The construction landscape in the United States of America has been undergoing a structural shift driven by cost pressures, labor shortages, and the need for faster, more adaptable building solutions. In this environment, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems are no longer viewed as alternative options—they are increasingly becoming part of mainstream project planning for both public and private sector decision-makers. From large-scale infrastructure projects to temporary operational facilities, these building methods offer measurable advantages aligned with U.S. market realities.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in United States of America
One of the main drivers behind the growing adoption of modular buildings in the United States of America is the rising cost of skilled labor. Traditional on-site construction requires large teams over extended periods, which directly increases project budgets. Modular construction, by contrast, shifts a significant portion of the work to controlled factory environments, reducing on-site labor dependency and minimizing cost volatility.
Construction timelines also play a decisive role. In the U.S., delays caused by weather conditions, permitting processes, and subcontractor availability can significantly impact delivery schedules. Modular buildings allow parallel progress—site preparation and building production happen simultaneously—resulting in substantially shorter project durations. For industries where time-to-operation is critical, this speed translates directly into financial efficiency.
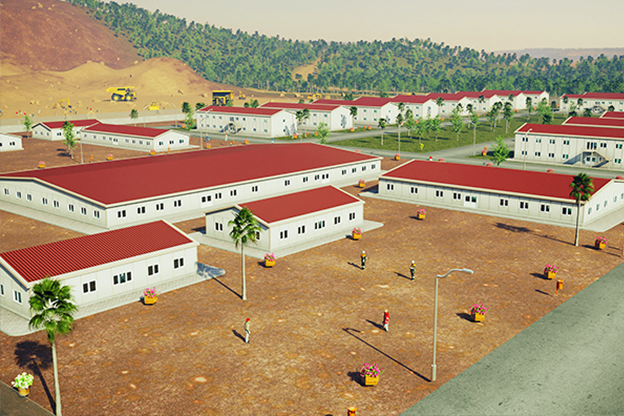
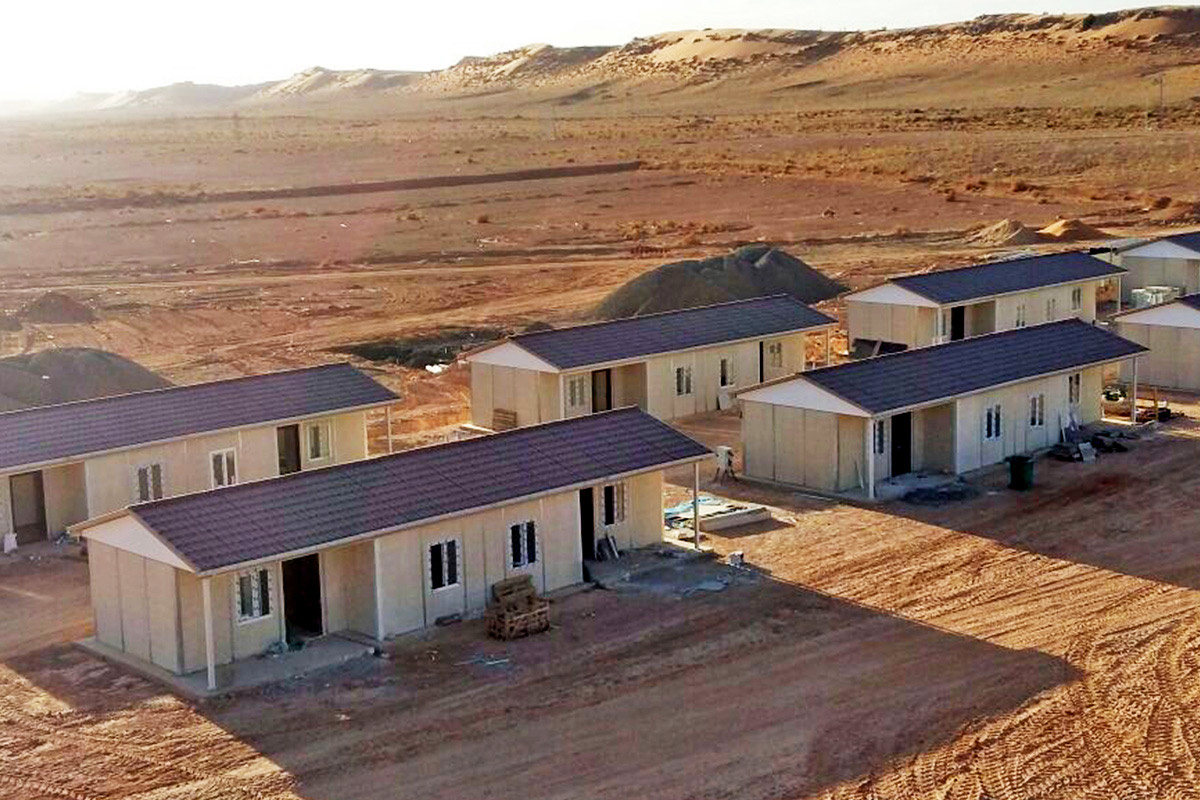
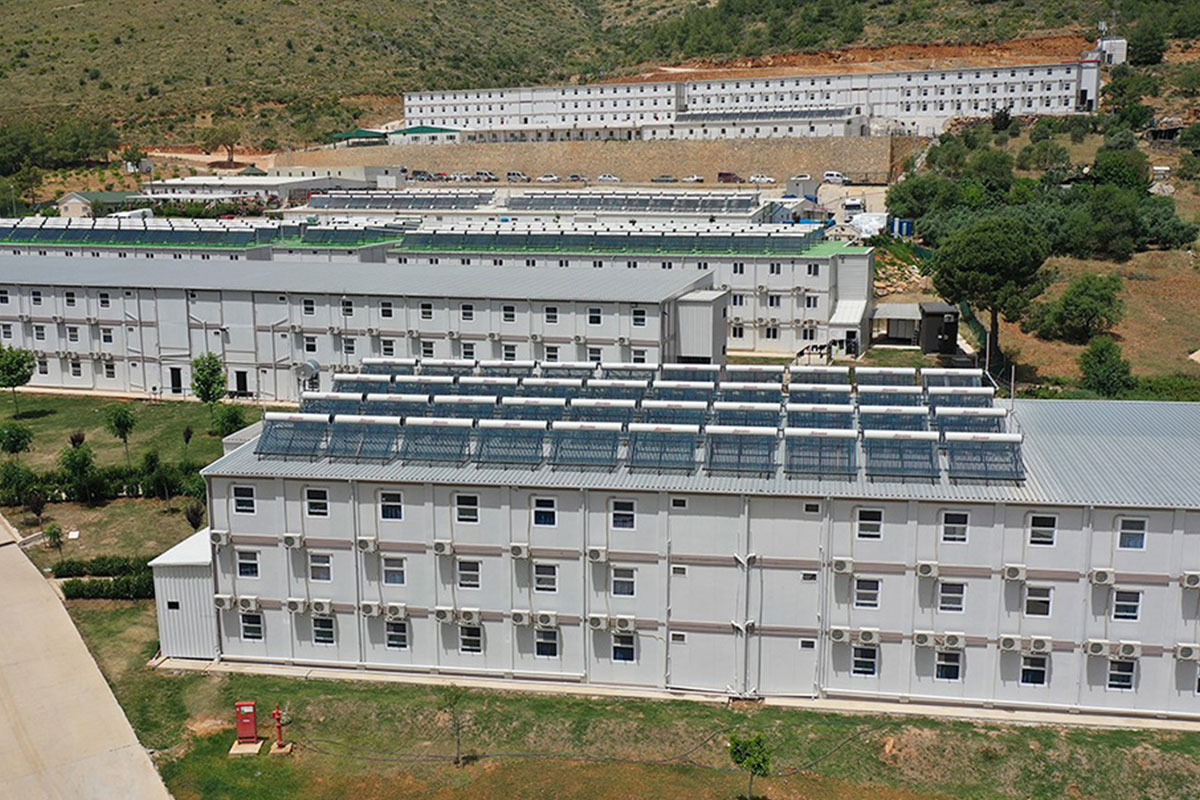
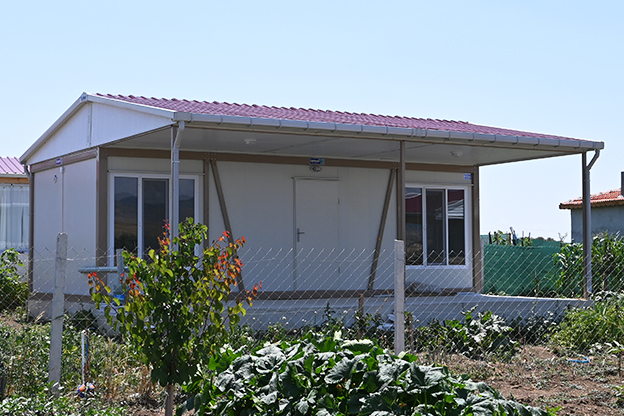
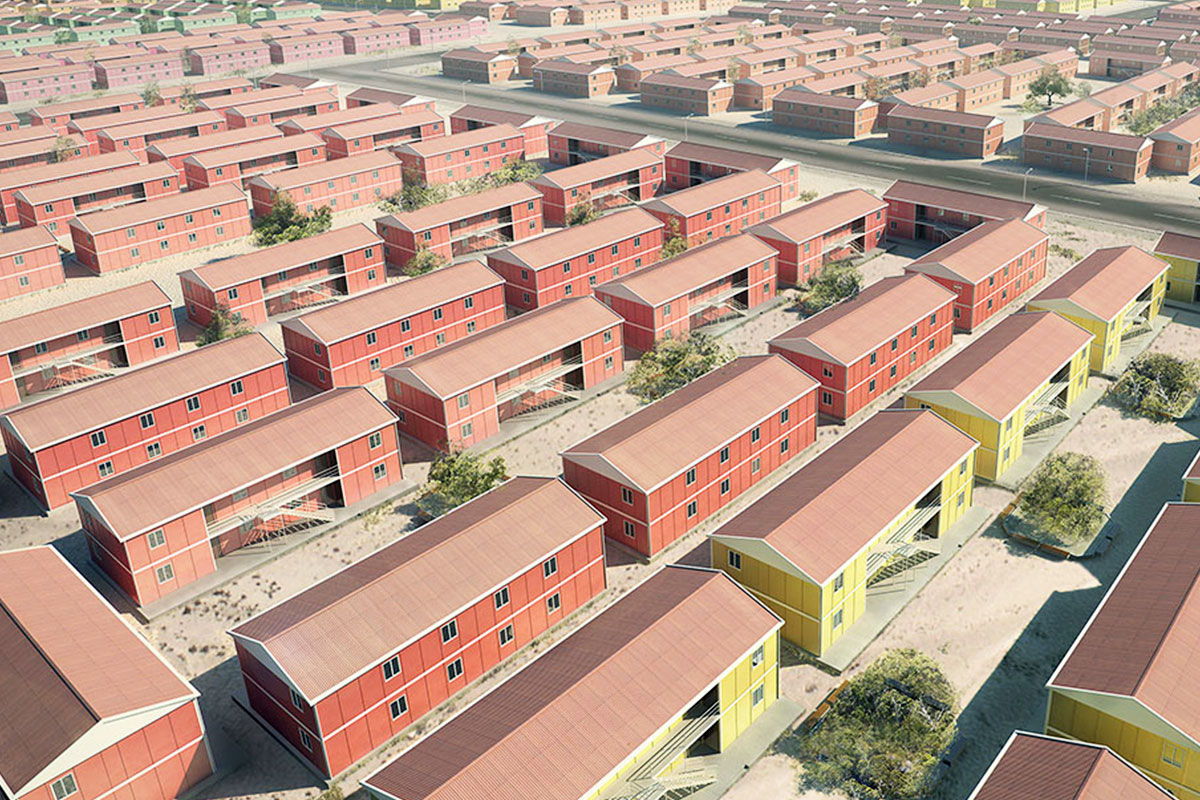
Another important factor is the balance between temporary and permanent building needs. The United States of America hosts a wide range of projects that require structures for defined timeframes, such as infrastructure expansions, energy projects, or disaster recovery operations. At the same time, there is strong demand for permanent facilities in logistics, manufacturing, public services, and education. Modular systems respond well to both scenarios by offering relocatable or long-term solutions without compromising structural performance.
Sector-specific demand further reinforces this trend. Logistics hubs, industrial plants, public sector facilities, and energy projects—particularly in oil, gas, and renewables—frequently require fast-deployed, scalable buildings. Modular buildings align with these sectors by offering flexibility, repeatability, and predictable quality.
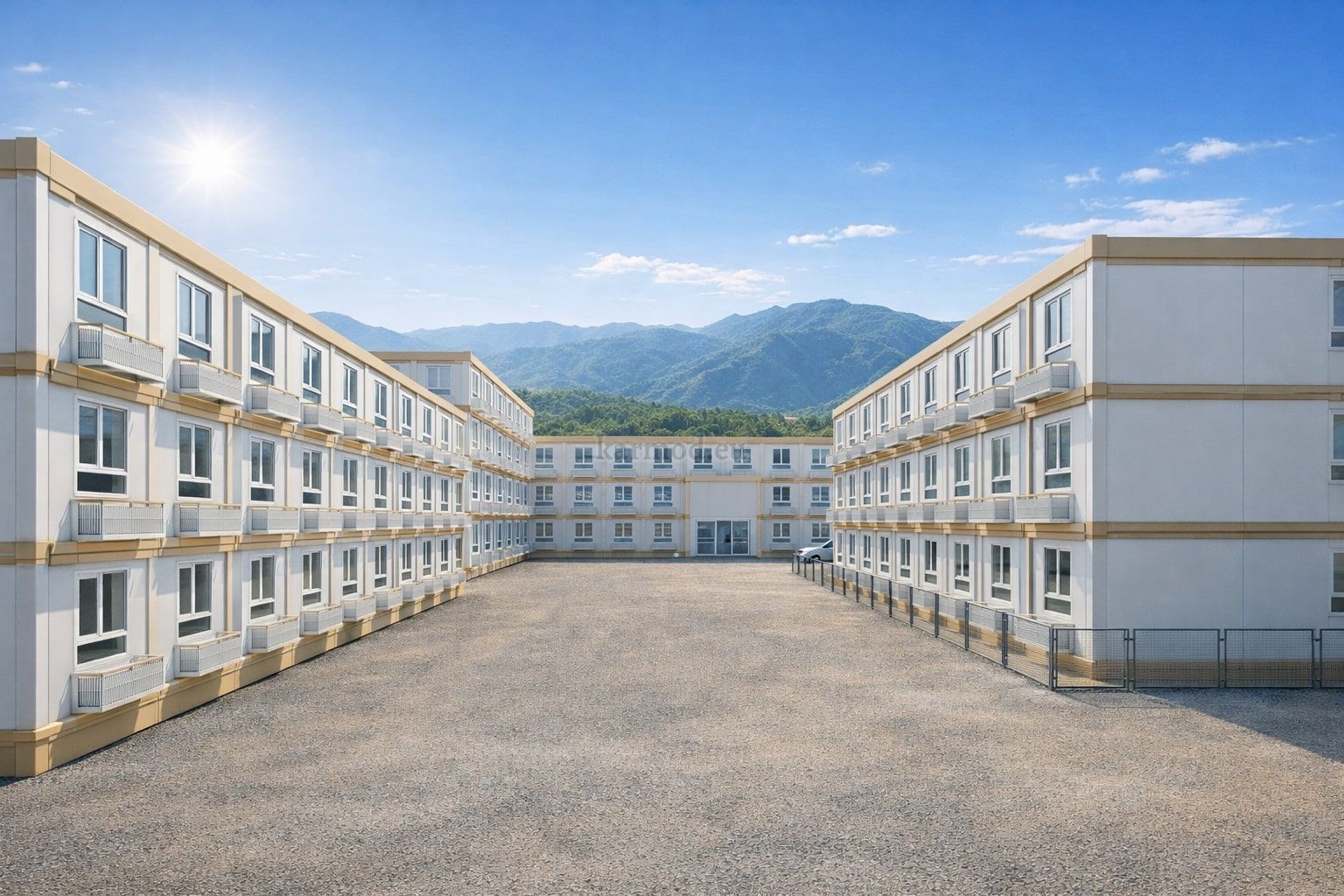

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
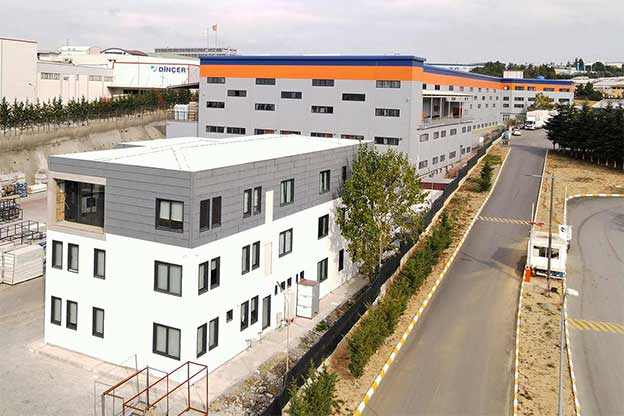
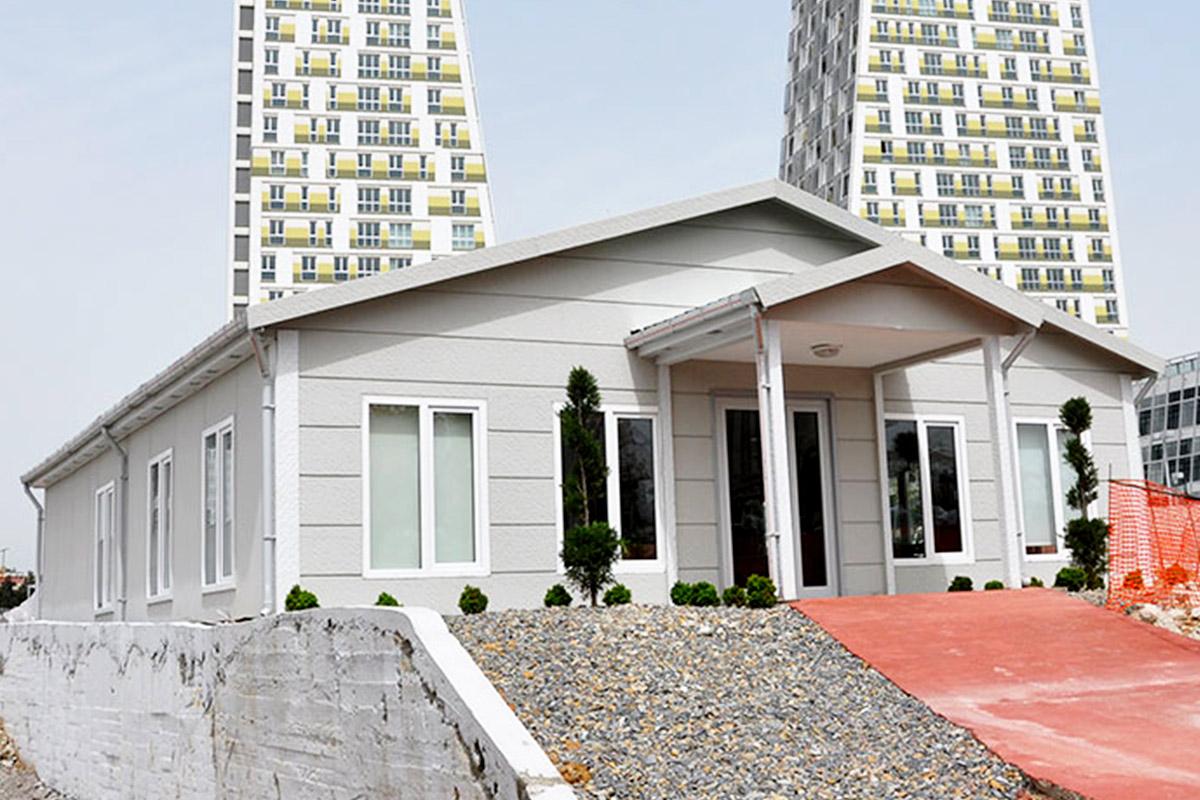
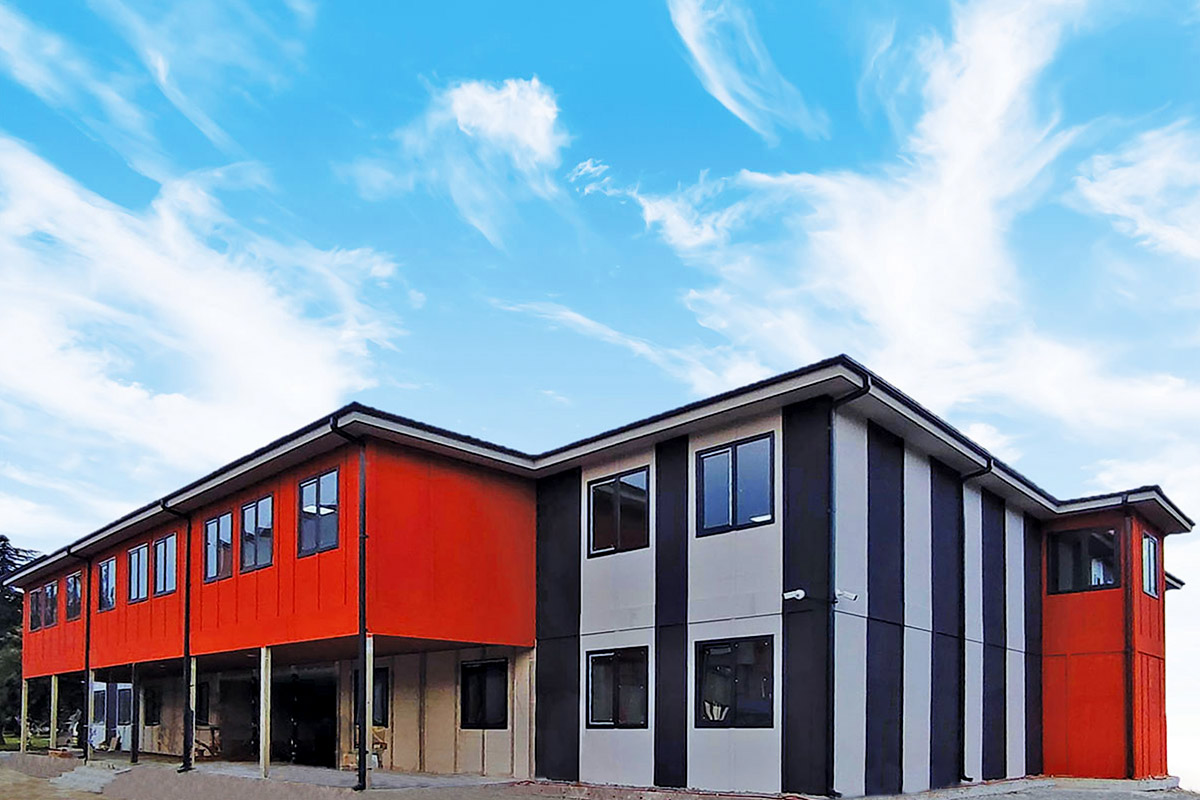
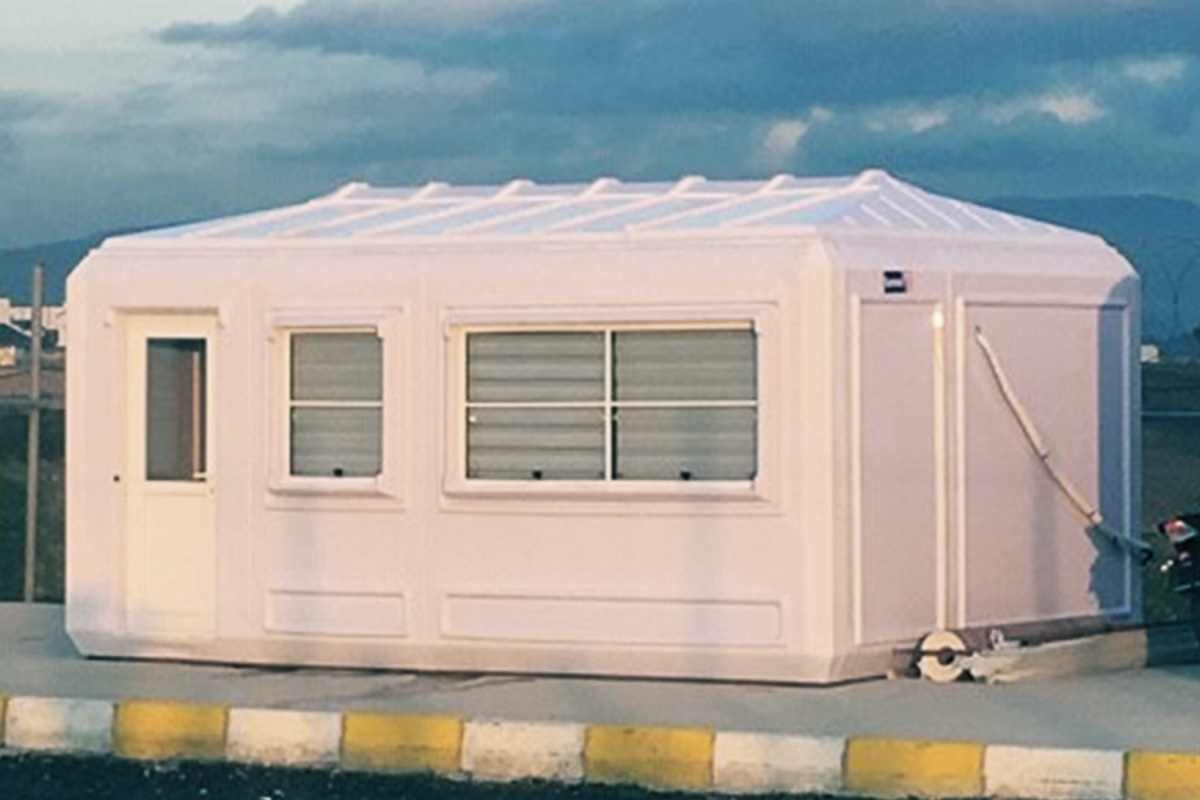
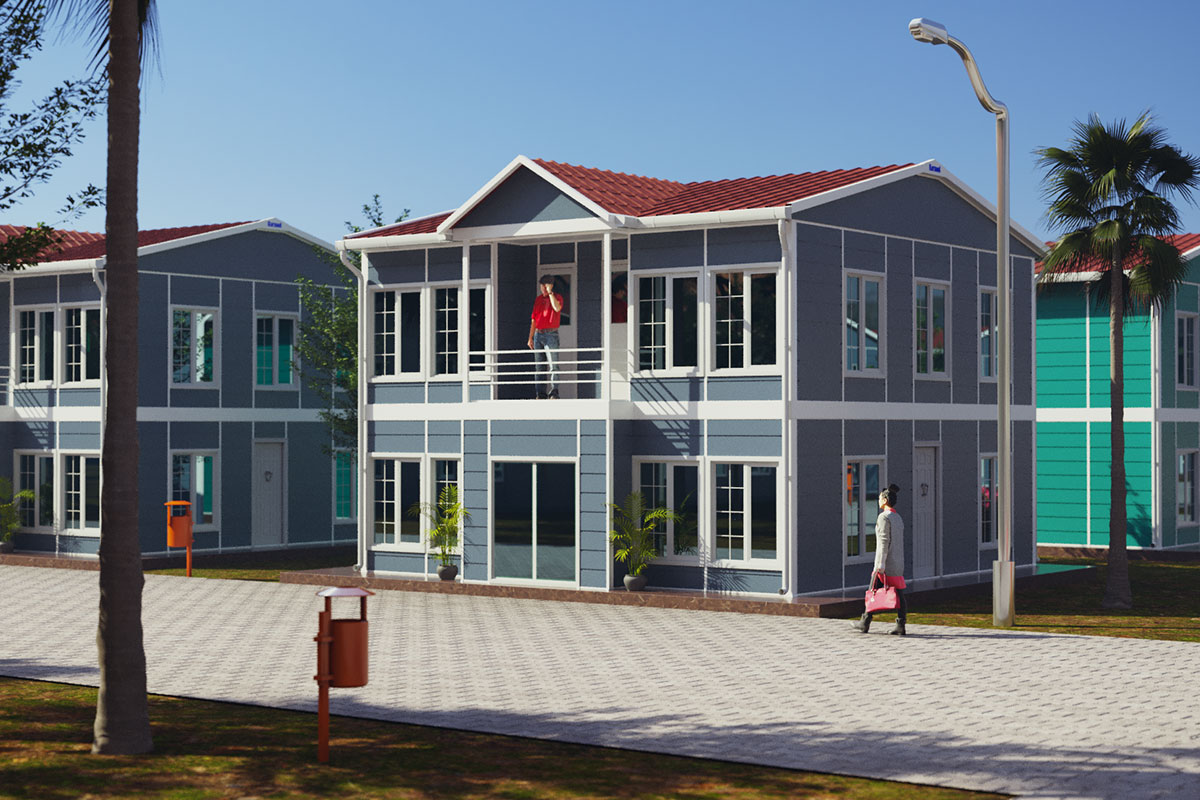
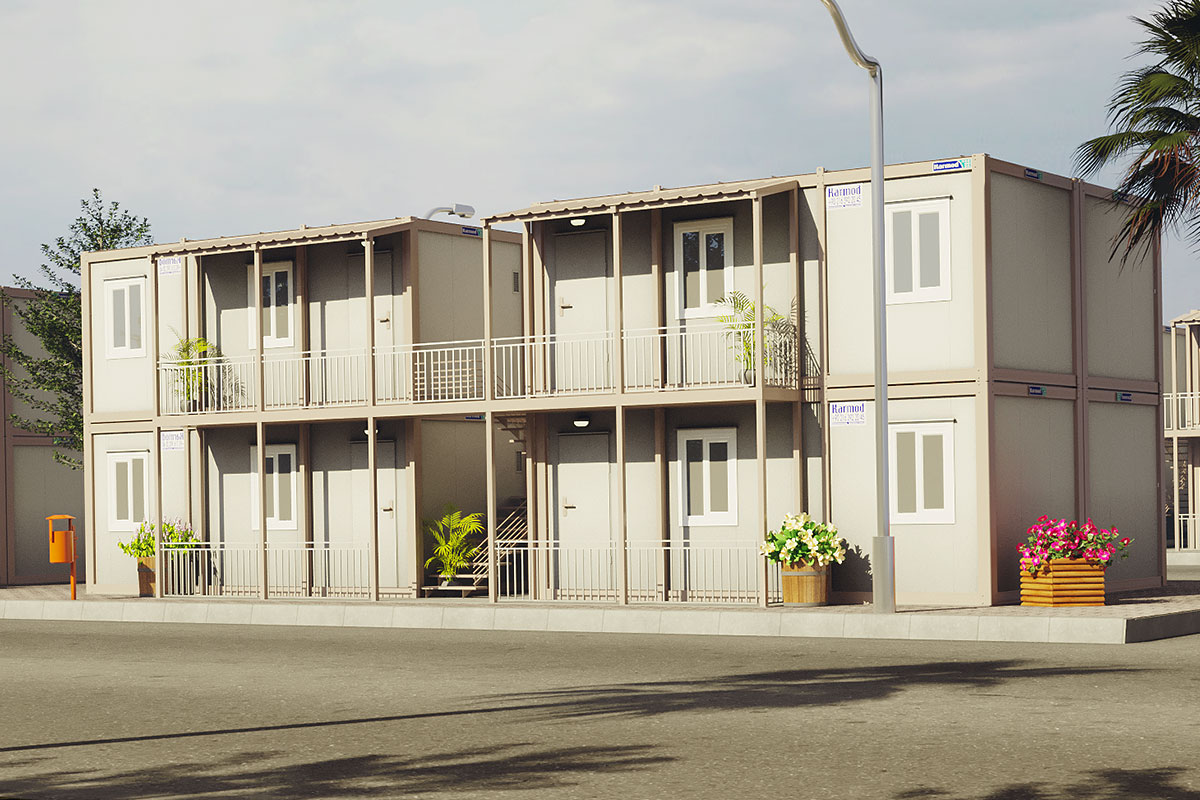
Although often discussed together, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve different strategic purposes. Modular buildings are based on volumetric modules that are produced in factories as near-complete units. These modules can be transported, installed quickly on-site, relocated if necessary, and expanded over time. This makes modular buildings particularly suitable for projects where flexibility and mobility are essential.
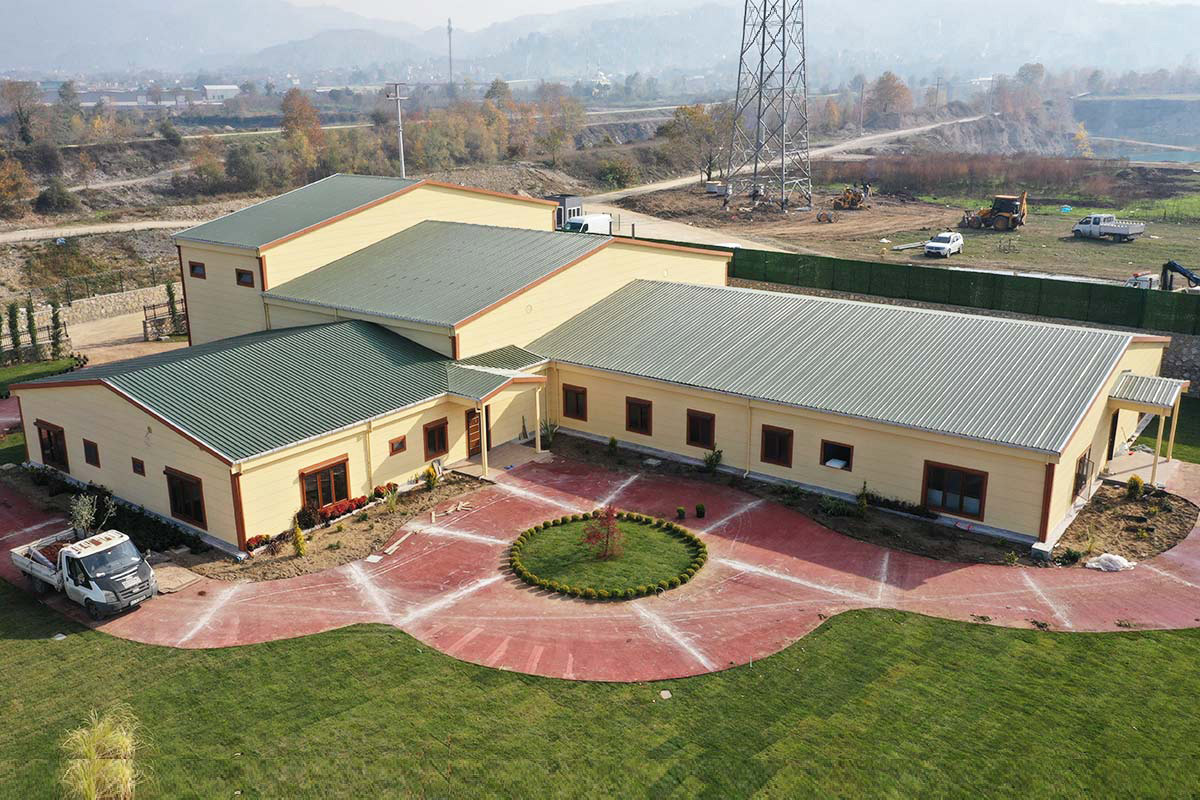
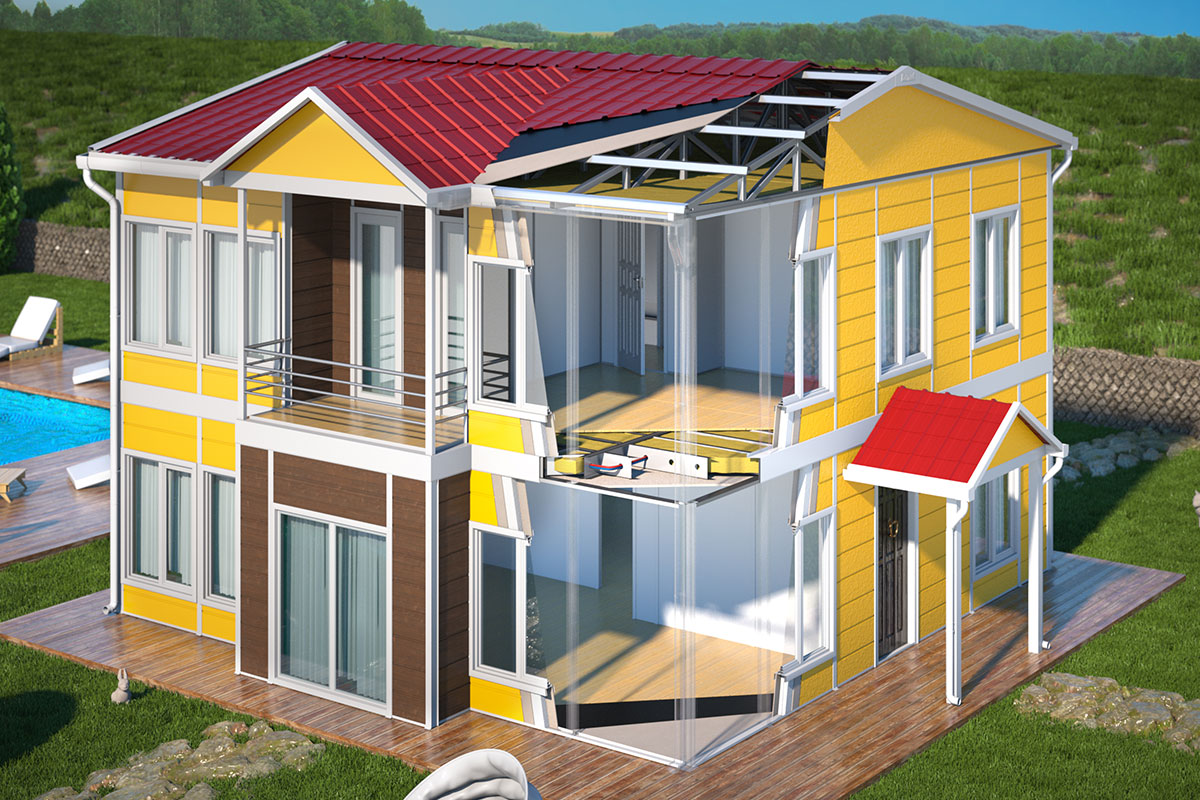
A prefabricated building, on the other hand, is typically constructed using panels or pre-engineered structural elements that are assembled on-site into a permanent structure. These systems are ideal for long-term facilities where customization, architectural integration, and fixed layouts are priorities. Prefabricated building solutions often resemble traditional construction in appearance while benefiting from factory-controlled quality and efficiency.
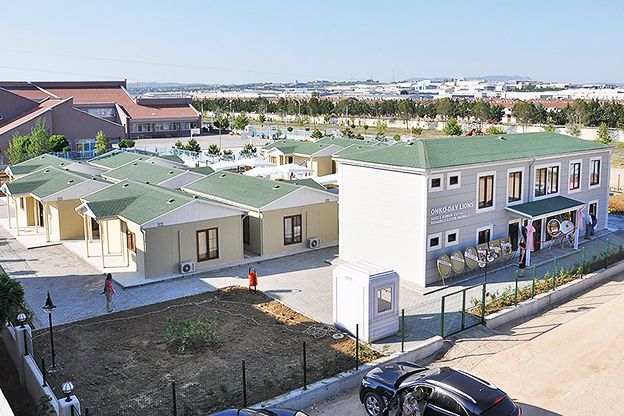
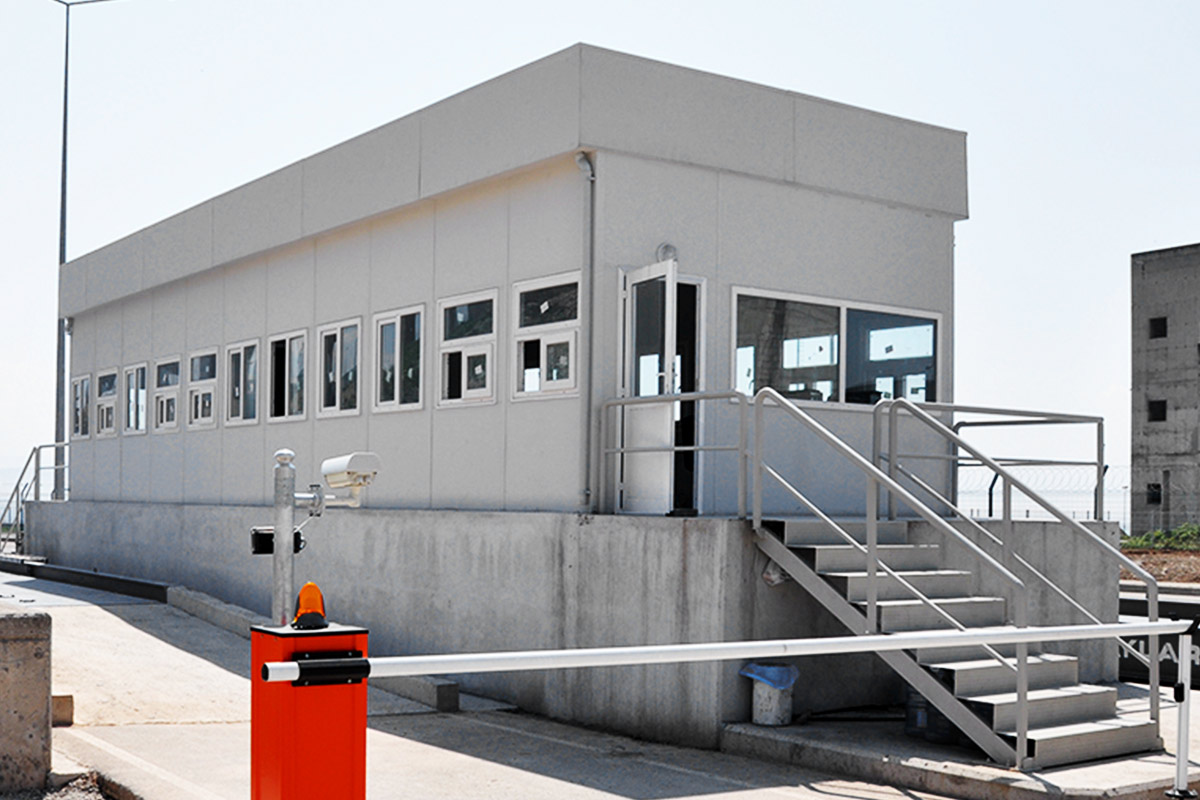
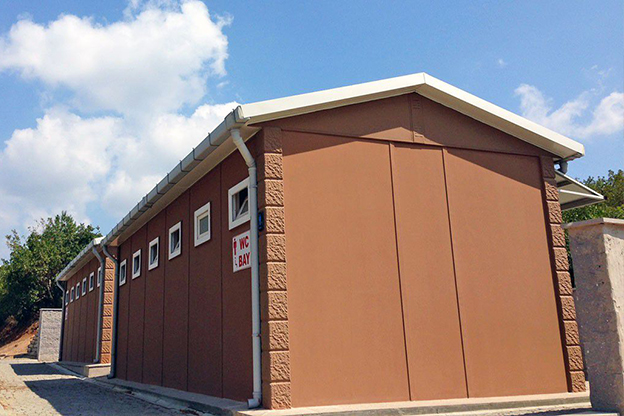
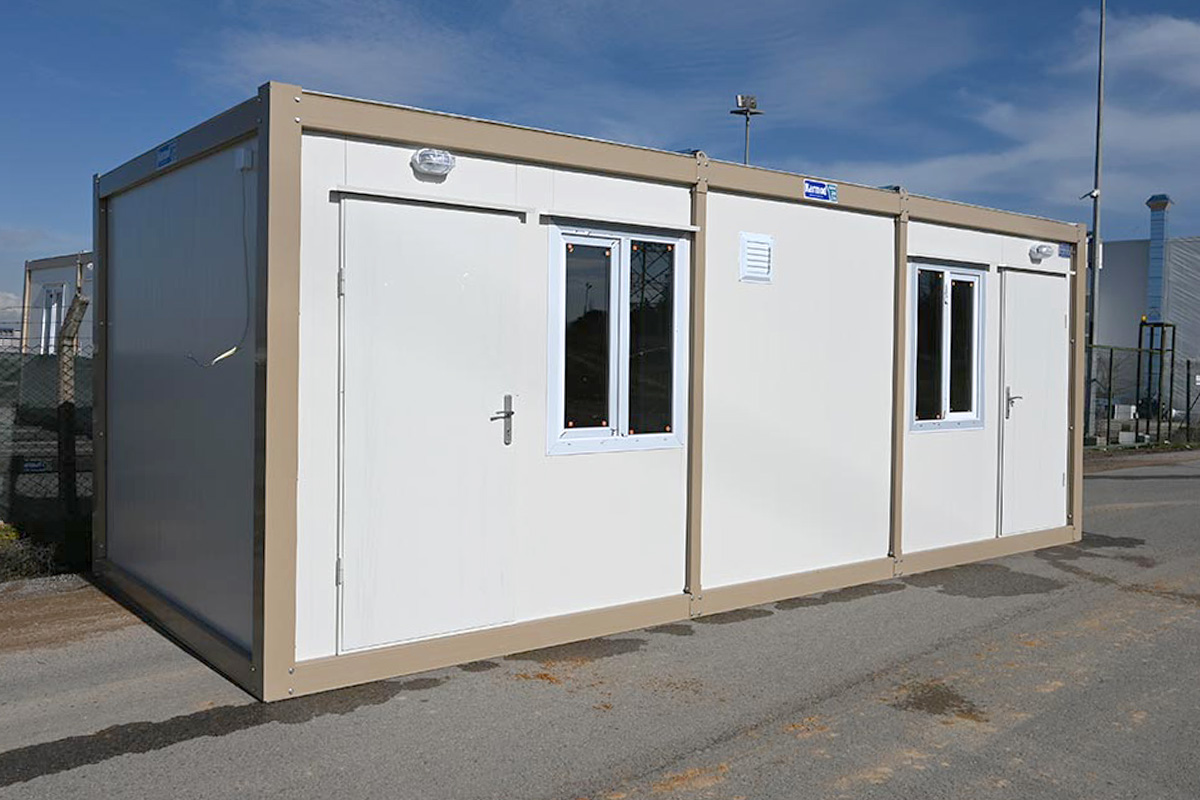
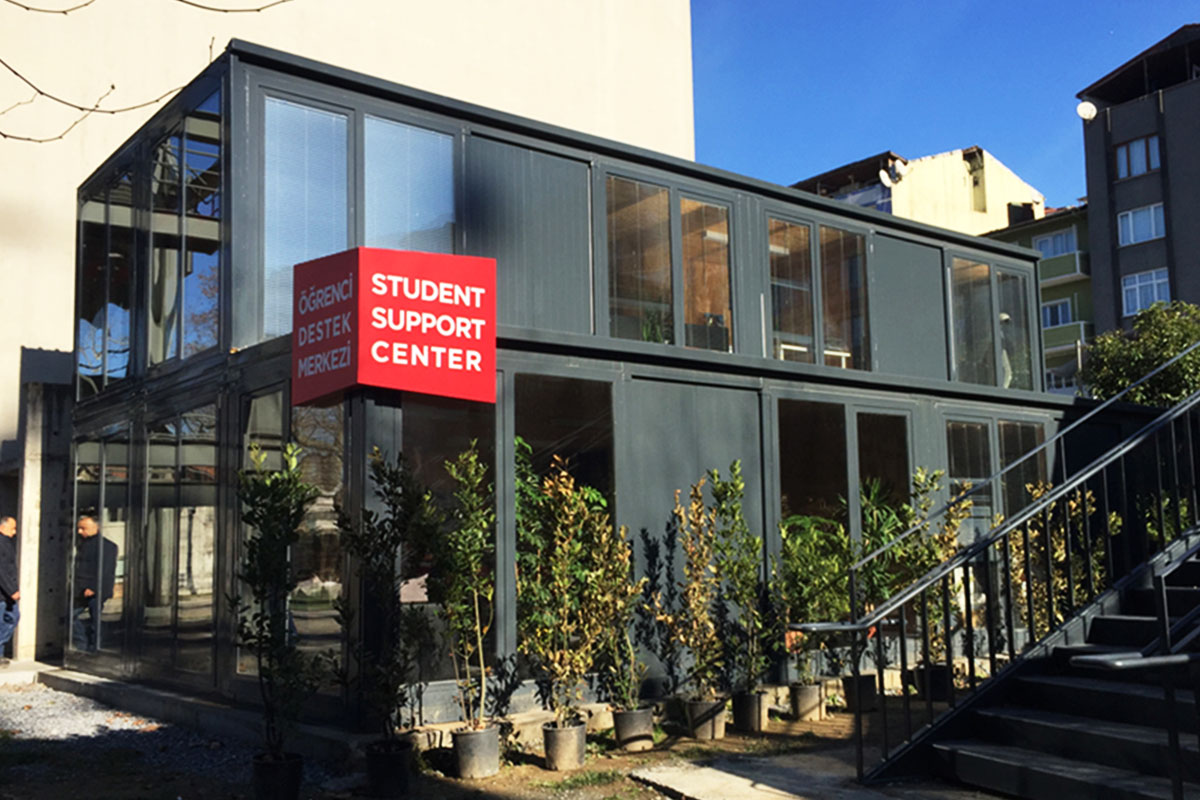
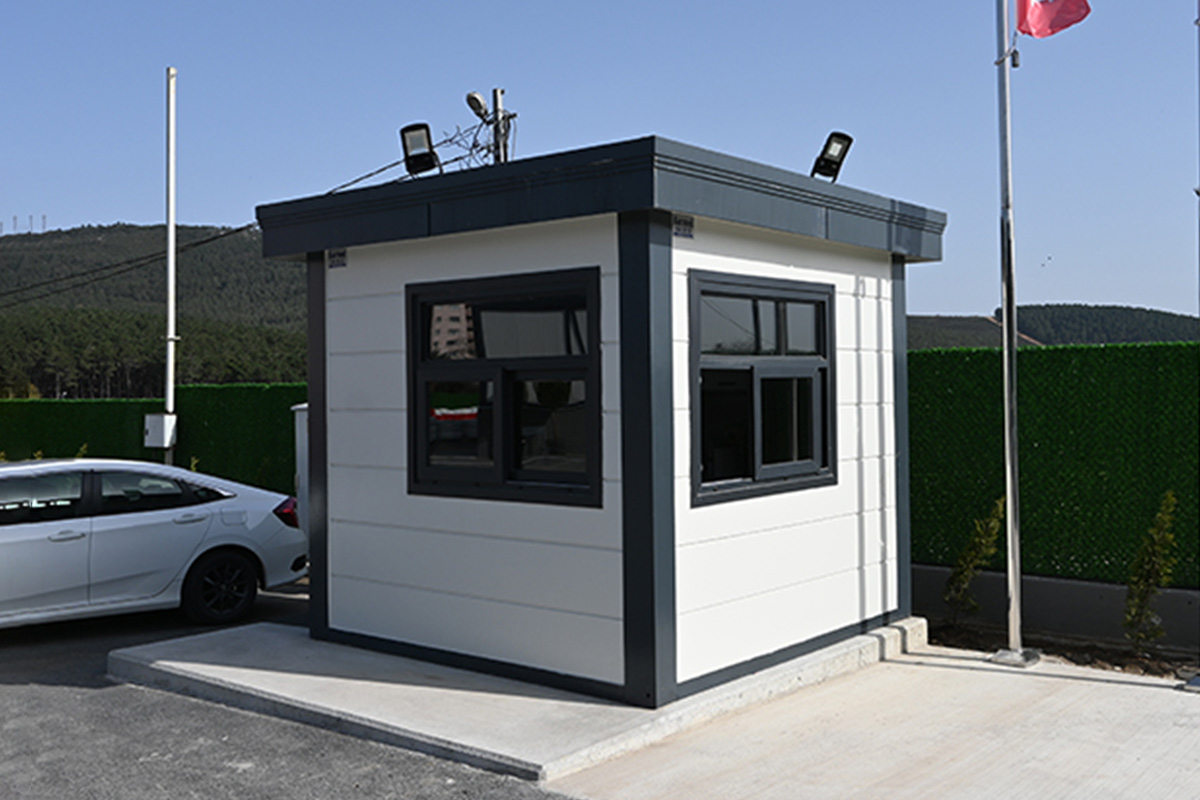
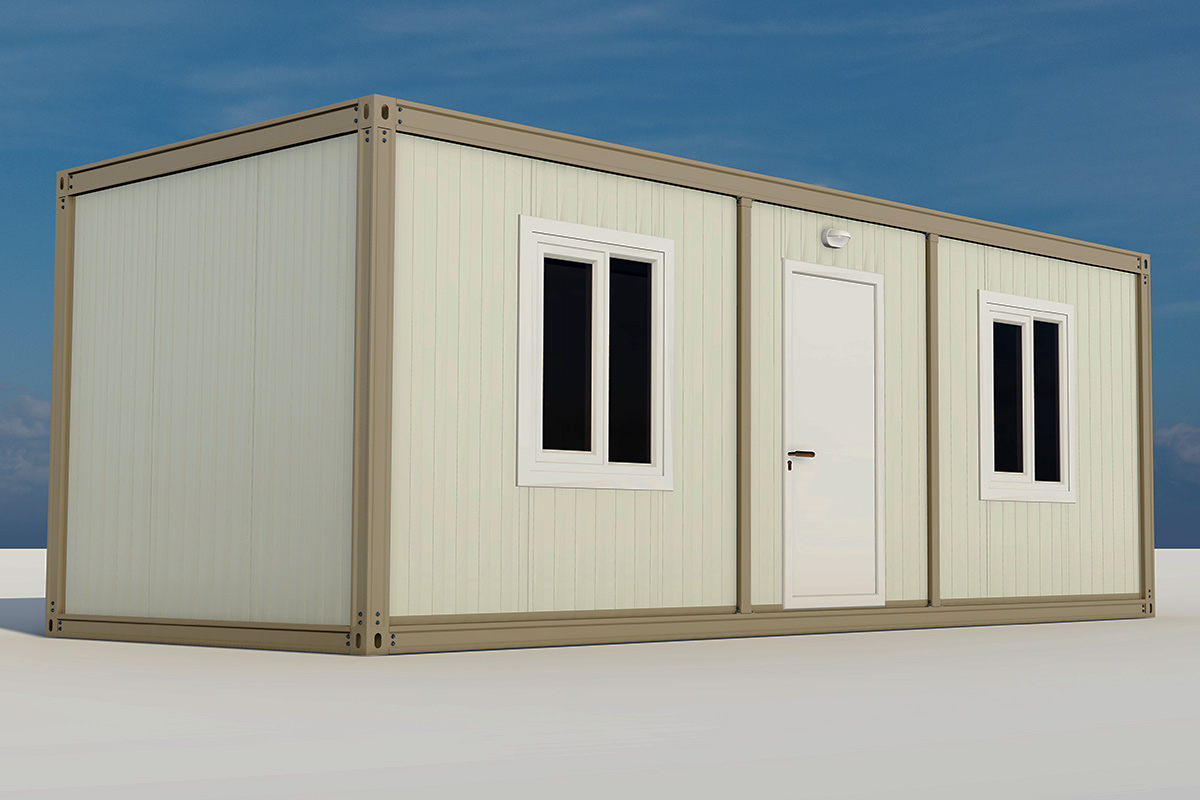
In the United States of America, modular buildings are commonly preferred for site offices, temporary accommodation, technical units, and rapid-deployment facilities. Prefabricated building systems are more frequently selected for permanent schools, healthcare facilities, administrative buildings, and industrial structures where long service life and design continuity are required. Understanding this distinction helps decision-makers select the most suitable system based on operational goals rather than short-term cost alone.
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in United States of America
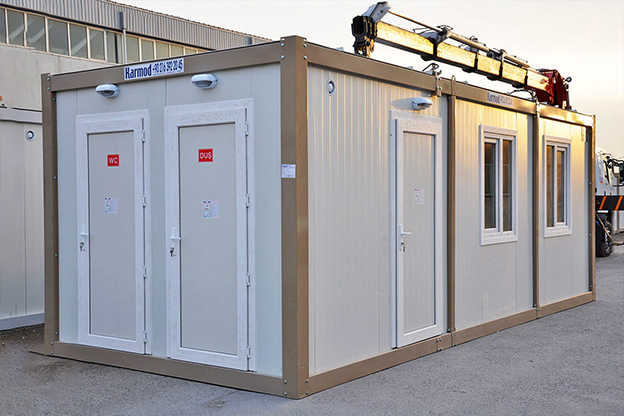
- Site offices & construction camps used across infrastructure, transportation, and large-scale commercial projects
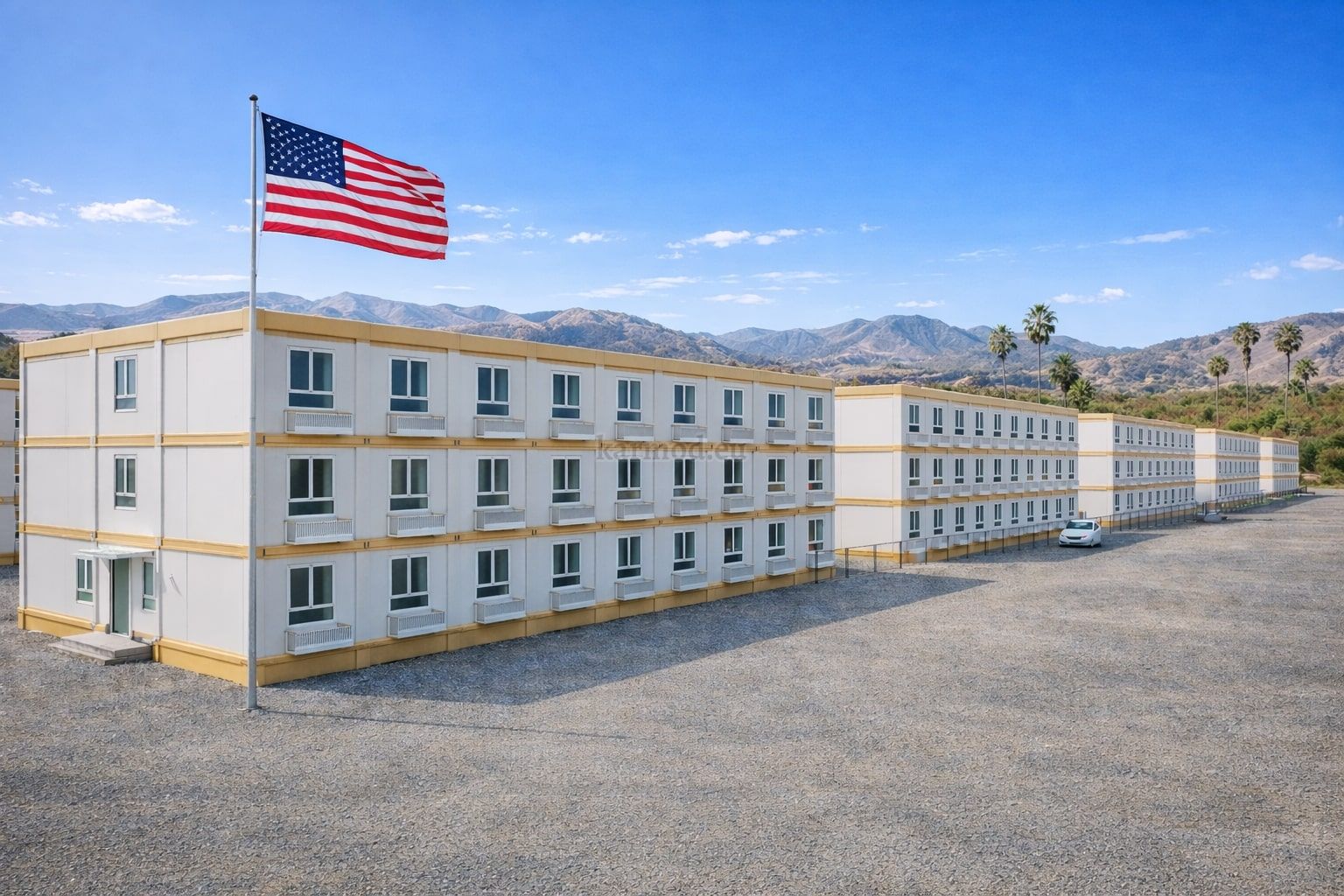
- Worker accommodation buildings for energy, mining, and industrial developments in remote or high-demand regions
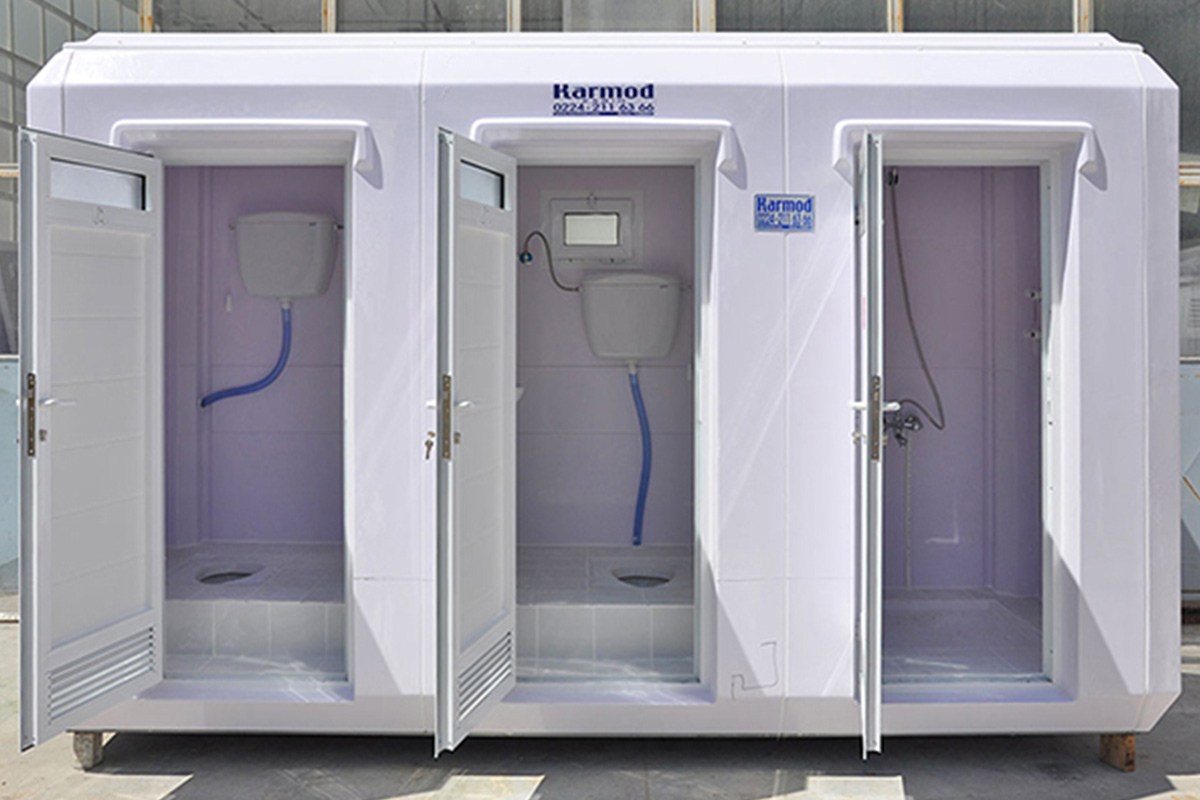
- Temporary schools & healthcare units supporting population growth, renovations, or emergency response needs
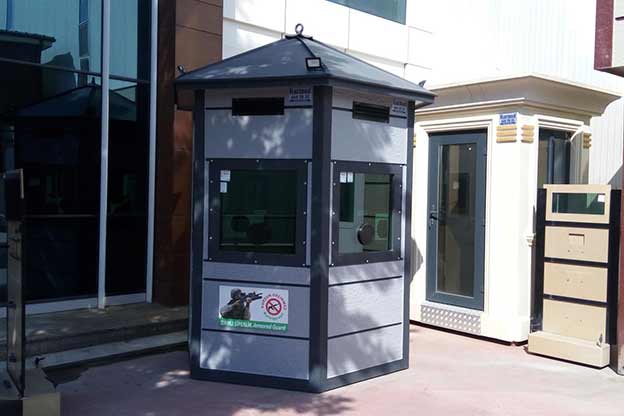
- Security buildings & technical units for controlled access points, data centers, and critical infrastructure sites
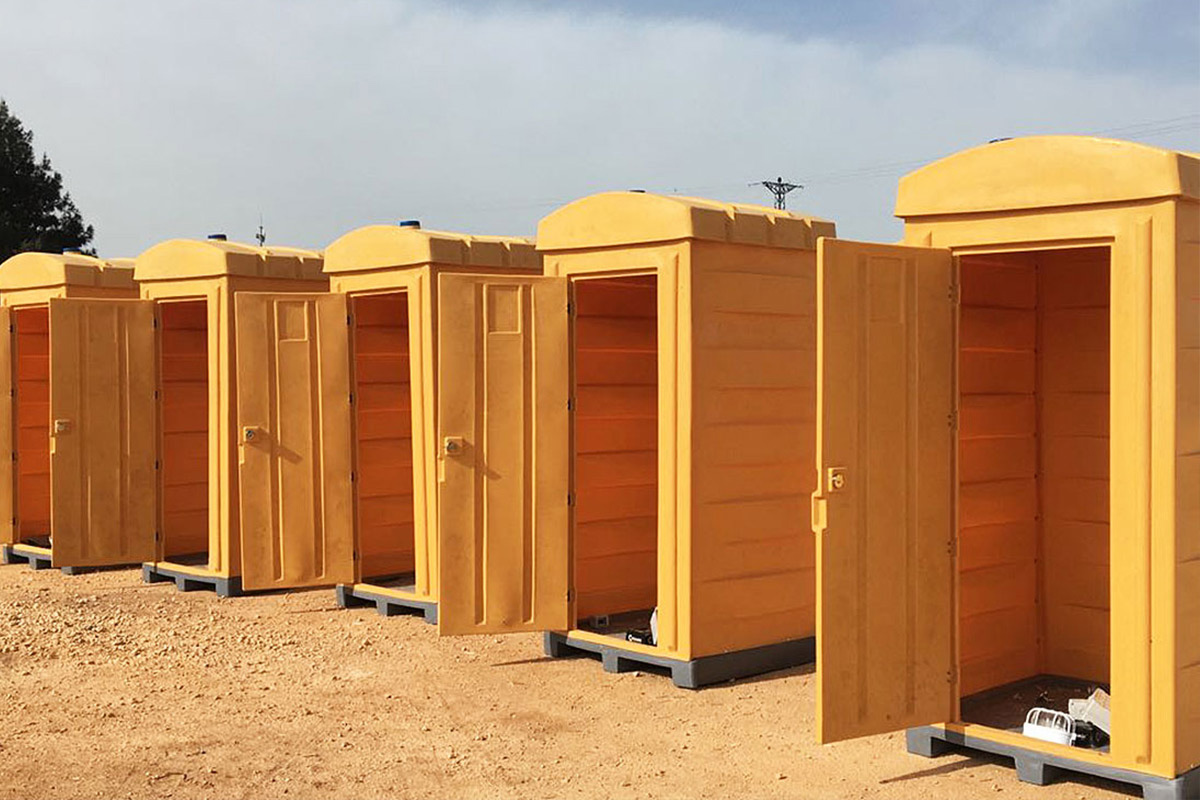
- Storage and logistics facilities that require rapid setup and scalable capacity near distribution hubs
These applications highlight how both modular buildings and prefabricated building systems integrate seamlessly into U.S. operational environments without disrupting existing workflows.
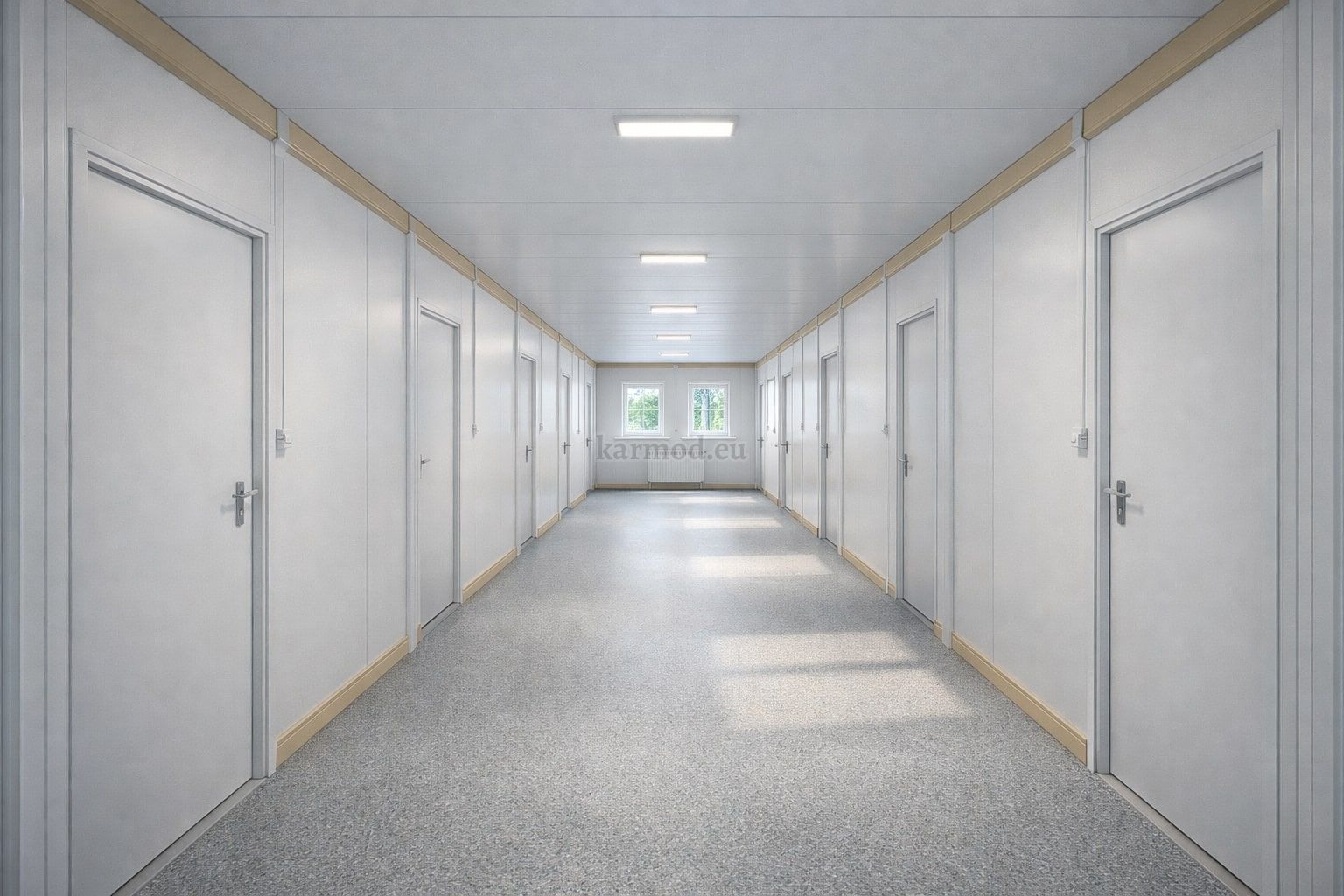

From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The process begins with a detailed project needs analysis. This stage focuses on usage requirements, occupancy levels, regulatory considerations, and site conditions specific to the United States of America. Clear definition at this stage ensures efficiency throughout the project lifecycle.
Next comes custom design and technical specification development. Layouts, insulation levels, fire safety measures, and mechanical systems are tailored to project requirements and local codes. This customization phase is critical for aligning performance expectations with operational realities.
Factory production follows, where building components or modules are manufactured under controlled conditions. This approach ensures consistent quality, minimizes material waste, and reduces the risk of on-site errors.
Once production is completed, units are delivered to the United States of America project location using optimized logistics planning. On-site installation is then carried out rapidly, often within days, depending on project scale. This streamlined process significantly reduces site disruption and accelerates operational readiness.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in United States of America
Thermal insulation is a primary consideration due to the diverse climate zones across the country. Buildings must perform efficiently in both extreme cold and high-temperature regions, making insulation design a critical decision point.
Fire safety standards are equally important. Compliance with U.S. fire regulations and project-specific safety requirements must be integrated into both design and material selection from the outset.
Climate suitability extends beyond temperature. Wind loads, seismic considerations, and regional weather patterns influence structural engineering decisions, especially for long-term installations.
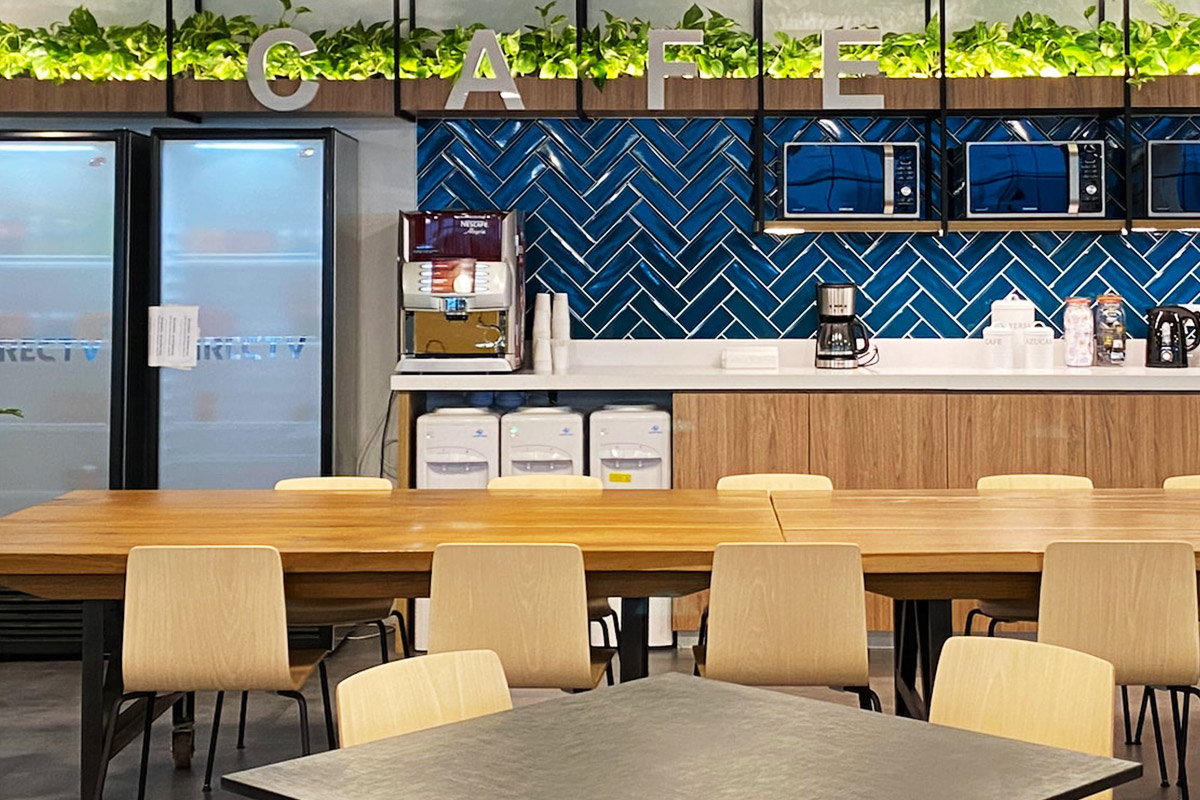
Custom layouts allow organizations to align building design with operational workflows. From office configurations to accommodation layouts, flexibility in design ensures that buildings support productivity rather than constrain it.
With extensive experience in international markets, Karmod brings a refined understanding of how modular buildings and prefabricated building systems should be adapted for different regulatory and operational contexts. Drawing on its European project background, Karmod modular building solutions are designed to balance durability, speed, and functional efficiency without relying on short-term construction compromises. For U.S.-based decision-makers seeking reliable, scalable building solutions, this level of experience provides confidence throughout the project lifecycle.
By addressing real operational challenges rather than focusing on surface-level advantages, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems continue to establish themselves as practical, future-oriented solutions in the United States of America construction market.