, and expandable facilities for ports and logistics centers all benefit from modular flexibility.
Country-specific sectors play a major role. Spain’s logistics and port infrastructure, industrial manufacturing zones, renewable energy projects, and public sector investments all demand buildings that can be deployed quickly, meet regulations, and adapt to future needs.
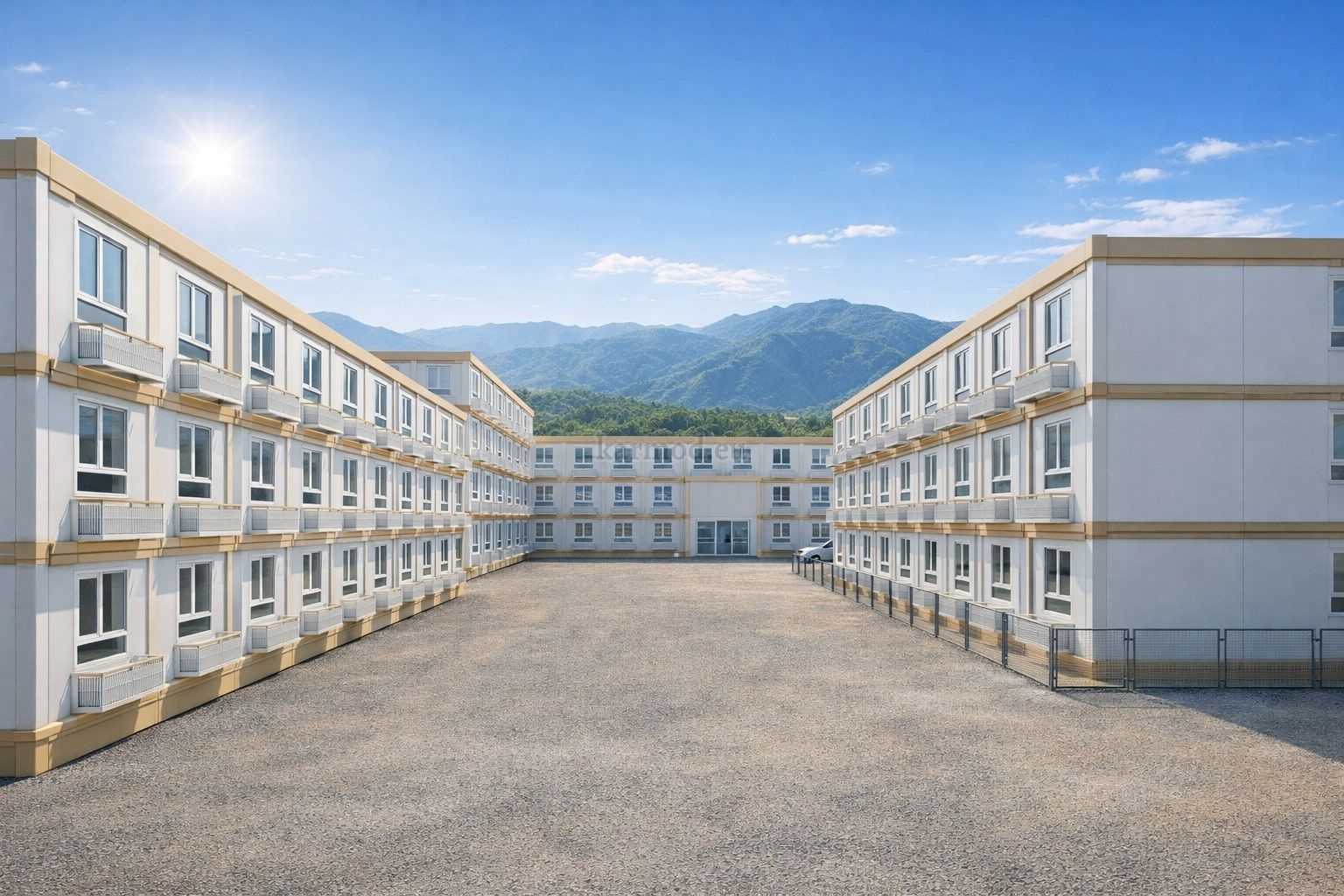

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
Although often mentioned together, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve different planning priorities.
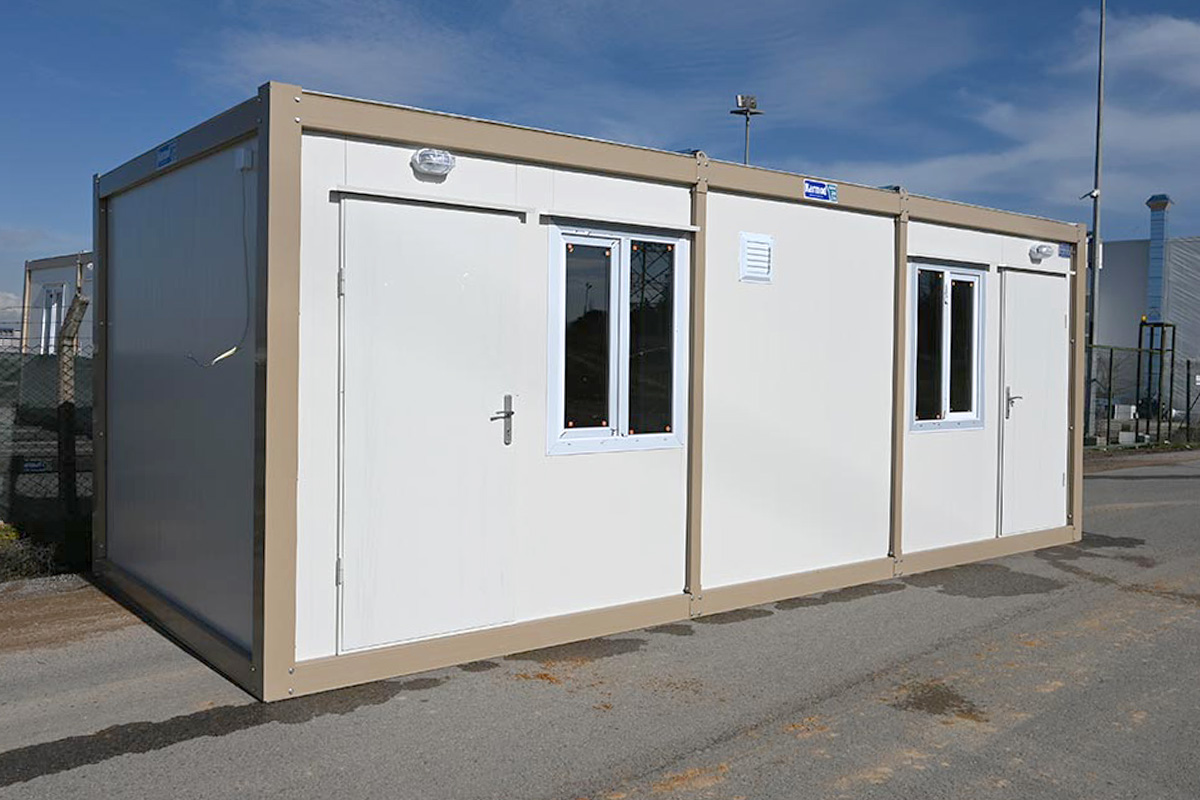
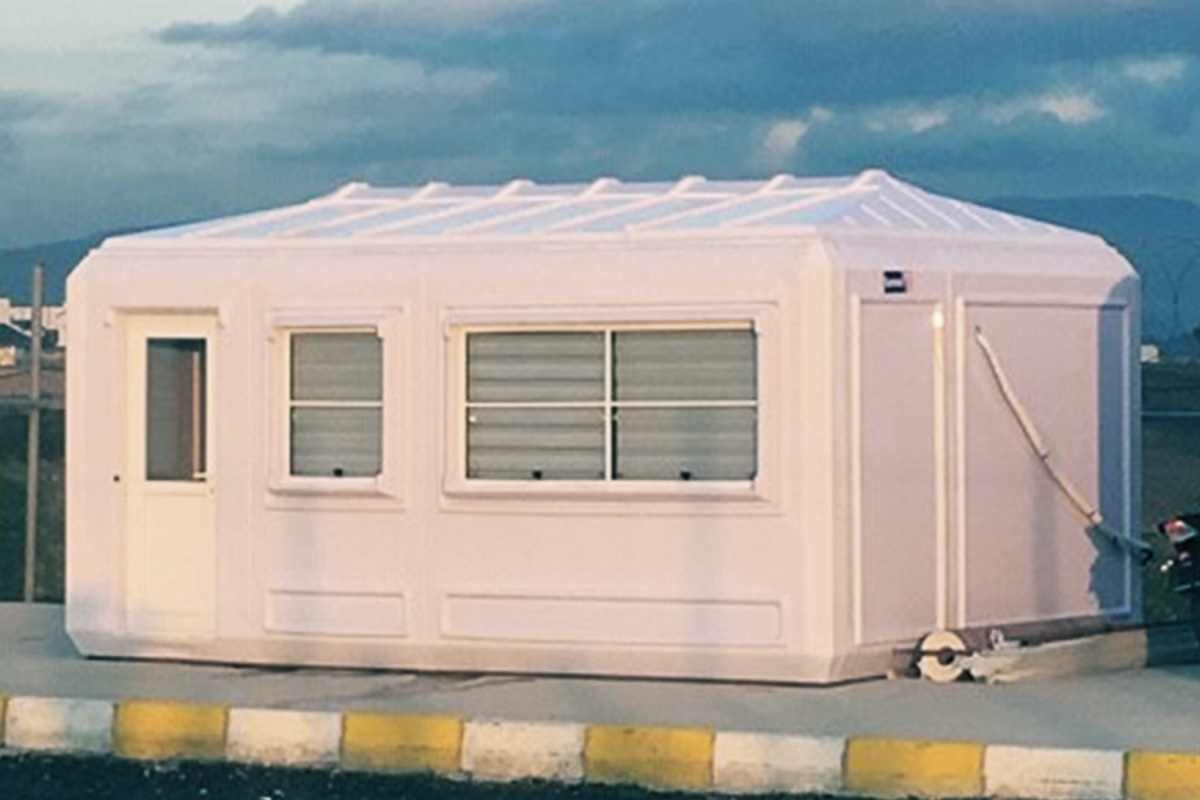
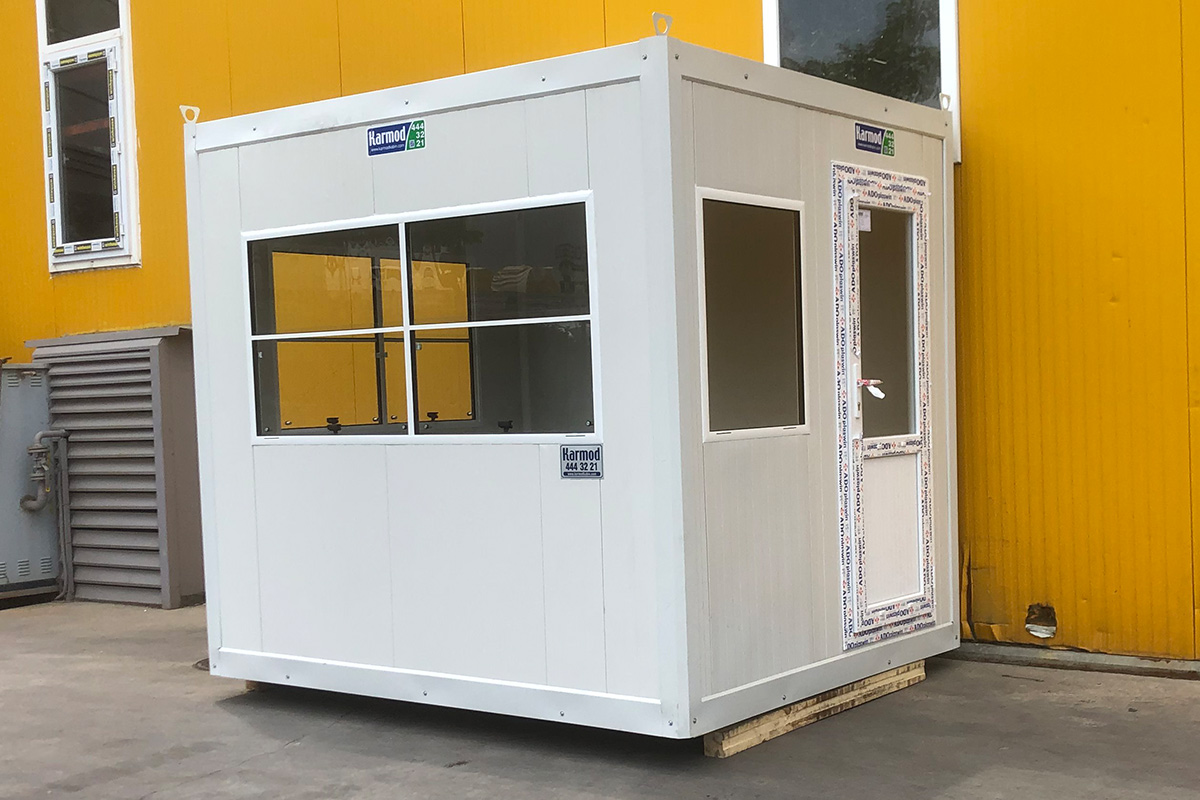
Modular buildings are produced as volumetric modules that are transportable, relocatable, and expandable. In Spain, this makes them particularly suitable for:
- Construction site offices and camps
- Temporary or semi-permanent accommodation
- Facilities requiring relocation or future expansion
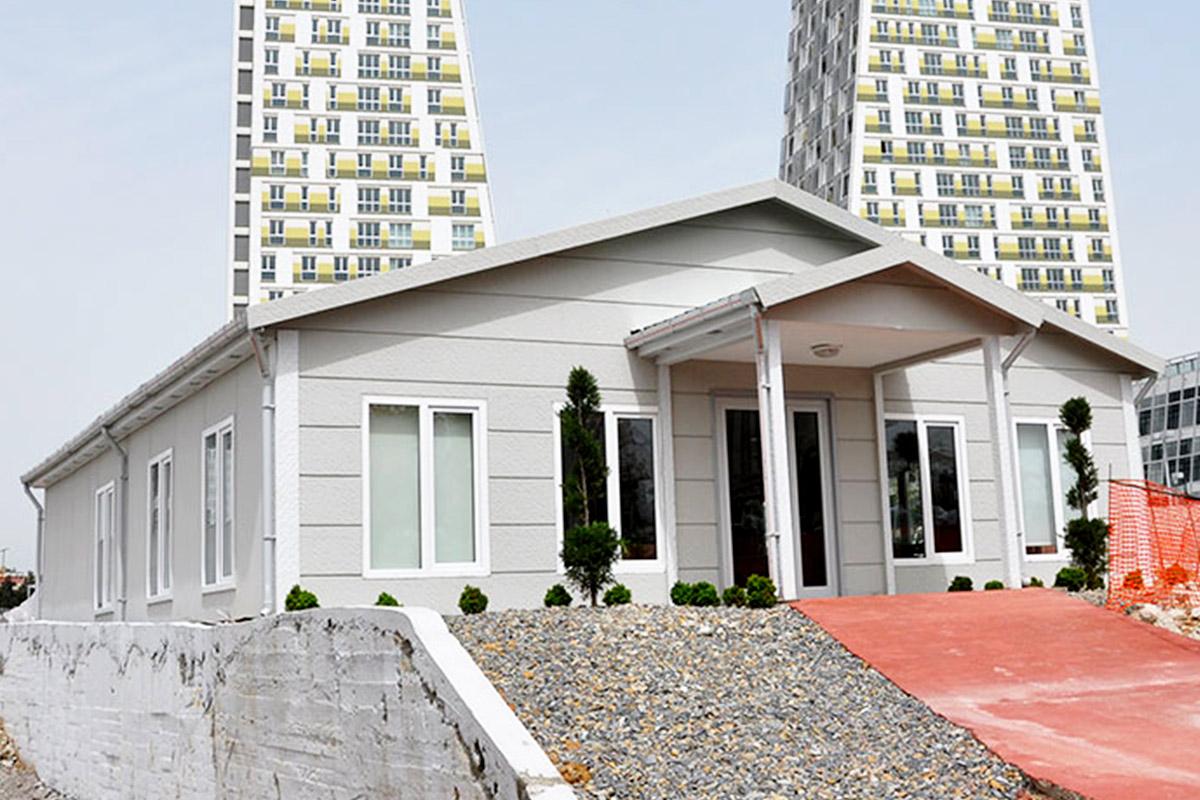
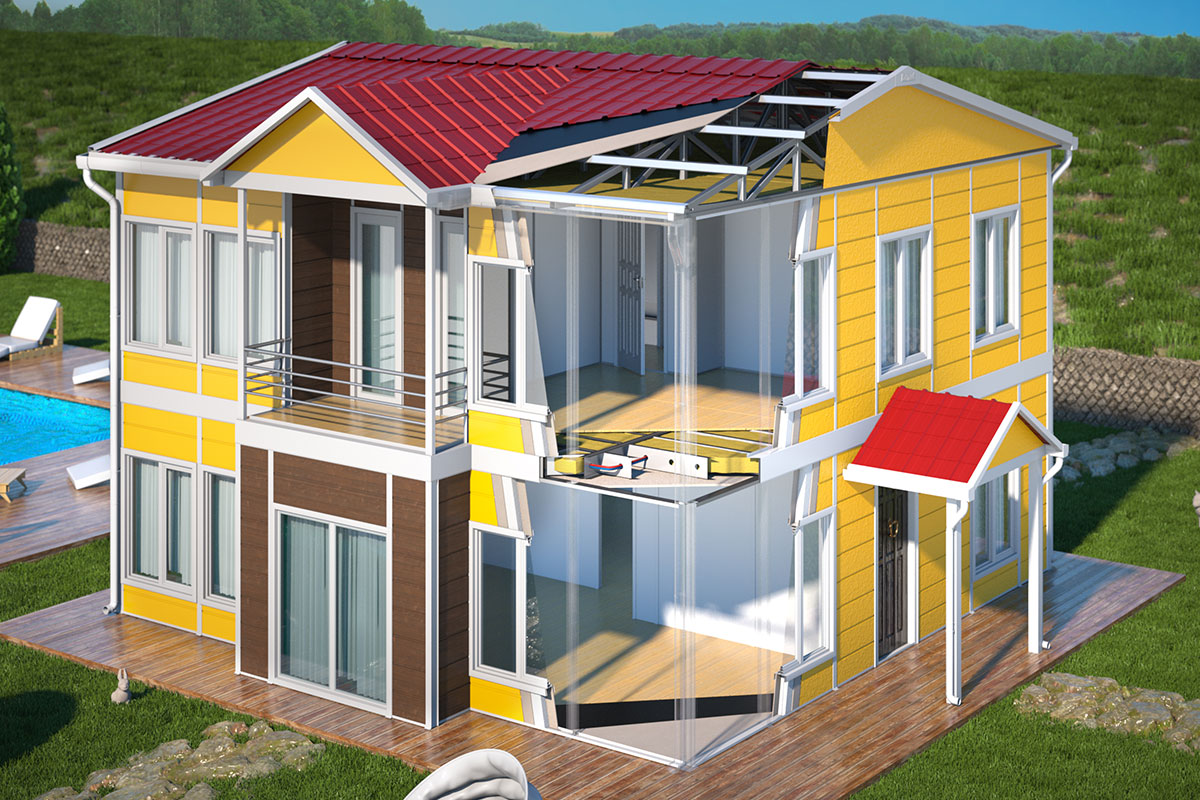
Prefabricated building systems, by contrast, are typically based on panels or structural components assembled on-site into permanent structures. This approach is preferred when:
- Long-term use is clearly defined
- Architectural integration is critical
- The building is intended as a fixed asset
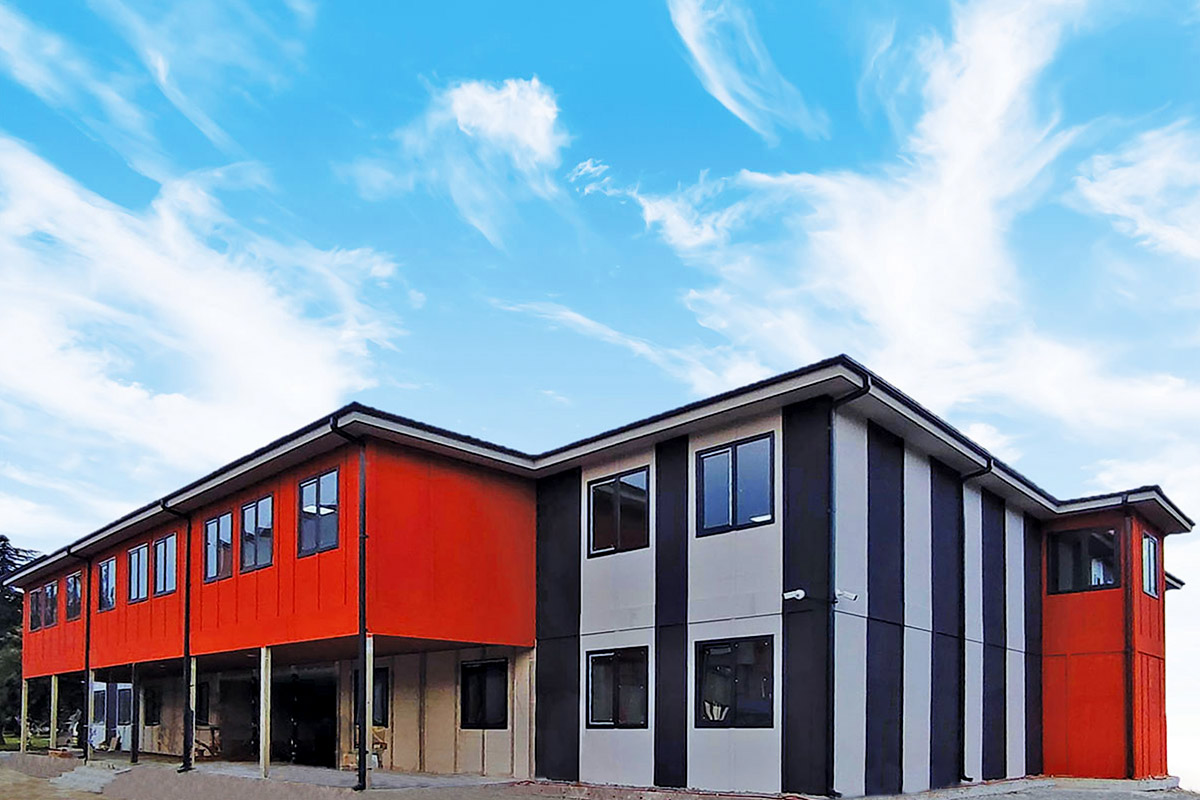
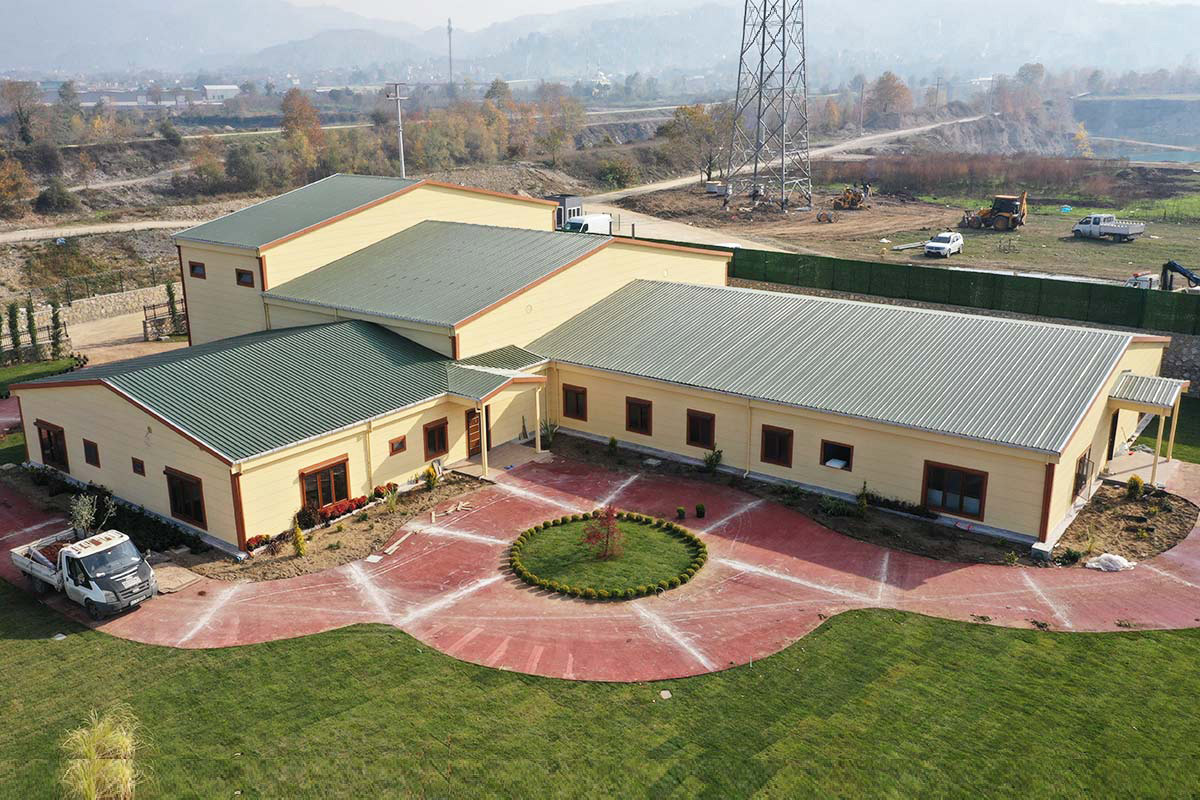
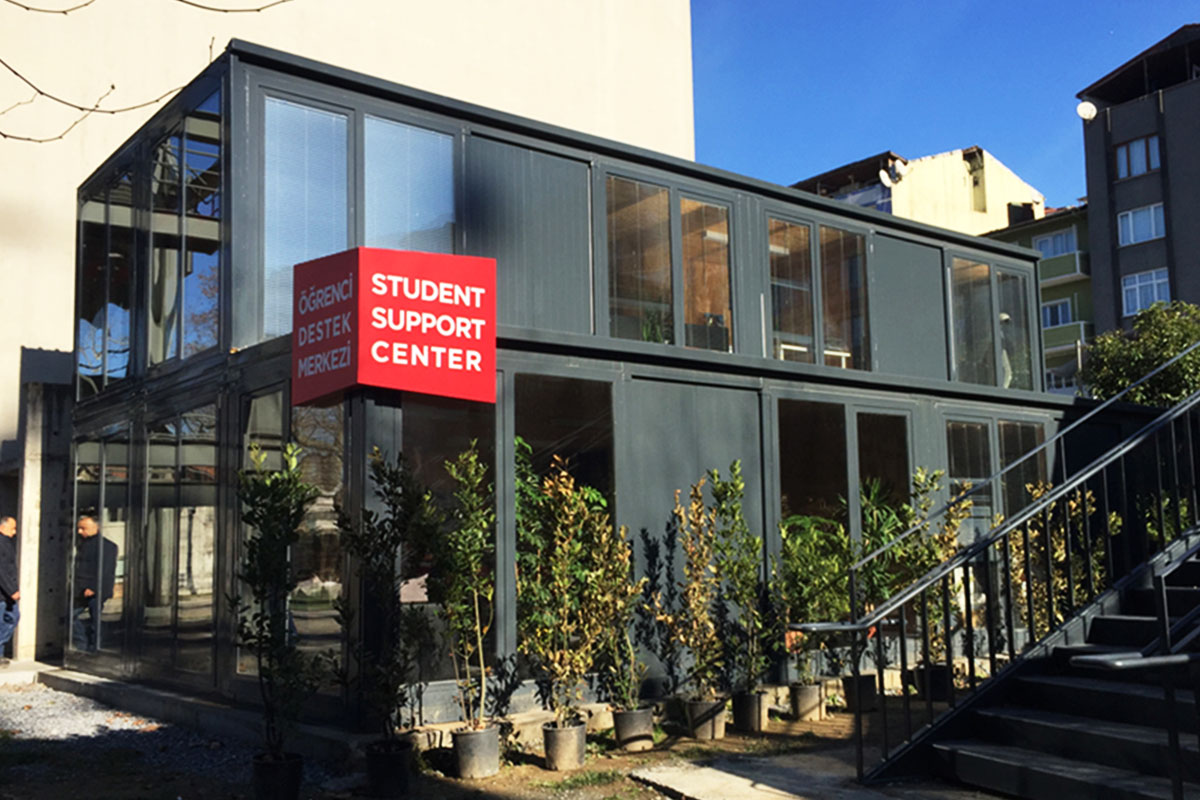
In the Spanish context, modular buildings are often chosen for logistics, energy, and infrastructure projects with evolving requirements, while prefabricated building solutions are favored for industrial facilities, public buildings, and long-term institutional use.
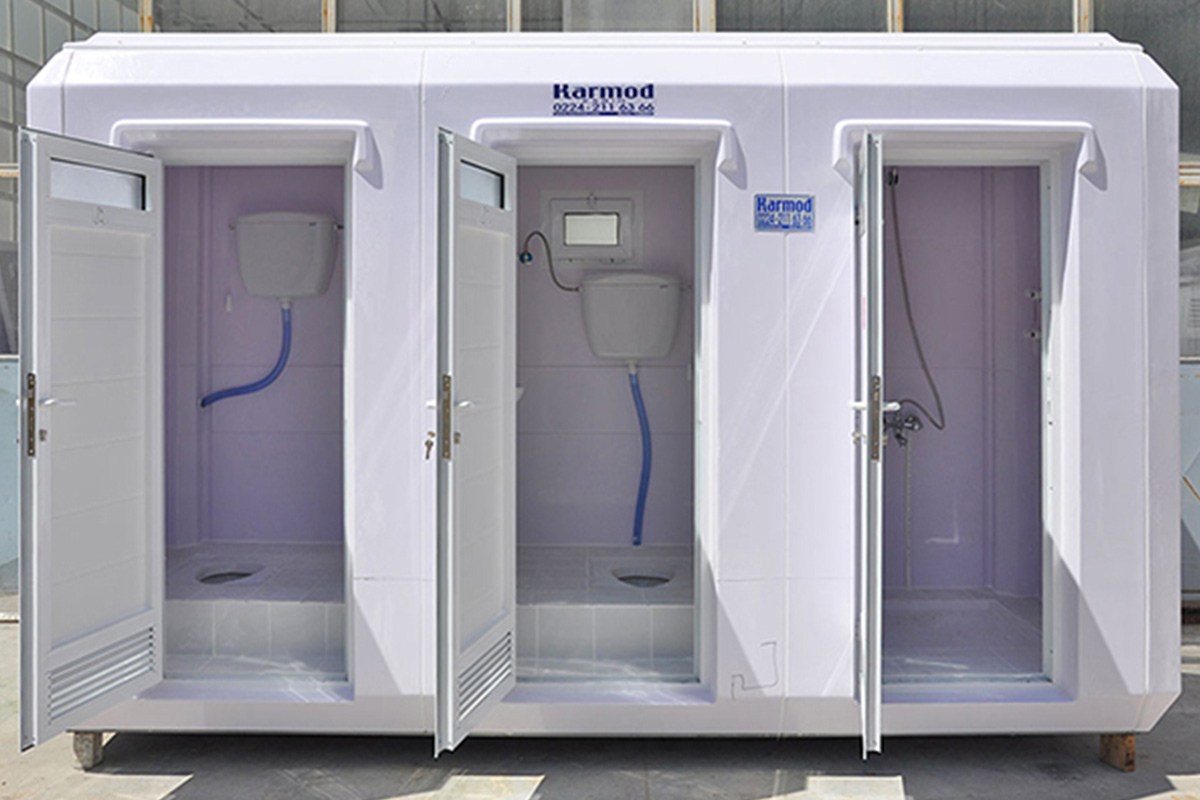
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Spain
Both systems are applied across a wide range of sectors. Typical use cases include:
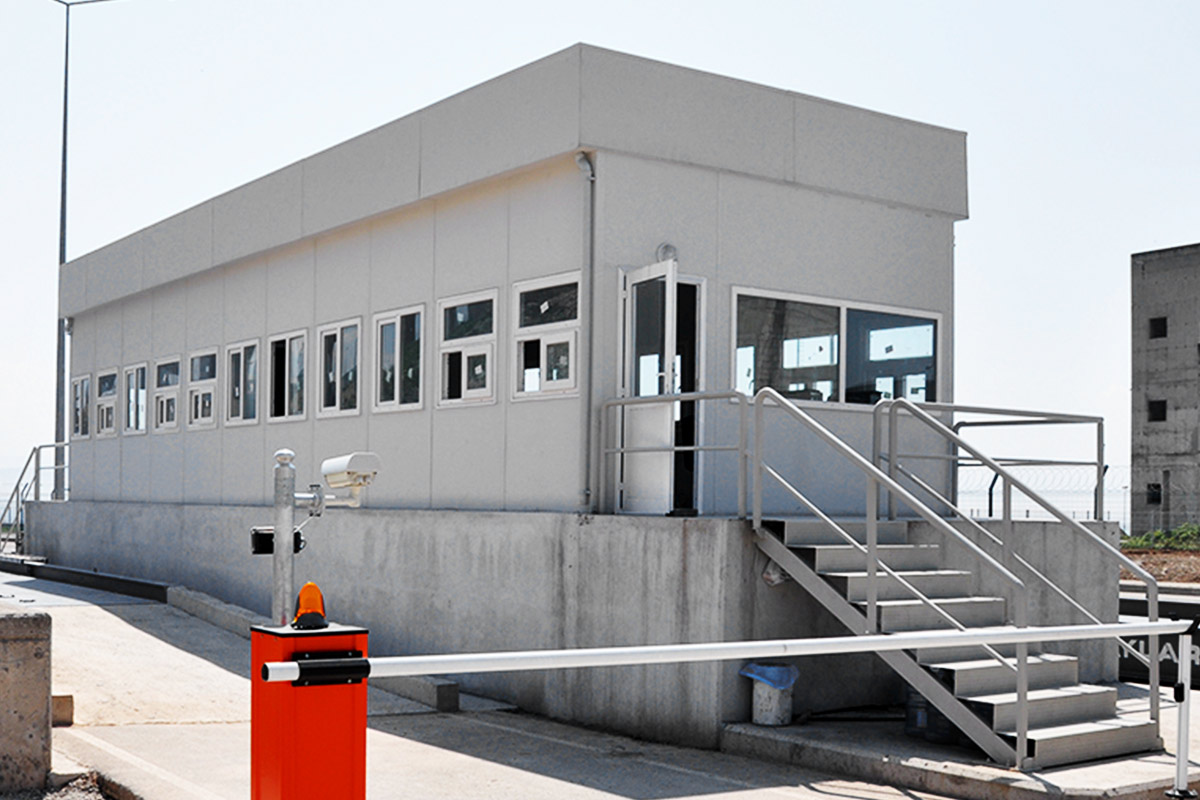
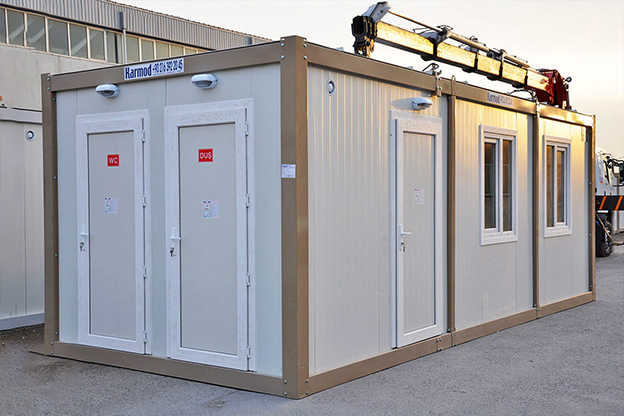
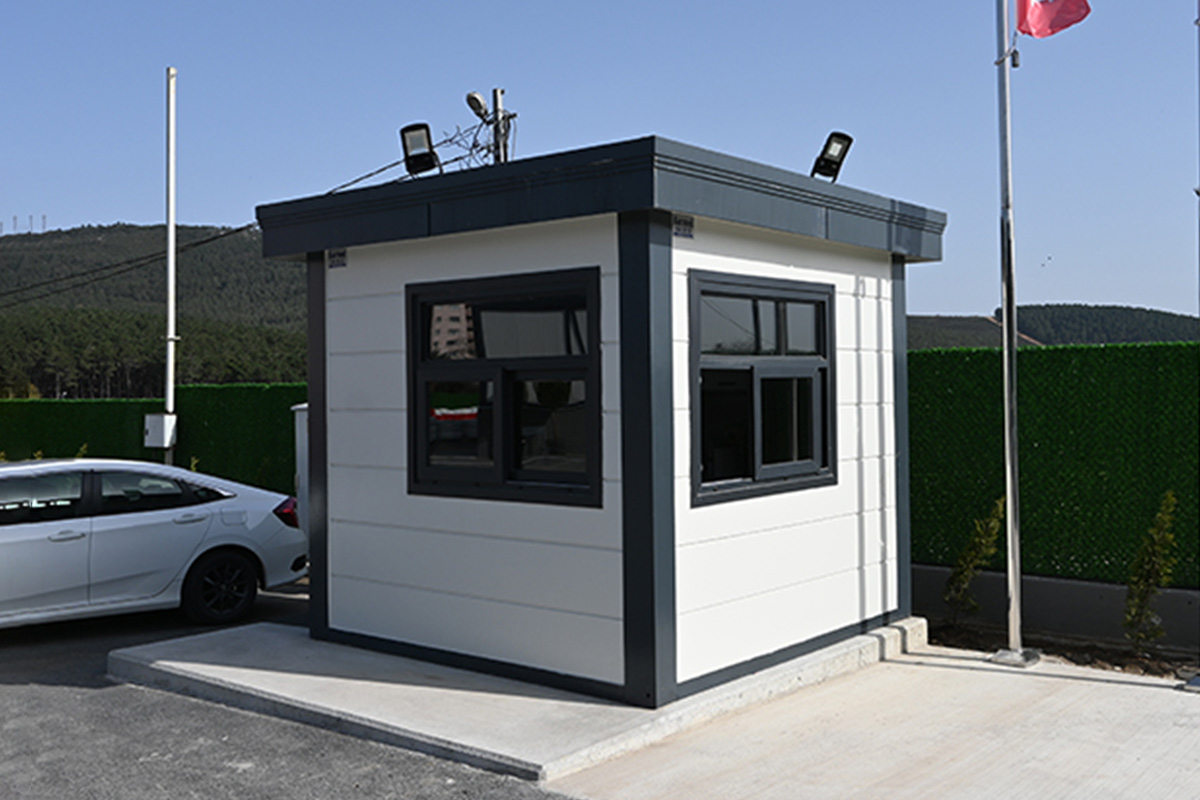
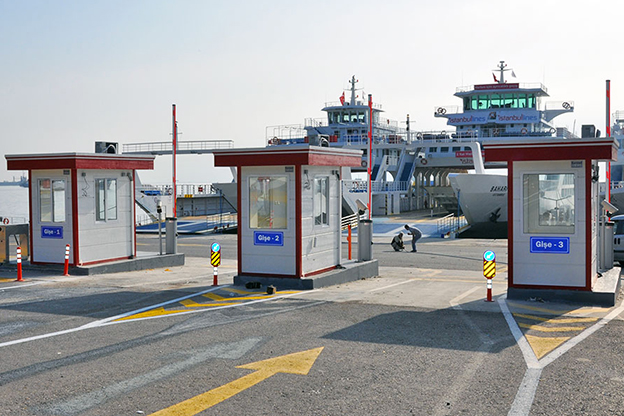
- Site offices & construction camps – Rapidly installed operational centers supporting infrastructure, transport, and energy projects.
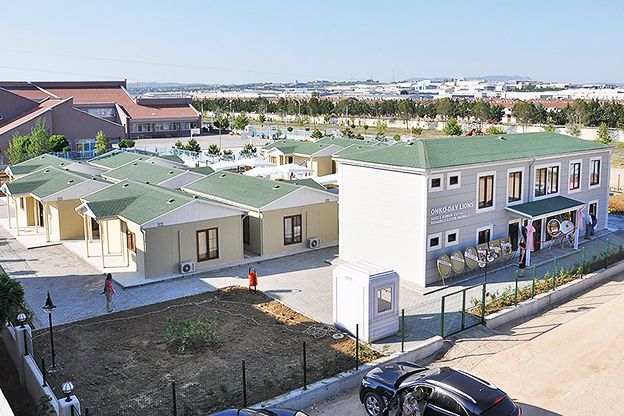
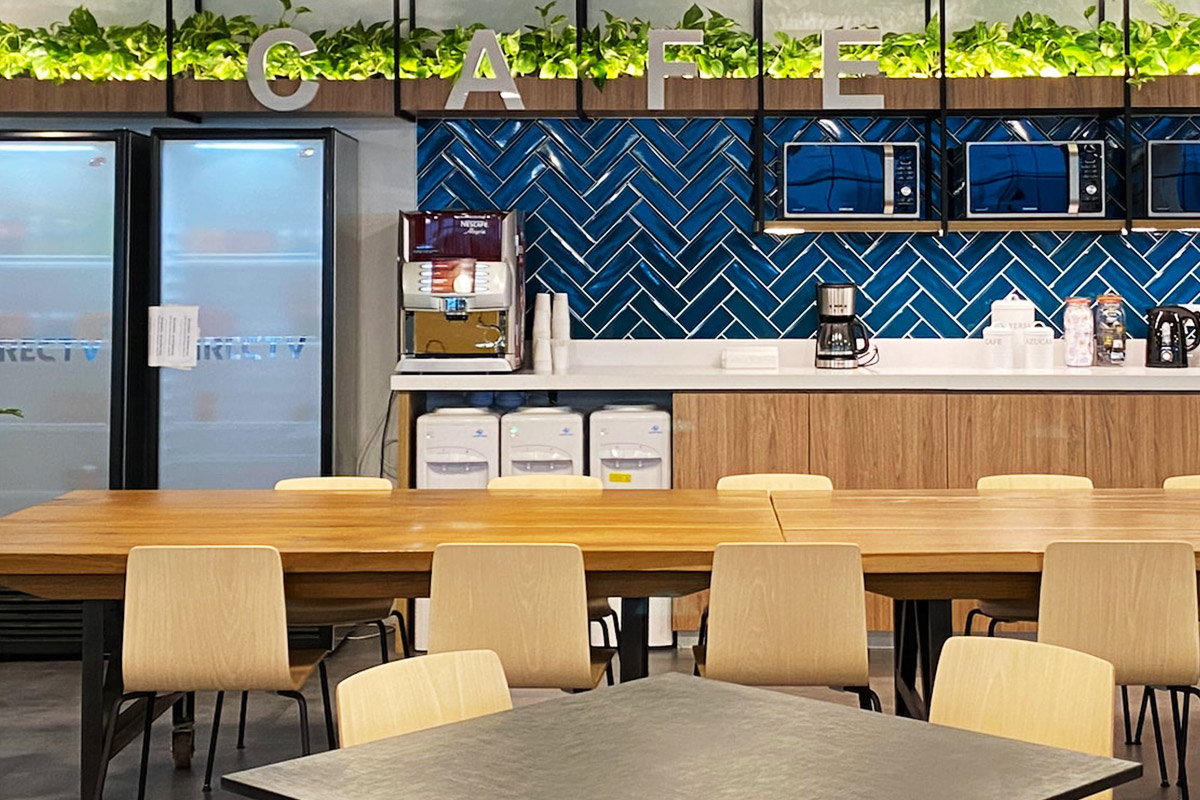
- Worker accommodation buildings – Compliant housing for industrial, agricultural, and energy sector workforces.
- Temporary schools & healthcare units – Flexible educational and medical facilities supporting regional capacity needs.
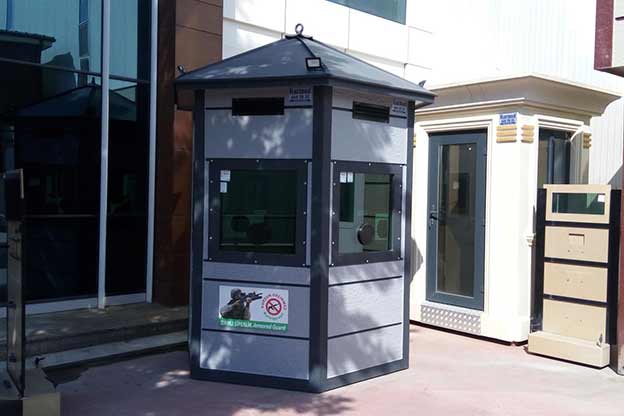
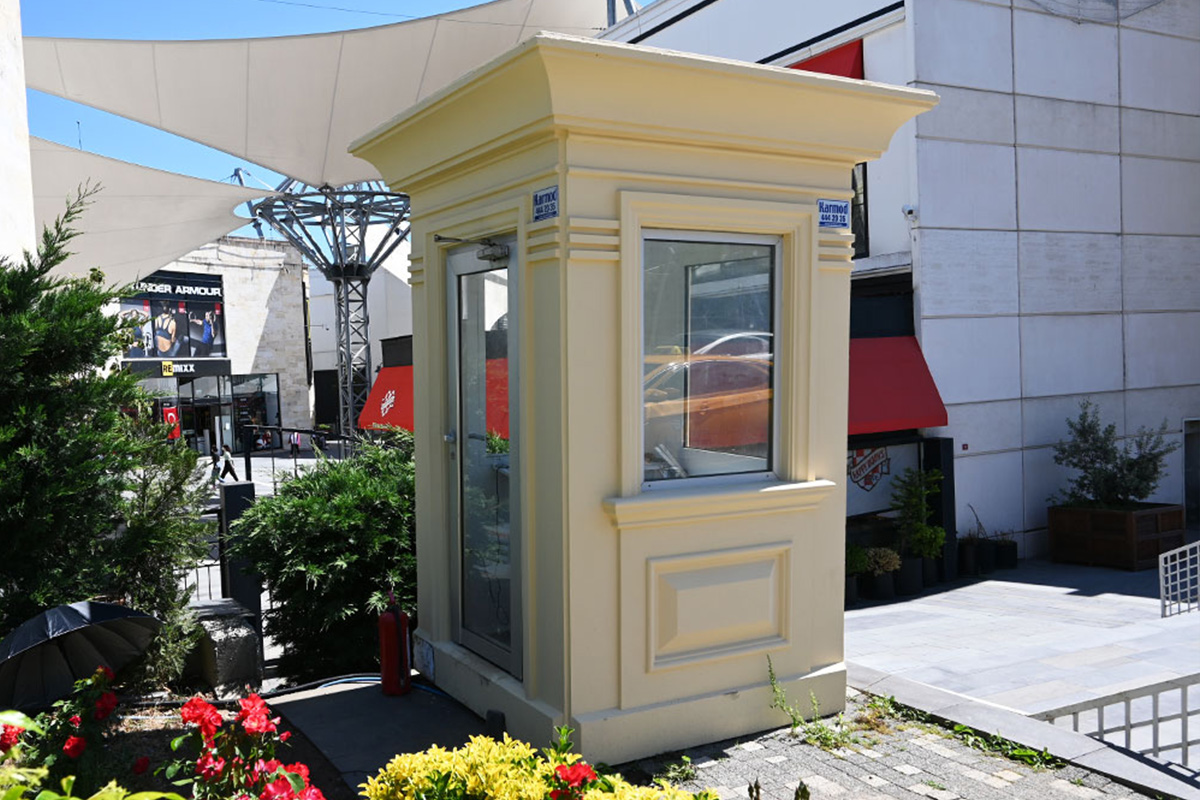
- Security buildings & technical units – Access control points and technical rooms for industrial and logistics sites.
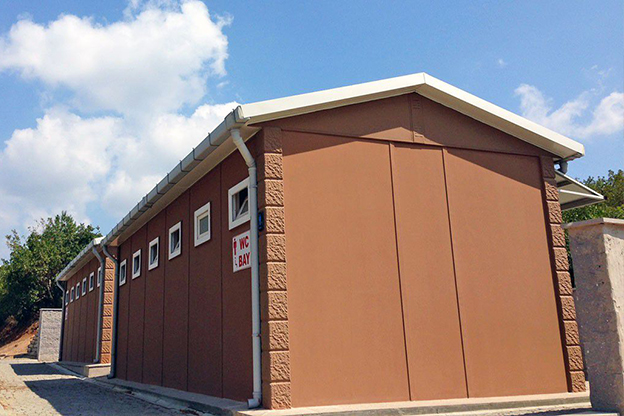
- Storage and logistics facilities – Auxiliary buildings for ports, distribution centers, and intermodal hubs.
These applications demonstrate how modular and prefabricated approaches align with Spain’s operational and regulatory realities.
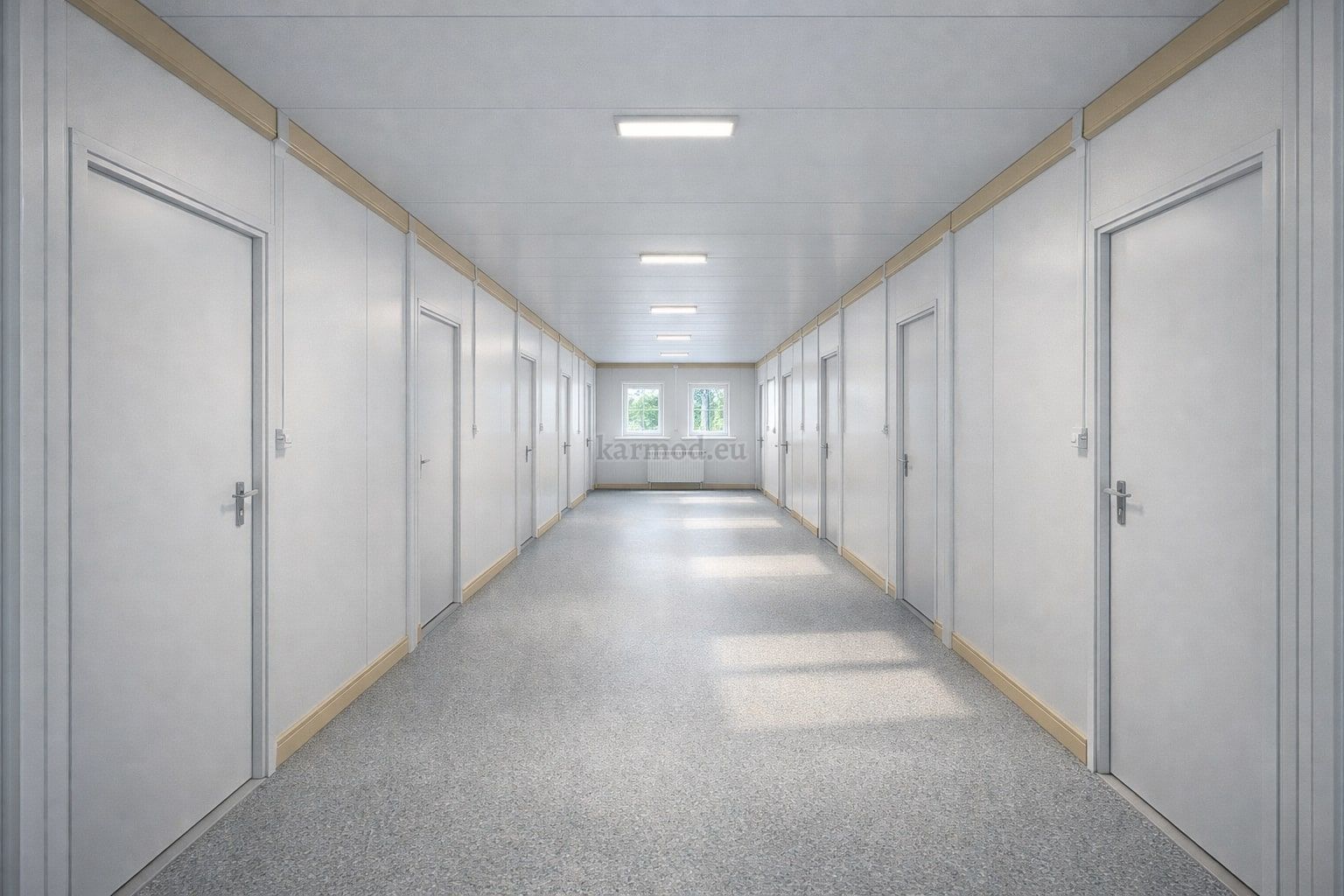

From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
Successful modular and prefabricated projects follow a structured process designed to minimize risk and ensure compliance.
- Project needs analysis – Functional requirements, regulatory constraints, and site conditions are defined early.
- Custom design & specifications – Layouts, insulation, fire safety systems, and finishes are adapted to use case and standards.
- Factory production – Modules or components are manufactured under controlled conditions for consistent quality.
- Delivery to Spain – Transport is coordinated to reduce handling time and site disruption.
- On-site installation – Assembly and commissioning are completed in a short timeframe.
Manufacturers such as Karmod structure this process using experience gained across European markets, aligning delivery with Spain’s regulatory and climatic requirements.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Spain
Thermal insulation: Spain’s climate varies by region. Proper insulation ensures energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
Fire safety standards: Compliance with national and EU fire regulations is essential for all building types.
Climate suitability: Coastal humidity, inland heat, and altitude variations influence material selection and detailing.
Custom layouts: Modular systems support layouts tailored to workflow, occupancy, and future expansion without structural redesign.
Karmod modular building solutions are designed to balance technical compliance with operational flexibility, reflecting experience from diverse European projects. The focus remains on fit-for-purpose structures rather than standardized units.
For organizations evaluating modular buildings or prefabricated building systems in Spain, the priority extends beyond speed to include regulatory confidence, long-term reliability, and adaptability—key factors for informed decision-making.