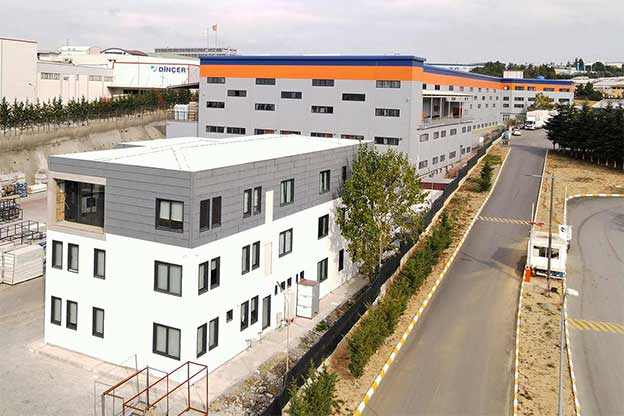
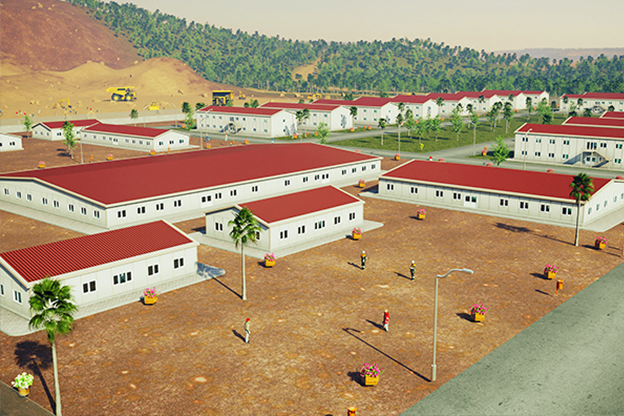
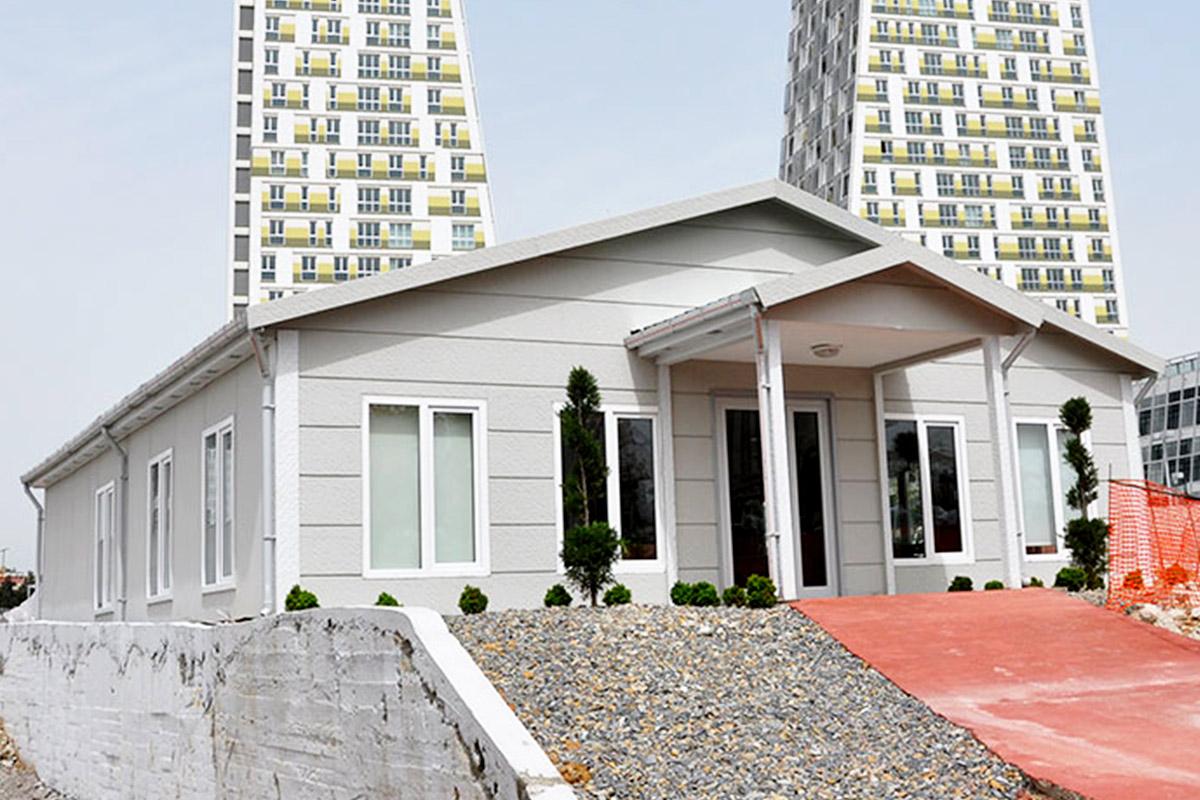
Tanzania continues to invest in infrastructure, energy, logistics, and public services as part of its long-term development agenda. Large-scale projects, regional connectivity initiatives, and growing industrial activity have increased demand for building solutions that can be delivered quickly, perform reliably, and remain adaptable over time. Within this framework, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems have gained strong relevance as structured construction methods that support planned growth rather than short-term fixes.
Why Modular Buildings Are in High Demand in Tanzania
Labour availability and cost control are important factors influencing construction decisions in Tanzania. While the country has an active construction workforce, traditional on-site building methods can lead to variability in quality and timelines, particularly in remote or rapidly developing regions. Modular buildings help reduce on-site complexity by shifting most production activities to factory-controlled environments, improving consistency and predictability.
Construction speed is another critical driver. Many projects in Tanzania—such as infrastructure support facilities, energy projects, and logistics developments—operate under strict timelines. Modular construction allows site preparation and building production to progress simultaneously. This parallel workflow shortens project durations and enables facilities to become operational sooner, which is especially valuable in regions with limited access to skilled on-site resources.
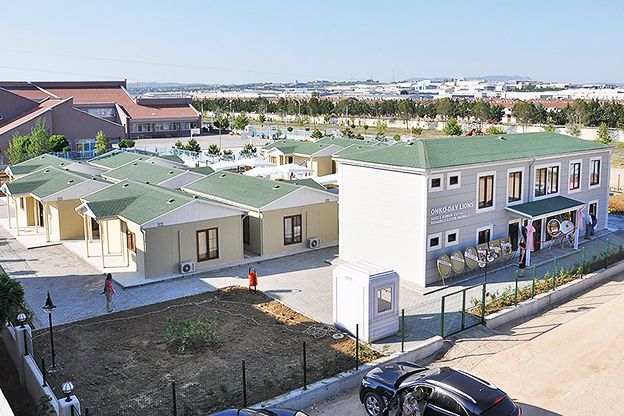
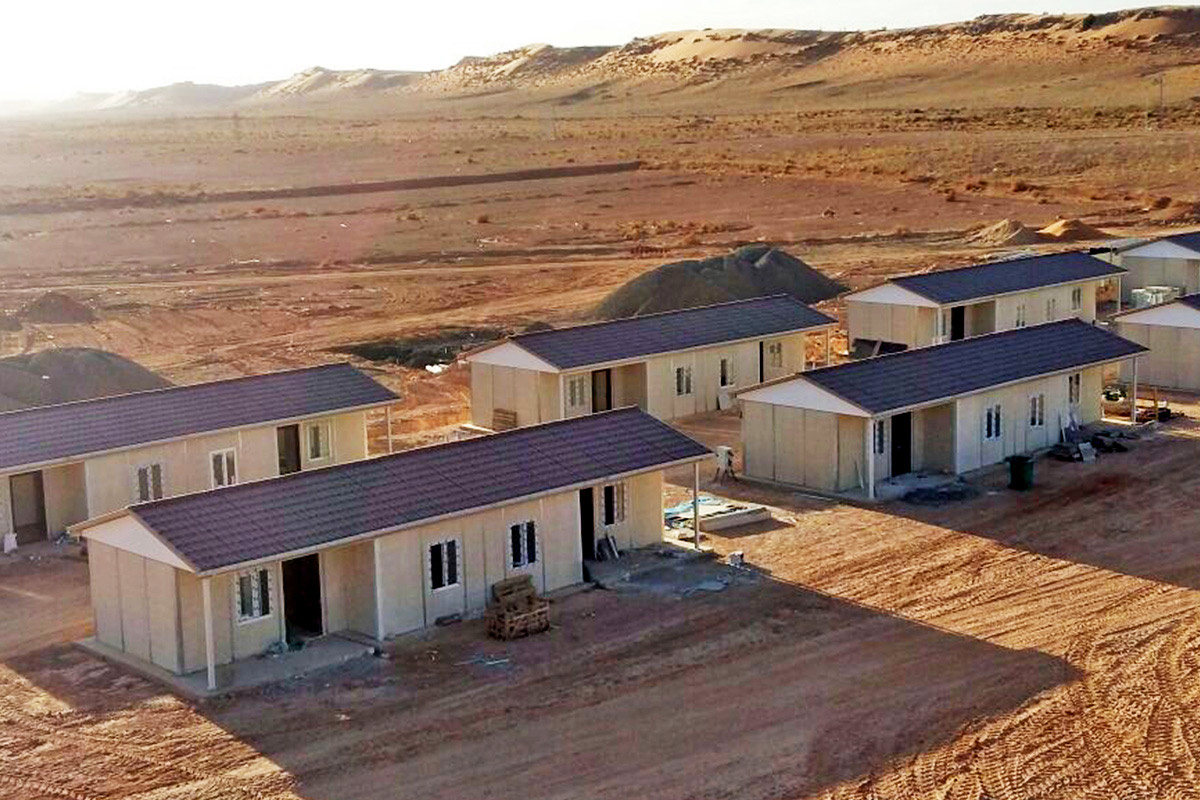
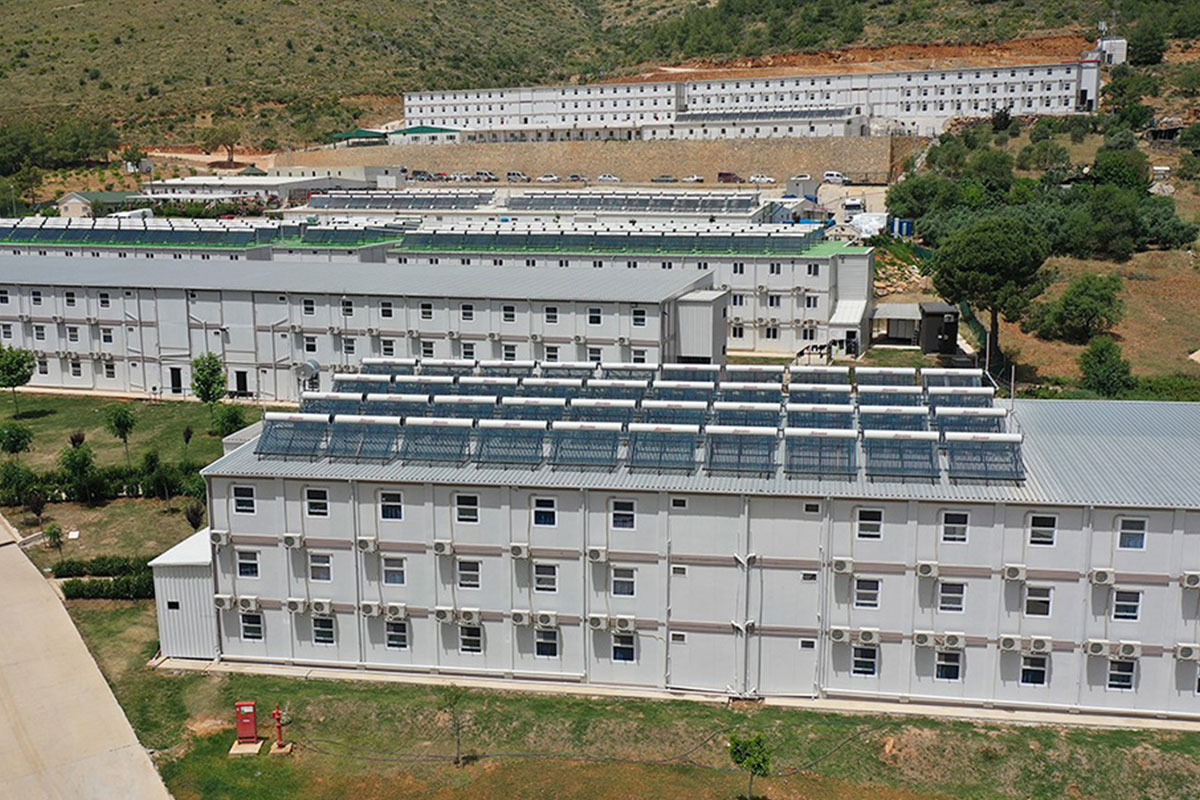
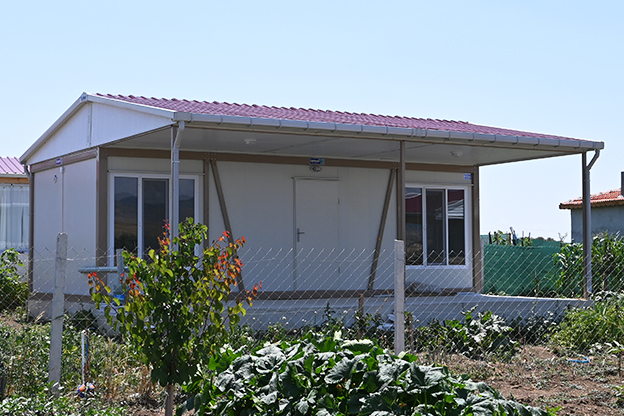
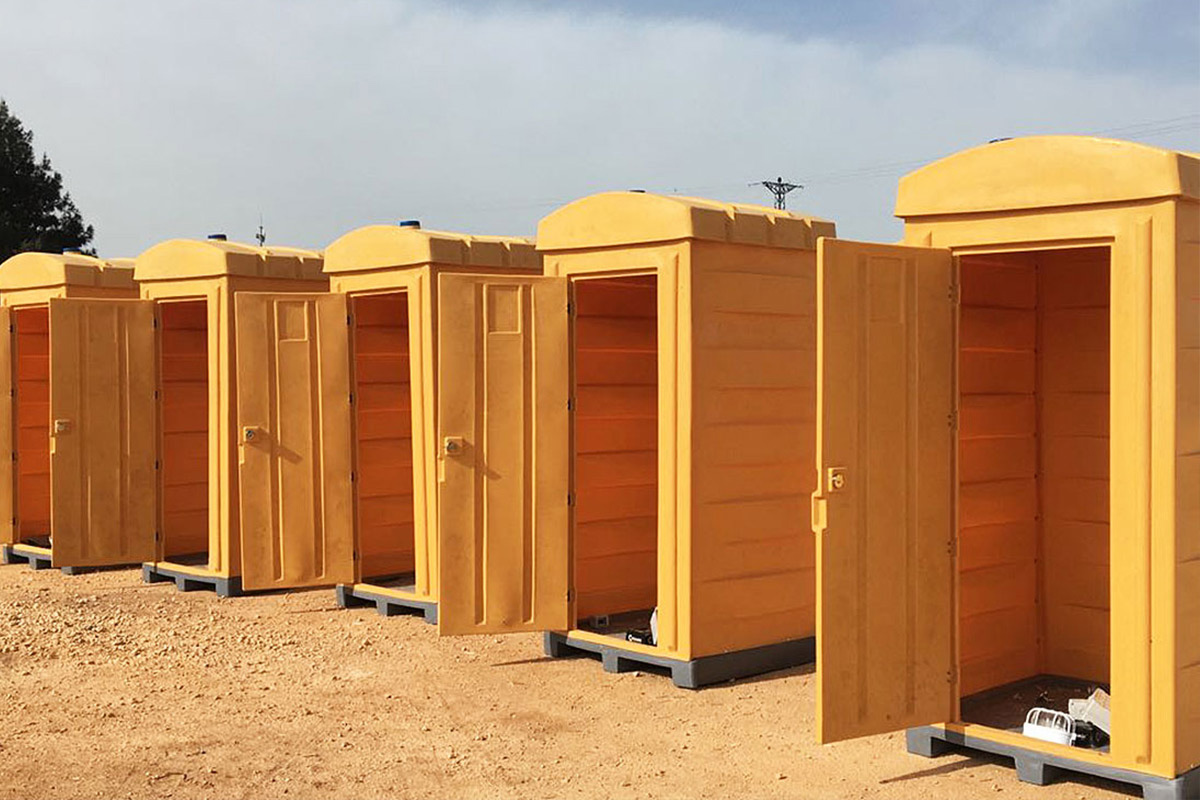
The need for both temporary and permanent structures also plays a significant role. Tanzania requires temporary buildings for construction camps, project offices, and workforce accommodation, alongside permanent facilities for education, healthcare, administration, and industry. Modular buildings respond to this mixed demand by offering structures that can be relocated, expanded, or adapted as project requirements change.
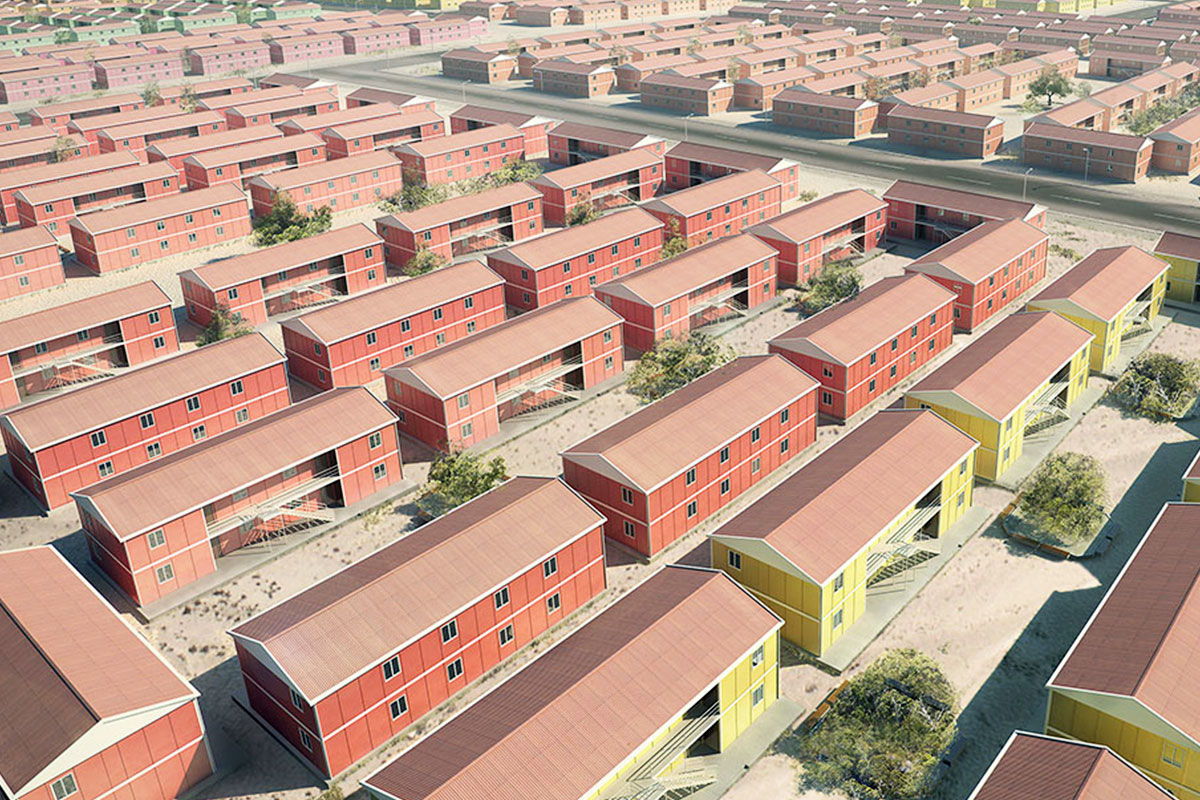
Country-specific sector activity further increases demand. Transport and logistics corridors, mining and energy operations, industrial processing zones, agriculture-related facilities, and public infrastructure projects all require buildings that can be deployed efficiently while maintaining functional reliability. Modular and prefabricated systems provide a practical response to these sectoral needs across Tanzania.
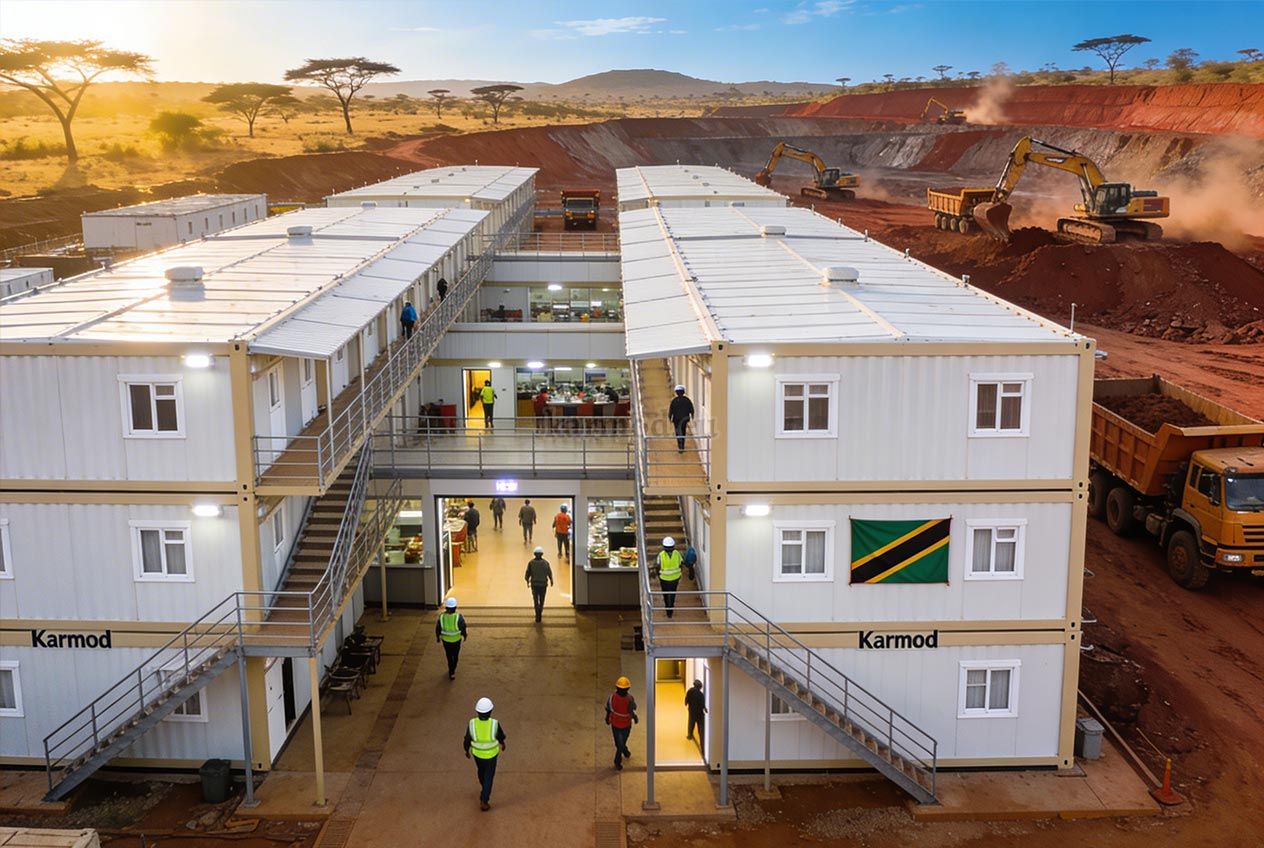

Modular Buildings vs. Prefabricated Building Systems
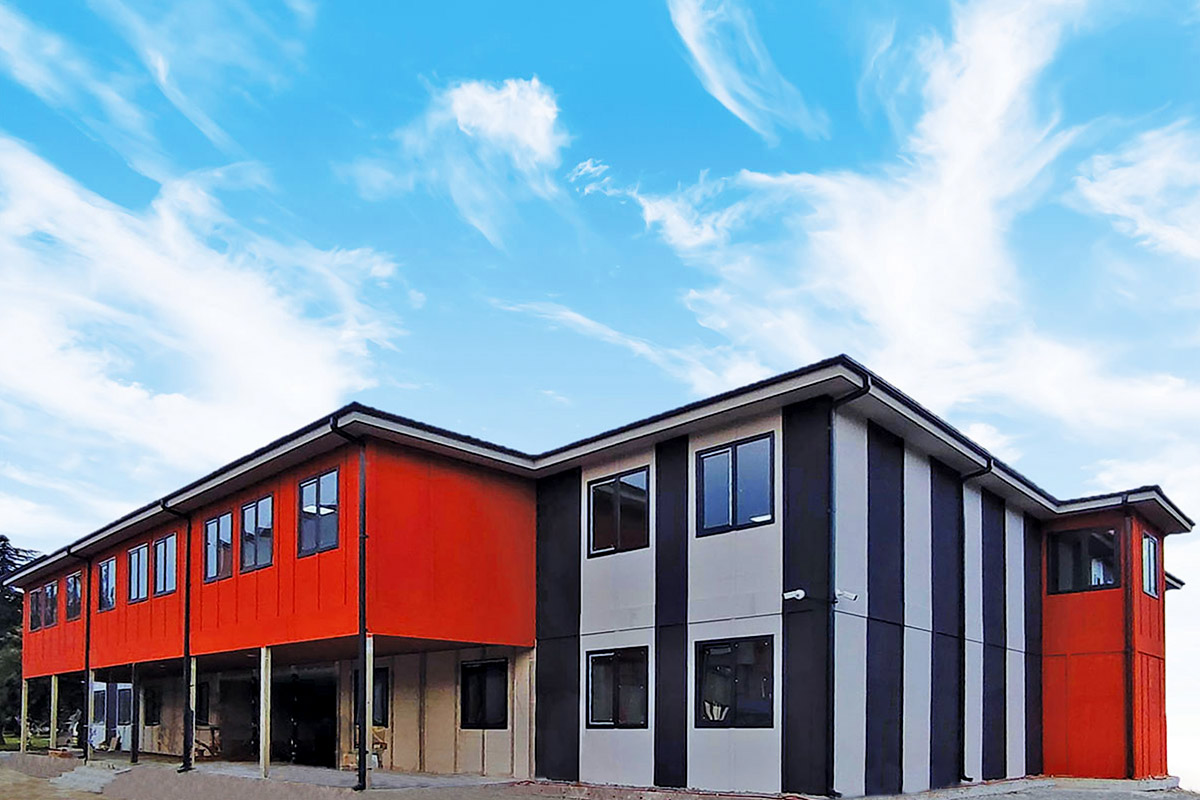
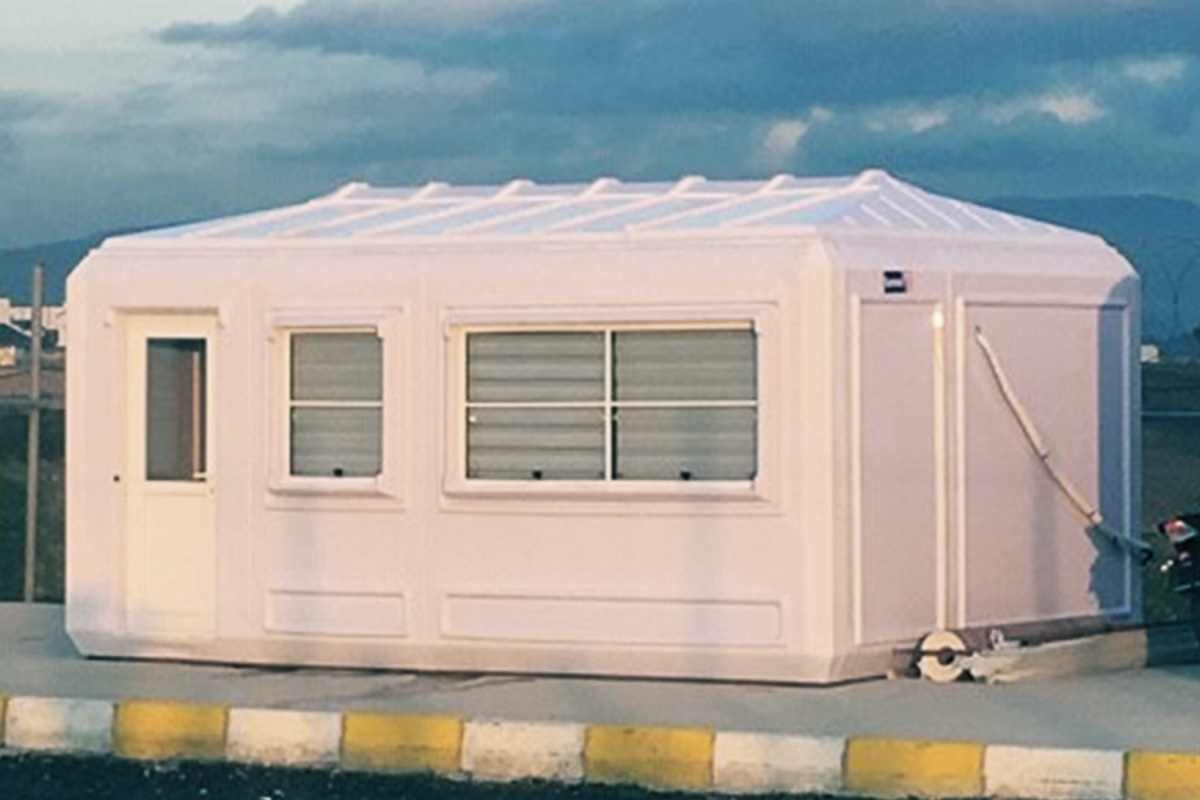
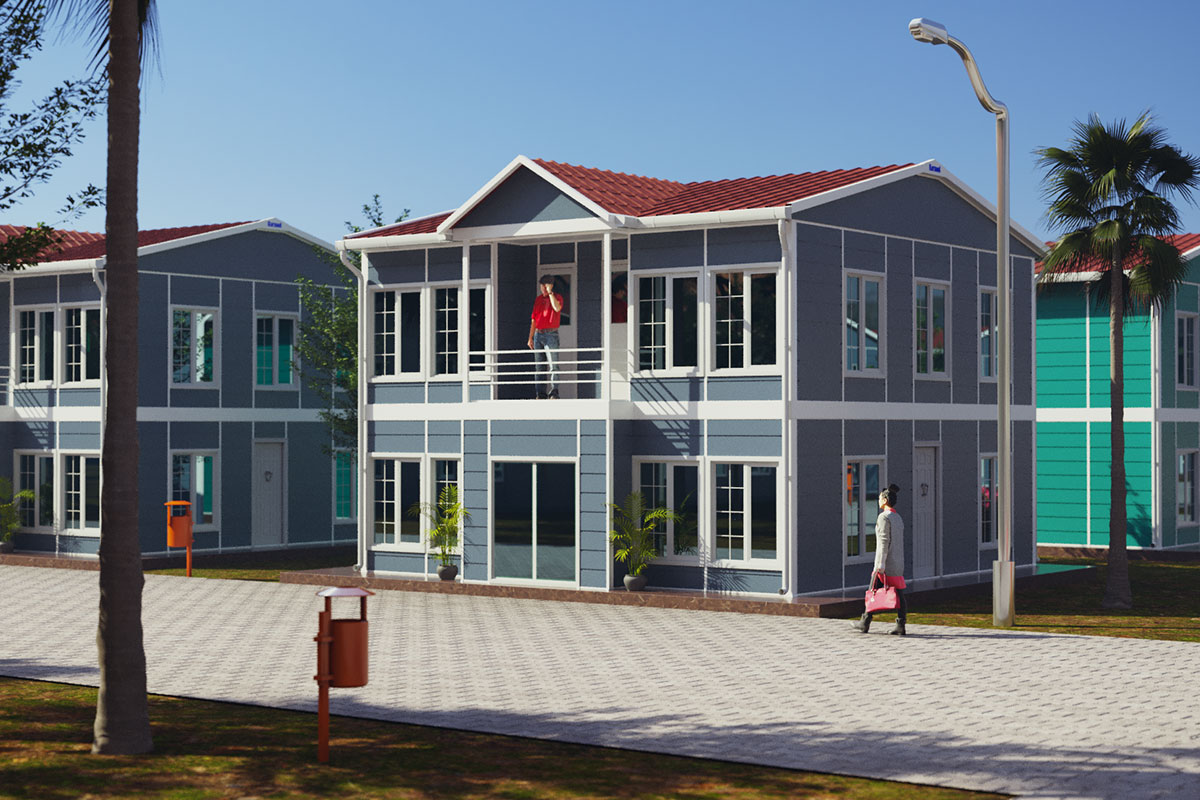
Although they share off-site production principles, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems serve different construction objectives in Tanzania. Modular buildings are produced as volumetric units, delivered to site with a high level of completion, and installed rapidly. Their modular nature allows for phased expansion and relocation, making them suitable for projects that may evolve over time or operate in multiple locations.
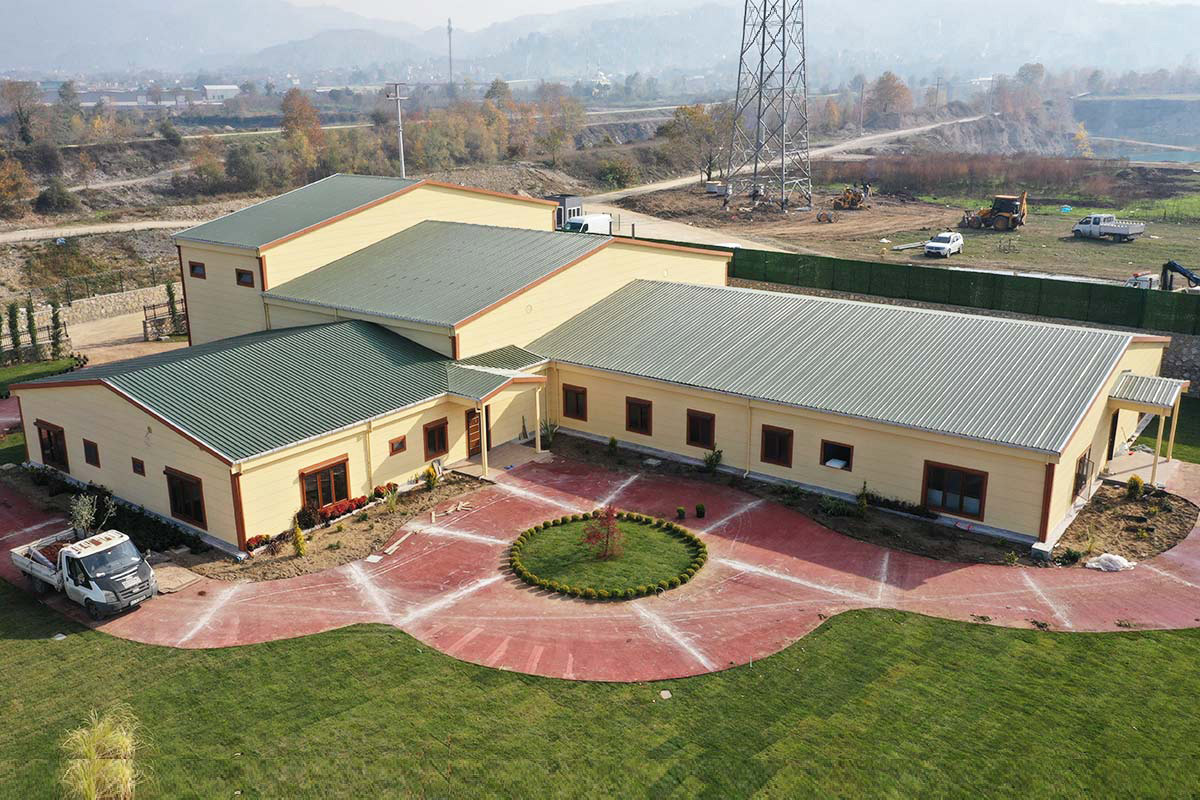
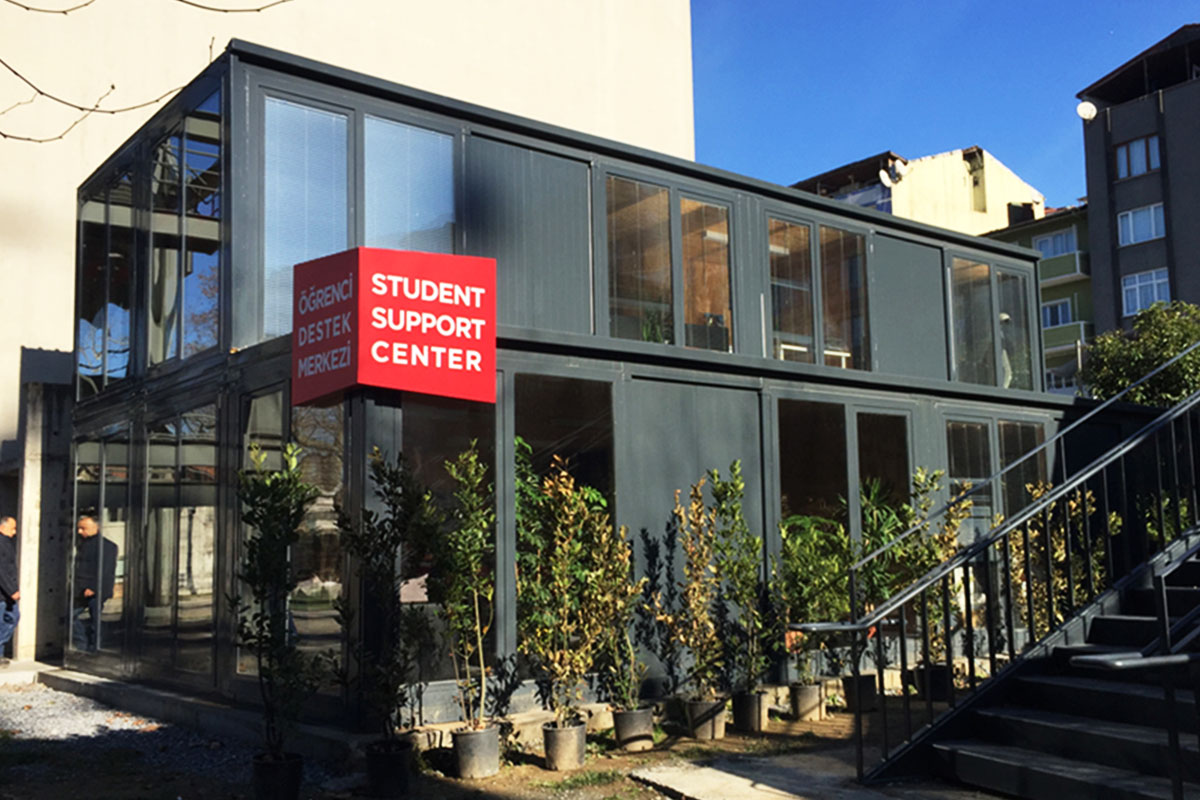
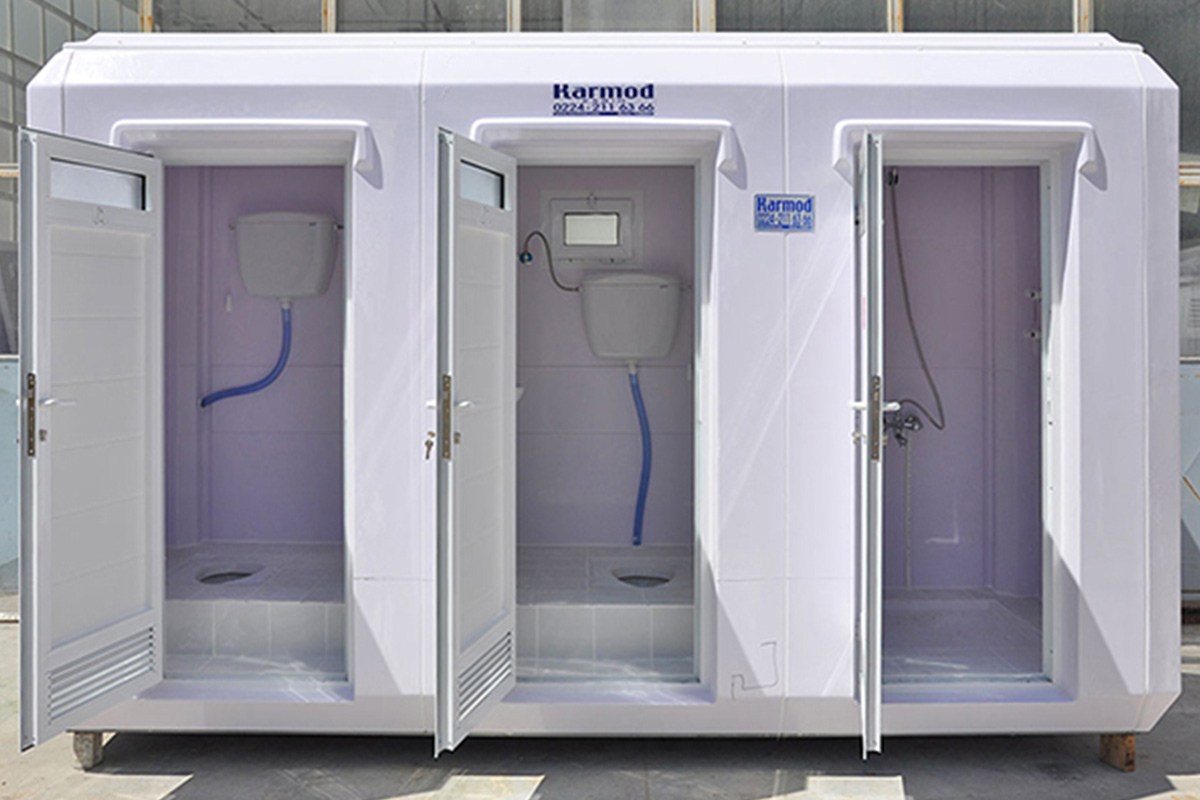
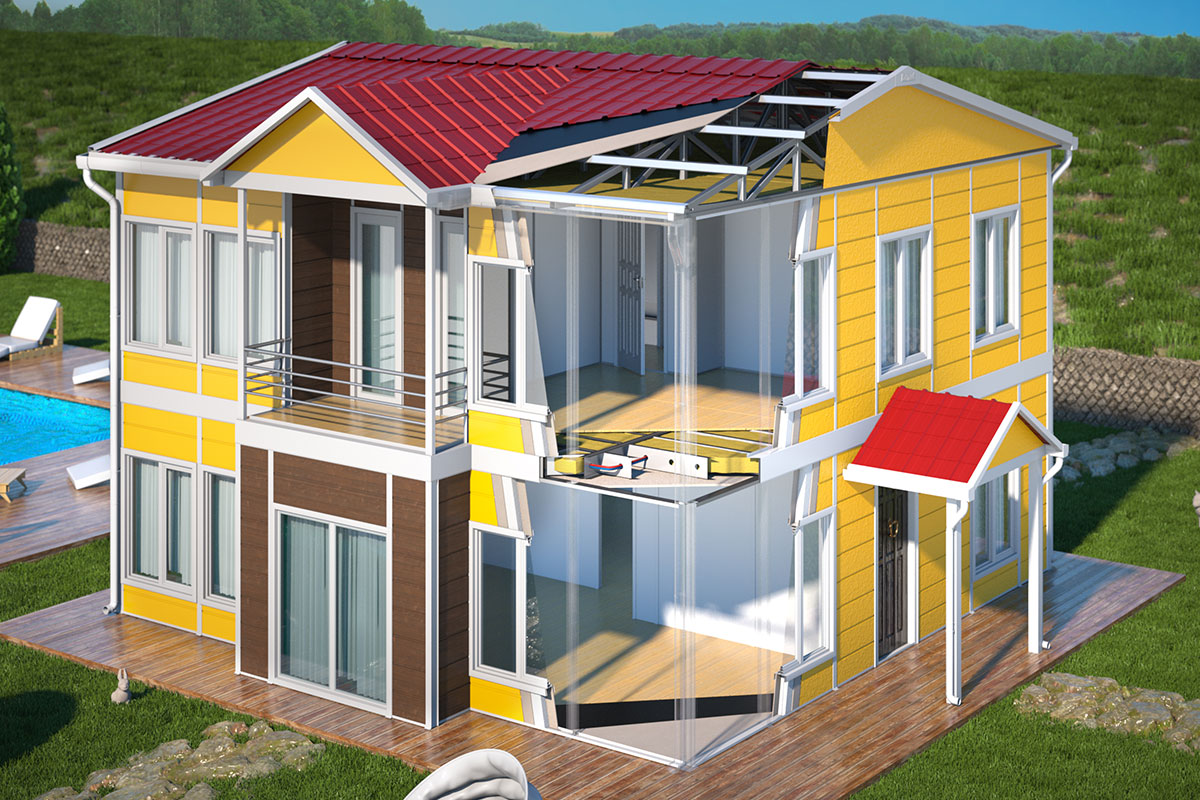
Prefabricated building systems are based on panels or structural components manufactured off-site and assembled on location. These systems are typically selected for permanent buildings where long-term use, structural integration, and fixed layouts are priorities. In Tanzania, prefabricated building solutions are often used for permanent offices, schools, healthcare facilities, and administrative buildings that require durability and stable performance.
The decision between these two approaches depends on project duration and functional intent. Modular buildings are frequently preferred for operational facilities and temporary needs, while prefabricated building systems are chosen for permanent investments with clearly defined lifecycles.
Applications of Modular and Prefabricated Buildings in Tanzania
Across Tanzania, modular and prefabricated construction methods are applied in a wide range of professional settings:
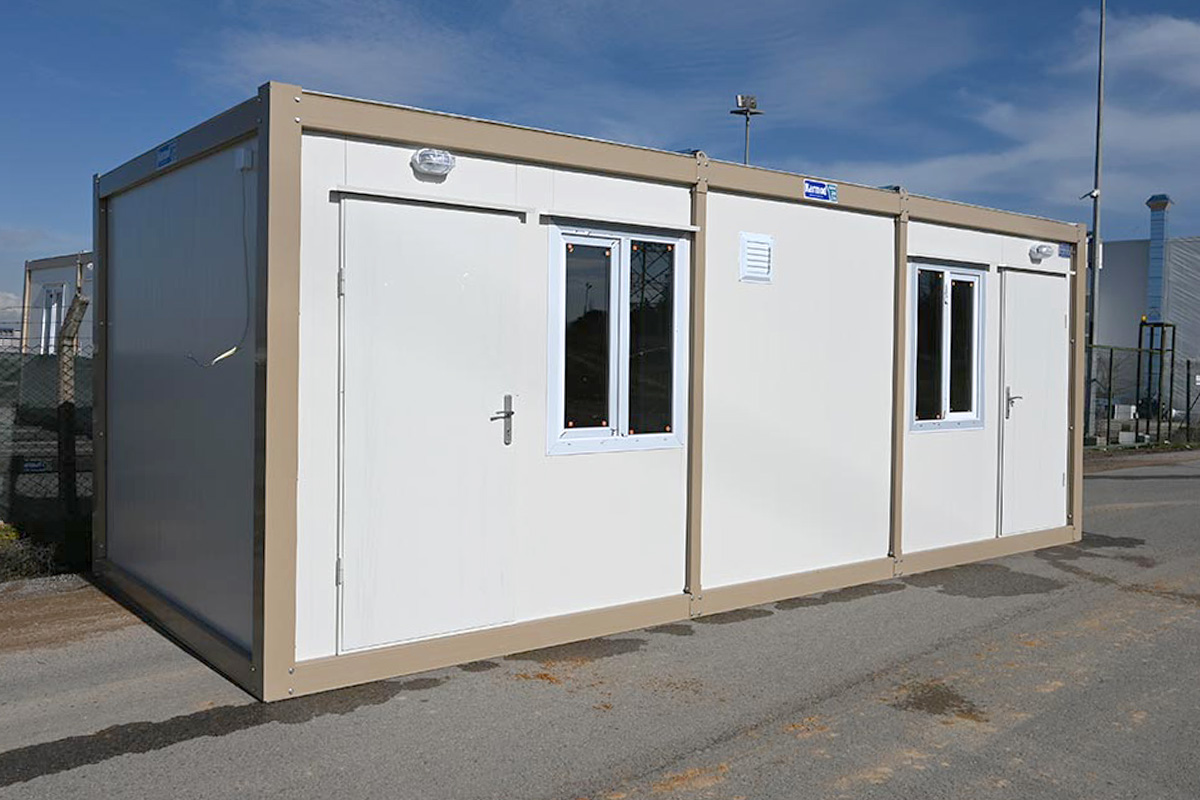
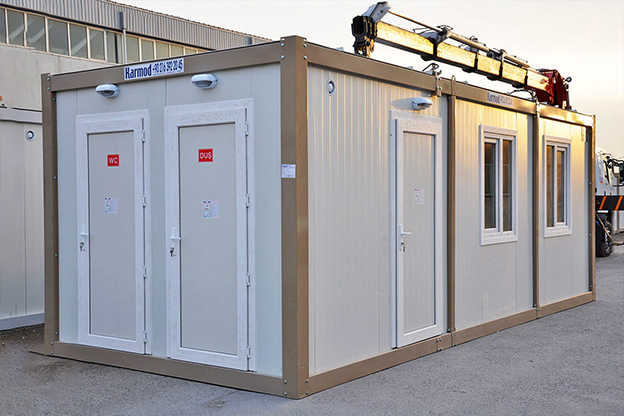
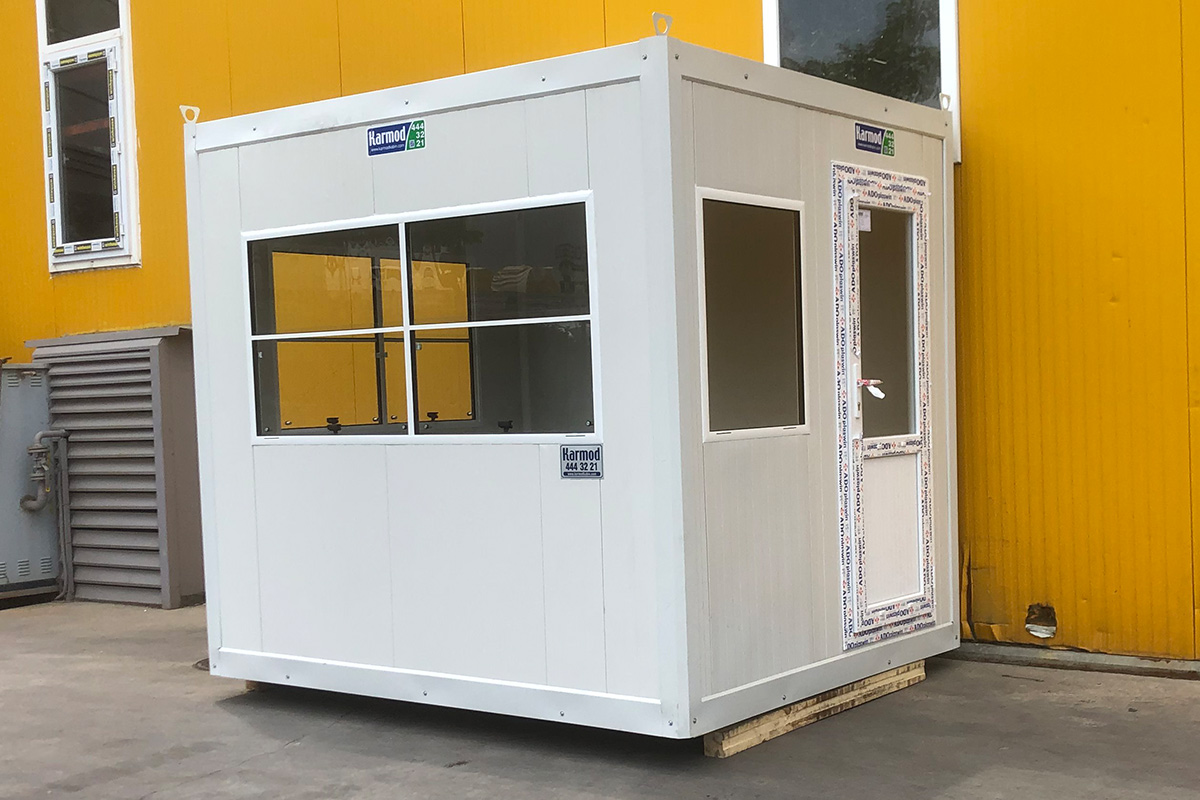
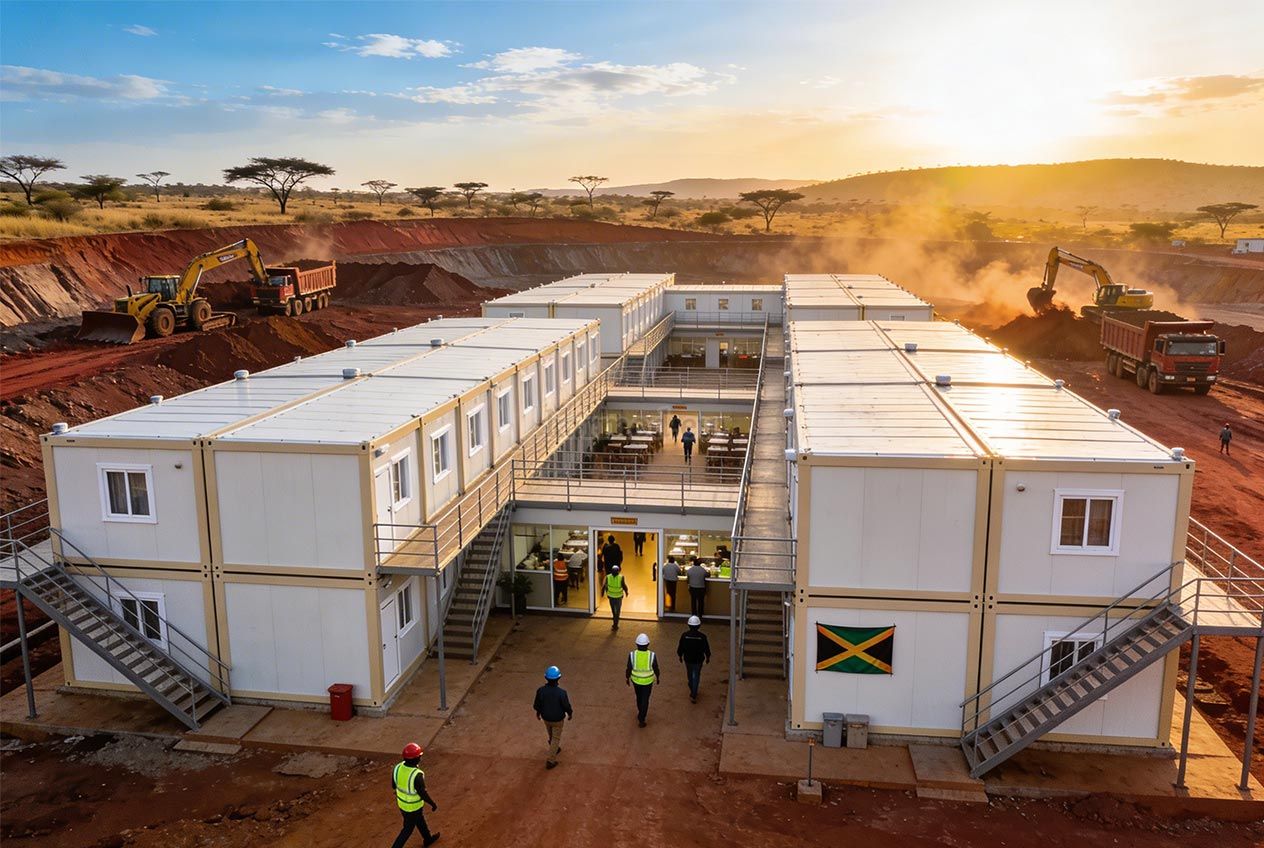
- Site offices & construction camps, supporting infrastructure, road, and industrial projects
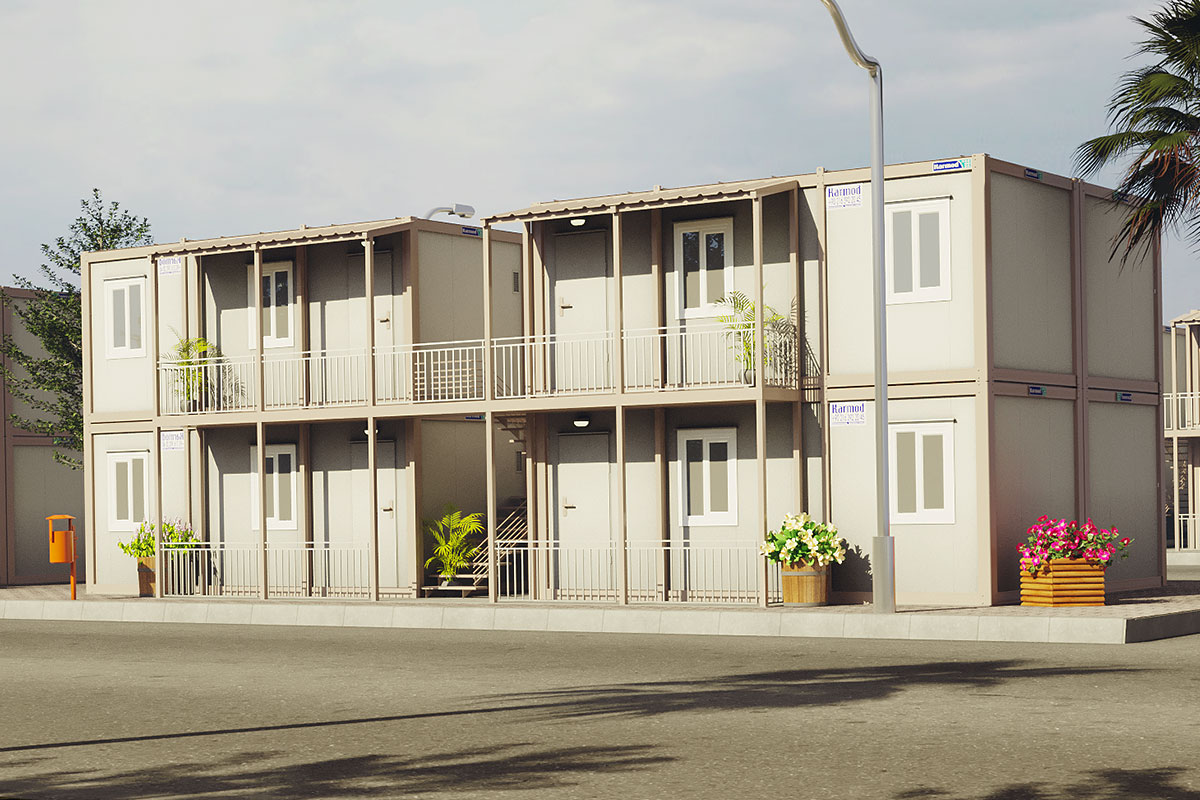
- Worker accommodation buildings, particularly near mining, energy, and logistics operations
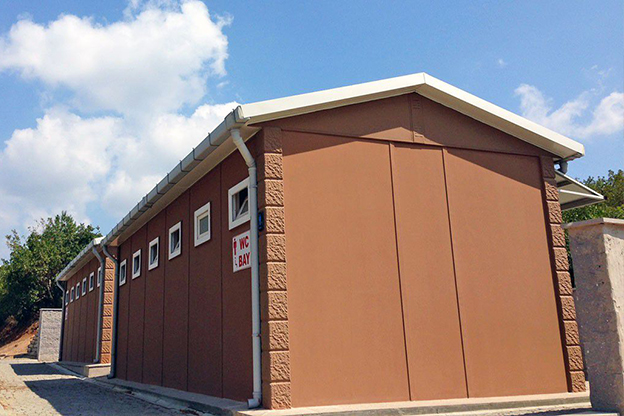
- Temporary schools & healthcare units, enabling rapid capacity expansion where needed
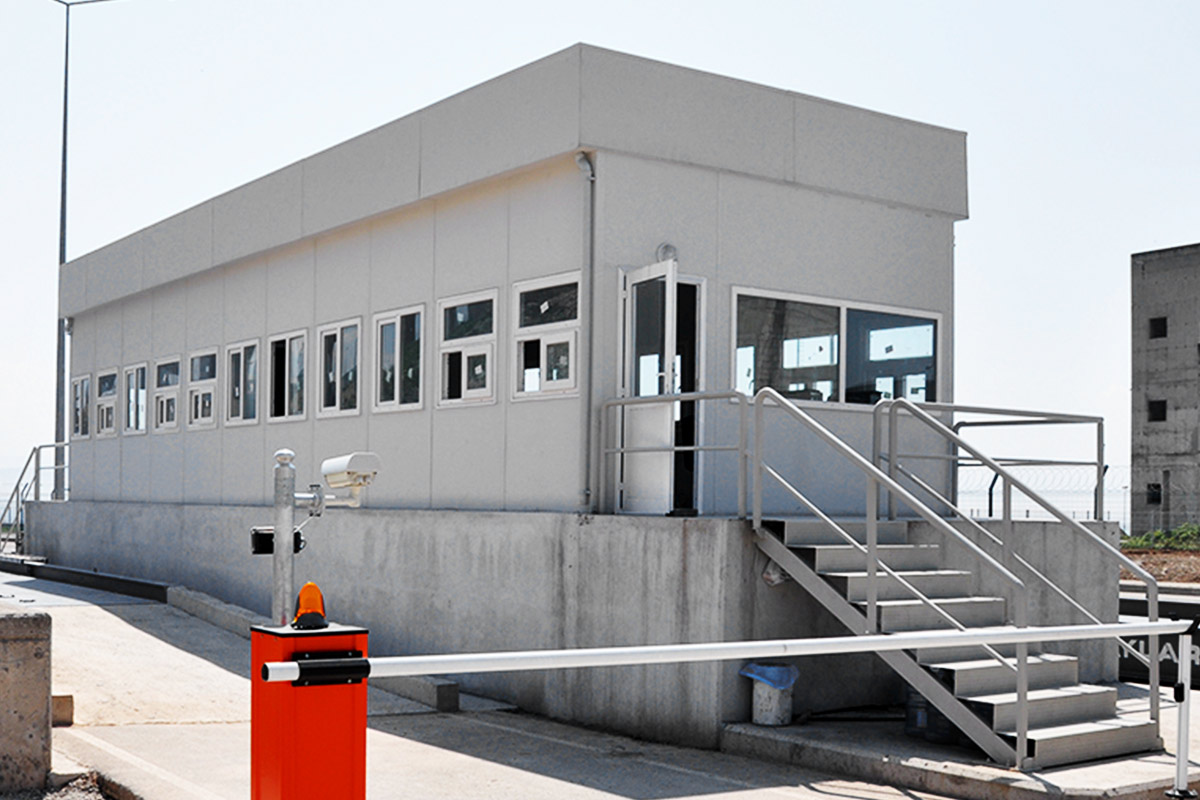
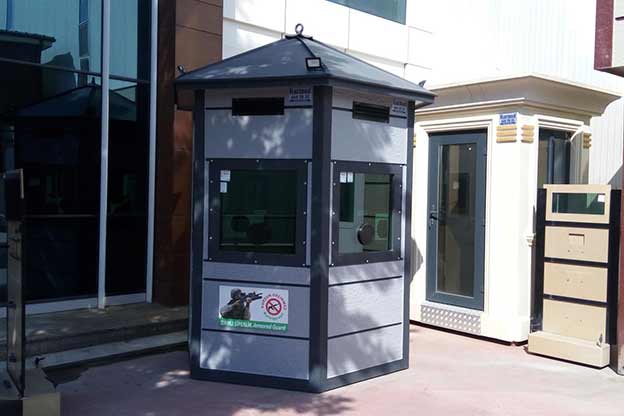
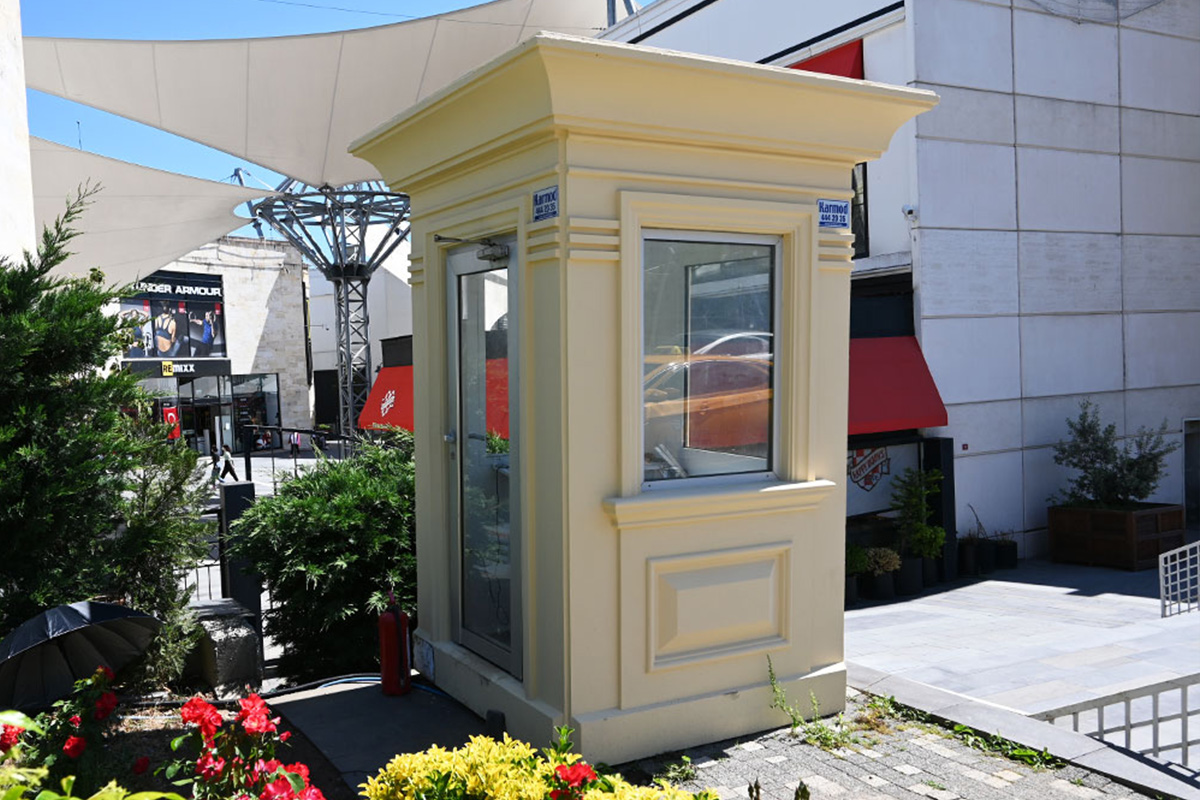
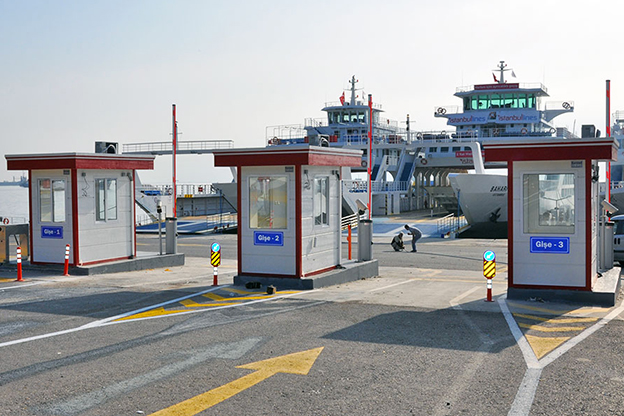
- Security buildings & technical units, including access control and operational support spaces
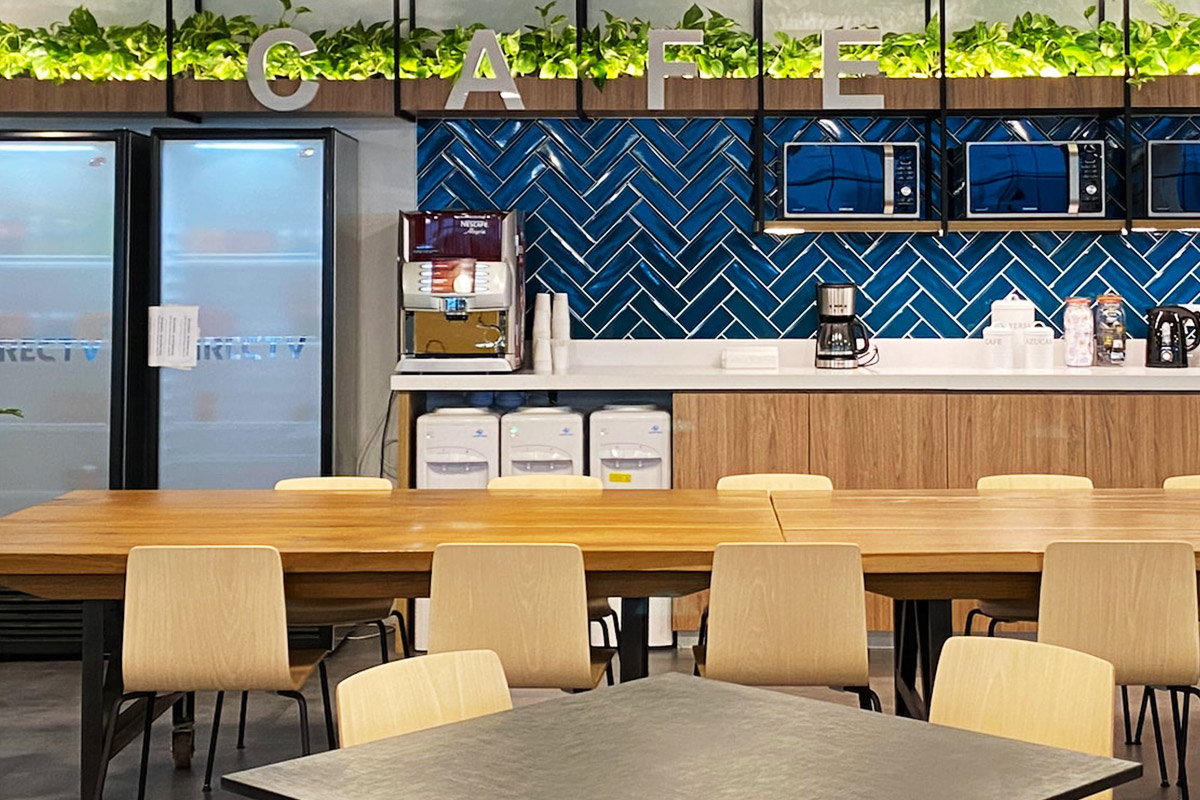
- Storage and logistics facilities, improving efficiency across supply chains and transport hubs
These applications show how modular buildings and prefabricated building systems are integrated into core project planning and operational strategies.
From Design to Installation: How the Process Works
The process begins with a detailed project needs analysis. This stage defines capacity requirements, functional use, regulatory considerations, and site-specific conditions within Tanzania. Clear planning at this point helps ensure that the selected building system aligns with both operational goals and local constraints.
Custom design and technical specifications follow, translating project requirements into optimized layouts and structural solutions. Considerations such as ventilation, insulation, material durability, and internal configurations are addressed before production begins.
Factory production is a key advantage of these systems. Manufacturing in controlled environments ensures consistent quality, efficient material use, and predictable timelines. Once production is completed, modules or components are prepared for delivery to Tanzania, with logistics planning adapted to regional access and site conditions.
On-site installation is typically fast and organized. Reduced on-site construction activity minimizes disruption and allows buildings to be commissioned quickly, supporting operational continuity in demanding project environments.
Key Considerations for Modular Buildings in Tanzania
Thermal insulation is important for maintaining indoor comfort across Tanzania’s varied climate zones. Appropriate insulation and ventilation systems help regulate internal temperatures and support energy efficiency.
Fire safety standards must be integrated into the design from the outset. Quality modular and prefabricated systems use certified materials and structural solutions that support compliance with applicable safety requirements.
Climate suitability includes moisture resistance, corrosion protection, and long-term structural durability. These factors directly affect maintenance needs and overall lifecycle performance.
Custom layouts enable buildings to align with specific operational workflows. Flexible interior planning allows organizations to adapt spaces as functional needs evolve.
In this context, experience and production discipline are essential. Karmod, with its long-standing involvement in modular construction across international markets, brings a structured approach to design, manufacturing, and delivery that aligns with Tanzania’s project-driven construction environment. Rather than positioning modular buildings as short-term solutions, Karmod focuses on engineered systems designed for durability, adaptability, and consistent performance.
With international experience shaping its processes, Karmod modular building solutions are designed to support both immediate operational requirements and longer-term planning objectives. For organizations developing projects in Tanzania, modular buildings and prefabricated building systems offer a practical construction pathway—one that supports controlled delivery, functional reliability, and informed investment decisions in a growing and diverse market.